Abstract
In the title compound, C18H18F2N2O3S, the piperazine ring adopts a chair conformation. The dihedral angle between the sulfonyl-bound benzene ring and the best fit plane throught the six non-H atoms of the piperazine ring is 69.4 (2)°, while those between the fluorobenzene and sulfonyl rings and the fluorobenzene and piperazine rings are 30.97 (2) and 75.98 (2)°, respectively. In the crystal, molecules are connected to form a tetrameric unit through C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. The structure is further stabilized by weak intermolecular C—H⋯F interactions, generating C(8) and C(7) chains running along [100].
Related literature
For the synthesis, characterization and biological activity of piperazine and its derivatives, see: Gan et al. (2009a
▶,b
▶). For hydrogen-bond motifs, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C18H18F2N2O3S
M r = 380.40
Monoclinic,

a = 17.0456 (4) Å
b = 7.6026 (1) Å
c = 15.5113 (3) Å
β = 113.513 (1)°
V = 1843.22 (6) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.22 mm−1
T = 298 K
0.28 × 0.26 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009 ▶) T min = 0.942, T max = 0.958
11988 measured reflections
2359 independent reflections
1930 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.023
θmax = 22.4°
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.033
wR(F 2) = 0.092
S = 1.06
2359 reflections
236 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.15 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2009 ▶); cell refinement: APEX2 and SAINT-Plus (Bruker, 2009 ▶); data reduction: SAINT-Plus and XPREP (Bruker,2009 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 2012 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812051690/sj5290sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812051690/sj5290Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812051690/sj5290Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C4—H4⋯O3i | 0.93 | 2.58 | 3.495 (3) | 169 |
| C8—H8A⋯O3ii | 0.97 | 2.34 | 3.255 (3) | 157 |
| C10—H10B⋯O1iii | 0.97 | 2.48 | 3.402 (3) | 159 |
| C8—H8B⋯F1iv | 0.97 | 2.57 | 3.518 (3) | 165 |
| C11—H11A⋯F2iv | 0.97 | 2.56 | 3.296 (3) | 133 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 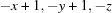 ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr S. C. Sharma, Vice Chancellor, Tumkur University, for his constant encouragement. JT also thanks the DST, New Delhi, for the SCXRD facility under the PURSE Grant (SR/S9/Z-23/2008/11, 2009) at USIC, Karnatak University.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Numerous piperazine derivatives such as aryl amides, sulphonamides, Mannich bases, Schiff's bases, thiazolidinones, azetidinones, imidazolinones have shown a wide spectrum of biological activities viz. anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antimalarial, anticonvulsant, antipyretic, antitumor, anthelmintics, analgesic, antidepressant, antifungal, antitubercular, anticancer, antidiabetic effects (Gan et al., 2009a, 2009b). Keeping this in mind, we synthesized the title compound to study its crystal structure.
The compound crystallizes in monoclinic crystal system and the space group P21/c. In the crystal structure, the piperazine ring adopts chair conformation. The dihedral angle between the sulfonyl bound benzene ring and the best fit plane through all six atoms of the piperazine ring is 69.4 (2)°, while those between the fluorobenzene and the sulfonyl rings and the fluorobenzene and the piperazine rings are 30.97 (2)° and 75.98 (2)° respectively. In the crystal structure molecules form a tetrameric unit generating alternate R22(22), (C8—H8A···O3, C10—H10B···O1) and inversion related C4—H4···O3 R22(10) rings (Bernstein et al.1995). The structure is further stabilized by weak intermolecular C11—H11A···F2 and C8—H8B···F1 interactions.
Experimental
1-Tosylpiperazine (0.01 mmol) and triethylamine (0.02 mmol) were dissolved in 10 ml of dichloromethane (CH2Cl2). The mixture was cooled to 0°C and 1-propanephosphonic acid anhydride (0.02 mmol) and 2,4-diflurobenzoic acid (0.01 mmol) added. The reaction mixture was stirred at 80°C for 14 h. The reaction was monitored by TLC and the solvent removed yielding the crude product. The crude mass was purified by chromatography on 230–400 silica gel with petroleum ether and ethyl acetate as eluents. Single crystals of the title compound were obtained from slow evaporation of a solution of the compound in petroleum ether and ethyl acetate (1:4).
Refinement
H atoms were positioned with idealized geometry using a riding model with C—H = 0.93 - 0.97 Å. The isotropic displacement parameters for all H atoms were set to 1.2 times Ueq of the parent atom or 1.5 times that of the parent atom for CH3.
Figures
Fig. 1.

