Abstract
In the title compound, C21H18O2S, the central aromatic ring makes dihedral angles of 5.86 (12) and 72.02 (6)° with the rings of the terminal O-benzyl and S-benzyl groups, respectively. The dihedral angle between the peripheral phenyl rings is 66.16 (6)°. In the crystal, molecules are linked by pairs of C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming inversion dimers. These dimers are linked via C—H⋯π interactions, forming a three-dimensional network.
Related literature
For related structures, see: Radić et al. (2012 ▶); Lucena et al. (1996 ▶); Sillanpää et al. (1994 ▶); Alhadi et al. (2010 ▶). For the biological activity of thiosalicylic acid derivatives, see: Bernardelli et al. (2005 ▶); Halaschek-Wiener et al. (2003 ▶); Sadao et al. (2000 ▶).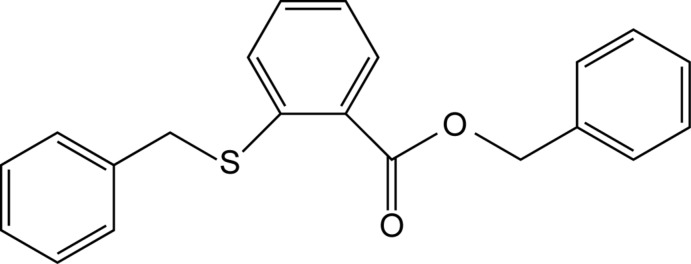
Experimental
Crystal data
C21H18O2S
M r = 334.41
Triclinic,
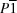
a = 5.6957 (3) Å
b = 12.1117 (11) Å
c = 13.0813 (11) Å
α = 72.748 (8)°
β = 86.477 (6)°
γ = 89.941 (6)°
V = 860.04 (12) Å3
Z = 2
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 1.74 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.11 × 0.10 × 0.05 mm
Data collection
Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur Gemini Sapphire3 diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Oxford Diffraction, 2012 ▶) T min = 0.944, T max = 1.000
5368 measured reflections
3299 independent reflections
2554 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.018
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.040
wR(F 2) = 0.113
S = 1.04
3299 reflections
217 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.21 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Oxford Diffraction, 2012 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis PRO; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 2012 ▶) and Mercury (Macrae et al., 2006 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 2012 ▶), PLATON (Spek, 2009) ▶ and PARST (Nardelli, 1995 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813001761/rz5036sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813001761/rz5036Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813001761/rz5036Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Geometry of hydrogen bonds and weak C—H⋯π interactions (Å, °).
Cg1, Cg2 and Cg3 are the centroids of the C2–C7, C9–C14 and C16–C21 rings, respectively.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C14—H14⋯O2i | 0.93 | 2.63 | 3.408 (3) | 142 |
| C4—H4⋯Cg3ii | 0.93 | 3.11 | 3.846 (3) | 137 |
| C13—H13⋯Cg3i | 0.93 | 2.88 | 3.653 (3) | 141 |
| C18—H18⋯Cg1iii | 0.93 | 3.20 | 3.820 (3) | 126 |
| C20—H20⋯Cg2iv | 0.93 | 2.96 | 3.651 (3) | 132 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 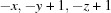 ; (ii)
; (ii) 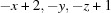 ; (iii)
; (iii) 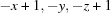 ; (iv)
; (iv) 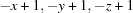 .
.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education and Science of the Republic of Serbia (Project Nos. 172016, 172034, 172014 and 172035). We thank Professor V. Divjakovic, University of Novi Sad, for help with the X-ray data collection.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Thiosalicylic acid and its derivatives find potential application in numerous disease treatments, in particular inflammatory, allergic and respiratory diseases (Bernardelli et al., 2005) as well as Ras tumor growth inhibitors (Halaschek-Wiener et al., 2003). Ketones derived from thiosalicylic acids have application as bile acid transport inhibitors (Sadao et al., 2000). In continuation of our work on structural and biological properties of thiosalicylic derivatives and their metal complexes (Radić et al., 2012) here we present the crystal structure of the novel ligand benzyl 2-(benzylsulfanyl)benzoate.
