Abstract
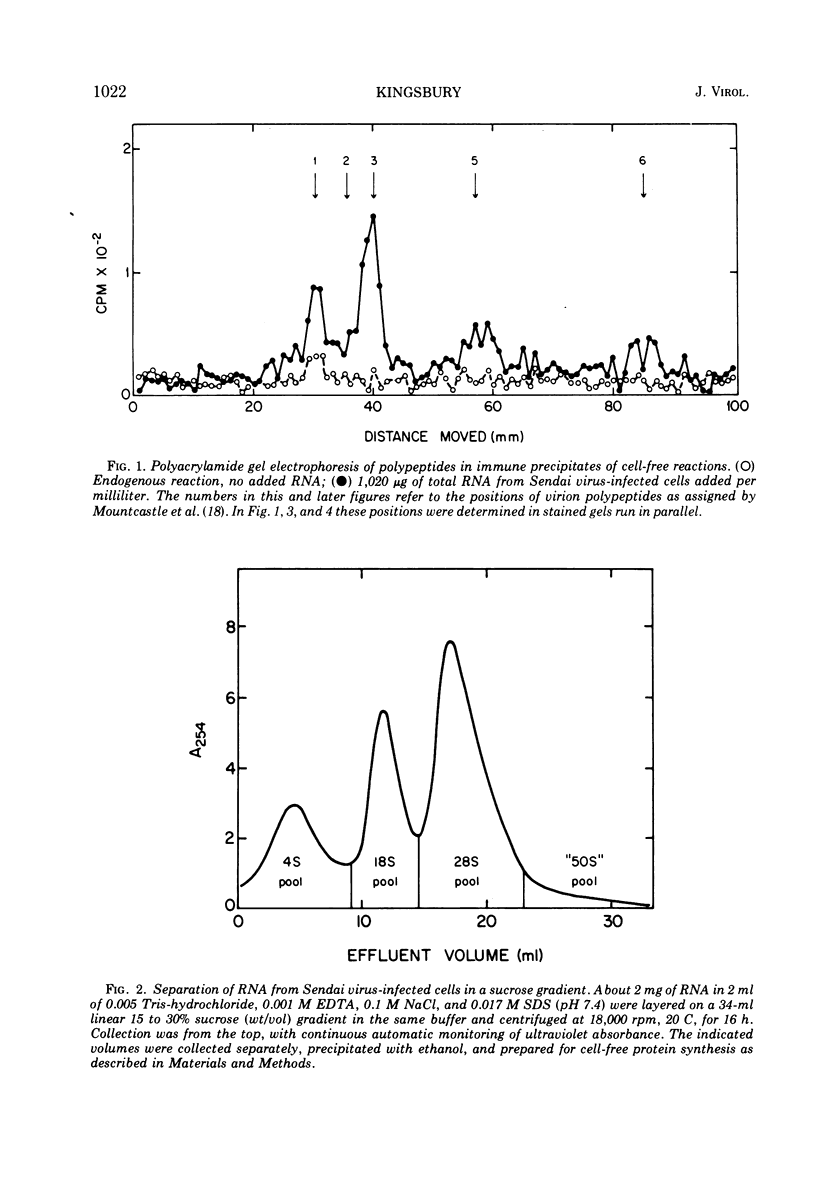
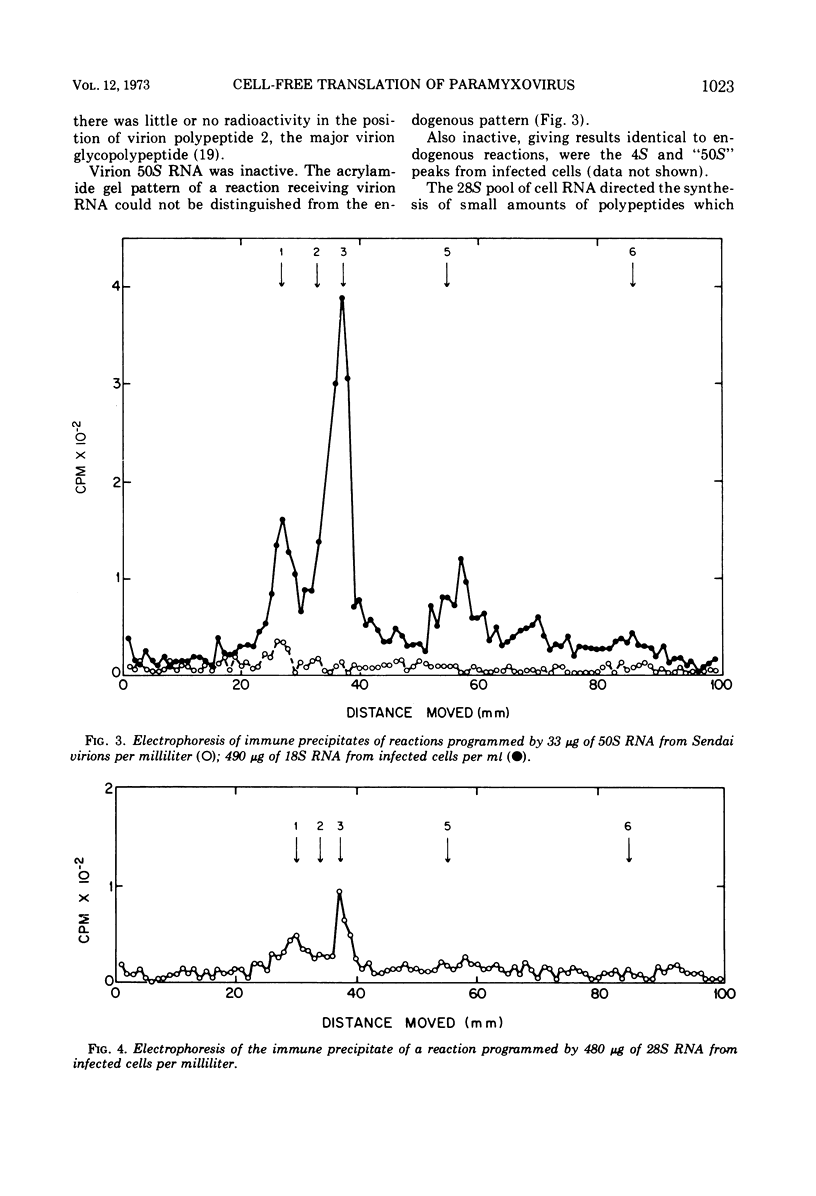
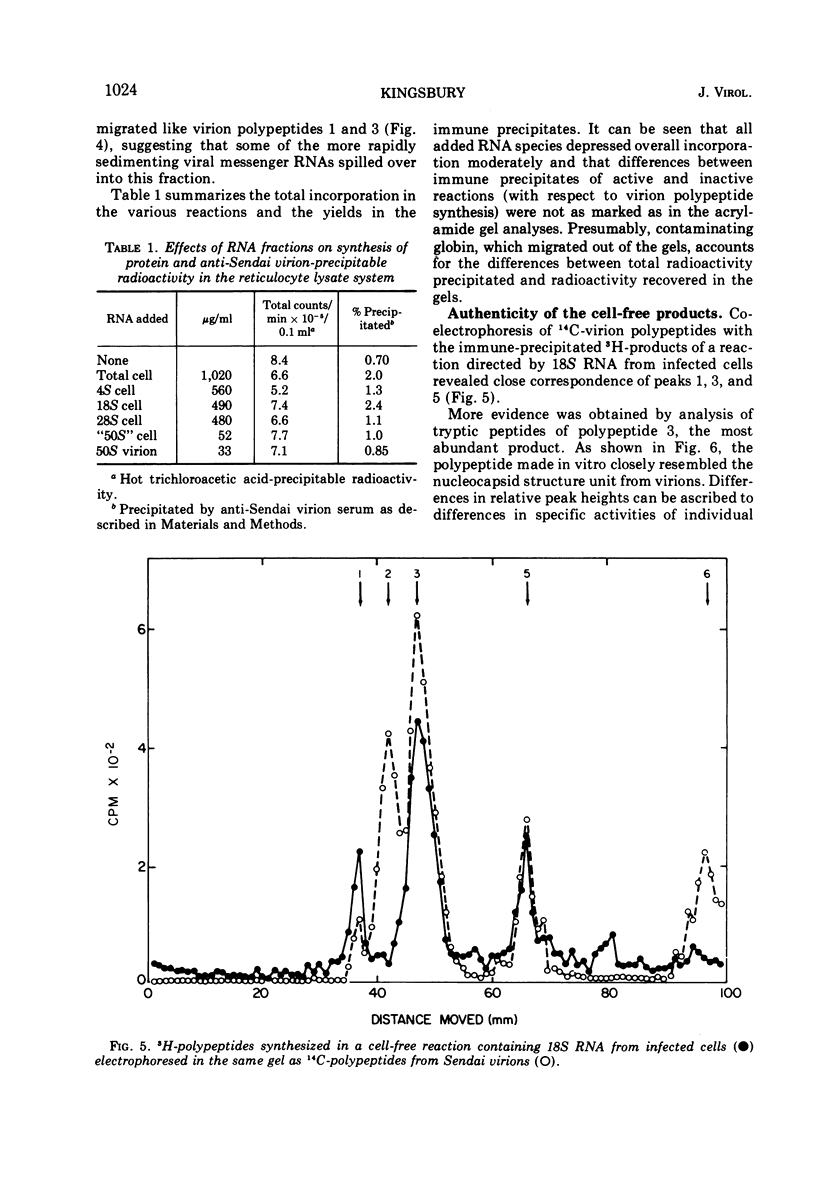
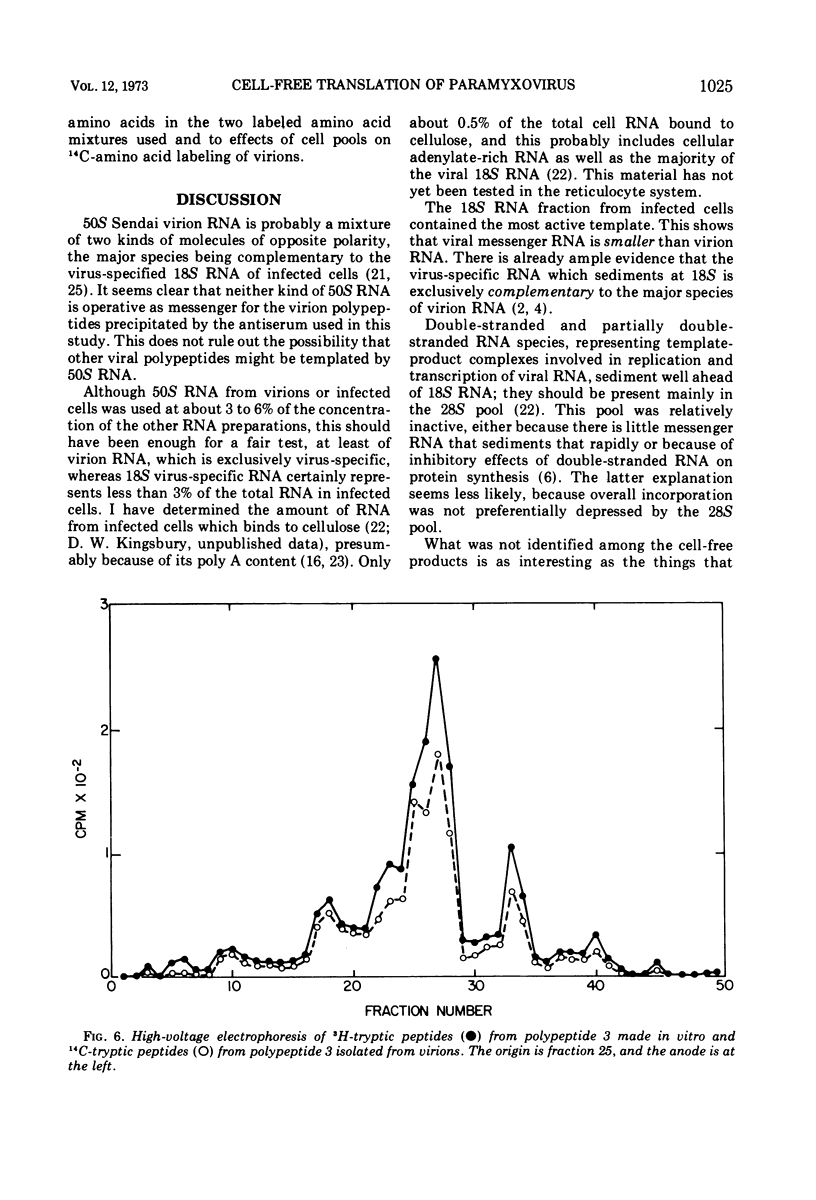
Polypeptides corresponding in electrophoretic mobility to virion polypeptides 1, 3, and 5 were made in a reticulocyte cell-free system to which 18S RNA from Sendai virus-infected cells was added. Immune precipitation was used to select relevant polypeptides from endogenous products. The cell-free product corresponding to virion polypeptide 3 (the nucleocapsid structure unit) was the most abundant; its tryptic peptides comigrated electrophoretically with tryptic peptides of polypeptide 3 isolated from virions. Other sedimenting classes of RNA from infected cells were tested; only the 28S fraction showed slight activity. Virion 50S RNA was inactive. These findings support the hypothesis that complementary RNA transcripts of paramyxovirion RNA are the templates for viral proteins.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D. Expression of animal virus genomes. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Sep;35(3):235–241. doi: 10.1128/br.35.3.235-241.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair C. D., Robinson W. S. Replication of Sendai virus. I. Comparison of the viral RNA and virus-specific RNA synthesis with Newcastle disease virus. Virology. 1968 Aug;35(4):537–549. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90284-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair C. D., Robinson W. S. Replication of Sendai virus. II. Steps in virus assembly. J Virol. 1970 May;5(5):639–650. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.5.639-650.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H. Physical properties of Rous Sarcoma Virus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1511–1518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfeld E., Hunt T. Double-stranded poliovirus RNA inhibits initiation of protein synthesis by reticulocyte lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):1075–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Housman D., Jacobs-Lorena M., Rajbhandary U. L., Lodish H. F. Initiation of haemoglobin synthesis by methionyl-tRNA. Nature. 