Abstract
In the title compound, C16H22Cl2N2O2, the substituted piperidine ring adopts a chair conformation with both substituents in equatorial positions. In the crystal, N—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds connect molecules into ribbons along the a-axis direction.
Related literature
For the biological activity of piperazine derivatives, see: Hamed et al. (2012 ▶); Joergen et al. (1997 ▶); Peter et al. (2009 ▶). For the synthesis of the title compound, see: Vardanyan et al. (2009 ▶).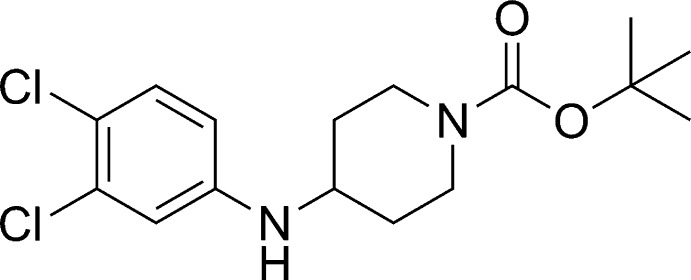
Experimental
Crystal data
C16H22Cl2N2O2
M r = 345.25
Orthorhombic,
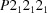
a = 9.7825 (6) Å
b = 10.6075 (6) Å
c = 16.8215 (10) Å
V = 1745.53 (18) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.38 mm−1
T = 100 K
0.40 × 0.40 × 0.30 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa APEXII DUO CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009 ▶) T min = 0.662, T max = 0.749
34136 measured reflections
13197 independent reflections
11079 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.024
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.034
wR(F 2) = 0.079
S = 1.00
13197 reflections
202 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.44 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.19 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), 6110 Friedel pairs
Flack parameter: −0.01 (2)
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2009 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2009 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: OLEX2 (Dolomanov et al., 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812051896/zl2529sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812051896/zl2529Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812051896/zl2529Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯O2i | 0.88 | 2.12 | 2.9740 (8) | 163 |
| C3—H3⋯O2i | 0.95 | 2.58 | 3.3486 (9) | 138 |
Symmetry code: (i) 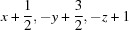 .
.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge a grant from the Higher Education Commission of Pakistan under the IRSIP programme to support PhD students. The Bruker Kappa APEXII DUO was purchased with funding from NSF grant CHE-0741837. The work was supported in part by grants from the US Public Health Service and National Institutes of Health (DA06284 and DA13449).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Piperazine derivatives have been shown to inhibit re-uptake of the monoamines dopamine, noradrenaline and serotonin in synaptosomes (Joergen et al., 1997), and their use for the treatment of protozoal infections, particularly malaria, has also been reported (Hamed et al., 2012). Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI) provide efficacy in the treatment of numerous CNS disorders, including depression and panic disorders, and are usually observed to be effective, well tolerated and simply administered (Peter et al., 2009)). During our search to find new synthetic novel multivalent ligands for the treatment of pain and depression, the title compound was synthesized as an intermediate. Compounds prepared from this intermediate are now under study for possible opioid and SSRIs activities.
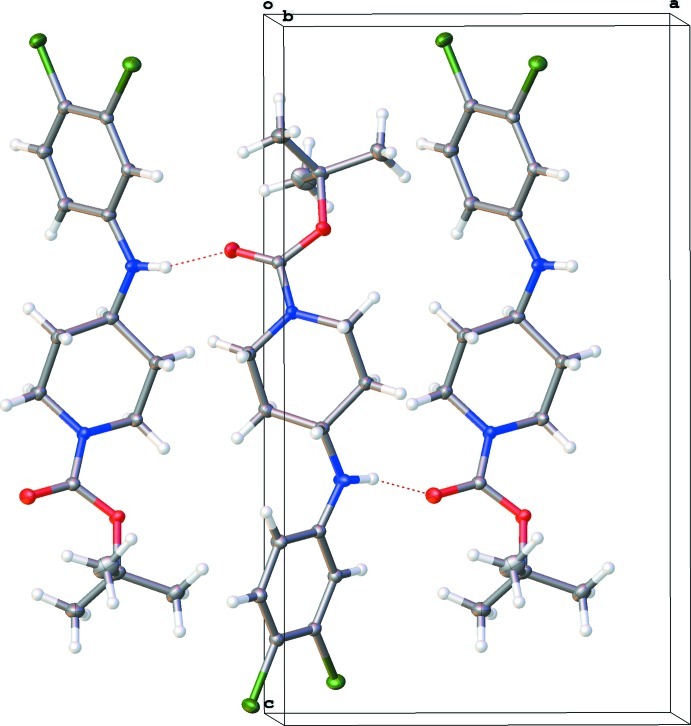
The piperidine ring is in a chair conformation with both substituents in equatorial positions. An intermolecular hydrogen bond is present between N1—H1 and O2 with a donor-hydrogen-acceptor angle of 163.40° and a donor-aceptor distance of 2.9740 (8) Å. Hydrogen bonds connect molecules into ribbons extending in the crystallographic a direction. The hydrogen bonding graph set is C1,1(8)a.
