Abstract
CCN family protein 2 (CCN2), also known as connective tissue growth factor, is a secreting protein that modulates multiple cellular events. We previously demonstrated the metastasis-suppressive effect of CCN2 in lung cancer cells. In this study, we investigate the role of CCN2 in anoikis, a form of programmed cell death that is critical in suppressing cancer metastasis. CCN2 binds to the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and triggers ubiquitination by inhibiting the formation of the β-pix/Cbl complex, resulting in the degradation of EGFR. Binding of CCN2 to EGFR suppresses the phosphorylation of c-Src and extracellular signal-regulated kinase but increases the expression of death-associated protein kinase, which leads to anoikis. Overall, our findings provide evidence validating the use of CCN2 as an anti-metastatic therapy in lung cancer patients, and prospect a potential therapeutic synergy between CCN2 and the anti-EGFR antibody for the treatment of lung cancer.
Keywords: CCN2, EGFR, anoikis, metastasis
Epithelial cells grow, survive, and bestow their cellular functions by attaching to the extracellular matrix (ECM). In attached cells, the activation of the secretion-dependent autocrine pathway provides the most efficient route for cellular functioning. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-induced signal pathways are recognized as pivotal signal for cellular survival in attached epithelial cells.1, 2 Disruption of cell–ECM contact triggers contact-free cell death, termed anoikis. Anoikis restrains cellular detachment and prevents cells from developing in inappropriate locations.3, 4 Detached epithelial cells are destroyed by anoikis before they can reattach in situ or start to migrate; thus, anoikis is considered a critical mechanism for preventing metastasis.5 During metastatic evolution, cancer cells amplify certain growth factor receptors, including c-Met, Trk, and EGFR, to activate their downstream signal pathways. This process causes resistance to anoikis.6, 7, 8 However, the factors involved in anoikis signaling of cancer cells remain largely unknown.
The CCN family protein 2 (CCN2), also known as connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), is a member of the CCN2 family of secreted, matrix-associated proteins. CCN2 interacts with a number of extracellular molecules to modulate diverse cellular functions, including chemotaxis, invasion, and metastasis.9, 10, 11 Increased CCN2 expression is associated with an aggressive and advanced state of disease for breast cancer,12 glioblastoma,13 esophageal cancer,14 gastric cancer,15 and hepatocellular carcinoma.16 However, CTGF also acts as a metastatic suppressor. We previously demonstrated that CCN2 inhibited the invasiveness and metastatic ability of colon cancer and non-small cell lung cancer.17, 18, 19 These results suggested variable effects of CCN2 among different cancers and indicated that CCN2 may help prevent metastasis in certain types of cancers.
The EGFR signal pathway has been shown to be critical in lung cancer. However, despite the effectiveness of anti-EGFR therapies, the failure of some patients constitutes a serious problem. Therefore, the development of a novel therapy that works synergistically with anti-EGFR therapy will be valuable. This study investigated the role of CCN2 in preventing metastasis by inducing anoikis even in the presence of EGF and suggested a potential therapeutic synergy between CCN2 and anti-EGFR antibody for lung cancer treatment.
Results
CCN2 binds to EGFR through the carboxyl-terminal cystine knot (CT) domain
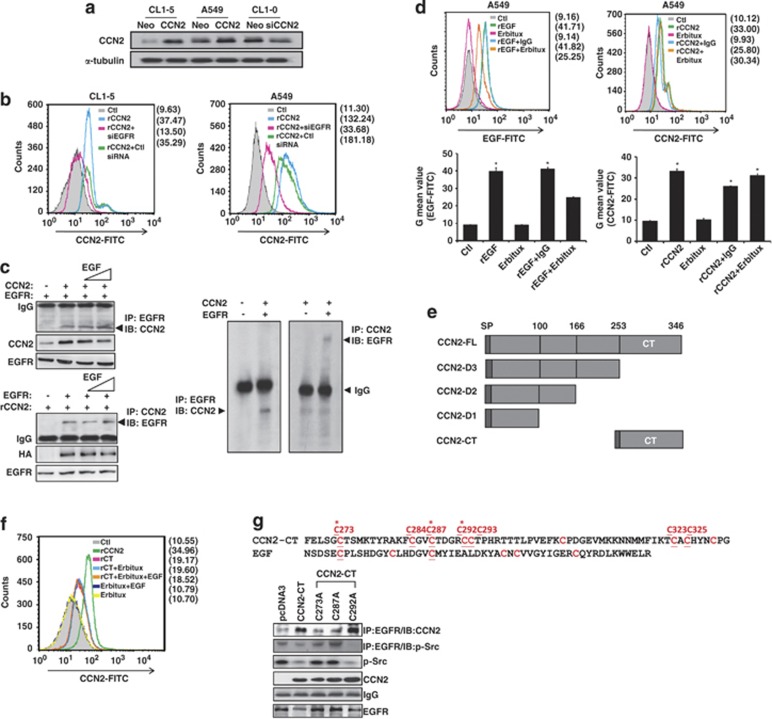
Because CCN2 is a matrix-associated protein, we investigated the putative receptors interacting with CCN2. Three lung cancer cell lines were selected to generate stable transfectants (Figure 1a), and immunoprecipitation assay was performed by anti-CCN2 antibody, two-dimensional electrophoresis, and mass spectrometry. According to our finding, CCN2-expression level would decrease significantly in advanced lung cancer cells,18 and we revealed that CCN2 evokes a negative downstream signaling in lung cancer; therefore, we expected that the receptor might decrease expression after physical interaction with CCN2. In our screen, a more than two-fold decreased amount of EGFR occurred, collected from A549/CCN2 clone, compared with control clone (Supplementary Figure S1). Subsequently, we confirmed the membranous association between EGFR and CCN2 in lung cancer cells by flow cytometer. The results demonstrated that recombinant CCN2 (rCCN2) enhanced the detection of membranous CCN2 and that depletion of EGFR in these cells abolished the CCN2 located on cell membrane (Figure 1b).
Figure 1.
CCN2 binds to EGFR though the carboxyl-terminal CT domain. (a) Western blot analysis of CCN2 in CL1-5, A549, CL1-0 cells transduced with either CCN2 or siCCN2 and the corresponding control vectors as indicated. α-tubulin levels were used as loading control. One representative experiment of three is shown. (b) CCN2 bound to EGFR was FACS analyzed in control siRNA, or siRNA for EGFR depletion (siEGFR) transfected CL1-5 (left) or A549 (right) cells. (c) A549 cells were cotransfected with CCN2- and EGFR-expression plasmids (top left) or transfected with EGFR-expression plasmid and treated with rCCN2 (100 ng/ml) (bottom left), and then incubated with rEGF (20 ng/ml) for 24 h. Cells were collected and western-immunoprecipitation analysis (WB-IP) was performed to detect CCN2 and EGFR expression as indicated. In vitro recombinant protein: CCN2 and EGFR were mixed and subjected to western-immunoprecipitation analysis (right). Immunoblotting showed the resulting expression and monitored for expression of EGFR and CCN2 complex. The data was represented as four times. (d) CCN2 was compared with EGF (20 nM) and EGFR monoclonal antibody Erbitux (1 μM) for EGFR association in A549 cells under the conditions of detachment (top) for 24 h. The quantitative values were shown in the bottom. (e) Illustration of the sequential CT-domain deletion constructs or CT-domain construct of CCN2. (f) FACS analysis of cell membrane binding in rCCN2 (100 ng/ml), CT domain only recombinant protein (rCT, 100 ng/ml), and Erbitux (1 μM) treatment in A549 cells. After starvation, cells were treated as indicated and harvested to incubate with CCN2 antibody and secondary-FITC antibody. Cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. (g) Cys→Ala (C273A, C287A, and C292A) substitution of the CT domain constructs (top). Mutated CCN2 (C273A and C287A) lost its interaction with EGFR. WB-IP analysis of transfected wild-type/point mutation CCN2 (C273A, C287A and C292A) and vector (pcDNA3) expression plasmids in CL1-5 cells. Cells were transfected for 48 h and collected, and western blot and WB-IP were performed as indicated antibodies (bottom)
Our experiment supported the hypothesis of an association between CCN2 and EGFR in low-endogenous CCN2 CL1-5 cells. After ectopic expression of CCN2 or/and EGFR (HA-tag) in CL1-5, CCN2 was found to be present in the immunoprecipitants obtained by the anti-EGFR antibody, and EGFR was present in the immunoprecipitants retrieved by an anti-CCN2 antibody. Furthermore, addition of the EGFR ligand, EGF, did not disrupt CCN2–EGFR association (Figure 1c, left). In vitro binding assay further confirmed the physical association between EGFR and CCN2 (Figure 1c, right). In A549 cells, the depletion of TrkA, a tyrosine kinase receptor reportedly associated with CCN2,7 did not alter CCN2–EGFR association (Supplementary Figure S2). Because the endogenous CCN2-expression protein level is extremely low in CL1-5, the G mean value of CCN2-fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) in CL1-5, transfected with siCCN2 (20 nM), analyzed by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) is much closer to that in CL1-5/Neo scramble control, CL1-5/Neo clone, and immunoglobulin G (IgG) control group (Supplementary Figure S3). To exam if there was any overlapping of CCN2 and EGF docking to EGFR, Erbitux, an EGFR monoclonal antibody that binds to the extracellular subdomain III of EGFR,20, 21 was used to abolish the EGF–EGFR interaction. However, CCN2–EGFR association was not affected by Erbitux (Figure 1d). These results suggested that EGFR is physically associated with CCN2, and this association is unaffected by the presence of EGFR native ligands, blocking antibody, or a known CCN2-binding protein, such as TrkA.