The bond lengths and angles in the title compound are within the expected ranges. The dihedral angle between aromatic rings of the central thiosalicylic and terminal O-benzyl group is 5.86 (12)° indicating a nearly co-planar orientation of these two fragments. On the other hand, the ring of the S-benzyl group is significantly twisted with respect to the central ring forming a dihedral angle of 72.02 (6)°. In the previously reported crystal structures with S-benzyl derivatives of thiosalicylic acid the analogue dihedral angle varies from 13.4 to 88.9°, suggesting the free rotation of the S-benzyl ring around the single bonds of the C3–S1–C15–C16 fragment. The specific property of the present compound is that the atoms S1, C15 are C16 all lie in the plane of the central ring within 0.03 Å. In the cases of similar uncoordinated (Sillanpää et al., 1994; Alhadi et al., 2010] as well as coordinated ligands (Radić et al., 2012; Lucena et al., 1996) the corresponding atom C16 is significantly out of the central ring plane (1.57 Å in average).
The pair of C14—H14···O2 interactions connects inversion related molecules into dimers (Table 1, Fig. 2). This connection is reinforced by means of C—H···π interactions involving the O-benzyl C13—H13 donor and the S-benzyl ring from an inversion-related molecule as acceptor (Table 1; Cg3 is the centroid of the S-benzyl ring). The S-benzyl ring also serves as a π-acceptor for C—H donors of a neighboring molecular pair; in that way the pairs of molecules further arrange into chain by C4— H4···Cg3 interactions (Table 1, Fig. 2). The molecules are further associated into a three-dimensional structure by C—H···π interactions which engage two remaining phenyl rings as π-acceptors (Table 1, Cg1 and Cg2 are centroids of central thiosalicylic and terminal O-benzyl rings, respectively).
Experimental
The thioacid ligand was prepared by alkylation of thiosalicylic acid by means of the corresponding alkyl halogenides in alkaline water-ethanol solution. Thiosalicylic acid (1 mmol) was added to a 100 cm3 round bottom flask containing 50 cm3 of a 30% solution of ethanol in water and stirred. A solution of NaOH (2 mmol in 5 cm3 of water) was added to the acid suspension, whereupon the solution became clear. The corresponding benzyl halogenide (2 mmol) was dissolved in 5 cm3 of ethanol and transferred to the stirred solution. The resulting mixture was kept overnight at 60°C. The reaction mixture was transffered into a beaker and ethanol was evaporated off on a water bath. Diluted hydrochloric acid (2 mol/dm3) was added to the resulting water solution and S-benzyl thiosalicylic acid was precipitated as a white powder. The obtained acid was filtered off and washed with plenty of distilled water. The product was dried under vacuum overnight. Crystals of the title compound suitable for X-ray determination were obtained by slow evaporation of a benzyl alcohol solution, which unexpectedly resulted in the esterification of the carboxylic group of thiosalicylic acid.
Refinement
H atoms bonded to C atoms were placed at geometrically calculated positions and refined using a riding model. C—H distances were fixed to 0.93 and 0.97 Å from aromatic and methylene C atoms, respectively. The Uiso(H) values were equal to 1.2 times Ueq of the corresponding aromatic C(sp2) and methylene C(sp3) atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
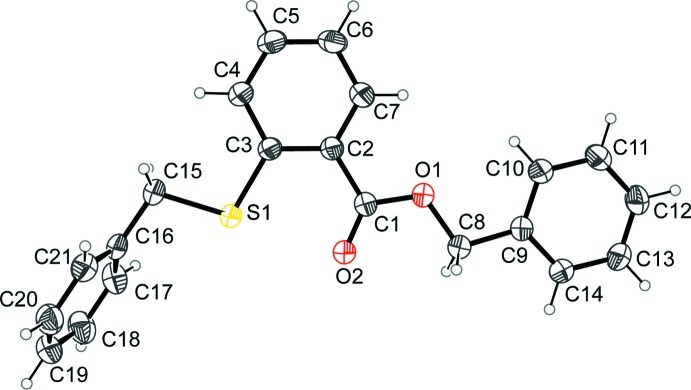
The molecular structure of the title compound with 40% probability displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms.
Fig. 2.