1970 Aug 29;227(5261):913–918. doi: 10.1038/227913a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Baltimore D., Bratt M. A. Ribonucleic acid polymerase in virions of Newcastle disease virus: comparison with the vesicular stomatitis virus polymerase. J Virol. 1971 Mar;7(3):389–394. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.3.389-394.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. F., Asso J., Baltimore D. Further evidence on the formation of poliovirus proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 May 14;49(3):657–669. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90289-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury D. W. Newcastle disease virus RNA. I. Isolation and preliminary characterization of RNA from virus particles. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jun;18(1):195–203. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80085-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury D. W. Newcastle disease virus RNA. II. Preferential synthesis of RNA complementary to parental viral RNA by chick embryo cells. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jun;18(1):204–214. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80086-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury D. W. Paramyxovirus replication. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1972;59:1–33. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65444-2_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitos P. A., Saxon G., Amos H. The isolation of polyadenylate with unreacted cellulose. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jun 28;47(6):1426–1437. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90232-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowell M. J., Joklik W. K., Villa-Komaroff L., Lodish H. F. Translation of reovirus messenger RNAs synthetesized in vitro into reovirus polypeptides by several mammalian cell-free extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2649–2653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountcastle W. E., Compans R. W., Caliguiri L. A., Choppin P. W. Nucleocapsid protein subunits of simian virus 5, Newcastle disease virus, and Sendai virus. J Virol. 1970 Nov;6(5):677–684. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.5.677-684.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountcastle W. E., Compans R. W., Choppin P. W. Proteins and glycoproteins of paramyxoviruses: a comparison of simian virus 5, Newcastle disease virus, and Sendai virus. J Virol. 1971 Jan;7(1):47–52. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.1.47-52.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D. Ovalbumin messenger ribonucleic acid translation. Comparable rates of polypeptide initiation and elongation on ovalbumin and globin messenger ribonucleic acid in a rabbit reticulocyte lysate. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 25;248(6):2095–2106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portner A., Kingsbury D. W. Complementary RNAs in paramyxovirions and paramyxovirus-infected cells. Nature. 1970 Dec 19;228(5277):1196–1197. doi: 10.1038/2281196a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portner A., Kingsbury D. W. Identification of transcriptive and replicative intermediates in Sendai virus-infected cells. Virology. 1972 Mar;47(3):711–725. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90561-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pridgen C., Kingsbury D. W. Adenylate-rich sequences in Sendai virus transcripts from infected cells. J Virol. 1972 Aug;10(2):314–317. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.2.314-317.