To identify the domain of CCN2 responsible for EGFR binding, we applied a series of CCN2-deletion mutant constructs (Figure 1e). The results showed that the carboxyl-terminal CT domain, which is highly conserved with EGF, was responsible for EGFR binding of CCN2 (Figures 1f and g). The FACS data further showed that CT domain associated with membrane EGFR was not affected by the presence of EGFR ligands and Erbitux (Figure 1f). Mutation of the EGF-conserved cysteine residues C273A and C287A significantly reduced CCN2–EGFR association (Figure 1g, bottom). On the contrary, CCN2-CT and C292A construct could decrease EGFR–Src association. Therefore, we determined that EGF-conserved cysteine residues C273 and C287 are responsible for the effects of CT domain. Overall, these results indicated that CT domain of CCN2 is responsible for EGFR binding.
CCN2 inhibits EGFR-mediated phosphorylation of c-Src and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)
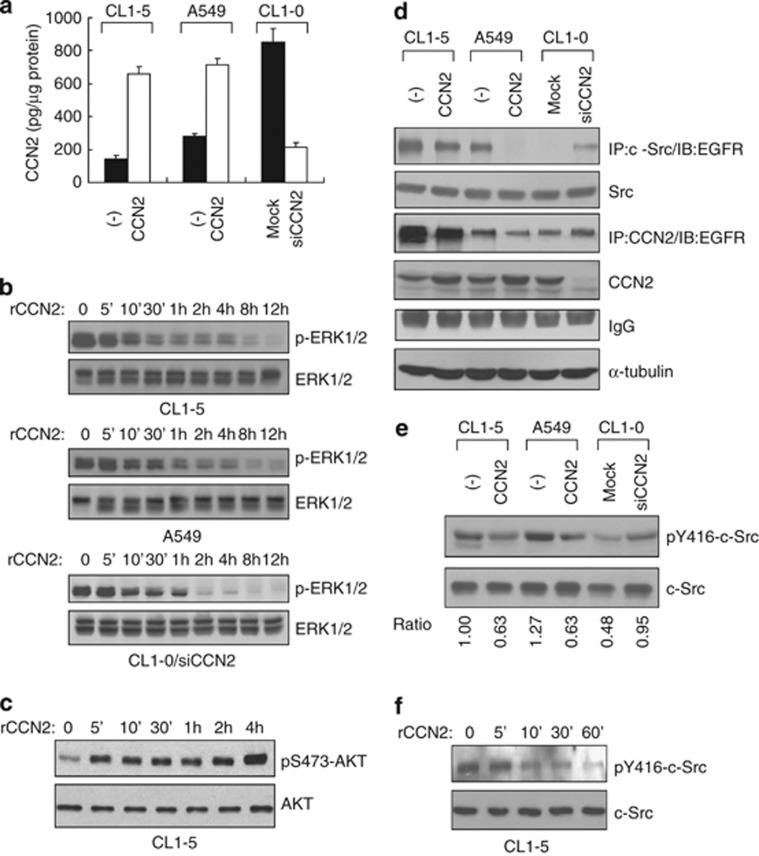
We next examined the effect of CCN2 on the EGFR-activated signaling pathways by investigating the pathways induced by EGFR. After collect condition media, we showed that the amount of secreted CCN2 corresponded to the expression level of CCN2 in transfectants (Figure 2a). We investigated the influence of CCN2 on the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and AKT pathways. The result demonstrated that exogenous CCN2 gradually reduced the phosphorylation of ERK (Figure 2b), but increased phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT phosphorylation in 5 min (Figure 2c). Moreover, in A549 and CL1-5 stable CCN2 transfectants, the protein level of phosphorylated ERK was significantly decreased (Supplementary Figures S4a and b). Although AKT signaling was enhanced in rCCN2 treatment, phosphorylated AKT had no obvious change in CCN2-stable transfectants (Supplementary Figure S4a). Interestingly, Supplementary Figure S4c showed that overexpressed MEK-1 to upregulate the MAPK/ERK pathway in CCN2 transfectants could restore apoptotic-related protein: death-associated protein kinase (DAPK) expression and suspended cell survival. We further treated PD98059 or LY294002, chemical inhibitors of ERK or AKT signaling, respectively, and found that only PD98059 treatment could enhance DAPK expression (Supplementary Figure S5). Therefore, CCN2 treatment showed AKT phosphorylation, but this regulation maybe independent on anoikis sensitivity or apoptosis gene induction (Supplementary Figures S4c, right, and Supplementary Figure S5). Taken together, CCN2 suppressed the survival-benefit pathway, including MAPK/ERK signaling.
Figure 2.
CCN2 inactivates the Src-MAPK pathway without attenuation of the AKT-PI3K pathway. (a) ELISA results of CCN2 secretion in three lung cancer lines. (b) A time course of rCCN2 treatment in MAPK-phosphorylation (p-ERK-1/2) inhibition in above three lung adenocarcinoma cell lines and CL1-0/siCCN2 clones. (c) Western blotting analysis of AKT phosphorylation on S473 in CL1-5 cells treated with rCCN2 for indicated times. (d) In CCN2-stable transfectants as indicated, after MG132 treatment, whole-cell lysates were prepared for immunoprecipitation with anti-Src or anti-CCN2 followed by immunoblotting with anti-EGFR. α-tubulin was an internal control. (e) Western blotting assay in phospho-Src protein expression in CCN2 transfectants. (f) rCCN2-treated CL1-5 cells and phospho-Src protein expression was detected by western blotting assay. Total Src is loading control
Because EGF-bound EGFR recruits c-Src for activation,22, 23 we investigated the influence of CCN2 expression on c-Src–EGFR complex formation and c-SrcY416 autophosphorylation. MG132 is a proteosome inhibitor and functions to block protein degradation. Thus, we added MG132 in CCN2 transfectants to stabilize EGFR-related protein-degradation complexes. The results showed that ectopic expression of CCN2 resulted in significant inhibition of c-Src–EGFR complex formation and c-SrcY416 autophosphorylation. Consistently, knockdown of CCN2 in high-endogenous CCN2 CL1-0 cells enhanced c-Src–EGFR association and c-SrcY416 phosphorylation (Figures 2d and e). The addition of rCCN2 attenuated c-SrcY416 autophosphorylation in CL1-5 cells (Figure 2f). Furthermore, CT domain of CCN2 significantly decreased Src phosphorylation, and point mutations C273A and C287A could restore Src phosphorylation and EGFR/Src complex formation (Figure 1g). Overall, the results indicated that CCN2, especially CT domain, disrupted EGFR–Src association and repressed the phosphorylation of c-Src and ERK.
CCN2 induces ubiquitination-dependent degradation of EGFR by disrupting the β-pix/c-casitas B-lineage lymphoma (c-Cbl) complex
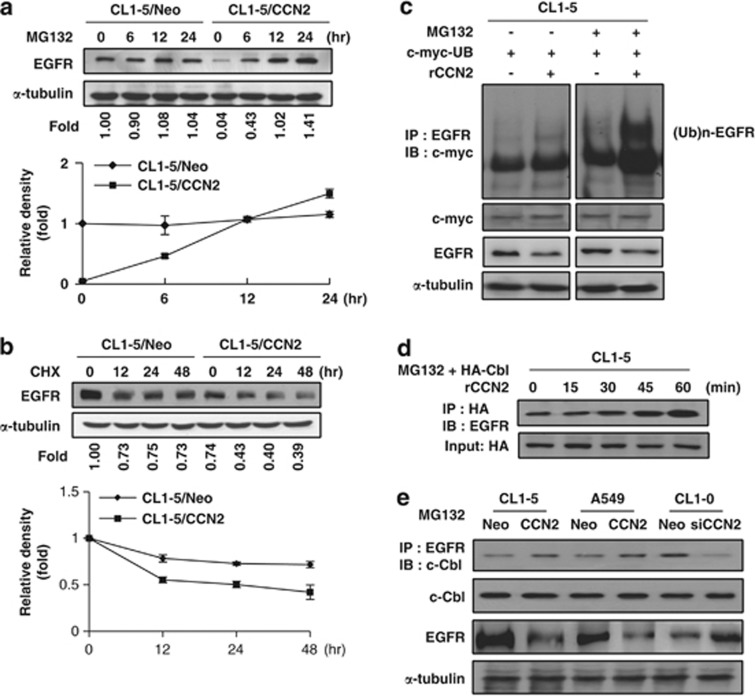
To investigate whether CCN2 interacts with EGFR, we assessed whether mRNA and protein levels of EGFR were changed by rCCN2 treatment. The mRNA level of EGFR was unchanged after rCCN2 treatment (Supplementary Figure S6), whereas the ectopic expression of CCN2 promoted EGFR degradation, and MG132 attenuated this effect (Figure 3a). A rapid decline in EGFR was observed in CCN2 transfectants treated with protein-synthesis inhibitor, cycloheximide; this finding suggested that CCN2 destabilized EGFR (Figure 3b). We then examined EGFR ubiquitination status. Increased ubiquitination was observed treated with rCCN2 (Figure 3c). The E3-ubiquitin ligase c-Cbl has been shown to ensure EGFR degradation.24, 25, 26 We examined the effect of CCN2 on EGFR/c-Cbl complex formation and found that the EGFR/c-Cbl complex was increased by rCCN2 treatment in a time-dependent manner (Figure 3d). Moreover, the EGFR/c-Cbl complex was more abundant in CCN2-stable transfectants than control clones, and knockdown of CCN2 decreased the EGFR/c-Cbl complex (Figure 3e). To further exam that c-Cbl was necessary for CCN2-induced EGFR degradation machinery, we transiently transfected various dosage of silencing c-Cbl plasmids in CCN2-expressing clones. The data showed that EGFR significantly restored in CCN2-stable transfectants in a dose-dependent manner after si-Cbl transfection (Supplementary Figure S7). The data further support that CCN2 could improve EGFR degradation via ubiquitination system in lung adenocarcinoma.