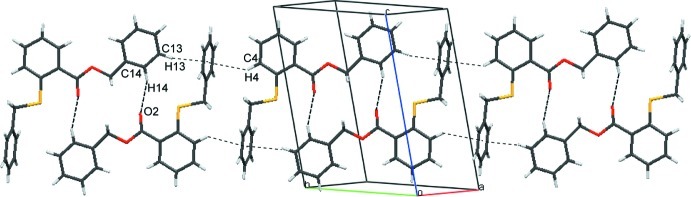
Partial crystal packing of the title compound. The C14—H···O2 and C13—H···π connected pairs of molecules are linked into a chain by C4—H4···π interactions.
Crystal data
| C21H18O2S | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 334.41 | F(000) = 352 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.291 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54180 Å |
| a = 5.6957 (3) Å | Cell parameters from 2123 reflections |
| b = 12.1117 (11) Å | θ = 3.5–72.3° |
| c = 13.0813 (11) Å | µ = 1.74 mm−1 |
| α = 72.748 (8)° | T = 293 K |
| β = 86.477 (6)° | Prism, colourless |
| γ = 89.941 (6)° | 0.11 × 0.10 × 0.05 mm |
| V = 860.04 (12) Å3 |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur Gemini Sapphire3 diffractometer | 3299 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Enhance (Cu) X-ray Source | 2554 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.018 |
| Detector resolution: 16.3280 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 72.4°, θmin = 3.6° |
| ω scans | h = −5→7 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Oxford Diffraction, 2012) | k = −14→14 |
| Tmin = 0.944, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −16→15 |
| 5368 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.040 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.113 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.04 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0493P)2 + 0.0651P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3299 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 217 parameters | Δρmax = 0.21 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. IR (KBr, cm-1): 3414, 3061, 2920, 2648, 2559, 1674, 1584, 1562, 1463, 1412, 1317, 1272, 1255, 1154, 1062, 1046, 897, 743, 711, 652, 551. 1H NMR (200 MHz, CDCl3, δ p.p.m.): 4.11 (s, 2H, C15H2), 5.45 (s, 2H, C8H2), 7.00–7.93 (m, 17H, Ar and bz). 13C NMR (50 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ p.p.m.): 38.5 (C15H2), 68.3 (C8H2) 125.0; 126.3; 126.8; 127.0; 127.2; 127.5; 127.8; 127.9; 128.1; 128.3; 128.8; 128.9, 129.3; 130.2; 133.5; 139.5; 141.7; 142.3 (Ar and bz), 166.8 (COObz). |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.60616 (9) | 0.22258 (5) | 0.48163 (4) | 0.06178 (18) | |
| O1 | 0.1278 (2) | 0.47589 (12) | 0.28903 (10) | 0.0595 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.2518 (3) | 0.37675 (15) | 0.44697 (11) | 0.0859 (6) | |
| C1 | 0.2696 (3) | 0.40163 (17) | 0.35128 (15) | 0.0549 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.4509 (3) | 0.35644 (16) | 0.28855 (14) | 0.0519 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.6149 (3) | 0.27491 (16) | 0.34054 (14) | 0.0519 (4) | |
| C4 | 0.7850 (4) | 0.23806 (19) | 0.27595 (16) | 0.0632 (5) | |
| H4 | 0.8945 | 0.1838 | 0.3081 | 0.076* | |
| C5 | 0.7919 (4) | 0.2808 (2) | 0.16621 (17) | 0.0728 (6) | |
| H5 | 0.9072 | 0.2555 | 0.1253 | 0.087* | |
| C6 | 0.6324 (4) | 0.3601 (2) | 0.11575 (17) | 0.0743 (6) | |
| H6 | 0.6388 | 0.3885 | 0.0413 | 0.089* | |
| C7 | 0.4622 (4) | 0.39694 (19) | 0.17718 (15) | 0.0650 (5) | |
| H7 | 0.3525 | 0.4501 | 0.1433 | 0.078* | |
| C8 | −0.0440 (4) | 0.53023 (19) | 0.34328 (15) | 0.0602 (5) | |