Molecular structure of the title compound, showing the atom-labeling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.

Molecular packing in the title compound. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C18H18F2N2O3S | Prism |
| Mr = 380.40 | Dx = 1.371 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Melting point: 457 K |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 17.0456 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 2364 reflections |
| b = 7.6026 (1) Å | θ = 2.6–22.4° |
| c = 15.5113 (3) Å | µ = 0.22 mm−1 |
| β = 113.513 (1)° | T = 298 K |
| V = 1843.22 (6) Å3 | Prism, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.28 × 0.26 × 0.20 mm |
| F(000) = 792 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2359 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1930 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.023 |
| Detector resolution: 0.95 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 22.4°, θmin = 2.6° |
| φ and ω scans | h = −18→15 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009) | k = −8→7 |
| Tmin = 0.942, Tmax = 0.958 | l = −16→16 |
| 11988 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.033 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.092 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.06 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0494P)2 + 0.3661P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2359 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 236 parameters | Δρmax = 0.15 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3 |
| 0 constraints |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.56842 (15) | 0.1855 (3) | −0.19563 (16) | 0.0606 (6) | |
| C2 | 0.50273 (17) | 0.2154 (3) | −0.28076 (15) | 0.0652 (6) | |
| C3 | 0.42103 (17) | 0.2278 (3) | −0.28889 (17) | 0.0712 (7) | |
| H3 | 0.3767 | 0.2486 | −0.3470 | 0.085* | |
| C4 | 0.40468 (16) | 0.2091 (3) | −0.20946 (19) | 0.0788 (7) | |
| H4 | 0.3488 | 0.2165 | −0.2137 | 0.095* | |
| C5 | 0.47062 (17) | 0.1794 (3) | −0.12370 (17) | 0.0710 (7) | |
| H5 | 0.4587 | 0.1672 | −0.0705 | 0.085* | |
| C6 | 0.55410 (14) | 0.1675 (3) | −0.11526 (14) | 0.0542 (6) | |
| C7 | 0.62575 (15) | 0.1198 (3) | −0.02411 (15) | 0.0599 (6) | |
| C8 | 0.71988 (15) | 0.1996 (3) | 0.13429 (14) | 0.0644 (6) | |
| H8A | 0.7369 | 0.0777 | 0.1353 | 0.077* | |
| H8B | 0.6944 | 0.2135 | 0.1797 | 0.077* | |
| C9 | 0.79693 (15) | 0.3155 (3) | 0.16094 (15) | 0.0632 (6) | |
| H9A | 0.8364 | 0.2901 | 0.2249 | 0.076* | |
| H9B | 0.8260 | 0.2935 | 0.1195 | 0.076* | |
| C10 | 0.71040 (13) | 0.5453 (3) | 0.05710 (14) | 0.0574 (6) | |
| H10A | 0.7382 | 0.5278 | 0.0141 | 0.069* | |
| H10B | 0.6938 | 0.6679 | 0.0542 | 0.069* | |
| C11 | 0.63270 (14) | 0.4302 (3) | 0.02931 (15) | 0.0598 (6) | |
| H11A | 0.6015 | 0.4580 | 0.0679 | 0.072* | |
| H11B | 0.5954 | 0.4525 | −0.0358 | 0.072* | |
| C12 | 0.91357 (14) | 0.6645 (3) | 0.15849 (14) | 0.0584 (6) | |
| C13 | 0.98919 (15) | 0.5691 (3) | 0.19152 (16) | 0.0659 (6) | |
| H13 | 1.0022 | 0.4951 | 0.2431 | 0.079* | |
| C14 | 1.04489 (16) | 0.5843 (3) | 0.14784 (19) | 0.0746 (7) | |
| H14 | 1.0952 | 0.5191 | 0.1702 | 0.089* | |
| C15 | 1.02791 (17) | 0.6943 (3) | 0.07146 (18) | 0.0730 (7) | |
| C16 | 0.95135 (18) | 0.7848 (3) | 0.03828 (17) | 0.0742 (7) | |
| H16 | 0.9379 | 0.8565 | −0.0143 | 0.089* | |