Experimental
tert-Butyl 4-((3,4-dichlorophenyl)amino)piperidine-1-carboxylate (1) was synthesized by modification of a reported method (Vardanyan et al., 2009) by refluxing N-Boc-4-piperidone (5.0 g, 25.1 mmol) and 3,4-dichloroaniline (4.07 g, 25.1 mmol) in toluene (100 ml) with a catalytic amount of p-toluene sulphonic acid using a Dean and Stark apparatus for 4–5 h. The reaction was left to cool overnight. Toluene was evaporated under reduced pressure. The crude product was dissolved in diethyl ether, passed through a bed of neutral alumina, and the ether evaporated under reduced pressure. The residue was dissolved in CH3OH (50 ml) and NaBH4 (1.05 g, 27.6 mmol) was added slowly at room temperature. The reaction mixture was left to stir overnight. The reaction was quenched with aqueous NaHCO3 (5 ml). The solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the residue was dissolved in diethyl ether, dried over anhydrous MgSO4, filtered and evaporated under reduced pressure. The residue was recrystallized from CH3OH to obtain (1) as a white crystalline solid. Crystals appropriate for X-ray diffraction were grown from methanol by slow evaporation at room temperature. 8.22 g (95%) yield; m.p. 155–157 °C; MS (ESI): m/z: [M+H]+: 345; HRMS: Calcd for C16H23Cl2N2O2: 345.113; found: 345.1131.
Refinement
All hydrogen atoms were visible in a difference Fourier map and were added at calculated positions. Bond distances are set to 0.95 Å for carbon-hydrogen bonds, and 0.88 Å for nitrogen-hydrogen bonds. Thermal parameters for hydrogen atoms were set to 1.2 times the isotropic equivalent thermal parameter of the atom to which the hydrogen atom is bonded.
Figures
Fig. 1.
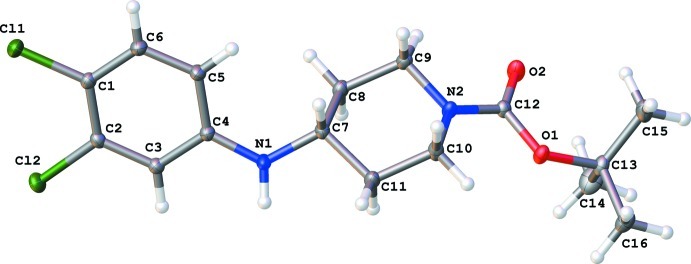
The molecular structure of the title compound. Anisotropically refined atoms are shown as 50% probability ellipsoids.
Fig. 2.
Hydrogen bonding interactions, shown as dashed lines. The molecules are connected into a chain running along the a direction in the crystal.
