Abstract
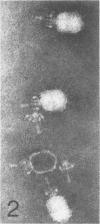
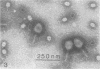
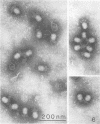
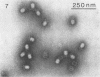
Serological methods and electron microscopy were used to study the structural proteins of the small Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage φ29. This virus has a large number of fibers attached at both ends of its prolate head. A complex neck assembly is comprised of 12 symmetrically arranged appendages as the outer component. Head fibers, neck appendages, and the head surface bind anti-φ29 antibodies. Immune sera absorbed with defective lysates of suppressor-sensitive (sus) mutants have been used to determine the genetic control of neck appendages production. Studies on the serum-blocking power of lysates defective in different tail components showed that appendages contain the main serum-blocking protein. This finding suggests an essential role of the neck appendages in phage adsorption or DNA injection.
Full text
PDF

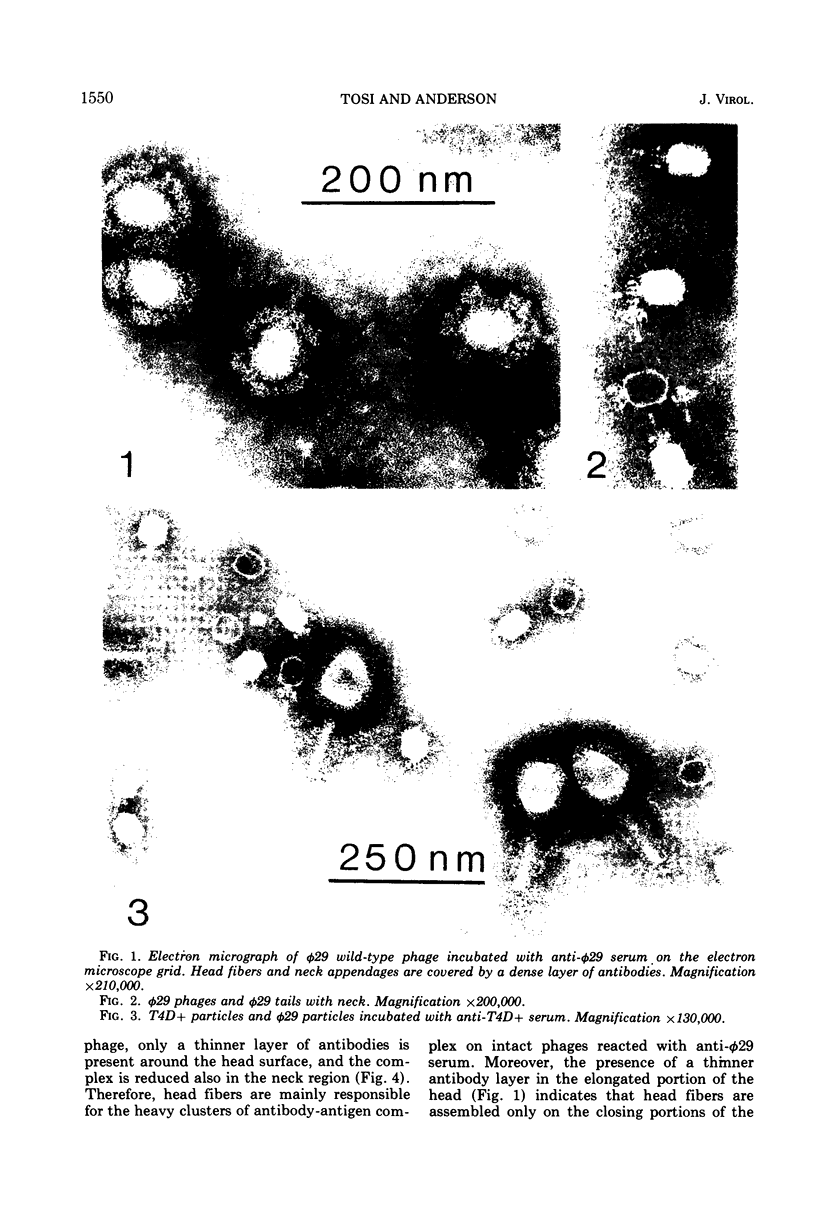
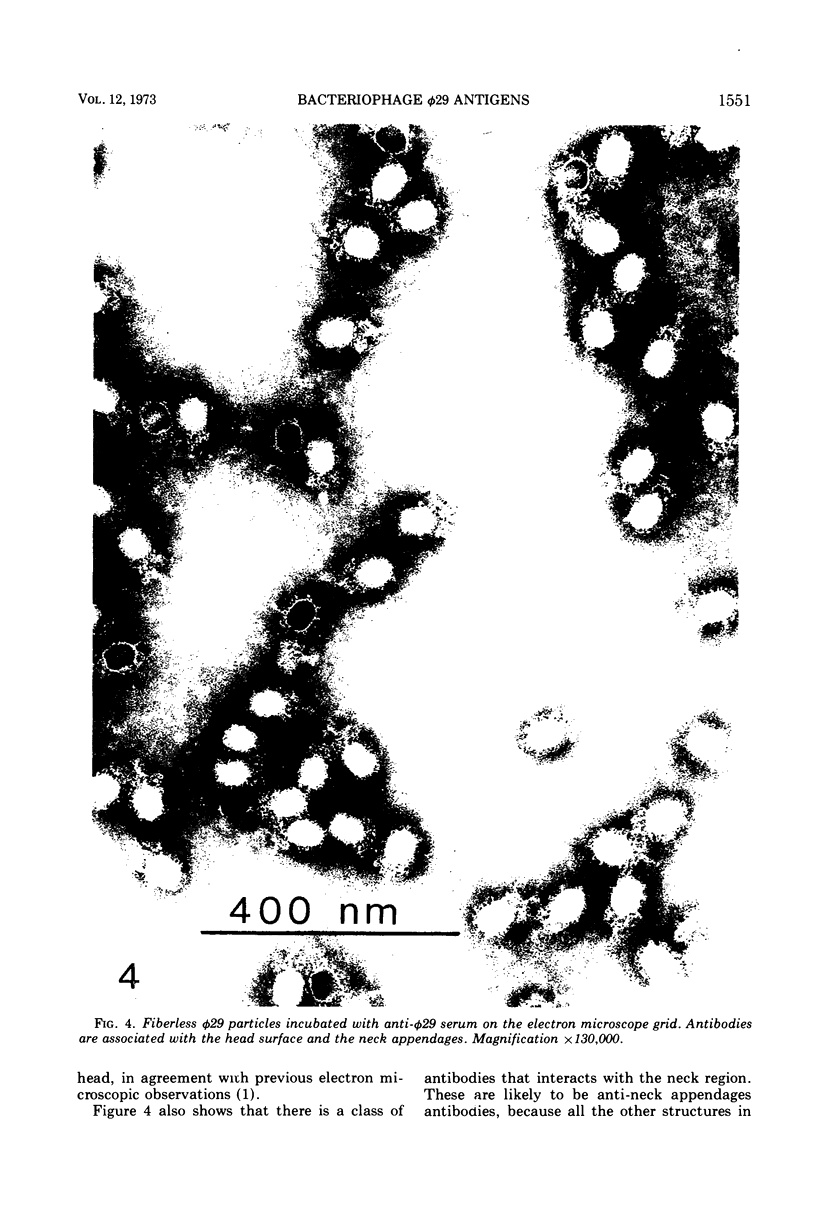

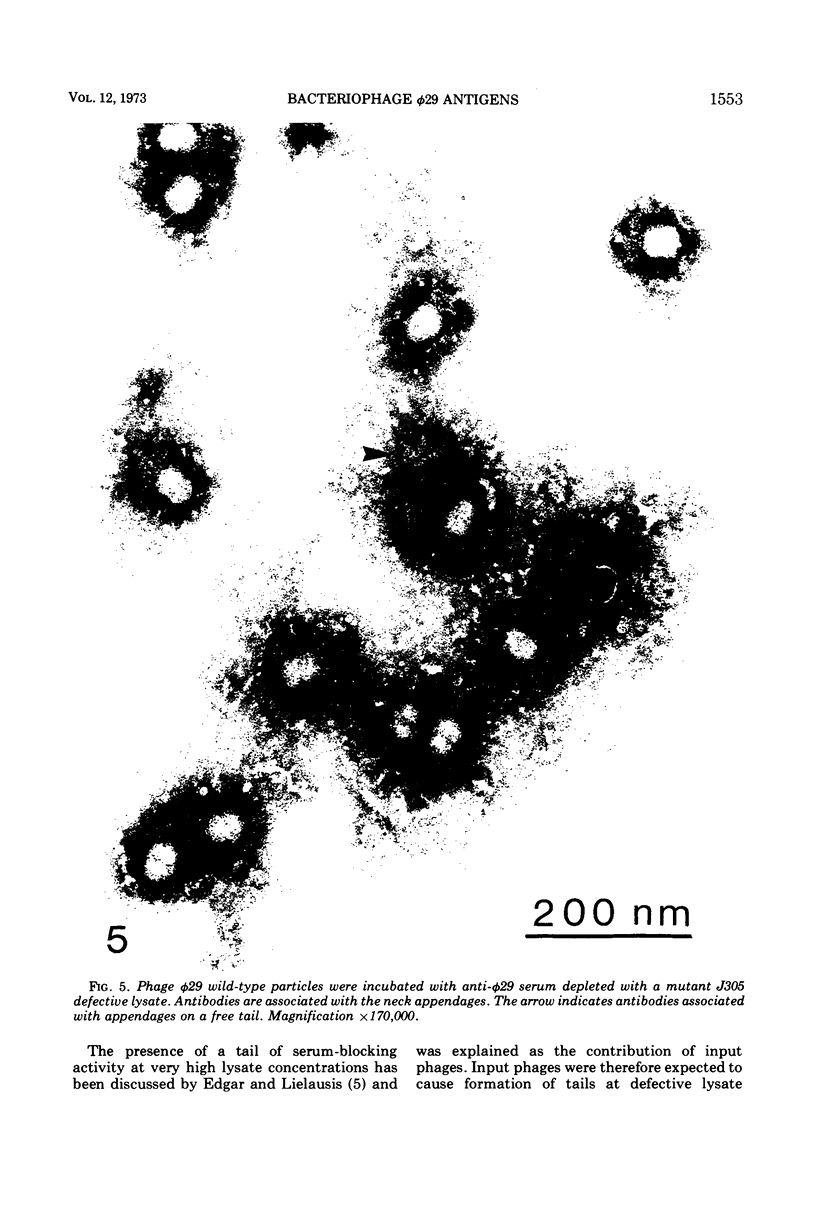





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. L., Hickman D. D., Reilly B. E. Structure of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi 29 and the length of phi 29 deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):2081–2089. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.2081-2089.