Figure 3.
CCN2 accelerates ubiquitination-dependent EGFR degradation in lung adenocarcinoma cells. (a) CL1-5/CCN2 and CL1-5/Neo stably transfected clones were treated with 10 μM MG132. Cell lysates are subjected to western blotting with anti-EGFR and monoclonal anti-human α-tubulin as an internal control. Relative ratios of EGFR protein signal intensity to that of the internal control are shown below the graph (top). EGFR levels from CL1-5/Neo are assigned as onefold at 0 min time. Means and S.E.M. of four experiments performed in duplicate are shown (bottom). (b) CCN2 transfectants are treated with either vehicle (0.01% dimethyl sulfoxide) or 10 μM cycloheximide (CHX) for the indicated time. Proteins (CL1-5/Neo=50 μg per lane; CL1-5/CCN2=100 μg per lane) were subjected to western blotting using anti-EGFR and anti-α-tubulin (top). Densitometry quantification of EGFR by western blot following normalization to α-tubulin levels. EGFR levels from CL1-5/Neo or CL1-5/CCN2 cells were arbitrarily assigned a value of 100% at 0 min time. Means and S.E.M. of three experiments performed in duplicate were shown (bottom). (c) With or without MG132 or rCCN2 protein treatment, cell lysates of CL1-5 cells transiently transfected with c-myc-ubiquitin-expressing plasmids were immunoprecipitated with anti-EGFR and immunoblotted with monoclonal mouse anti-c-myc-ubiquitin. Internal controls were performed by α-tubulin and c-myc total protein. (d) WB-IP analysis of CL1-5 transiently transfected HA-tag c-Cbl-expressing plasmids with MG132. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA and immunoblotted with anti-EGFR. HA was used as loading control. (e) WB-IP analysis of CCN2-stable transfectants with MG132 treatment. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-EGFR and immunoblotted with anti-c-Cbl. Input controls were including total c-Cbl and α-tubulin
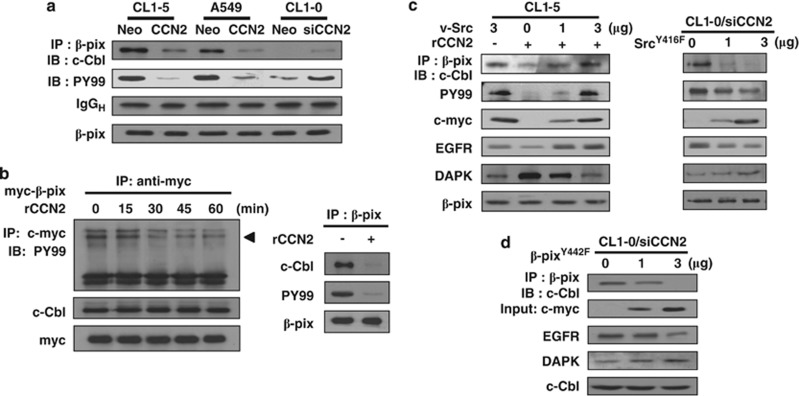
Previous research has shown that β-pix binds to Cbl and sequesters Cbl proteins from EGFR, resulting in the inhibition of EGFR ubiquitylation and degradation.27 The interaction between β-pix and c-Cbl and β-pix phosphorylation was attenuated in CCN2-overexpressed CL1-5 and A549 cells, and knockdown of CCN2 in CL1-0 cells enhanced β-pix/c-Cbl complex formation and β-pix phosphorylation (Figure 4a). Exogenous CCN2 resulted in decreased phosphorylation of β-pix and the dissociation of β-pix/c-Cbl complex (Figure 4b). Because β-pix is a substrate of Src and phosphorylation of β-pix on tyrosine 442 regulates EGFR degradation,28 we examined whether Src restored CCN2-induced EGFR degradation. Ectopic expression of v-Src effectively restored β-pix/c-Cbl complex formation and β-pix phosphorylation, resulting in an increased EGFR level. In contrast, transfection of kinase-dead SrcY416F mutant into the CL1-0/siCCN2 clone inhibited β-pix phosphorylation and β-pix/c-Cbl complex formation and enhanced EGFR degradation (Figure 4c). Moreover, expression of β-pixY442F in CCN2-depleted CL1-0 cells disrupted the β-pix/c-Cbl association, promoted EGFR degradation, and enhanced DAPK protein expression (Figure 4d). After coexpressing Src and wild-type β-p21-activated kinase-interacting exchange factor (β-pix) or point-mutated construct β-pixY442F in CL1-5/CCN2 clones, we found that only wild-type β-pix group reversed CCN2-induced EGFR degradation, but not β-pixY442F (Supplementary Figure S8). Overall, these results suggested that CCN2 induced EGFR degradation by inhibiting Src-mediated β-pix phosphorylation, leading to disruption of β-pix/c-Cbl complex and enhanced EGFR ubiquitination.
Figure 4.
CCN2 decreases Src phosphorylation, which results in β-pix dephosphorylation, and dissociated with c-Cbl complex. (a) Lysates of CCN2-stable transfectants were immunoprecipitated with anti-human β-pix antibody. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated and subjected to western blot analysis with anti-c-Cbl. Total cell lysates were immunoblotted with anti-PY99 and anti-β-pix. (b) CL1-5 cells were transiently transfected with c-myc-tagged β-pix-expressing plasmids and treated with rCCN2 protein for indicated times. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-myc and immunoblotted with PY99. Loading controls were performed by c-myc and c-Cbl protein (left). After treated with rCCN2 for 30 min, CL1-5 cell lysates were collected, immunoprecipitated with anti-β-pix, and immunoblotted with c-Cbl, PY99, and β-pix as internal control (right). (c) WB-IP analysis of CL1-5 transiently transfected v-Src-expressing plasmids with rCCN2 treatment for 15 min (left), and CL1-0/siCCN2 clone transiently transfected point mutation of SrcY416F-expressing plasmids for 48 h (right). Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-β-pix and immunoblotted with anti-c-Cbl and PY99. Total cell lysates were immunoblotted with anti-c-myc, anti-EGFR, anti-DAPK. β-pix was used as control. (d) WB-IP analysis of CL1-0/siCCN2 transiently transfected point mutation of β-pixY442F-expressing plasmids. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-β-pix and immunoblotted with anti-c-Cbl. Total cell lysates were immunoblotted with anti-c-myc, anti-EGFR, and anti-DAPK. c-Cbl was used as loading control
CCN2 induces anoikis in lung cancer cells
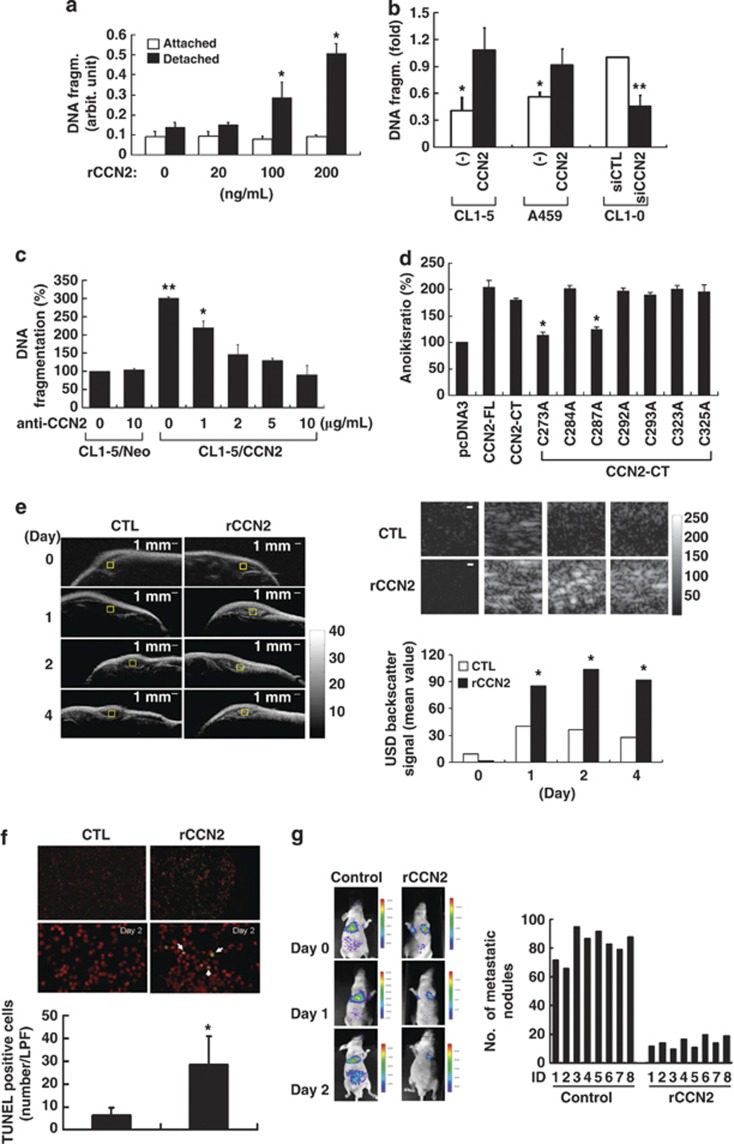
Because CCN2 suppresses metastasis in lung cancer18 and inhibits Src activity, and Src represses anoikis,29, 30 we hypothesized that CCN2 reduces lung cancer metastasis by inducing anoikis. We examined the effect of CCN2 on the induction of anoikis in vitro. The results showed that both DNA fragmentation and cell-cycle arrest occurred in detached cells; no significant effect of rCCN2 was found in attached cells (Figure 5a and Supplementary Figure S9). Ectopic expression of CCN2 in suspended CL1-5 and A549 cells increased DNA fragmentation, and abrogation of CCN2 in CL1-0 attenuated anoikis (Figure 5b). To confirm the outside-in signaling of CCN2 in inducing anoikis, cells were incubated with a CCN2-neutralizing antibody after 48 h of cultivation in suspension. As shown in Figure 5c, anti-CCN2 abrogated anoikis significantly in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, we tested the tendency toward anoikis induction in various CCN2 mutants. The data showed that C273A and C287A mutants abrogated anoikis (Figure 5d), which was in line with the finding that these cysteine residues have a critical role in EGFR binding. Ectopic expression of v-Src, but not SrcY416F, inhibited rCCN2-induced anoikis as expected. Transfection of β-pix also abrogated anoikis induced by rCCN2, whereas β-pixY442F did not show the same effect (Supplementary Figure S10). These results suggest that CCN2 induced anoikis by inhibiting Src activation and β-pix phosphorylation.
