Abstract
In the title compound, C15H11BrO3, the dihedral angle between the naphthofuran ring system (r.m.s. deviation = 0.022 Å) and the side chain is 4.50 (2)°. In the crystal, short Br⋯Br [3.4435 (7) Å] contacts propagating along [010] in a zigzag manner and weak π–π interactions [shortest centroid–centroid separation = 3.573 (2) Å] directedalong [100] are observed.
Related literature
For background to the biological activity of naphthofuran derivatives, see: Vaidya et al. (2011 ▶).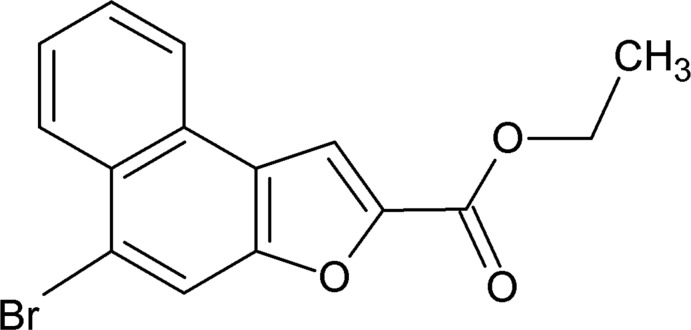
Experimental
Crystal data
C15H11BrO3
M r = 319.15
Monoclinic,

a = 7.3108 (4) Å
b = 11.1545 (6) Å
c = 15.9752 (10) Å
β = 100.921 (4)°
V = 1279.16 (13) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 3.21 mm−1
T = 298 K
0.28 × 0.24 × 0.18 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) ▶ T min = 0.467, T max = 0.595
10028 measured reflections
2249 independent reflections
1699 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.037
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.045
wR(F 2) = 0.127
S = 1.08
2249 reflections
172 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.59 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.54 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2004 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT-Plus (Bruker, 2004 ▶); data reduction: SAINT-Plus; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 2012 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681205204X/hb7019sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681205204X/hb7019Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681205204X/hb7019Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
BSPM thanks Dr H. C. Devarajegowda, Department of Physics, Yuvarajas College (constituent), University of Mysore and T. Srinivasan, Centre of Advanced Study in Crystallography and Biophysics, University of Madras Guindy Campus, Chennai for their support.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
As part of our ongoing studies of naphthofuran derivatives with possible biological activities (Vaidya et al., 2011), we now describe the structure of the title compound.
The title compound crystallizes in monoclinic crystal system with P21/c space group. The molecule is essentially planar with the dihedral angle between the mean planes defined by the naphthofuran moiety and the side chain is 4.50 (2)°, and the torsion angle of 179.81 (2)o for C15—C14—O3—C13 shows that the ethyl group is in planar orientation with the naphthofuran ring. In contrast to this, an antiperiplanar orientation is observed between the ethyl group and the naphthofuran ring in ethylnaphtho[2,1-b]furan-2-carboxylate. In the crystal, weak Br···Br and π–π interaction between the rings C1—C6 and O1—C12 occur.
Experimental
To a solution of ethyl naphtho[2,1-b]furan- 2-carboxylate (0.1 mol) in glacial acetic acid (20 ml) was added a solution of bromine (0.1 mol) in acetic acid (20 ml) with stirring during 1 h at 10–20°C and the stirring was continued for 3 h. The reaction mixture was poured into ice-cold water and the solid obtained was filtered out. It was washed with water, dried and the product was recrystallized from ethanol solution as colourless prisms.
Refinement
The H atoms were positioned with idealized geometry using a riding model with C—H = 0.93 - 0.97 Å. The isotropic displacement parameters for all H atoms were set to 1.2 times of the Ueq of the parent atom (1.5 times of the Ueq of the parent atom for CH3).
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of the title compound, showing displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
Molecular packing of the title compound. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Fig. 3.
