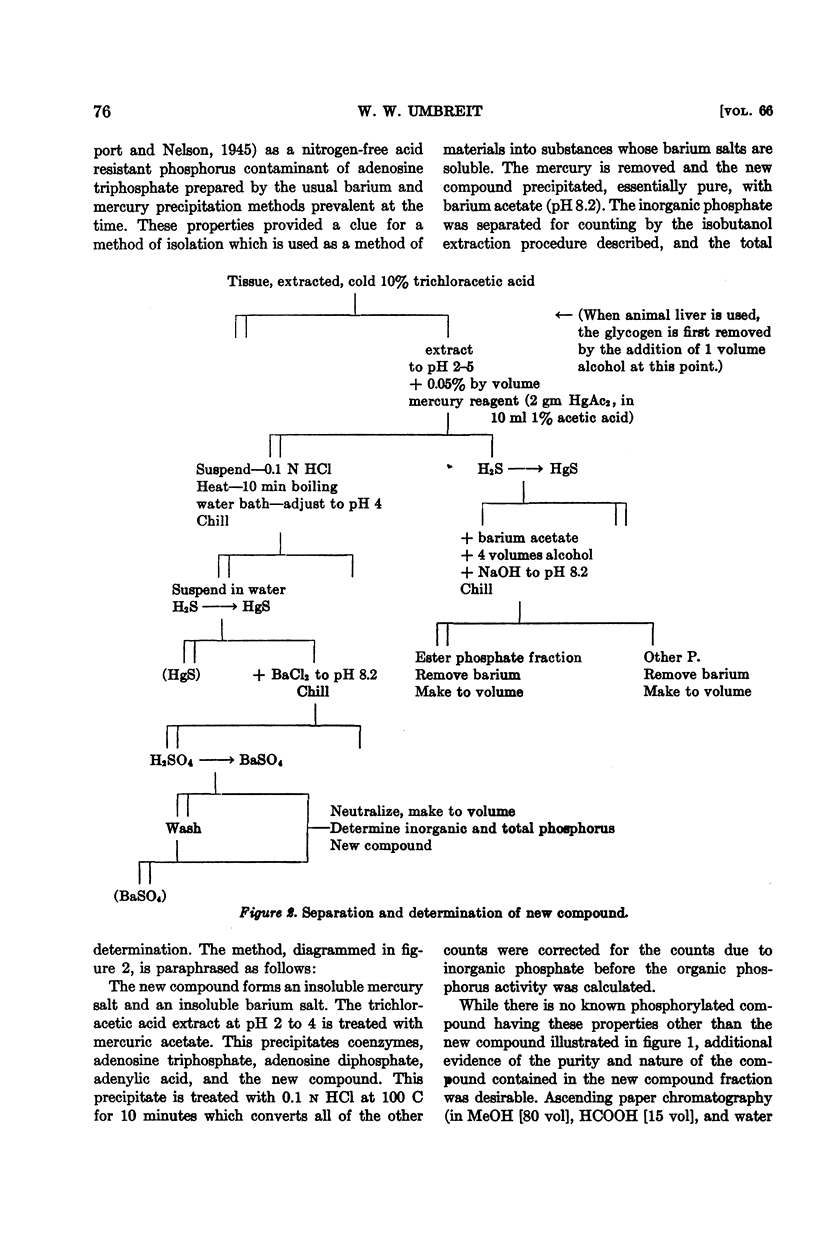
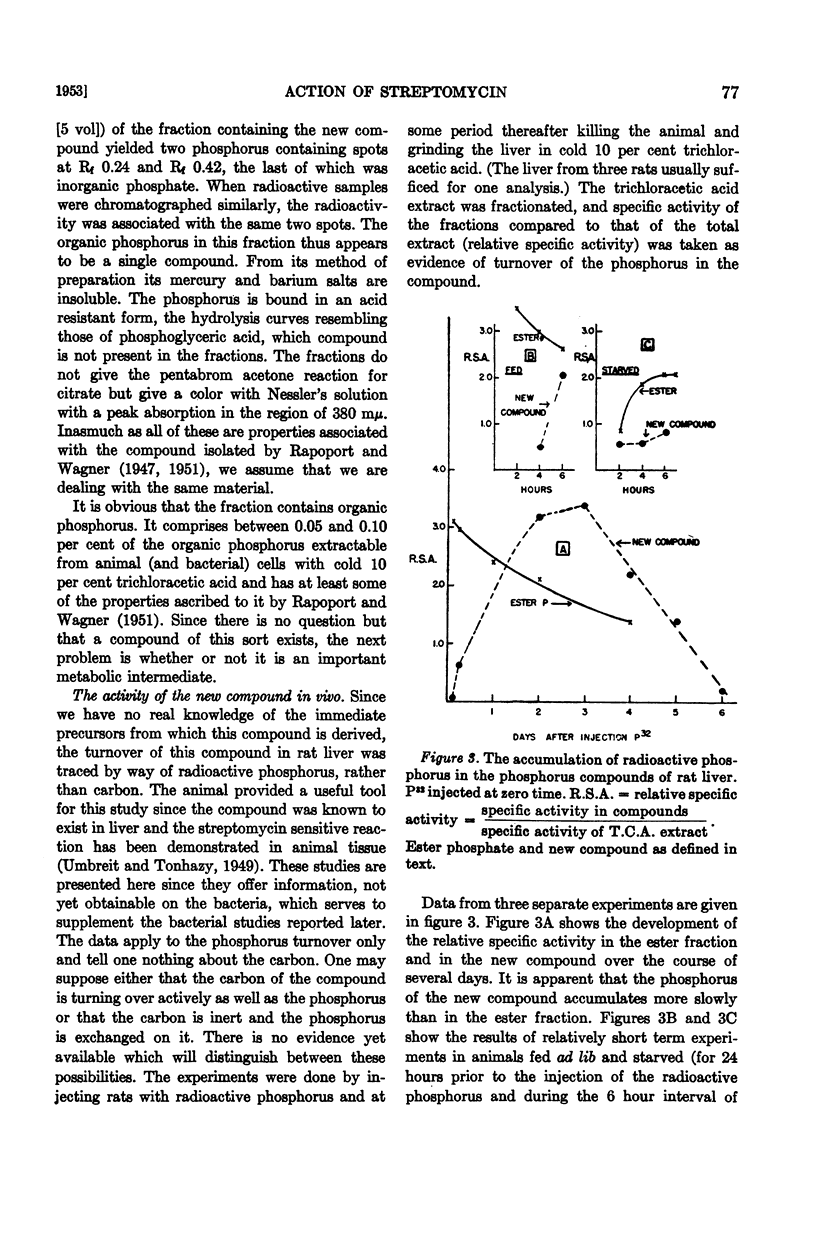
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARKULIS I. L. Inhibition of the anaerobic pyruvate dissimilation in Escherichia coli by dihydrostreptomycin. J Bacteriol. 1951 Mar;61(3):375–376. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.3.375-376.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENNOR A. H., ROSENBERG H. Observations on the determination of the specific activity of the inorganic phosphate fraction of trichloroacetic acid extracts of liver. Biochem J. 1952 Feb;50(4):524–530. doi: 10.1042/bj0500524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OGINSKY E. L., SMITH P. H., UMBREIT W. W. The action of streptomycin; the nature of the reaction inhibited. J Bacteriol. 1949 Dec;58(6):747–759. doi: 10.1128/jb.58.6.747-759.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPOPORT S., WAGNER R. H. A phosphate ester of a tricarboxylic acid in liver. Nature. 1951 Aug 18;168(4268):295–296. doi: 10.1038/168295a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH P. H., OGINSKY E. L., UMBREIT W. W. The action of streptomycin; the metabolic properties of resistant and dependent strains. J Bacteriol. 1949 Dec;58(6):761–767. doi: 10.1128/jb.58.6.761-767.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UMBREIT W. W., SMITH P. H., OGINSKY E. L. The action of streptomycin. V. The formation of citrate. J Bacteriol. 1951 May;61(5):595–604. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.5.595-604.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UMBREIT W. W., TONHAZY N. E. The action of streptomycin in tissue homogenates. J Bacteriol. 1949 Dec;58(6):769–776. doi: 10.1128/jb.58.6.769-776.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