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE MARS R. I. The production of phage-related materials when bacteriophage development in interrupted by proflavine. Virology. 1955 May;1(1):83–99. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(55)90007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doermann A. H. Lysis and Lysis Inhibition with Escherichia coli Bacteriophage. J Bacteriol. 1948 Feb;55(2):257–276. doi: 10.1128/jb.55.2.257-276.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar R. S., Lielausis I. Serological studies with mutants of phage T4D defective in genes determining tail fiber structure. Genetics. 1965 Dec;52(6):1187–1200. doi: 10.1093/genetics/52.6.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höglund S., Levin O. Electron microscopic studies of some proteins from normal human serum. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):866–871. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80333-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méndez E., Ramírez G., Salas M., Viñuela E. Structural proteins of bacteriophage phi 29. Virology. 1971 Sep;45(3):567–576. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90172-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REILLY B. E., SPIZIZEN J. BACTERIOPHAGE DEOXYRIBONUCLEATE INFECTION OF COMPETENT BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Mar;89:782–790. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.3.782-790.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly B. E., Zeece V. M., Anderson D. L. Genetic study of suppressor-sensitive mutants of the Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi 29. J Virol. 1973 May;11(5):756–760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.5.756-760.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salas M., Vásquez C., Méndez E., Viñuela E. Head fibers of bacteriophage phi 29. Virology. 1972 Oct;50(1):180–188. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90358-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentine R. C., Green N. M. Electron microscopy of an antibody-hapten complex. J Mol Biol. 1967 Aug 14;27(3):615–617. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welker N. E., Campbell L. L. Unrelatedness of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1124–1130. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1124-1130.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagida M., Ahmad-Zadeh C. Determination of gene product positions in bacteriophage T4 by specific antibody association. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jul 28;51(2):411–421. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90151-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yguerabide J., Epstein H. F., Stryer L. Segmental flexibility in an antibody molecule. J Mol Biol. 1970 Aug;51(3):573–590. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]