| H8A | 0.0348 | 0.5751 | 0.3817 | 0.072* | |
| H8B | −0.1426 | 0.4718 | 0.3946 | 0.072* | |
| C9 | −0.1923 (3) | 0.60777 (16) | 0.26112 (15) | 0.0522 (4) | |
| C10 | −0.1380 (4) | 0.6363 (2) | 0.15204 (16) | 0.0659 (6) | |
| H10 | −0.0031 | 0.6073 | 0.1264 | 0.079* | |
| C11 | −0.2821 (4) | 0.7076 (2) | 0.08082 (17) | 0.0725 (6) | |
| H11 | −0.2437 | 0.7260 | 0.0075 | 0.087* | |
| C12 | −0.4810 (4) | 0.7514 (2) | 0.11702 (18) | 0.0712 (6) | |
| H12 | −0.5780 | 0.7990 | 0.0686 | 0.085* | |
| C13 | −0.5362 (4) | 0.7247 (2) | 0.22537 (18) | 0.0678 (6) | |
| H13 | −0.6698 | 0.7552 | 0.2505 | 0.081* | |
| C14 | −0.3935 (3) | 0.65252 (18) | 0.29709 (16) | 0.0592 (5) | |
| H14 | −0.4332 | 0.6339 | 0.3703 | 0.071* | |
| C15 | 0.8417 (4) | 0.11867 (19) | 0.50644 (16) | 0.0637 (5) | |
| H15A | 0.8106 | 0.0571 | 0.4754 | 0.076* | |
| H15B | 0.9904 | 0.1561 | 0.4746 | 0.076* | |
| C16 | 0.8515 (3) | 0.07081 (16) | 0.62584 (15) | 0.0555 (5) | |
| C17 | 0.6840 (4) | −0.0071 (2) | 0.68695 (18) | 0.0715 (6) | |
| H17 | 0.5632 | −0.0315 | 0.6536 | 0.086* | |
| C18 | 0.6927 (4) | −0.0493 (2) | 0.79649 (19) | 0.0817 (7) | |
| H18 | 0.5787 | −0.1022 | 0.8364 | 0.098* | |
| C19 | 0.8689 (4) | −0.0138 (2) | 0.84739 (19) | 0.0757 (6) | |
| H19 | 0.8743 | −0.0418 | 0.9215 | 0.091* | |
| C20 | 1.0364 (4) | 0.0634 (2) | 0.78757 (19) | 0.0746 (6) | |
| H20 | 1.1571 | 0.0872 | 0.8214 | 0.090* | |
| C21 | 1.0283 (4) | 0.10629 (19) | 0.67754 (17) | 0.0641 (5) | |
| H21 | 1.1423 | 0.1594 | 0.6380 | 0.077* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0688 (3) | 0.0641 (3) | 0.0475 (3) | 0.0269 (2) | −0.0004 (2) | −0.0098 (2) |
| O1 | 0.0647 (8) | 0.0623 (8) | 0.0502 (7) | 0.0208 (7) | −0.0064 (6) | −0.0145 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0995 (12) | 0.1023 (13) | 0.0475 (8) | 0.0567 (10) | −0.0012 (7) | −0.0103 (8) |
| C1 | 0.0607 (11) | 0.0530 (11) | 0.0481 (10) | 0.0107 (9) | −0.0047 (8) | −0.0106 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0601 (11) | 0.0465 (10) | 0.0469 (10) | 0.0058 (8) | 0.0000 (8) | −0.0111 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0570 (11) | 0.0489 (10) | 0.0483 (10) | 0.0060 (8) | 0.0028 (8) | −0.0136 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0660 (12) | 0.0638 (13) | 0.0567 (11) | 0.0154 (10) | 0.0050 (9) | −0.0152 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0790 (15) | 0.0769 (15) | 0.0615 (13) | 0.0124 (12) | 0.0148 (10) | −0.0229 (11) |
| C6 | 0.0987 (17) | 0.0748 (15) | 0.0450 (11) | 0.0102 (13) | 0.0089 (11) | −0.0139 (10) |
| C7 | 0.0794 (14) | 0.0618 (13) | 0.0501 (11) | 0.0136 (11) | −0.0039 (10) | −0.0109 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0645 (12) | 0.0638 (12) | 0.0502 (11) | 0.0173 (10) | −0.0028 (9) | −0.0138 (9) |
| C9 | 0.0542 (10) | 0.0489 (10) | 0.0523 (10) | 0.0059 (8) | −0.0050 (8) | −0.0129 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0618 (12) | 0.0783 (15) | 0.0537 (11) | 0.0165 (11) | −0.0007 (9) | −0.0142 (10) |
| C11 | 0.0755 (14) | 0.0837 (16) | 0.0506 (11) | 0.0134 (12) | −0.0052 (10) | −0.0077 (10) |
| C12 | 0.0655 (13) | 0.0764 (15) | 0.0673 (14) | 0.0172 (11) | −0.0186 (10) | −0.0120 (11) |
| C13 | 0.0591 (12) | 0.0716 (14) | 0.0738 (14) | 0.0181 (10) | −0.0061 (10) | −0.0228 (11) |