Figure 5.
CCN2 induces anoikis and inhibits metastasis of lung cancer cells. (a) Anoikis of CL1-5 cells growing under attached or suspended conditions received indicated dosages of rCCN2 treatment for at 24 h. Data was means±S.E. (n=6 per group). *P<0.05. (b) CL1-5, A549, and CL1-0 cells were transfected with either CCN2 or siCCN2 and the corresponding control vectors as indicated. Anoikis cell ratio at suspended for 24 h (means±S.D. of five independent experiments). (c) Anoikis in CCN2 transfectants with CCN2-neutralizing antibody treatment. CL1-5/Neo cell apoptosis in 24 h suspension represents the 100% control. Data was means±S.E. (n=4 per group). *P<0.05 and **P<0.01. (d) In CL1-5 cells, CCN2 variants were transiently transfected and suspended for 24 h, and anoikis ratio was analyzed. (e) Representative high-frequency ultrasonic imaging showing DNA apoptotic signaling (left, and top right indicated as the amplification view of the yellow squares) as s.c. tumor-bearing mice. Scale bar: 1 mm. The quantification data (bottom right) was presented from rCCN2 treatment and control group. *P<0.05. (f) Increased anoikis ratio at day 2 in fresh tumor section of i.p. injected rCCN2 in tumor s.c. injected mice, compared with vehicle control mice. The fresh sample as assessed by TUNEL staining (top). Quantified data are means±S.D. (bottom, n=8 mice per group). Low power field (LPF: × 40 original magnification), *P<0.05. (g) Fluorescence imaging of mice in vehicle or rCCN2 treatment (1 mg/kg per day; i.p. injection) after i.v. injecting CL1-5 cells at indicated days (left). Distal metastasis of lung nodules are presented at 2 months (right). Bars represent numbers (n=8 mice per group)
To confirm whether CCN2 induced anoikis in vivo, we injected CL1-5 cells into the s.c. region of nude mice to mimic inappropriate cellular matrix and treated the mice i.p. either with rCCN2 (1 mg/kg per day) or a control solution (citrate buffer). The ultracellular nuclear changes, including DNA fragmentation followed by chromosome condensation, were examined by ultrasound imaging. An increase in high-frequency scattering efficiency, indicating anoikis cells, was found in rCCN2 treatment group (Figure 5e). TUNEL assay confirmed the anoikis induction (Figure 5f). We next used Celltracker probe (Molecular Probes, Invitrogen Corporation, Carlsbad, CA, USA) to trace the long-term fluorescent image of CL1-5 cells i.v. injected into nude mice treated with or without CCN2 (1 mg/kg per day). The signals in lungs were found to be much weaker in CCN2-treated mice compared with controls (Figure 5g, left). Treatment with CCN2 also resulted in a decrease in the number of metastatic lung nodules after 6 week (Figure 5g, right). Overall, these findings suggested that CCN2 effectively induced anoikis and suppressed the metastasis of lung cancer cells.
DAPK-dependent anoikis is critical in CCN2-mediated metastatic suppression
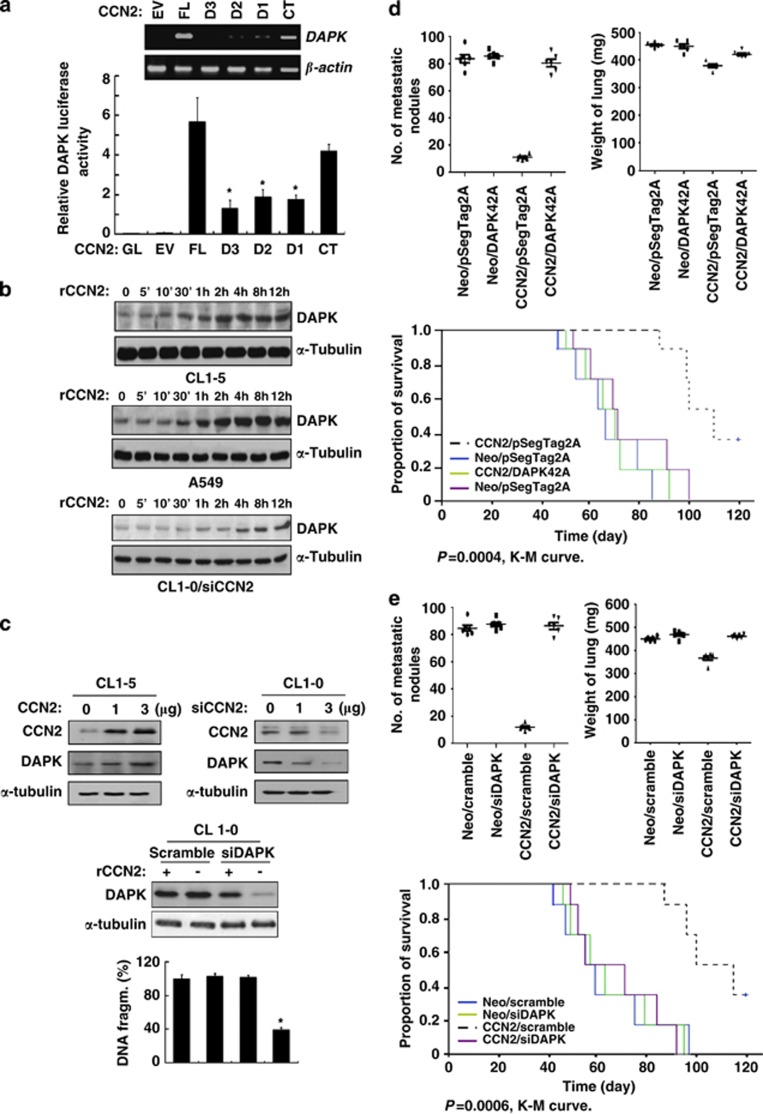
To explore the downstream signaling in CCN2-induced anoikis, we performed a cDNA microarray of CL1-5/CCN2 versus CL1-5/Neo. The CCN2-downregulated and -upregulated genes are shown in Supplementary Table S1. We used the bioinformatics approach of the Pathway Interaction Database, a curate collection of biomolecular interactions and key cellular processes assembled into signaling pathways.31 Thirteen pathways involving anoikis were identified (data not shown). Among them, the mRNA level of DAPK (a kinase involved in pro-anoikis and metastasis suppression32, 33) was upregulated 5.36-fold in CL1-5/CCN2 compared with control (Supplementary Table S1). In CL1-5 cells, we found increased levels of promoter activity and transcription of DAPK associated with the ectopic expression of CCN2 or its CT domain. In contrast, CCN2 without CT domain did not induce DAPK promoter activity or mRNA induction (Figure 6a). Furthermore, DAPK mRNA and protein levels were closely correlated with CCN2 level (Supplementary Figure S11), and exogenous CCN2 induced DAPK expression in time- and dose-dependent manners (Figures 6b and c, top left). We also found increased DAPK kinase activity in CCN2 transfectants, compared with neo (Supplementary Figure S12). To support, a dose-dependent effect of reduced DAPK expression was shown in CL1-0 cells receiving siRNA against CCN2 (Figure 6c, top right). Knockdown of DAPK significantly reduced CCN2-induced DNA fragmentation (Figure 6c, bottom). In signaling transduction level, transiently transfected MEK-1 in CL1-5/CCN2 to restore phosphorylated ERK could reinhibit DAPK expression, and resulted in anoikis resistance (Supplementary Figure S4c). We further treated PD98059 or LY294002 to observe DAPK expression. The data demonstrated that only the regulated MAPK/ERK pathway could restore DAPK expression (Supplementary Figure S5). These data supported that CCN2 promotes DAPK-dependent anoikis through ERK/MAPK signaling pathway.
Figure 6.
