Abstract
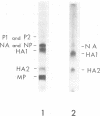
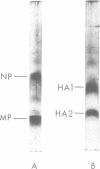
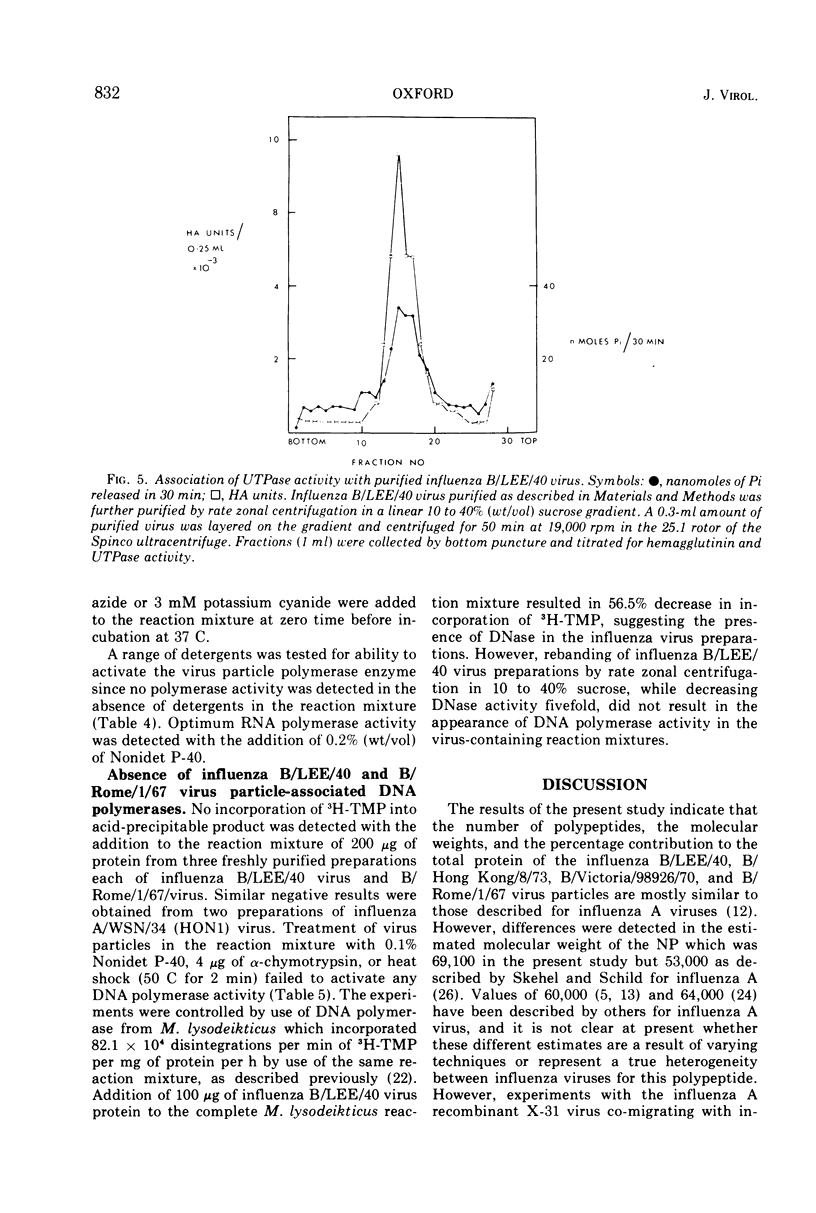
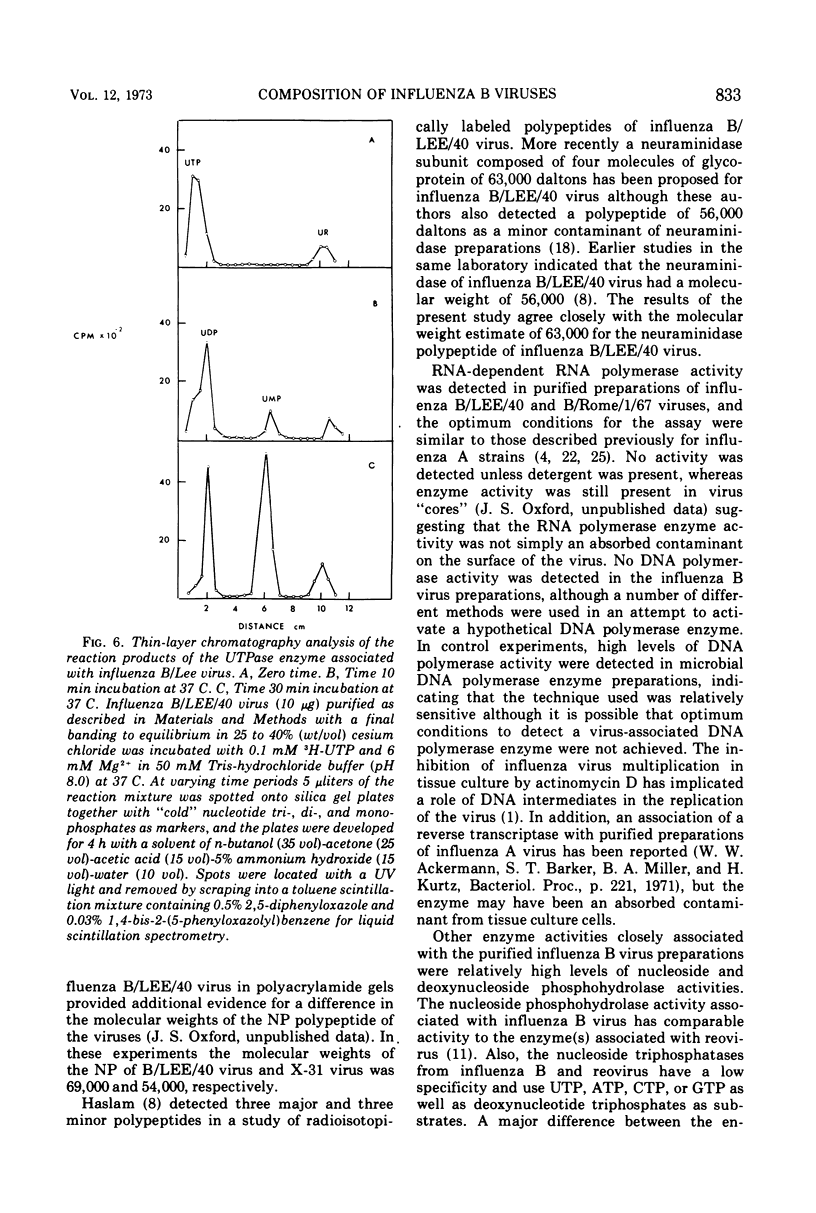
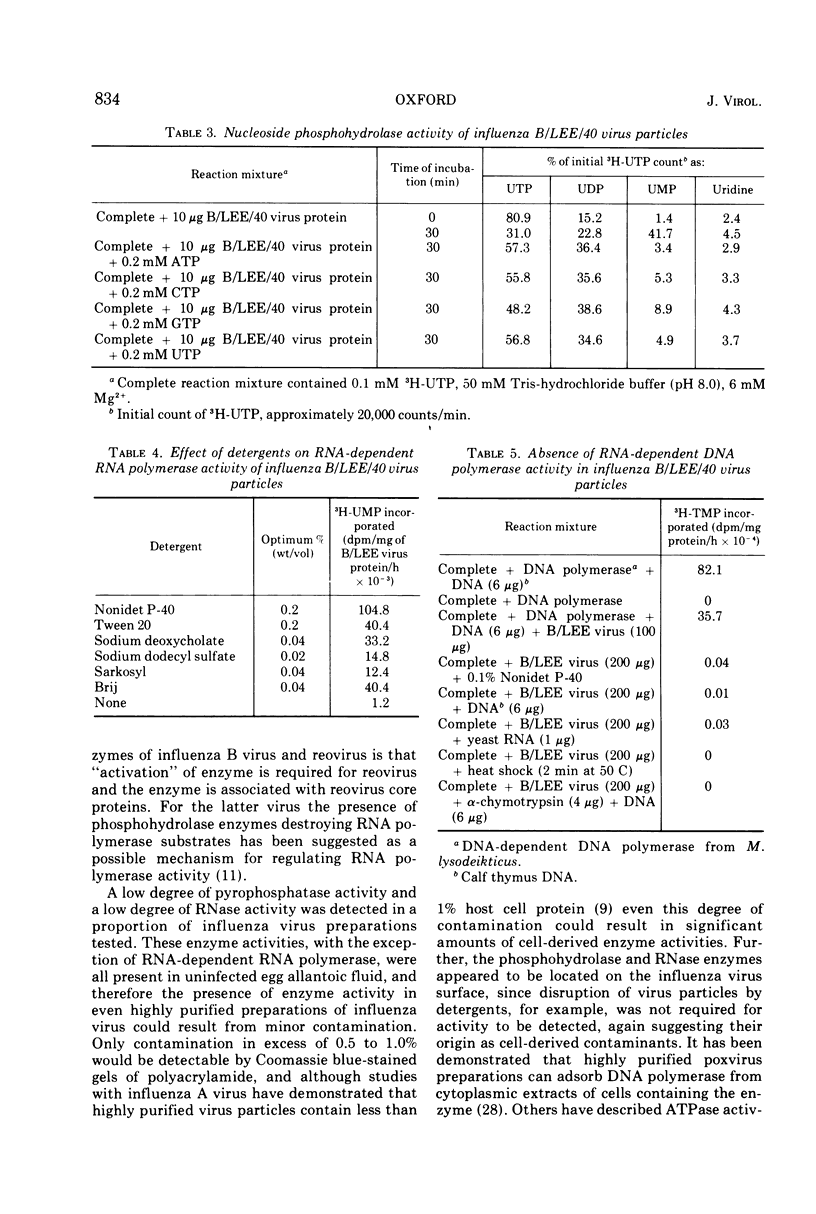
Influenza B/LEE/40, B/Rome/1/67, B/Hong Kong/8/73, and B/Victoria/98926/70 viruses have a similar polypeptide composition as analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. These viruses are composed of six or seven polypeptides, depending on whether one or two high-molecular-weight polypeptides are resolved, ranging in molecular weights from 27,000 to 90,400. Three of these polypeptides, namely the heavy and light hemagglutinin chains and the neuraminidase, have attached carbohydrate. Highly purified influenza B/LEE/40 and B/Rome/1/67 virus preparations have RNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity equivalent to the incorporation of 100 and 30 pmol, respectively, of 3H-UMP per mg of virus protein per h at 37 C, which is demonstrated only in detergent-treated virus suspensions. However, no RNA-dependent DNA polymerase enzyme activity was detected in the two viruses although virus suspensions were “activated” by heat, α-chymotrypsin, and detergents. Other enzymatic activities were associated with purified preparations of influenza B virus and were attributed to minor contamination of virus with host cell enzymes. Thus, nucleoside and deoxynucleoside phosphohydrolase enzymes were active in the absence of detergents and catalyzed the release of 1,200 and 1,800 nmol of Pi per mg of virus protein in 30 min at 37 C from ATP and dATP substrates. Thin-layer chromatography indicated that the products of the phosphohydrolase enzymes of influenza B/LEE/40 were mainly nucleoside diphosphate and monophosphate. The latter enzymes were tightly bound to influenza B/LEE/40 virus and could not be removed completely by repeated centrifugation, including centrifugation of the virus to equilibrium in density gradients of 25 to 40% (wt/vol) cesium chloride. A low degree of RNase (approximately 0.01 μg% contamination) and phosphatase (10-30 nmol of Pi released per mg of virus protein per 30 min) activity was detected in some, but not all, influenza B/LEE/40 virus preparations.