| C14 | 0.0609 (12) | 0.0636 (12) | 0.0546 (11) | 0.0099 (10) | −0.0031 (9) | −0.0202 (9) |
| C15 | 0.0637 (12) | 0.0635 (12) | 0.0621 (12) | 0.0257 (10) | −0.0048 (9) | −0.0160 (10) |
| C16 | 0.0553 (11) | 0.0490 (10) | 0.0615 (12) | 0.0180 (9) | −0.0052 (9) | −0.0150 (9) |
| C17 | 0.0682 (13) | 0.0626 (13) | 0.0766 (15) | 0.0004 (11) | −0.0176 (11) | −0.0073 (11) |
| C18 | 0.0813 (16) | 0.0699 (15) | 0.0762 (16) | −0.0043 (12) | −0.0062 (12) | 0.0059 (12) |
| C19 | 0.0878 (17) | 0.0730 (15) | 0.0603 (13) | 0.0167 (13) | −0.0134 (12) | −0.0091 (11) |
| C20 | 0.0734 (15) | 0.0783 (16) | 0.0769 (15) | 0.0095 (12) | −0.0201 (12) | −0.0272 (13) |
| C21 | 0.0563 (12) | 0.0637 (13) | 0.0717 (14) | 0.0039 (10) | −0.0022 (10) | −0.0197 (10) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—C3 | 1.7623 (19) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| S1—C15 | 1.8159 (18) | C11—C12 | 1.368 (3) |
| O1—C1 | 1.331 (2) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| O1—C8 | 1.444 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.373 (3) |
| O2—C1 | 1.195 (2) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.483 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.382 (3) |
| C2—C7 | 1.390 (2) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.410 (3) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.405 (2) | C15—C16 | 1.501 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.372 (3) | C15—H15A | 0.9700 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C15—H15B | 0.9700 |
| C5—C6 | 1.371 (3) | C16—C17 | 1.379 (3) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C16—C21 | 1.383 (3) |
| C6—C7 | 1.379 (3) | C17—C18 | 1.375 (3) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C17—H17 | 0.9300 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9300 | C18—C19 | 1.375 (3) |
| C8—C9 | 1.504 (2) | C18—H18 | 0.9300 |
| C8—H8A | 0.9700 | C19—C20 | 1.368 (3) |
| C8—H8B | 0.9700 | C19—H19 | 0.9300 |
| C9—C10 | 1.380 (3) | C20—C21 | 1.381 (3) |
| C9—C14 | 1.383 (3) | C20—H20 | 0.9300 |
| C10—C11 | 1.379 (3) | C21—H21 | 0.9300 |
| C3—S1—C15 | 103.19 (9) | C12—C11—H11 | 119.7 |
| C1—O1—C8 | 116.17 (14) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.7 |
| O2—C1—O1 | 122.68 (18) | C11—C12—C13 | 119.5 (2) |
| O2—C1—C2 | 124.83 (17) | C11—C12—H12 | 120.2 |
| O1—C1—C2 | 112.48 (16) | C13—C12—H12 | 120.2 |
| C7—C2—C3 | 119.66 (17) | C12—C13—C14 | 120.1 (2) |
| C7—C2—C1 | 119.51 (17) | C12—C13—H13 | 120.0 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.82 (16) | C14—C13—H13 | 120.0 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 117.65 (17) | C13—C14—C9 | 120.71 (19) |
| C4—C3—S1 | 121.64 (15) | C13—C14—H14 | 119.6 |
| C2—C3—S1 | 120.71 (14) | C9—C14—H14 | 119.6 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 121.03 (19) | C16—C15—S1 | 107.11 (13) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.5 | C16—C15—H15A | 110.3 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.5 | S1—C15—H15A | 110.3 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 121.3 (2) | C16—C15—H15B | 110.3 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.4 | S1—C15—H15B | 110.3 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.4 | H15A—C15—H15B | 108.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 118.9 (2) | C17—C16—C21 | 118.3 (2) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.5 | C17—C16—C15 | 121.5 (2) |