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads R. E., McKnight G. S., Schimke R. T. Synthesis of ovalbumin in a rabbit reticulocyte cell-free system programmed with hen oviduct ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 10;246(23):7407–7410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. S. Ribonucleic acid polymerase activity in Sendai virions and nucleocapsid. J Virol. 1971 Jul;8(1):81–86. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.1.81-86.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. S. Self-annealing of subgroup 2 myxovirus RNAs. Nature. 1970 Mar 7;225(5236):944–945. doi: 10.1038/225944a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. S. Sendai virus RNA synthesis and nucleocapsid formation in the presence of cycloheximide. Virology. 1971 Jun;44(3):494–502. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90362-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHERRER K., DARNELL J. E. Sedimentation characteristics of rapidly labelled RNA from HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Jun 4;7:486–490. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90341-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Caliguiri L. A., Compans R. W., Choppin P. W. Isolation of paramyxovirus glycoproteins. Association of both hemagglutinating and neuraminidase activities with the larger SV5 glycoprotein. Virology. 1972 Dec;50(3):640–652. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90418-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone H. O., Kingsbury D. W., Darlington R. W. Sendai virus-induced transcriptase from infected cells: polypeptides in the transcriptive complex. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):1037–1043. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.1037-1043.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone H. O., Portner A., Kingsbury D. W. Ribonucleic acid transcriptases in Sendai Virions and infected cells. J Virol. 1971 Aug;8(2):174–180. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.2.174-180.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