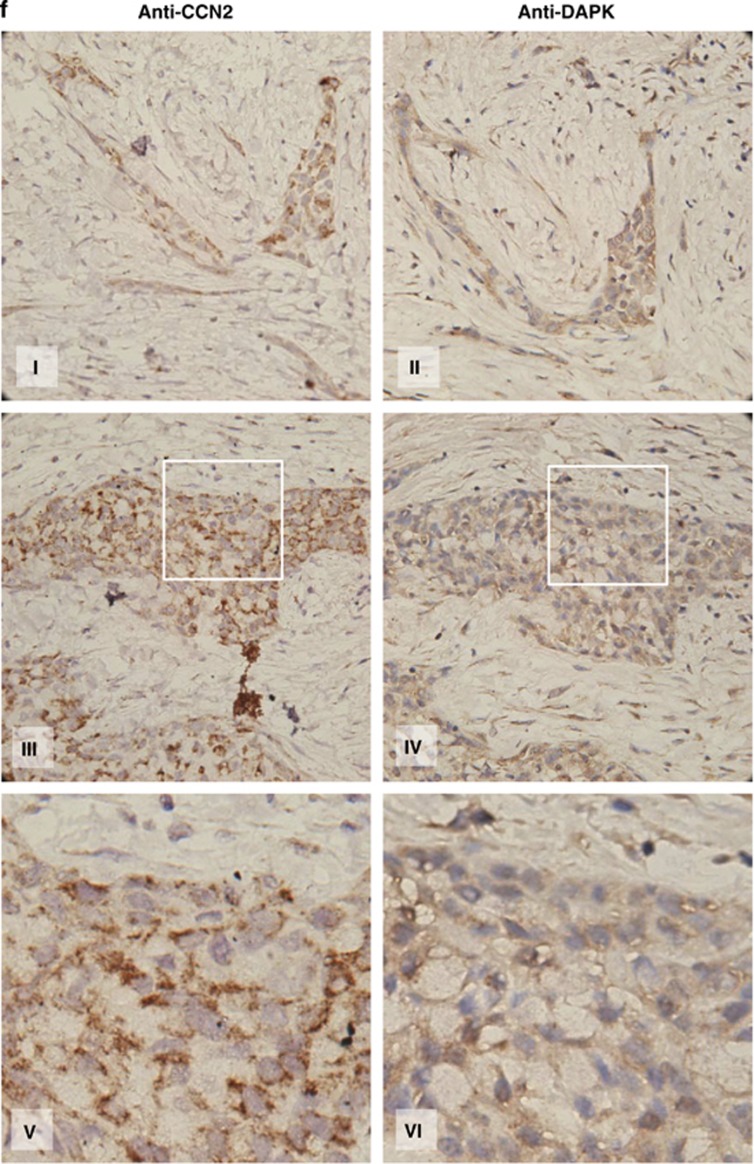
CCN2 increases DAPK expression, and DAPK is critical in CCN2-mediated metastatic suppression. (a) RT-PCR analysis (top) and reporter assay of CCN2 transfectants indicating DAPK mRNA expression (bottom) in CL1-5 cells. Cells were transfected for 48 h and extracted mRNA to perform the RT-PCR analysis. β-actin was used as internal loading control. DAPK promoter-luc reporter was transfected along with PGL2 empty vector (EV) or indicated CCN2 constructs for 48 h. Whole-cell lysates were prepared for the luciferase reporter activity analysis. Data are means±S.E.M. (n=6). *P<0.05. (b) A time course of DAPK expression induction by rCCN2 treatment in CL1-5, A549, and CL1-0/siCCN2 cells. (c) In CL1-5 cells (top left), DAPK induction in CCN2 transiently transfected dose-dependent manner. In CL1-0 cells (top right), DAPK protein level was downregulated by transfected cells with siCCN2. siRNA-mediated knockdown of DAPK in CL1-0 cotreated with rCCN2 (100 ng/ml) was confirmed by immunoblotting (middle). Apoptotic cells in suspension were detected at 24 h (bottom). Values indicate the mean percentage and S.D. of anoikis cells for six experiments. *P<0.05. (d) CL1-5 cells transfected with control vector, control vector plus kinase-dead DAPK, CCN2, or CCN2 plus kinase-dead DAPK plasmids were injected into the lateral tail vein of SCID mice. Metastatic lung nodules (top left) and weight (top right) were indicated in these four transfectants. Kaplan–Meier survival plots (bottom) bearing lung adenocarcinoma CL1-5 cells. P-value was determined by a two-sided log-rank test. (e) CL1-5 cells transfected with control vector with scramble, control vector plus siDAPK, CCN2 with scramble, or CCN2 plus siDAPK were injected into the lateral tail vein of SCID mice. Metastatic lung nodules (top left) and weight (top right) were indicated in these four transfectants. Kaplan–Meier survival plots (bottom) bearing lung adenocarcinoma CL1-5 cells. P-value is determined by a two-sided log-rank test. (f) Immunohistochemistry of lung cancer tissue for CCN2 and DAPK expression from human lung cancer patients at different stages as indicated. Areas with carcinoma staining positive for these two proteins were colocalized at intensity levels 3
We reasoned that CCN2-induced metastatic suppression of detached cells, and the autocrine control of their fate might act through DAPK-mediated cell death. To confirm this speculation, we examined the effect of DAPK on DNA fragmentation in CL1-5 cells receiving ectopic CCN2 expression/rCCN2 treatment. The results showed that full-length CCN2 or its CT domain, but not CCN2 mutants lacking a CT domain, induced DNA fragmentation (Supplementary Figure S13). To confirm the synergistic effect of CCN2 and anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody (Erbitux) in repressing lung cancer, we tested the survival of CL1-5 receiving Erbitux and different doses of rCCN2 in attachment condition. Only rCCN2 did not induce cancer cell apoptosis while attached, however, cotreatment with Erbitux and rCCN2 for 24 h could significantly enhance CL1-5 cell apoptosis (Supplementary Figure S14). The result showed a synergistic effect of CCN2 and Erbitux in inducing lung cancer cell apoptosis.
Next, we investigated the role of DAPK in CCN2-induced metastatic suppression. We generated eight stable clones expressing the control vectors (CL1-5/Neo/pSecTag2A, CL1-5/Neo/scramble), control vector/kinase-dead DAPK (CL1-5/Neo/DAPK42A), control vector/silencing DAPK (siDAPK) (CL1-5/Neo/siDAPK), CCN2 (CL1-5/CCN2/pSecTag2A, CL1-5/CCN2/scramble), coexpressing CCN2/kinase-dead DAPK (CL1-5/CCN2/DAPK42A) or CCN2-silencing DAPK (CL1-5/CCN2/siDAPK). The results indicated that mice that received an i.v. injection of the CCN2-expressing clones CL1-5/CCN2/pSecTag2A or CL1-5/CCN2/scramble exhibited fewer metastatic nodules and a decrease in lung weight, compared with mice that received an injection of the vector control clones. The expression of kinase-dead DAPK (DAPK42A) or silencing DAPK (siDAPK) in CCN2 transfectants restored metastatic ability. Moreover, mice injected with control clones, CCN2-DAPK42A-coexpressing clone or CCN2-silencing DAPK clone showed a significantly reduced survival period, compared with mice injected with CCN2 clone (Figures 6d and e).
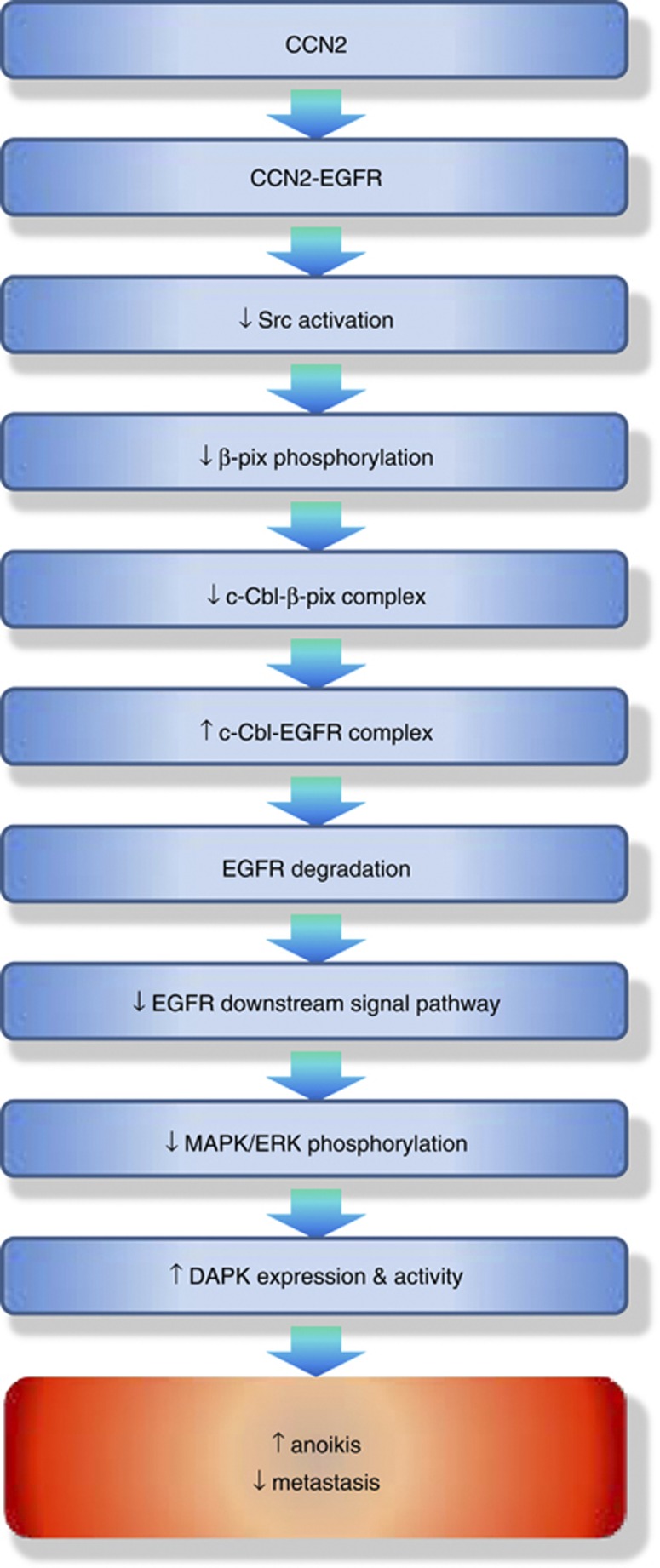
Finally, we investigated the correlation between the expression of CCN2 and DAPK in lung cancer patients. Immunohistochemistry analysis was performed in 27 lung cancer patient samples, and the results confirmed a positive correlation between DAPK and CCN2 protein levels (Figure 6f and Supplementary Table S2). These findings confirmed that a CCN2-DAPK signal axis occurred in human lung cancer samples. A model representing the mechanism of CCN2-induced anoikis and EGFR degradation is depicted in Figure 7.