Molecular packing of the title compound through π–π interactions are shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C15H11BrO3 | prism |
| Mr = 319.15 | Dx = 1.657 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Melting point: 402 K |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 7.3108 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 2249 reflections |
| b = 11.1545 (6) Å | θ = 2.2–25.0° |
| c = 15.9752 (10) Å | µ = 3.21 mm−1 |
| β = 100.921 (4)° | T = 298 K |
| V = 1279.16 (13) Å3 | Prism, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.28 × 0.24 × 0.18 mm |
| F(000) = 640 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2249 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1699 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.037 |
| Detector resolution: 0.95 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 2.2° |
| phi and ω scans | h = −8→8 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | k = −12→13 |
| Tmin = 0.467, Tmax = 0.595 | l = −18→18 |
| 10028 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.045 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.127 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.08 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0587P)2 + 1.4776P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2249 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 172 parameters | Δρmax = 0.59 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.54 e Å−3 |
| 0 constraints |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C15 | −0.1065 (7) | −0.5565 (4) | 0.3863 (3) | 0.0671 (13) | |
| H15A | −0.1556 | −0.6243 | 0.3523 | 0.101* | |
| H15B | −0.1951 | −0.5306 | 0.4198 | 0.101* | |
| H15C | 0.0077 | −0.5787 | 0.4233 | 0.101* | |
| O1 | 0.1492 (4) | −0.0566 (2) | 0.36398 (17) | 0.0472 (7) | |
| C1 | 0.3625 (5) | 0.1416 (3) | 0.5778 (3) | 0.0429 (10) | |
| C2 | 0.4360 (6) | 0.2041 (4) | 0.6518 (3) | 0.0584 (12) | |
| H2 | 0.4792 | 0.2821 | 0.6487 | 0.070* | |
| C3 | 0.4446 (7) | 0.1483 (5) | 0.7312 (4) | 0.0722 (15) | |
| H3 | 0.4956 | 0.1924 | 0.7794 | 0.087* | |
| C4 | 0.3872 (6) | 0.0395 (4) | 0.7436 (3) | 0.0581 (12) | |
| H4 | 0.3924 | 0.0076 | 0.7978 | 0.070* | |
| C5 | 0.3127 (6) | −0.0296 (4) | 0.6643 (3) | 0.0552 (11) | |
| H5 | 0.2734 | −0.1083 | 0.6687 | 0.066* | |
| C6 | 0.3009 (5) | 0.0217 (3) | 0.5838 (3) | 0.0442 (9) | |
| C7 | 0.2283 (5) | −0.0402 (3) | 0.5065 (3) | 0.0402 (9) | |
| C8 | 0.2182 (5) | 0.0167 (3) | 0.4302 (3) | 0.0420 (9) | |
| C9 | 0.2729 (6) | 0.1358 (3) | 0.4210 (3) | 0.0497 (10) | |
| H9 | 0.2609 | 0.1722 | 0.3678 | 0.060* | |
| C10 | 0.3435 (5) | 0.1938 (3) | 0.4934 (3) | 0.0487 (11) | |
| C11 | 0.1573 (5) | −0.1595 (3) | 0.4862 (3) | 0.0422 (9) | |
| H11 | 0.1442 | −0.2204 | 0.5244 | 0.051* | |
| C12 | 0.1141 (5) | −0.1642 (3) | 0.4006 (3) | 0.0421 (9) | |
| C13 | 0.0419 (6) | −0.2605 (4) | 0.3405 (3) | 0.0488 (10) | |
| C14 | −0.0706 (7) | −0.4583 (4) | 0.3302 (3) | 0.0616 (12) | |
| H14A | 0.0183 | −0.4838 | 0.2958 | 0.074* | |
| H14B | −0.1852 | −0.4355 | 0.2923 | 0.074* | |
| O2 | 0.0212 (6) | −0.2527 (3) | 0.2649 (2) | 0.0744 (10) | |
| O3 | 0.0034 (4) | −0.3571 (2) | 0.38317 (19) | 0.0535 (8) | |
| Br1 | 0.42767 (7) | 0.35357 (4) | 0.48343 (4) | 0.0708 (2) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C15 | 0.088 (3) | 0.045 (3) | 0.069 (3) | −0.018 (2) | 0.017 (3) | −0.009 (2) |
| O1 | 0.0569 (16) | 0.0351 (15) | 0.0501 (17) | −0.0048 (12) | 0.0113 (13) | 0.0043 (12) |
| C1 | 0.0341 (18) | 0.034 (2) | 0.063 (3) | 0.0046 (16) | 0.0143 (18) | −0.0021 (19) |
| C2 | 0.053 (3) | 0.045 (3) | 0.075 (3) | 0.000 (2) | 0.007 (2) | −0.014 (2) |
| C3 | 0.064 (3) | 0.082 (4) | 0.065 (4) | 0.009 (3) | −0.003 (3) | −0.029 (3) |
| C4 | 0.046 (2) | 0.059 (3) | 0.069 (3) | 0.007 (2) | 0.009 (2) | 0.030 (2) |
| C5 | 0.057 (2) | 0.051 (3) | 0.059 (3) | 0.006 (2) | 0.014 (2) | 0.007 (2) |
| C6 | 0.0378 (19) | 0.040 (2) | 0.056 (3) | 0.0072 (16) | 0.0116 (18) | 0.0010 (19) |
| C7 | 0.0356 (18) | 0.033 (2) | 0.052 (2) | 0.0031 (15) | 0.0074 (17) | −0.0044 (18) |
| C8 | 0.0411 (19) | 0.034 (2) | 0.053 (3) | 0.0019 (16) | 0.0152 (18) | 0.0009 (19) |
| C9 | 0.053 (2) | 0.037 (2) | 0.063 (3) | 0.0029 (18) | 0.020 (2) | 0.008 (2) |