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARRY R. D., IVES D. R., CRUICKSHANK J. G. Participation of deoxyribonucleic acid in the multiplication of influenza virus. Nature. 1962 Jun 23;194:1139–1140. doi: 10.1038/1941139a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraverty P. Antigenic relationship between influenza B viruses. Bull World Health Organ. 1971;45(6):755–766. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow N. L., Simpson R. W. RNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity associated with virions and subviral particles of myxoviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):752–756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compans R. W., Klenk H. D., Caliguiri L. A., Choppin P. W. Influenza virus proteins. I. Analysis of polypeptides of the virion and identification of spike glycoproteins. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):880–889. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90337-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold P. H., Dales S. Localization of nucleotide phosphohydrolase activity within vaccinia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jul;60(3):845–852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.3.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam E. A., Hampson A. W., Radiskevics I., White D. O. The polypeptides of influenza virus. 3. Identification of the hemagglutinin, neuraminidase and nucleocapsid proteins. Virology. 1970 Nov;42(3):566–575. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90303-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. J., Kiehn E. D. Influenza virus effects on cell membrane proteins. Science. 1970 Jan 9;167(3915):202–205. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3915.202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapuler A. M., Mendelsohn N., Klett H., Acs G. Four base-specific nucleoside 5'-triphosphatases in the subviral core of reovirus. Nature. 1970 Mar 28;225(5239):1209–1213. doi: 10.1038/2251209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Rott R., Becht H. On the structure of the influenza virus envelope. Virology. 1972 Mar;47(3):579–591. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90547-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAVER W. G. STRUCTURAL STUDIES ON THE PROTEIN SUBUNITS FROM THREE STRAINS OF INFLUENZA VIRUS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Jul;9:109–124. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laver W. G., Baker N. Amino acid composition of polypeptides from influenza virus particles. J Gen Virol. 1972 Oct;17(1):61–67. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-17-1-61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laver W. G., Wrigley N. G., Pereira H. G. Removal of pentons from particles of adenovirus type 2. Virology. 1969 Nov;39(3):599–604. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90111-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazdins I., Haslam E. A., White D. O. The polypeptides of influenza virus. VI. Composition of the neuraminidase. Virology. 1972 Sep;49(3):758–765. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90532-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani S., Temin H. M. Enzymes and nucleotides in virions of Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1971 Oct;8(4):409–416. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.4.409-416.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEURATH A. R., SOKOL F. ASSOCIATION OF MYXOVIRUSES WITH AN ADENOSINE DIPHOSPHATASE/ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATASE/AS REVEALED BY CHROMATOGRAPHY ON DEAE-CELLULOSE AND BY DENSITY GRADIENT CENTRIFUGATION. Z Naturforsch B. 1963 Dec;18:1050–1052. doi: 10.1515/znb-1963-1208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R. Study on the adenosine diphosphatase (adenosine triphosphatase) associated with Sendai virus. Acta Virol. 1965 Jul;9(4):313–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxford J. S. An inhibitor of the particle-associated RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of influenza A and B viruses. J Gen Virol. 1973 Jan;18(1):11–19. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-18-1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbergová M., Pristasová S. Nuclease activity of large RNA viruses. Acta Virol. 1972 Jun;16(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze I. T. The structure of influenza virus. I. The polypeptides of the virion. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):890–904. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90338-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J. RNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity of the influenza virus. Virology. 1971 Sep;45(3):793–796. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90197-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J., Schild G. C. The polypeptide composition of influenza A viruses. Virology. 1971 May;44(2):396–408. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90270-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone H. O., Portner A., Kingsbury D. W. Ribonucleic acid transcriptases in Sendai Virions and infected cells. J Virol. 1971 Aug;8(2):174–180. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.2.174-180.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan K. B., McAuslan B. R. Binding of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase to poxvirus. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):70–74. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.70-74.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]