Figure 7.
A proposed model of CCN2-induced anoikis in lung adenocarcinoma
Discussion
Various ligands have been shown to interact with EGFR and activate downstream signal pathways that favor cellular growth and survival,34 however, scant evidence has been documented on ligands of EGFR that stimulate the tumor-suppressive signal pathways. We identified CCN2 as a novel ligand of EGFR. The CCN2–EGFR interaction deactivated c-Src, which resulted in EGFR degradation through DAPK-dependent anoikis and the c-Cbl-mediated ubiquitination of EGFR. To our knowledge, this is the first report on the induction of anoikis and the metastatic-suppressive effect of a matrix-associated protein interacting with EGFR. For the binding of CCN2 to EGFR, a highly conservative sequence was shown between the CT domain of CCN2 and EGF. For EGF, cysteine residues are critical in forming the intramolecular disulfide bonds for EGFR binding.35 The cysteine residues in the CT domain of CCN2 are also important for EGFR binding. Despite the structural homology between CCN2 and EGF, the presence of the EGF or anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody did not affect the association between CCN2 and EGFR. Our result indicated an anti-metastatic effect of CCN2 even in the presence of EGF, and also suggested a potential therapeutic synergy between CCN2 and the anti-EGFR antibody for the treatment of lung cancer.
DAPK is a serine/threonine kinase in promoting the apoptosis or anoikis of tumor cells. After EGF stimulation, DAPK activity is inhibited by c-Src through phosphorylation at Y491/Y492.36 We found that CCN2 increased the activity of DAPK promoter and enhanced DAPK expression. Knockdown of DAPK or the expression of kinase-dead DAPK abrogated the CCN2-induced anoikis and metastasis suppression. Our research had provided a novel biological defense mechanism in which CCN2, a secretory cytokine, is used to suppress lung cancer metastasis and its progression. The anticancer function of CCN2 was not major in blocking primary tumor proliferation, but in suppressing distal metastasis. In this study, we found that the survival pathways in exogenous CCN2-treated, or stable/transient transfected CCN2-expression plasmid, adherent and suspended cells, such as EGFR and MAPK/ERK signaling, were significantly suppressed. On the contrary, the apoptotic DAPK signaling was also increased in CCN2-treated adherent and suspended cells. However, CCN2-mediated DNA fragmentation is only observed in cells in suspension. The adherent cancer cells resistant to CCN2-induced DNA fragmentation might be due to other survival signaling pathways, which are provided by interaction of cell–cell matrix, such as integrin-, vimentin-, or fibroblast growth factor-related pathways. Once the attached cancer cells lose the supporting from cell–cell matrix, the apoptotic effects of CCN2 could be significantly observed. This is a native defense mechanism we provided in lung cancer model: CCN2 only induces cell fragmentation when cancer cells in suspension are ready to metastasis. Although their signaling pathways related to CCN2 were significantly decreased, the interaction of cell–cell matrix could provide the compensatory survival effects to keep adherent cancer cells alive.
In summary, this study provides a model for anoikis induced in lung cancer cells by the secreted protein CCN2, causing EGFR degradation and DAPK activation. Our research offers a paradigm for investigating a novel biological defense mechanism in which a secretary protein is used to suppress metastasis and alter the progression of cancer. This approach provides a new strategy to prevent lung cancer metastasis by combining therapies formulated on the basis of biological insights.
Materials and Methods
Cell culture
Lung adenocarcinoma cells were grown in RPMI-1640 medium with 10% fetal bovine serum and 2 mM ℒ-glutamine (Biological Industries Ltd., Beit Haemek, Israel) at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2–95% air. CL1-0 was the parent cell line. CL1-5 was selected from CL1-0 cultures with a polycarbonate membrane coated with Matrigel (Collaborative Biomedical, BD Biosciences, Bedford, MA, USA) in a Transwell invasion chamber as described previously.4 A549 cells were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection. Adherent cells were detached from the culture dishes with trypsin-EDTA (Biological Industries Ltd.).
Two-dimensional difference gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry fingerprinting
Lysate protein of CCN2-stable transfectants was analyzed using 2D electrophoresis. Differentially regulated protein spots were excised and isolated from the gel after staining with Coomassie blue. Proteins were in-gel digested with trypsin. The resulting peptides were extracted and purified on C18-Ziptips (Millipore, Bedford, MA, USA) according to the manufacturer's protocol and harvested in 10 μl of acetonitrile. The purified peptides were analyzed by LTQ-FT Ultra (Thermo, Epsom, UK) using the standard protocols. Peak data were searched by Mascot (v.2.2) search engine (Matrix Science, Boston, MA, USA) using the IPI and swissprot database restricted to human taxonomy. The search parameters were as follows: peptide mass fingerprint, trypsin specificity, peptide mass tolerance ±0.05 Da, and a maximum of one miscleavage allowed.
Sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
The CCN2 primary antibody (PeproTech, London, UK) was precoated on EIA strips at a density of 2 μg per well. After adding 100 μl of blocking buffer and washing the wells with PBST buffer, a condition medium of CCN2 transfectants collected for 48 h was added to separate wells. Another CCN2 antibody (R&D Techne Corporation, Minneapolis, MN, USA) was then added to incubate for 1 h. Thereafter, the unbound antibodies were washed and anti-rabbit IgG-horseradish peroxidase (HRP) conjugate was added to X. The plates were washed and a substrate was added for 5 min to develop the colors. Absorbance was read at 650 nm. In this test, the amount of color is directly proportional to the amount of antibodies.
Anoikis assay
Cells were placed in growth medium in suspension at a density of 500 000 cells per ml. They were then either placed on ultralow-binding hydrogel-coated 35-mm culture plates (Corning Incorporated Life Sciences, Lowell, MA, USA) for 24 h. Condition media was collected and used to determine apoptosis with the cell-death detection ELISA kit (Roche Corporation, Boulder, CO, USA) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Each point was performed in duplicate and each experiment was conducted at least six times.
Propidium iodide (PI)-stained fluorescence microscopy
For PI staining, cells were washed with ice-cold phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), fixed in 70% ethanol at −20°C for at least 1 h. After fixation, cells were washed twice and then incubated in 0.5 ml of 0.5% Triton X-100/PBS at 37°C for 30 min with 1 mg/ml of RNase A. The cells were then stained with 50 mg/ml PI (Pharmingen, BD Biosciences, Bedford, MA, USA) for 10 min. The samples were analyzed by FACS (Collaborative Biomedical, BD Biosciences) using Cell Quest Research Software (Collaborative Biomedical, BD Biosciences).
Biofluorescence imaging with IVIS
Mice were anesthetized with isoflurane inhalation, and biofluorescence images were photographed with a CCD camera (IVIS; Xenogen Corporation, Caliper Life Sciences, Hopkinton, MA, USA) at specific times. Imaging times ranged from 1 to 60 s, depending on the amount of fluorescence activity. Biofluorescence from the region of interest (ROI) was defined manually, and the data were expressed as photon flux (photons/s/cm2/steradian). Background photon flux was defined using an ROI from a mouse that was not given an i.p. injection of cancer cells. All biofluorescence data were collected and analyzed using IVIS. Celltracker dye was purchased from Molecular Probes, Invitrogen Corporation.