| C10 | 0.040 (2) | 0.0272 (19) | 0.081 (3) | −0.0003 (16) | 0.018 (2) | −0.001 (2) |
| C11 | 0.044 (2) | 0.035 (2) | 0.049 (3) | 0.0037 (16) | 0.0113 (18) | 0.0072 (18) |
| C12 | 0.042 (2) | 0.030 (2) | 0.054 (3) | −0.0015 (16) | 0.0098 (18) | 0.0041 (17) |
| C13 | 0.051 (2) | 0.044 (2) | 0.052 (3) | −0.0052 (18) | 0.010 (2) | 0.000 (2) |
| C14 | 0.083 (3) | 0.045 (2) | 0.057 (3) | −0.015 (2) | 0.014 (2) | −0.015 (2) |
| O2 | 0.114 (3) | 0.063 (2) | 0.046 (2) | −0.027 (2) | 0.0132 (19) | −0.0010 (16) |
| O3 | 0.0742 (19) | 0.0390 (16) | 0.0463 (17) | −0.0151 (14) | 0.0087 (15) | −0.0038 (13) |
| Br1 | 0.0814 (4) | 0.0354 (3) | 0.0987 (5) | −0.0111 (2) | 0.0247 (3) | 0.0021 (2) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C15—C14 | 1.470 (7) | C6—C7 | 1.426 (6) |
| C15—H15A | 0.9600 | C7—C8 | 1.363 (6) |
| C15—H15B | 0.9600 | C7—C11 | 1.443 (5) |
| C15—H15C | 0.9600 | C8—C9 | 1.403 (5) |
| O1—C8 | 1.357 (5) | C9—C10 | 1.341 (6) |
| O1—C12 | 1.380 (4) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.389 (6) | C10—Br1 | 1.902 (4) |
| C1—C6 | 1.420 (5) | C10—Br1 | 1.902 (4) |
| C1—C10 | 1.451 (6) | C11—C12 | 1.345 (6) |
| C2—C3 | 1.404 (8) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C12—C13 | 1.471 (6) |
| C3—C4 | 1.311 (7) | C13—O2 | 1.192 (5) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C13—O3 | 1.333 (5) |
| C4—C5 | 1.495 (7) | C14—O3 | 1.452 (5) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C14—H14A | 0.9700 |
| C5—C6 | 1.396 (6) | C14—H14B | 0.9700 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | Br1—Br1 | 0.0000 |
| C14—C15—H15A | 109.5 | O1—C8—C9 | 124.0 (4) |
| C14—C15—H15B | 109.5 | C7—C8—C9 | 124.5 (4) |
| H15A—C15—H15B | 109.5 | C10—C9—C8 | 115.9 (4) |
| C14—C15—H15C | 109.5 | C10—C9—H9 | 122.1 |
| H15A—C15—H15C | 109.5 | C8—C9—H9 | 122.1 |
| H15B—C15—H15C | 109.5 | C9—C10—C1 | 124.2 (4) |
| C8—O1—C12 | 105.4 (3) | C9—C10—Br1 | 117.2 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 119.5 (4) | C1—C10—Br1 | 118.5 (3) |
| C2—C1—C10 | 122.9 (4) | C9—C10—Br1 | 117.2 (3) |
| C6—C1—C10 | 117.6 (4) | C1—C10—Br1 | 118.5 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.4 (4) | Br1—C10—Br1 | 0.00 (4) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.3 | C12—C11—C7 | 105.7 (3) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.3 | C12—C11—H11 | 127.2 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 125.9 (5) | C7—C11—H11 | 127.2 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 117.1 | C11—C12—O1 | 111.7 (3) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 117.1 | C11—C12—C13 | 132.7 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 115.1 (5) | O1—C12—C13 | 115.6 (4) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 122.4 | O2—C13—O3 | 125.4 (4) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 122.4 | O2—C13—C12 | 124.7 (4) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 121.2 (4) | O3—C13—C12 | 110.0 (4) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.4 | O3—C14—C15 | 108.3 (4) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.4 | O3—C14—H14A | 110.0 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 118.9 (4) | C15—C14—H14A | 110.0 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 123.1 (4) | O3—C14—H14B | 110.0 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 118.0 (4) | C15—C14—H14B | 110.0 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 119.8 (4) | H14A—C14—H14B | 108.4 |
| C8—C7—C11 | 105.8 (4) | C13—O3—C14 | 114.9 (3) |
| C6—C7—C11 | 134.4 (4) | Br1—Br1—C10 | 0 |
| O1—C8—C7 | 111.4 (3) |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HB7019).
References
- Bruker (2004). APEX2 and SAINT-Plus. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Vaidya, V. P., Mahadevan, K. M., Shet Prakash, M., Sreenivas, S. & Shivananda, M. K. (2011). Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2, 334–342.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681205204X/hb7019sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681205204X/hb7019Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681205204X/hb7019Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report