| C17 | 0.89459 (16) | 0.7722 (3) | 0.08056 (16) | 0.0659 (6) | |
| H17 | 0.8437 | 0.8354 | 0.0571 | 0.079* | |
| C18 | 1.0916 (2) | 0.7155 (4) | 0.0280 (2) | 0.1021 (10) | |
| H18A | 1.0634 | 0.7612 | −0.0346 | 0.153* | |
| H18B | 1.1165 | 0.6034 | 0.0256 | 0.153* | |
| H18C | 1.1357 | 0.7956 | 0.0651 | 0.153* | |
| N1 | 0.65731 (11) | 0.2441 (2) | 0.04104 (11) | 0.0572 (5) | |
| N2 | 0.76965 (11) | 0.5003 (2) | 0.15333 (11) | 0.0571 (5) | |
| O1 | 0.65057 (13) | −0.0330 (2) | −0.01083 (11) | 0.0937 (6) | |
| O2 | 0.88639 (11) | 0.5727 (2) | 0.30408 (10) | 0.0772 (5) | |
| O3 | 0.79753 (10) | 0.8085 (2) | 0.20235 (11) | 0.0740 (5) | |
| F1 | 0.64895 (9) | 0.1741 (2) | −0.19068 (10) | 0.0971 (5) | |
| F2 | 0.52079 (11) | 0.2303 (2) | −0.35774 (10) | 0.1029 (6) | |
| S1 | 0.84155 (4) | 0.64492 (7) | 0.21283 (4) | 0.0619 (2) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0636 (15) | 0.0573 (14) | 0.0623 (15) | 0.0075 (12) | 0.0267 (13) | 0.0050 (11) |
| C2 | 0.0869 (18) | 0.0589 (15) | 0.0500 (14) | 0.0087 (13) | 0.0274 (14) | 0.0016 (10) |
| C3 | 0.0761 (18) | 0.0625 (16) | 0.0607 (15) | 0.0060 (13) | 0.0122 (13) | −0.0038 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0635 (16) | 0.0821 (19) | 0.087 (2) | 0.0011 (14) | 0.0268 (16) | −0.0009 (14) |
| C5 | 0.0809 (18) | 0.0705 (16) | 0.0687 (16) | 0.0017 (14) | 0.0372 (15) | 0.0020 (12) |
| C6 | 0.0702 (15) | 0.0380 (12) | 0.0526 (13) | 0.0016 (10) | 0.0226 (11) | −0.0001 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0803 (16) | 0.0451 (15) | 0.0530 (13) | 0.0055 (12) | 0.0252 (12) | 0.0038 (11) |
| C8 | 0.0877 (17) | 0.0441 (13) | 0.0535 (13) | 0.0094 (12) | 0.0198 (12) | 0.0069 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0733 (15) | 0.0474 (14) | 0.0556 (13) | 0.0164 (12) | 0.0117 (12) | 0.0094 (10) |
| C10 | 0.0643 (14) | 0.0413 (13) | 0.0549 (13) | 0.0079 (11) | 0.0115 (11) | 0.0077 (9) |
| C11 | 0.0672 (14) | 0.0435 (13) | 0.0596 (13) | 0.0097 (11) | 0.0158 (11) | 0.0037 (10) |
| C12 | 0.0631 (14) | 0.0409 (12) | 0.0522 (12) | −0.0002 (11) | 0.0031 (11) | −0.0037 (10) |
| C13 | 0.0656 (15) | 0.0497 (14) | 0.0621 (14) | 0.0027 (12) | 0.0040 (13) | −0.0012 (11) |
| C14 | 0.0597 (15) | 0.0575 (16) | 0.0884 (18) | 0.0001 (13) | 0.0105 (14) | −0.0153 (14) |
| C15 | 0.0815 (18) | 0.0529 (15) | 0.0763 (17) | −0.0159 (14) | 0.0227 (15) | −0.0202 (13) |
| C16 | 0.0898 (19) | 0.0559 (16) | 0.0635 (15) | −0.0092 (14) | 0.0163 (15) | −0.0017 (12) |
| C17 | 0.0702 (15) | 0.0513 (15) | 0.0592 (14) | 0.0028 (12) | 0.0079 (13) | 0.0031 (11) |
| C18 | 0.109 (2) | 0.089 (2) | 0.120 (2) | −0.0272 (18) | 0.058 (2) | −0.0307 (18) |
| N1 | 0.0741 (12) | 0.0373 (11) | 0.0504 (10) | 0.0061 (9) | 0.0144 (9) | 0.0024 (8) |
| N2 | 0.0660 (11) | 0.0395 (10) | 0.0518 (10) | 0.0089 (9) | 0.0089 (9) | 0.0057 (8) |
| O1 | 0.1381 (16) | 0.0460 (11) | 0.0679 (10) | 0.0203 (10) | 0.0104 (10) | −0.0024 (8) |
| O2 | 0.0933 (12) | 0.0732 (11) | 0.0470 (8) | 0.0107 (9) | 0.0088 (8) | 0.0031 (7) |
| O3 | 0.0833 (11) | 0.0487 (9) | 0.0760 (10) | 0.0128 (8) | 0.0169 (9) | −0.0088 (7) |
| F1 | 0.0793 (10) | 0.1325 (14) | 0.0878 (10) | 0.0192 (9) | 0.0422 (8) | 0.0291 (9) |
| F2 | 0.1248 (13) | 0.1301 (14) | 0.0601 (9) | 0.0342 (11) | 0.0437 (9) | 0.0201 (8) |
| S1 | 0.0722 (4) | 0.0485 (4) | 0.0499 (3) | 0.0083 (3) | 0.0084 (3) | −0.0018 (2) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—F1 | 1.347 (2) | C10—H10A | 0.9700 |