Immunoprecipitation and western blot analysis
CCN2 transfectants were seeded overnight and incubated in serum-free media for 24 h. For immunoprecipitations, cells were lysed in an RIPA buffer (150 mM NaCl, 50 mM Tris-base, 5 mM EDTA, 1% NP-40, and 0.25% deoxycholate; pH 7.4). Protein concentrations were determined using the BCA protein assay kit (Pierce, Rockford, IL, USA). Lysate was incubated for 2 h at 4°C with gentle rotation with rabbit polyclonal antibodies for human EGFR, CCN2, or Src immobilized onto protein A – sepharose beads (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA). Beads were washed twice with an IP buffer (137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 1 mM CaCl2, 1% NP-40, 10% glycerol, 1 mg/ml bovine serum albumin, and 20 mM Tris; pH 8.0), boiled in a sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) sample buffer, and centrifuged (12 000 × g, 4°C for 15 min). Supernatants were immediately subjected to western blot analysis. For western blotting, proteins (40 μg) were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane (Immobilon-P membrane; Millipore) by electrotransfer. The blot was blocked in a solution of 5% skim milk and 0.1% Tween 20 in PBS. Thereafter, membrane-bound proteins were probed with the following primary antibodies: CCN2, DAPK, phosphorylated ERK, ERK-1, phosphorylated Akt, Akt, TrkA, phosphorylated-Src, Src, β-actin, α-tubulin (Santa Cruz Biotechnology), p-EGFR, and EGFR (Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA). The membrane was washed and then incubated with HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies for 30 min. Enhanced chemiluminescence reagents (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech, Piscataway, NJ, USA) were employed to depict the protein bands on membranes. The light was captured on Kodak X-Omat Blue autoradiography film (PerkinElmer Life Sciences, Boston, MA, USA).
In vitro binding assay
The recombinant proteins rCCN2 (BioVendor Com. Heidelberg, Germany), rEGFR, and rEGF (R&D Techne Corporation) (2 μg) were added in binding buffer (50 mM sodium phosphate, pH 7.5, 500 mM NaCl, and 1% Nonidet P-40) and incubated with gentle rotation at 4°C for 2 h. Thereafter, cross-links were reversed by boiling in an SDS-PAGE sample buffer (containing 0.1 M dithiothreitol (DTT)) before loading on SDS-PAGE gels for immunoblotting analysis. To map EGFR and CCN2 interactions, CCN2 and EGFR antibodies (Cell Signaling Technology) were used to detect the specific bands.
Reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR)
Reverse transcription of RNA isolated from cells was performed in a final reaction containing the following: total RNA (5 μg), First Strand Buffer with DTT (10 mM), deoxy ribonucleotide triphosphate (dNTP) (2.5 mM), Oligo (dT) 12–18 primer (1 μg), and 200 U/l Moloney murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase (200 U). The reaction was conducted at 37°C for 2 h and was terminated by heating the solution to 70°C for 10 min. Thereafter, 1 l of the reaction mixture was amplified by PCR using the following pairs of primers: 5′-CCAGCAGCAGGCAGCACTTG-3′ (sense) and 5′-CACGGGCGCTGCACCACTAC-3′ (antisense), to produce a 420-bp fragment of the DAPK gene. The internal control gene was β-actin, for which we used 5′-GATGATGATATCGCCGCGCT-3′ (sense) and 5′-TGGGTCATCTTCTCGCGGTT-3′ (antisense) to produce a 320-bp fragment product. A 220-bp fragment of the Bcl-2 gene was produced by 5′-TGTGGCCTTCTTTGAGTTCG-3′ (sense) and 5′-AGCAGAGTCTTCAGAGACAG-3′ (antisense). The primers 5′-TGGTATCGTGGAAGGACTCATGAC-3′ (sense) and 5′-ATGCCAGTGAGCTTCCCGTTCAGC-3′ (antisense) produced a 189-bp fragment product of the internal control gene GAPDH. PCR amplification was conducted in a reaction buffer containing 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.4), 50 mM KCl, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 167 μm dNTPs, 2.5 U of Taq DNA polymerase, and 0.1 μm primers. The reactions were performed in a Biometra Thermaoblock (Biometra Inc, Baltimore, MD, USA) using the following program: denaturing for 1 min at 95°C, annealing for 1 min at 58°C, and elongating for 1 min at 72°C, 23 cycles in total; the final extension occurred at 72°C for 10 min. Equal volumes of each PCR sample were subjected to electrophoresis on a 1% agarose gel, which was then stained with ethidium bromide and photographed under UV illumination.
Construction of CCN2-expression plasmids and CCN2-deletion mutants
Total RNA was extracted from CL1-0 cells, and CCN2 cDNA was cloned and amplified by RT-PCR with the primers 5′-ATGACCGCCGCCAGTATGG-3′ and 5′-TCATGCCATGTCTCCGTACATCTT-3′ (PubMed serial number: XM-037056). The X was then subcloned into a pcDNA3/V5-His TOPO TA vector (Invitrogen Corporation). Serial deletion mutants of CCN2 were generated by deleting the CT domain, CT and TSP-1 domains, and CT, TSP-1, and VWC domains; designated as CCN2/d3, CCN2/d2, or CCN2/d1, respectively. The deletion constructs were generated using the reverse primer 5′-CGGAATTCAACCATGACCGCCGCCAGT-3′ in combination with the forward primers: 5′-GCTCTAGATCAGATGCACTTTTTGCCCTTC-3′ 5′-GCTCTAGATCAGTCTGGGCCAAACGTGTCT-3′ and 5′-GCTCTAGATCAGCAGGAGCACCATCTTTG-3′, respectively.
CCN2 siRNA constructs
Candidate siRNA oligos were targeted against the 379-bp region at the 3′ end of exon 2 of murine CCN2. The siRNA oligos were synthesized and cloned into the pSilencer 1.0 vector under control of the U6 RNA Polymerase III promoter, according to the manufacturer's instructions (Ambion, Austin, TX, USA). Of the two siRNA constructs tested, the greatest knockdown was seen with the oligo targeting CCN2379–397 (5′-CCTATTCTGTCACTTCGGC-3′). The ability to silence CCN2 was tested by transient cotransfection with expression vectors encoding murine CCN2 into human 293 cells and cells of the human lung adenocarcinoma cell lines A549 and CL1-5.
Plasmid and transient transfection
The deletion constructs, point mutation expression plasmids, and vectors were transiently transfected into CL1-5 and A549 cells using the TransFast transfection reagent (Promega Corporation). We used 3 μg plasmids and 8 μg transfection reagents, according to the manufacturer's instructions. One hour after transfection, the cells were placed in normal complete medium and cultured for a further 8 h. The transfected cells were harvested and subjected to invasion assay, promoter assay, and western blotting.
Stable transfected clone selection
Purified plasmid DNA (3 μg) was transfected into XΛ1-5 and A549 cells, or silence RNA plasmid (3 μg) of CCN2 was transfected into CL1-0 cells, using the TransFast transfection reagent (Promega Corporation). Twenty-four hours after transfection, gentamicin (G418; Life Technologies Corporation, Carlsbad, CA, USA) was added to 600 μg/ml for stable transfectant selection. Thereafter, the selection media was replaced every 3 days. After 2 week of selection in G418, clones of resistant cells were isolated and allowed to proliferate in 100 μg/ml G418-containing medium. Integration of transfected plasmid DNA was confirmed by RT-PCR and western blotting analysis.
Blocking antibody experiments
Vector control clone (CL1-5/Neo) and CCN2-stable transfectant (CL1-5/CCN2) were treated with anti-CCN2 blocking antibody (R&D Techne Corporation) or IgG control antibody, and suspended for 48 h. After treatment, cells were washed with PBS and analyzed by anoikis assay.
Promoter activity assay
For cell transfection, cells were seeded in six-well plates. After reaching approximately 70% confluence, cells were transfected with PGL2-basic and DAPK full-length promoter using TransFast (Promega Corporation). After transfection, the medium was replaced by fresh normal growth medium, and the cells were incubated for 24 h. After starvation in serum-free medium for 16 h, the cells were harvested. The luciferase activity was determined using a dual-luciferase reporter assay system (Promega Corporation) and was measured with a luminometer.
DAPK kinase assay
For assays using full-length DAPK as the kinase, immunopurified FLAG-DAPK and FLAG-tagged substrate were incubated for 15 min at 25°C in kinase buffer (50 mm Hepes, pH 7.5, 8 mM MgCl2, 2 mM MnCl2, and 0.1 mg/ml BSA) supplemented with 10 μCi/μl [γ-33P]ATP, 50 μm ATP, 2.5 μg MLC, 1 μm bovine calmodulin, and 0.5 mM CaCl2. Reactions were terminated by 95°C heating of SDS-loading buffer for 5 min and resolved on 7.5% acrylamide gel then keep on −20°C. Total levels of ATP were exposed and input was served as loading control.
In vivo experimental metastasis
Cells were washed and resuspended in PBS. Subsequently, 6-week-old SCID mice were injected in the lateral tail vein with a single-cell suspension containing 106 cells in 0.1 ml PBS. The mice were injected i.v. with cells so that we could measure the metastatic potential and perform biofluorescence imaging. The mice were killed after 8 weeks, and all of their organs were examined for metastasis formation. The lungs were removed and fixed in 10% formalin fixative. The number of lung-tumor colonies was counted under a dissecting microscope.
Immunohistochemistry
Tissue sections for immunostaining were obtained from formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded primary tumors produced in mice by tail vein-injected human lung adenocarcinoma cell lines. Sections were performed with anti-human DAPK, CCN2, and EGFR antibodies (Santa Cruz Biotechnology). After three washes in PBS, the samples were treated with biotin-labeled secondary antibodies (Vector Laboratories, Burlington, ON, USA) at a dilution of 1 : 500 for 1 h at room temperature. Bound antibodies were detected with an ABC kit (Vector Laboratories). The slides were stained with diaminobenzidine, washed, counterstained with Delafield's hematoxylin, dehydrated, treated with xylene, and mounted.