Crystal data
| C16H22Cl2N2O2 | Dx = 1.302 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 345.25 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Cell parameters from 9939 reflections |
| a = 9.7825 (6) Å | θ = 2.8–40.0° |
| b = 10.6075 (6) Å | µ = 0.38 mm−1 |
| c = 16.8215 (10) Å | T = 100 K |
| V = 1745.53 (18) Å3 | Rod, clear colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.40 × 0.40 × 0.30 mm |
| F(000) = 728 |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII DUO CCD diffractometer | 13197 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 11079 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.024 |
| Detector resolution: 8.3333 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 43.7°, θmin = 2.3° |
| φ and ω scans | h = −19→17 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009) | k = −20→15 |
| Tmin = 0.662, Tmax = 0.749 | l = −32→22 |
| 34136 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.034 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.079 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0361P)2 + 0.1129P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.00 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.002 |
| 13197 reflections | Δρmax = 0.44 e Å−3 |
| 202 parameters | Δρmin = −0.19 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), ???? Friedel pairs |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Flack parameter: −0.01 (2) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | −0.08164 (2) | 0.97197 (2) | 0.972015 (11) | 0.02294 (4) | |
| Cl2 | 0.13863 (19) | 0.75577 (18) | 0.941766 (10) | 0.01982 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.10534 (5) | 0.83348 (5) | 0.29230 (3) | 0.01589 (9) | |
| O2 | −0.11737 (5) | 0.79311 (6) | 0.32343 (3) | 0.01988 (10) | |
| C14 | 0.06777 (12) | 0.63102 (8) | 0.22473 (6) | 0.03006 (19) | |
| H14A | 0.1276 | 0.595 | 0.2655 | 0.045* | |
| H14B | 0.0822 | 0.5867 | 0.1743 | 0.045* | |
| H14C | −0.0278 | 0.6217 | 0.2412 | 0.045* | |
| C3 | 0.13364 (7) | 0.82954 (6) | 0.78917 (4) | 0.01425 (10) | |
| H3 | 0.2006 | 0.7658 | 0.7815 | 0.017* | |
| C13 | 0.10078 (8) | 0.77016 (7) | 0.21416 (4) | 0.01681 (11) | |
| C12 | −0.00406 (7) | 0.83543 (6) | 0.34047 (4) | 0.01344 (10) | |
| N2 | 0.02566 (6) | 0.89021 (6) | 0.41112 (4) | 0.01450 (9) | |
| C10 | 0.15552 (7) | 0.95171 (7) | 0.43015 (4) | 0.01648 (11) | |
| H10A | 0.1433 | 1.0444 | 0.4296 | 0.02* | |
| H10B | 0.2247 | 0.9295 | 0.3895 | 0.02* | |
| C11 | 0.20526 (7) | 0.90986 (8) | 0.51199 (4) | 0.01733 (12) | |
| H11A | 0.2881 | 0.9585 | 0.5263 | 0.021* | |
| H11B | 0.2306 | 0.8196 | 0.5099 | 0.021* | |
| C7 | 0.09632 (7) | 0.92909 (7) | 0.57613 (4) | 0.01480 (10) | |
| H7 | 0.0784 | 1.0215 | 0.5816 | 0.018* | |
| N1 | 0.14933 (7) | 0.88223 (7) | 0.65131 (4) | 0.01898 (11) | |
| H1 | 0.2255 | 0.8381 | 0.6502 | 0.023* | |
| C4 | 0.08893 (7) | 0.90197 (6) | 0.72395 (4) | 0.01433 (10) | |