| C7—C6—H6 | 120.5 | C21—C16—C15 | 120.2 (2) |
| C6—C7—C2 | 121.5 (2) | C18—C17—C16 | 121.0 (2) |
| C6—C7—H7 | 119.3 | C18—C17—H17 | 119.5 |
| C2—C7—H7 | 119.3 | C16—C17—H17 | 119.5 |
| O1—C8—C9 | 108.69 (15) | C19—C18—C17 | 120.4 (2) |
| O1—C8—H8A | 110.0 | C19—C18—H18 | 119.8 |
| C9—C8—H8A | 110.0 | C17—C18—H18 | 119.8 |
| O1—C8—H8B | 110.0 | C20—C19—C18 | 119.1 (2) |
| C9—C8—H8B | 110.0 | C20—C19—H19 | 120.4 |
| H8A—C8—H8B | 108.3 | C18—C19—H19 | 120.4 |
| C10—C9—C14 | 118.49 (17) | C19—C20—C21 | 120.8 (2) |
| C10—C9—C8 | 123.42 (17) | C19—C20—H20 | 119.6 |
| C14—C9—C8 | 118.09 (17) | C21—C20—H20 | 119.6 |
| C11—C10—C9 | 120.55 (19) | C20—C21—C16 | 120.4 (2) |
| C11—C10—H10 | 119.7 | C20—C21—H21 | 119.8 |
| C9—C10—H10 | 119.7 | C16—C21—H21 | 119.8 |
| C12—C11—C10 | 120.6 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1, Cg2 and Cg3 are the centroids of the C2–C7, C9–C14 and C16–C21 rings, respectively.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C14—H14···O2i | 0.93 | 2.63 | 3.408 (3) | 142 |
| C4—H4···Cg3ii | 0.93 | 3.11 | 3.846 (3) | 137 |
| C13—H13···Cg3i | 0.93 | 2.88 | 3.653 (3) | 141 |
| C18—H18···Cg1iii | 0.93 | 3.20 | 3.820 (3) | 126 |
| C20—H20···Cg2iv | 0.93 | 2.96 | 3.651 (3) | 132 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y+1, −z+1; (ii) −x+2, −y, −z+1; (iii) −x+1, −y, −z+1; (iv) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: RZ5036).
References
- Alhadi, A. A., Khaledi, H., Mohd Ali, H. & Olmstead, M. M. (2010). Acta Cryst E66, o1787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bernardelli, P., Cronin, A. M., Denis, A., Denton, S. M., Jacobelli, H., Kemp, M. I., Lorthiois, E., Rousseau, F., Serradeil-Civit, D. & Vergne, F. (2005). US Patent 20050267095.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Halaschek-Wiener, J., Kloog, Y., Wacheck, V. & Jansen, B. (2003). J. Invest. Dermatol. 120, 109–115. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Lucena, N., Casabó, J., Escriche, L., Sánchez-Castelló, G., Teixidor, F., Kivekäs, R. & Sillanpää, R. (1996). Polyhedron, 15, 3009–3018.
- Macrae, C. F., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Shields, G. P., Taylor, R., Towler, M. & van de Streek, J. (2006). J. Appl. Cryst. 39, 453–457.
- Nardelli, M. (1995). J. Appl. Cryst. 28, 659.
- Oxford Diffraction (2012). CrysAlis PRO Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Yarnton, England.
- Radić, G. P., Glodjović, V. V., Radojević, I. D., Stefanović, O. D., Čomić, Lj. R., Ratković, Z. R., Valkonen, A., Rissanen, K. & Trifunović, S. R. (2012). Polyhedron, 31, 69–76.
- Sadao, I., Fujio, S., Hidekazu, M. & Keita, K. (2000). Jpn Patent 2000-178188.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sillanpää, R., Kivekäs, R., Escriche, L., Lucena, N., Teixidor, F. & Casabó, J. (1994). Acta Cryst. C50, 2049–2051.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813001761/rz5036sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813001761/rz5036Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813001761/rz5036Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report