| C1—C2 | 1.367 (3) | C10—H10B | 0.9700 |
| C1—C6 | 1.369 (3) | C11—N1 | 1.466 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.351 (3) | C11—H11A | 0.9700 |
| C2—F2 | 1.352 (3) | C11—H11B | 0.9700 |
| C3—C4 | 1.375 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.387 (3) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C12—C17 | 1.387 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.375 (3) | C12—S1 | 1.751 (2) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C13—C14 | 1.374 (3) |
| C5—C6 | 1.379 (3) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C14—C15 | 1.383 (4) |
| C6—C7 | 1.498 (3) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C7—O1 | 1.225 (3) | C15—C16 | 1.380 (4) |
| C7—N1 | 1.330 (3) | C15—C18 | 1.497 (4) |
| C8—N1 | 1.454 (3) | C16—C17 | 1.372 (3) |
| C8—C9 | 1.496 (3) | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C8—H8A | 0.9700 | C17—H17 | 0.9300 |
| C8—H8B | 0.9700 | C18—H18A | 0.9600 |
| C9—N2 | 1.470 (3) | C18—H18B | 0.9600 |
| C9—H9A | 0.9700 | C18—H18C | 0.9600 |
| C9—H9B | 0.9700 | N2—S1 | 1.6311 (17) |
| C10—N2 | 1.470 (2) | O2—S1 | 1.4234 (15) |
| C10—C11 | 1.500 (3) | O3—S1 | 1.4281 (16) |
| F1—C1—C2 | 119.3 (2) | C10—C11—H11A | 109.5 |
| F1—C1—C6 | 119.3 (2) | N1—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 121.4 (2) | C10—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—F2 | 120.1 (2) | H11A—C11—H11B | 108.1 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 121.2 (2) | C13—C12—C17 | 119.3 (2) |
| F2—C2—C1 | 118.7 (2) | C13—C12—S1 | 120.31 (18) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 118.6 (2) | C17—C12—S1 | 120.34 (18) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.7 | C14—C13—C12 | 119.8 (2) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.7 | C14—C13—H13 | 120.1 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.3 (2) | C12—C13—H13 | 120.1 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.9 | C13—C14—C15 | 121.6 (2) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.9 | C13—C14—H14 | 119.2 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.1 (2) | C15—C14—H14 | 119.2 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.4 | C16—C15—C14 | 117.7 (3) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.4 | C16—C15—C18 | 121.7 (3) |
| C1—C6—C5 | 117.3 (2) | C14—C15—C18 | 120.6 (3) |
| C1—C6—C7 | 120.6 (2) | C17—C16—C15 | 121.9 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 121.8 (2) | C17—C16—H16 | 119.0 |
| O1—C7—N1 | 122.5 (2) | C15—C16—H16 | 119.0 |
| O1—C7—C6 | 119.0 (2) | C16—C17—C12 | 119.6 (2) |
| N1—C7—C6 | 118.36 (19) | C16—C17—H17 | 120.2 |
| N1—C8—C9 | 110.67 (17) | C12—C17—H17 | 120.2 |
| N1—C8—H8A | 109.5 | C15—C18—H18A | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8A | 109.5 | C15—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| N1—C8—H8B | 109.5 | H18A—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8B | 109.5 | C15—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| H8A—C8—H8B | 108.1 | H18A—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| N2—C9—C8 | 109.02 (18) | H18B—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| N2—C9—H9A | 109.9 | C7—N1—C8 | 120.31 (17) |
| C8—C9—H9A | 109.9 | C7—N1—C11 | 125.61 (17) |
| N2—C9—H9B | 109.9 | C8—N1—C11 | 114.06 (16) |