| C5 | −0.01262 (8) | 0.99380 (7) | 0.73731 (4) | 0.01686 (12) | |
| H5 | −0.0468 | 1.0417 | 0.6939 | 0.02* | |
| C6 | −0.06310 (7) | 1.01490 (7) | 0.81332 (4) | 0.01730 (11) | |
| H6 | −0.1303 | 1.0783 | 0.8215 | 0.021* | |
| C1 | −0.01660 (7) | 0.94440 (7) | 0.87772 (4) | 0.01538 (11) | |
| C2 | 0.08092 (7) | 0.85036 (6) | 0.86435 (4) | 0.01397 (10) | |
| C9 | −0.08241 (7) | 0.91113 (7) | 0.46944 (4) | 0.01573 (10) | |
| H9A | −0.1662 | 0.8659 | 0.4528 | 0.019* | |
| H9B | −0.1039 | 1.0022 | 0.4724 | 0.019* | |
| C8 | −0.03699 (7) | 0.86400 (7) | 0.55099 (4) | 0.01653 (11) | |
| H8A | −0.0228 | 0.7716 | 0.549 | 0.02* | |
| H8B | −0.1092 | 0.8818 | 0.5906 | 0.02* | |
| C16 | 0.24662 (8) | 0.78782 (8) | 0.18424 (5) | 0.02256 (14) | |
| H16A | 0.2688 | 0.8779 | 0.1832 | 0.034* | |
| H16B | 0.2547 | 0.753 | 0.1305 | 0.034* | |
| H16C | 0.3101 | 0.7439 | 0.2198 | 0.034* | |
| C15 | 0.00084 (9) | 0.83714 (10) | 0.15914 (5) | 0.02569 (16) | |
| H15A | −0.0908 | 0.8352 | 0.1826 | 0.039* | |
| H15B | −0.0007 | 0.7944 | 0.1075 | 0.039* | |
| H15C | 0.0297 | 0.9249 | 0.1519 | 0.039* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.01965 (7) | 0.03505 (10) | 0.01412 (7) | 0.00661 (7) | 0.00311 (6) | 0.00055 (6) |
| Cl2 | 0.02267 (7) | 0.02154 (7) | 0.01526 (6) | 0.00232 (6) | −0.00074 (6) | 0.00598 (6) |
| O1 | 0.0154 (2) | 0.0189 (2) | 0.01340 (19) | −0.00364 (16) | 0.00210 (15) | −0.00379 (17) |
| O2 | 0.0162 (2) | 0.0272 (3) | 0.0163 (2) | −0.00867 (19) | −0.00053 (17) | −0.00255 (19) |
| C14 | 0.0419 (5) | 0.0163 (3) | 0.0320 (4) | −0.0073 (3) | 0.0078 (4) | −0.0062 (3) |
| C3 | 0.0142 (2) | 0.0149 (2) | 0.0137 (2) | 0.0010 (2) | −0.0004 (2) | 0.0009 (2) |
| C13 | 0.0203 (3) | 0.0166 (3) | 0.0135 (2) | −0.0034 (2) | 0.0022 (2) | −0.0035 (2) |
| C12 | 0.0144 (2) | 0.0139 (2) | 0.0120 (2) | −0.0024 (2) | −0.00017 (19) | 0.00076 (19) |
| N2 | 0.0122 (2) | 0.0189 (2) | 0.0124 (2) | −0.00349 (18) | 0.00084 (17) | −0.00202 (18) |
| C10 | 0.0145 (2) | 0.0219 (3) | 0.0131 (2) | −0.0061 (2) | −0.0004 (2) | 0.0001 (2) |
| C11 | 0.0132 (2) | 0.0253 (3) | 0.0135 (3) | 0.0000 (2) | −0.0002 (2) | −0.0005 (2) |
| C7 | 0.0151 (2) | 0.0174 (3) | 0.0119 (2) | 0.0014 (2) | −0.00057 (19) | 0.0005 (2) |
| N1 | 0.0201 (3) | 0.0252 (3) | 0.0116 (2) | 0.0098 (2) | 0.0005 (2) | 0.0014 (2) |
| C4 | 0.0145 (2) | 0.0160 (2) | 0.0124 (2) | 0.0019 (2) | 0.0001 (2) | 0.00067 (19) |
| C5 | 0.0173 (3) | 0.0190 (3) | 0.0142 (3) | 0.0052 (2) | 0.0003 (2) | 0.0022 (2) |
| C6 | 0.0166 (3) | 0.0199 (3) | 0.0155 (3) | 0.0044 (2) | 0.0011 (2) | 0.0010 (2) |
| C1 | 0.0140 (2) | 0.0188 (3) | 0.0133 (2) | 0.0005 (2) | 0.0013 (2) | 0.0004 (2) |
| C2 | 0.0135 (2) | 0.0150 (2) | 0.0134 (2) | −0.0005 (2) | −0.0013 (2) | 0.00250 (19) |
| C9 | 0.0132 (2) | 0.0197 (3) | 0.0143 (2) | −0.0003 (2) | 0.0008 (2) | −0.0017 (2) |
| C8 | 0.0159 (3) | 0.0197 (3) | 0.0140 (3) | −0.0014 (2) | 0.0024 (2) | 0.0007 (2) |
| C16 | 0.0219 (3) | 0.0250 (3) | 0.0208 (3) | −0.0014 (3) | 0.0062 (3) | −0.0042 (3) |