Flow-cytometry protein-interaction assay
Cells at 80% confluent growth were placed in fresh serum-free medium for 16 h; thereafter, they were treated with 100 ng/ml rCCN2 (BioVendor Com.) or 20 ng/ml rEGF (R&D Techne Corporation) for 15 min. Cells were resuspended and incubated with primary polyclonal antibody against CCN2 or EGF (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) for 1 h at 4°C. After washing, cells were stained with an FITC-labelled goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) for 30 min in the dark. Analysis was then conducted with an FACS Calibur cytometer (Collaborative Biomedical, BD Biosciences).
Statistics
Summary statistics are presented as the mean±S.D. Where appropriate, data were evaluated by performing a simple comparison between two values using Student's t-test and the Tukey's Studentized Range (HSD) Test. All statistical analyses were performed with the SPSS program (version 10.0). Variables were retained in a model if the associated two-tailed P-values were ⩽0.10 (all statistical tests were two-tailed). A P-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Acknowledgments
We thank CH Chan for the bioinformatics analysis and CC Hong for the CCN2 serial deletion constructs. This work was supported by grants from the Department of Health, R.O.C. (DOH101-TD-PB-111-NSC007).
Glossary
- CCN2/CTGF
CCN family protein 2/connective tissue growth factor
- c-Cbl
c-casitas B-lineage lymphoma
- CT
cystine knot
- DAPK
death-associated protein kinase
- dNTP
deoxy ribonucleotide triphosphate
- DTT
dithiothreitol
- ECM
extracellular matrix
- EGF
epidermal growth factor
- EGFR
epidermal growth factor receptor
- ELISA
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- ERK
extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- FACS
fluorescence-activated cell sorting
- FITC
fluorescein isothiocyanate
- HRP
horseradish peroxidase
- IgG
immunoglobulin G
- MAPK
mitogen-activated protein kinase
- PBS
phosphate-buffered saline
- PI
propidium iodide
- PI3K
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- rCCN2
recombinant CCN2
- ROI
region of interest
- RT-PCR
reverse transcription PCR
- siDAPK
silencing DAPK
- SDS-PAGE
sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- WB-IP
western-immunoprecipitation analysis
- β-PIX
β-p21-activated kinase-interacting exchange factor
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website (http://www.nature.com/cdd)
Edited by P Mehlen
Supplementary Material
References
- Kari C, Chan TO, Rocha de Quadros M, Rodeck U. Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor in cancer: apoptosis takes center stage. Cancer Res. 2003;63:1–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider MR, Wolf E. The epidermal growth factor receptor ligands at a glance. J Cell Physiol. 2009;218:460–466. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta LA, Kohn E. Anoikis: cancer and the homeless cell. Nature. 2004;430:973–974. doi: 10.1038/430973a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douma S, Van Laar T, Zevenhoven J, Meuwissen R, Van Garderen E. Peeper DS Suppression of anoikis and induction of metastasis by the neurotrophic receptor TrkB. Nature. 2004;430:1034–1039. doi: 10.1038/nature02765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles SA, Welch DR. Metastasis: recent discoveries and novel treatment strategies. Lancet. 2007;369:1742–1757. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60781-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benvenuti S, Comoglio PM. The MET receptor tyrosine kinase in invasion and metastasis. J Cell Physiol. 2007;213:316–325. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger TR, Peeper DS. Critical role for TrkB kinase function in anoikis suppression, tumorigenesis, and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2007;67:6221–6229. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reginato MJ, Mills KR, Paulus JK, Lynch DK, Sgroi DC, Debnath J, et al. Integrins and EGFR coordinately regulate the pro-apoptotic protein Bim to prevent anoikis. Nat Cell Biol. 2003;5:733–740. doi: 10.1038/ncb1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen CC, Lau LF. Functions and mechanisms of action of CCN matricellular proteins. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009;41:771–783. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2008.07.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft FC. CCN2, the connective tissue growth factor. J Mol Med. 2008;86:1–3. doi: 10.1007/s00109-007-0287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu CY, Chang CC, Prakash E, Kuo ML. Connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) and cancer progression. J Biomed Sci. 2008;15:675–685. doi: 10.1007/s11373-008-9264-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang Y, Siegel PM, Shu W, Drobnjak M, Kakonen SM, Cordón-Cardo C, et al. A multigenic program mediating breast cancer metastasis to bone. Cancer Cell. 2003;3:537–549. doi: 10.1016/s1535-6108(03)00132-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie D, Yin D, Wang HJ, Liu GT, Elashoff R, Black K, et al. Levels of expression of CYR61 and CTGF are prognostic for tumor progression and survival of individuals with gliomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:2072–2081. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-0659-03. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koliopanos A, Friess H, di Mola FF, Tang WH, Kubulus D, Brigstock D, et al. Connective tissue growth factor gene expression alters tumor progression in esophageal cancer. World J Surg. 2002;26:420–427. doi: 10.1007/s00268-001-0242-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L, Li Z, Feng G, You W, Li J. Expression of connective tissue growth factor is in agreement with the expression of VEGF, VEGF-C, -D and associated with shorter survival in gastric cancer. Pathol Int. 2007;57:712–718. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.2007.02162.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeng ZJ, Yang LY, Ding X, Wang W. Expressions of cysteine-rich61, connective tissue growth factor and Nov genes in hepatocellular carcinoma and their clinical significance. World J Gastroenterol. 2004;10:3414–3418. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i23.3414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin BR, Chang CC, Che TF, Chen ST, Chen RJ, Yang CY, et al. Connective tissue growth factor inhibits metastasis and acts as an independent prognostic marker in colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:9–23. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2004.10.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang CC, Shih JY, Jeng YM, Su JL, Lin BZ, Chen ST, et al. Connective tissue growth factor and its role in lung adenocarcinoma invasion and metastasis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004;96:364–375. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djh059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang CC, Lin MT, Lin BR, Jeng YM, Chen ST, Chu CY, et al. Effect of connective tissue growth factor on hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha degradation and tumor angiogenesis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98:984–995. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djj242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogiso H, Ishitani R, Nureki O, Fukai S, Yamanaka M, Kim JH, et al. Crystal structure of the complex of human epidermal growth factor and receptor extracellular domains. Cell. 2002;110:775–787. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00963-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmiedel J, Blaukat A, Li S, Knöchel T, Ferguson KM. Matuzumab binding to EGFR prevents the conformational rearrangement required for dimerization. Cancer Cell. 2008;13:365–373. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.02.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim LC, Song L, Haura EB. Src kinases as therapeutic targets for cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2009;6:587–595. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2009.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muthuswamy SK, Muller WJ. Direct and specific interaction of c-Src with Neu is involved in signaling by the epidermal growth factor receptor. Oncogene. 1995;11:271–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padrón D, Sato M, Shay JW, Gazdar AF, Minna JD, Roth MG. Epidermal growth factor receptors with tyrosine kinase domain mutations exhibit reduced Cbl association, poor ubiquitylation, and down-regulation but are efficiently internalized. Cancer Res. 2007;67:7695–7702. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennock S, Wang Z. A tale of two Cbls: interplay of c-Cbl and Cbl-b in epidermal growth factor receptor downregulation. Mol Cell Biol. 2008;28:3020–3037. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01809-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umebayashi K, Stenmark H, Yoshimori T. Ubc4/5 and c-Cbl continue to ubiquitinate EGF receptor after internalization to facilitate polyubiquitination and degradation. Mol Biol Cell. 2008;19:3454–3462. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E07-10-0988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu WJ, Tu S, Cerione RA. Activated Cdc42 sequesters c-Cbl and prevents EGF receptor degradation. Cell. 2003;114:715–725. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00688-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng Q, Baird D, Peng X, Wang J, Ly T, Guan JL, et al. Cool-1 functions as an essential regulatory node for EGF receptor- and Src-mediated cell growth. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8:945–956. doi: 10.1038/ncb1453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi H, Woods NT, Dorsey JF, Takahashi Y, Gjertsen NR, Yeatman T, et al. SRC directly phosphorylates Bif-1 and prevents its interaction with Bax and the initiation of anoikis. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:19112–19118. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M709882200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara K, Senga T, Biswas MH, Hasegawa H, Ito S, Hyodo T, et al. Recovery of anoikis in Src-transformed cells and human breast carcinoma cells by restoration of the SIRP{alpha}1/SHP-2 signaling system. Cancer Res. 2011;71:1229–1234. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer CF, Anthony K, Krupa S, Buchoff J, Day M, Hannay T, et al. PID: the pathway interaction database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37:D674–D679. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inbal B, Cohen O, Polak-Charcon S, Kopolovic J, Vadai E, Eisenbach L, et al. DAP kinase links the control of apoptosis to metastasis. Nature. 1997;390:180–184. doi: 10.1038/36599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen RH, Wang WJ, Kuo JC. The tumor suppressor DAP-kinase links cell adhesion and cytoskeleton reorganization to cell death regulation. J Biomed Sci. 2006;13:193–199. doi: 10.1007/s11373-005-9063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh AB, Harris RC. Epidermal growth factor receptor activation differentially regulates claudin expression and enhances transepithelial resistance in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:3543–3552. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M308682200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorokin A, Lemmon MA, Ullrich A, Schlessinger J. Stabilization of an active dimeric form of the epidermal growth factor receptor by introduction of an inter-receptor disulfide bond. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:9752–9759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang WJ, Kuo JC, Ku W, Lee YR, Lin FC, Chang YL, et al. The tumor suppressor DAPK is reciprocally regulated by tyrosine kinase Src and phosphatase LAR. Mol Cell. 2007;27:701–716. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.06.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.