| C8—C9—H9B | 109.9 | C9—N2—C10 | 111.79 (16) |
| H9A—C9—H9B | 108.3 | C9—N2—S1 | 117.19 (14) |
| N2—C10—C11 | 109.02 (16) | C10—N2—S1 | 118.30 (13) |
| N2—C10—H10A | 109.9 | O2—S1—O3 | 119.91 (10) |
| C11—C10—H10A | 109.9 | O2—S1—N2 | 106.66 (9) |
| N2—C10—H10B | 109.9 | O3—S1—N2 | 106.31 (9) |
| C11—C10—H10B | 109.9 | O2—S1—C12 | 108.06 (10) |
| H10A—C10—H10B | 108.3 | O3—S1—C12 | 107.97 (10) |
| N1—C11—C10 | 110.57 (17) | N2—S1—C12 | 107.32 (9) |
| N1—C11—H11A | 109.5 | ||
| F1—C1—C2—C3 | 180.0 (2) | C15—C16—C17—C12 | −0.6 (3) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.2 (4) | C13—C12—C17—C16 | −1.0 (3) |
| F1—C1—C2—F2 | 0.8 (3) | S1—C12—C17—C16 | −179.41 (17) |
| C6—C1—C2—F2 | −179.4 (2) | O1—C7—N1—C8 | −4.0 (3) |
| F2—C2—C3—C4 | 178.9 (2) | C6—C7—N1—C8 | 172.92 (19) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.2 (4) | O1—C7—N1—C11 | 178.1 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.4 (4) | C6—C7—N1—C11 | −5.1 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.1 (4) | C9—C8—N1—C7 | 127.7 (2) |
| F1—C1—C6—C5 | −179.7 (2) | C9—C8—N1—C11 | −54.1 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.5 (3) | C10—C11—N1—C7 | −128.3 (2) |
| F1—C1—C6—C7 | −5.4 (3) | C10—C11—N1—C8 | 53.6 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | 174.8 (2) | C8—C9—N2—C10 | −60.2 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.3 (3) | C8—C9—N2—S1 | 158.59 (15) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −174.6 (2) | C11—C10—N2—C9 | 59.8 (2) |
| C1—C6—C7—O1 | −76.6 (3) | C11—C10—N2—S1 | −159.43 (14) |
| C5—C6—C7—O1 | 97.4 (3) | C9—N2—S1—O2 | −44.59 (18) |
| C1—C6—C7—N1 | 106.4 (2) | C10—N2—S1—O2 | 176.77 (15) |
| C5—C6—C7—N1 | −79.5 (3) | C9—N2—S1—O3 | −173.63 (15) |
| N1—C8—C9—N2 | 55.6 (2) | C10—N2—S1—O3 | 47.72 (18) |
| N2—C10—C11—N1 | −54.7 (2) | C9—N2—S1—C12 | 71.02 (17) |
| C17—C12—C13—C14 | 1.0 (3) | C10—N2—S1—C12 | −67.62 (17) |
| S1—C12—C13—C14 | 179.43 (16) | C13—C12—S1—O2 | 18.83 (19) |
| C12—C13—C14—C15 | 0.5 (3) | C17—C12—S1—O2 | −162.78 (17) |
| C13—C14—C15—C16 | −2.0 (3) | C13—C12—S1—O3 | 149.92 (17) |
| C13—C14—C15—C18 | 176.9 (2) | C17—C12—S1—O3 | −31.70 (19) |
| C14—C15—C16—C17 | 2.1 (3) | C13—C12—S1—N2 | −95.85 (17) |
| C18—C15—C16—C17 | −176.9 (2) | C17—C12—S1—N2 | 82.53 (18) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C4—H4···O3i | 0.93 | 2.58 | 3.495 (3) | 169 |
| C8—H8A···O3ii | 0.97 | 2.34 | 3.255 (3) | 157 |
| C10—H10B···O1iii | 0.97 | 2.48 | 3.402 (3) | 159 |
| C8—H8B···F1iv | 0.97 | 2.57 | 3.518 (3) | 165 |
| C11—H11A···F2iv | 0.97 | 2.56 | 3.296 (3) | 133 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z; (ii) x, y−1, z; (iii) x, y+1, z; (iv) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: SJ5290).
References
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Bruker (2009). APEX2, SADABS, SAINT-Plus and XPREP Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Gan, L. L., Cai, J. L. & Zhou, C. H. (2009a). Chin. Pharm. J. 44, 1361–1368.
- Gan, L. L., Lu, Y. H. & Zhou, C. H. (2009b). Chin. J. Biochem. Pharm 30, 127–131.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812051690/sj5290sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812051690/sj5290Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812051690/sj5290Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report