| C15 | 0.0246 (3) | 0.0378 (4) | 0.0147 (3) | 0.0000 (3) | −0.0006 (3) | 0.0007 (3) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cl1—C1 | 1.7338 (7) | C7—N1 | 1.4544 (9) |
| Cl2—C2 | 1.7382 (7) | C7—C8 | 1.5350 (10) |
| O1—C12 | 1.3425 (8) | C7—H7 | 1.0 |
| O1—C13 | 1.4767 (8) | N1—C4 | 1.3734 (9) |
| O2—C12 | 1.2298 (8) | N1—H1 | 0.88 |
| C14—C13 | 1.5213 (11) | C4—C5 | 1.4093 (10) |
| C14—H14A | 0.98 | C5—C6 | 1.3888 (10) |
| C14—H14B | 0.98 | C5—H5 | 0.95 |
| C14—H14C | 0.98 | C6—C1 | 1.3928 (10) |
| C3—C2 | 1.3835 (10) | C6—H6 | 0.95 |
| C3—C4 | 1.4090 (9) | C1—C2 | 1.3984 (10) |
| C3—H3 | 0.95 | C9—C8 | 1.5261 (10) |
| C13—C15 | 1.5223 (12) | C9—H9A | 0.99 |
| C13—C16 | 1.5244 (11) | C9—H9B | 0.99 |
| C12—N2 | 1.3545 (9) | C8—H8A | 0.99 |
| N2—C9 | 1.4592 (9) | C8—H8B | 0.99 |
| N2—C10 | 1.4635 (9) | C16—H16A | 0.98 |
| C10—C11 | 1.5260 (10) | C16—H16B | 0.98 |
| C10—H10A | 0.99 | C16—H16C | 0.98 |
| C10—H10B | 0.99 | C15—H15A | 0.98 |
| C11—C7 | 1.5302 (10) | C15—H15B | 0.98 |
| C11—H11A | 0.99 | C15—H15C | 0.98 |
| C11—H11B | 0.99 | ||
| C12—O1—C13 | 121.34 (5) | C4—N1—H1 | 117.7 |
| C13—C14—H14A | 109.5 | C7—N1—H1 | 117.7 |
| C13—C14—H14B | 109.5 | N1—C4—C3 | 118.43 (6) |
| H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 | N1—C4—C5 | 123.40 (6) |
| C13—C14—H14C | 109.5 | C3—C4—C5 | 118.14 (6) |
| H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 | C6—C5—C4 | 120.58 (6) |
| H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 | C6—C5—H5 | 119.7 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.59 (6) | C4—C5—H5 | 119.7 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.7 | C5—C6—C1 | 120.90 (7) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.7 | C5—C6—H6 | 119.6 |
| O1—C13—C15 | 110.38 (6) | C1—C6—H6 | 119.6 |
| O1—C13—C16 | 102.11 (6) | C6—C1—C2 | 118.73 (6) |
| C15—C13—C16 | 110.06 (7) | C6—C1—Cl1 | 120.08 (5) |
| O1—C13—C14 | 110.10 (6) | C2—C1—Cl1 | 121.19 (5) |
| C15—C13—C14 | 112.80 (7) | C3—C2—C1 | 121.01 (6) |
| C16—C13—C14 | 110.89 (7) | C3—C2—Cl2 | 118.14 (5) |
| O2—C12—O1 | 124.91 (6) | C1—C2—Cl2 | 120.85 (5) |
| O2—C12—N2 | 123.67 (6) | N2—C9—C8 | 110.10 (6) |
| O1—C12—N2 | 111.42 (6) | N2—C9—H9A | 109.6 |
| C12—N2—C9 | 119.98 (6) | C8—C9—H9A | 109.6 |
| C12—N2—C10 | 124.71 (6) | N2—C9—H9B | 109.6 |
| C9—N2—C10 | 114.45 (6) | C8—C9—H9B | 109.6 |
| N2—C10—C11 | 110.14 (6) | H9A—C9—H9B | 108.2 |
| N2—C10—H10A | 109.6 | C9—C8—C7 | 110.34 (6) |
| C11—C10—H10A | 109.6 | C9—C8—H8A | 109.6 |
| N2—C10—H10B | 109.6 | C7—C8—H8A | 109.6 |
| C11—C10—H10B | 109.6 | C9—C8—H8B | 109.6 |
| H10A—C10—H10B | 108.1 | C7—C8—H8B | 109.6 |
| C10—C11—C7 | 112.04 (6) | H8A—C8—H8B | 108.1 |
| C10—C11—H11A | 109.2 | C13—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| C7—C11—H11A | 109.2 | C13—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C10—C11—H11B | 109.2 | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C7—C11—H11B | 109.2 | C13—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| H11A—C11—H11B | 107.9 | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| N1—C7—C11 | 108.61 (6) | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| N1—C7—C8 | 112.88 (6) | C13—C15—H15A | 109.5 |
| C11—C7—C8 | 109.72 (6) | C13—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| N1—C7—H7 | 108.5 | H15A—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C11—C7—H7 | 108.5 | C13—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 108.5 | H15A—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C4—N1—C7 | 124.62 (6) | H15B—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C12—O1—C13—C15 | 65.40 (8) | C2—C3—C4—N1 | 176.69 (7) |
| C12—O1—C13—C16 | −177.61 (6) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | −1.34 (10) |
| C12—O1—C13—C14 | −59.79 (9) | N1—C4—C5—C6 | −175.62 (7) |
| C13—O1—C12—O2 | −4.42 (11) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | 2.31 (11) |
| C13—O1—C12—N2 | 175.50 (6) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | −1.23 (12) |
| O2—C12—N2—C9 | −5.18 (11) | C5—C6—C1—C2 | −0.86 (11) |
| O1—C12—N2—C9 | 174.90 (6) | C5—C6—C1—Cl1 | −179.73 (6) |
| O2—C12—N2—C10 | −174.00 (7) | C4—C3—C2—C1 | −0.72 (11) |
| O1—C12—N2—C10 | 6.08 (10) | C4—C3—C2—Cl2 | 178.95 (5) |
| C12—N2—C10—C11 | −134.30 (7) | C6—C1—C2—C3 | 1.83 (11) |
| C9—N2—C10—C11 | 56.33 (8) | Cl1—C1—C2—C3 | −179.31 (6) |
| N2—C10—C11—C7 | −53.30 (8) | C6—C1—C2—Cl2 | −177.83 (6) |
| C10—C11—C7—N1 | 177.63 (6) | Cl1—C1—C2—Cl2 | 1.03 (9) |
| C10—C11—C7—C8 | 53.82 (8) | C12—N2—C9—C8 | 131.49 (7) |
| C11—C7—N1—C4 | 169.17 (7) | C10—N2—C9—C8 | −58.59 (8) |
| C8—C7—N1—C4 | −68.92 (9) | N2—C9—C8—C7 | 56.87 (7) |
| C7—N1—C4—C3 | 166.47 (7) | N1—C7—C8—C9 | −176.41 (6) |
| C7—N1—C4—C5 | −15.61 (12) | C11—C7—C8—C9 | −55.13 (8) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···O2i | 0.88 | 2.12 | 2.9740 (8) | 163 |
| C3—H3···O2i | 0.95 | 2.58 | 3.3486 (9) | 138 |
Symmetry code: (i) x+1/2, −y+3/2, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: ZL2529).
References
- Bruker (2009). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Hamed, A., Christoph, B., Olivier, C., Bibia, H. & Romain, S. (2012). US Patent Appl. 2012316178.
- Joergen, S.-K., Peter, M. & Frank, W. (1997). World Patent WO9730997.
- Peter, D., Eriksen, B. L., Munro, G. & Nielsen, E. (2009). World Patent WO 2009/077585.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Vardanyan, R., Vijay, G., Nichol, G. S., Liu, L., Kumarasinghe, I., Davis, P., Vanderah, T., Porreca, F., Lai, J. & Hruby, V. J. (2009). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 14, 5044–5053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812051896/zl2529sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812051896/zl2529Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812051896/zl2529Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report