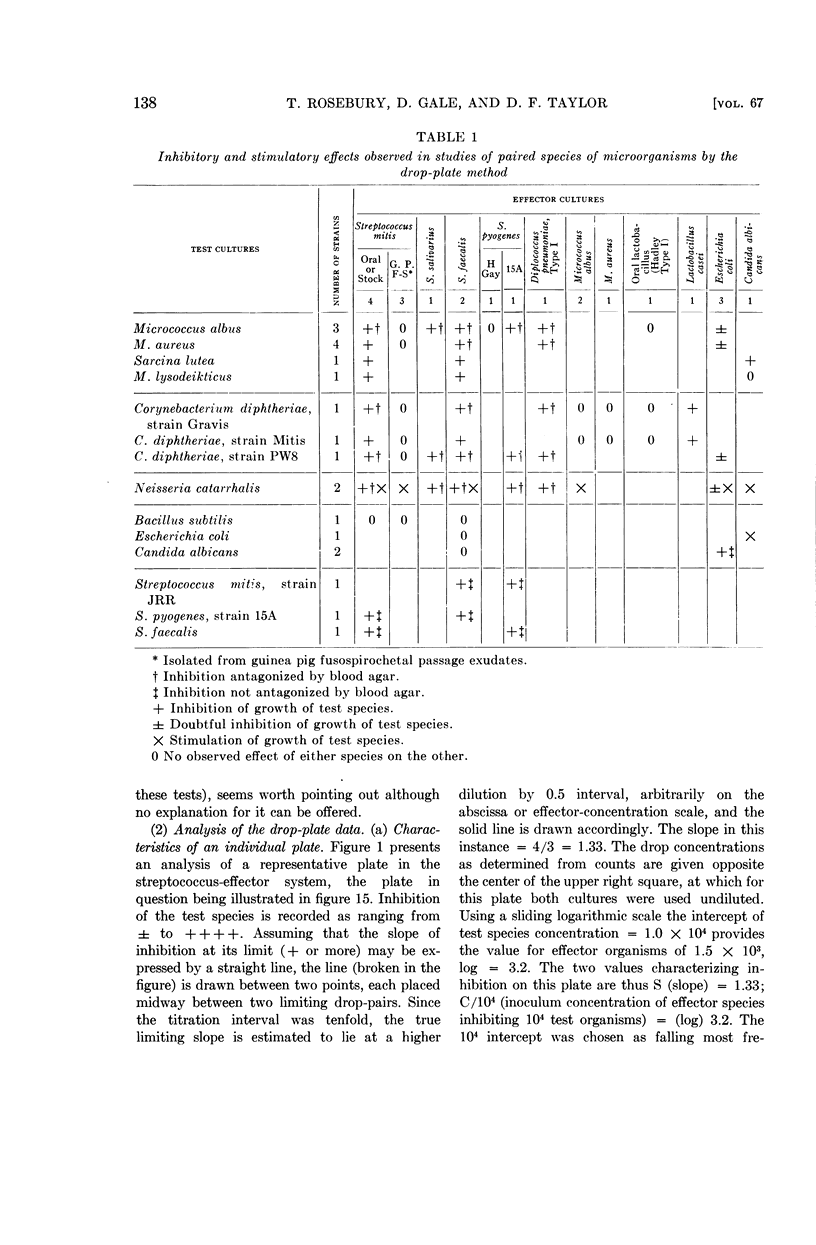
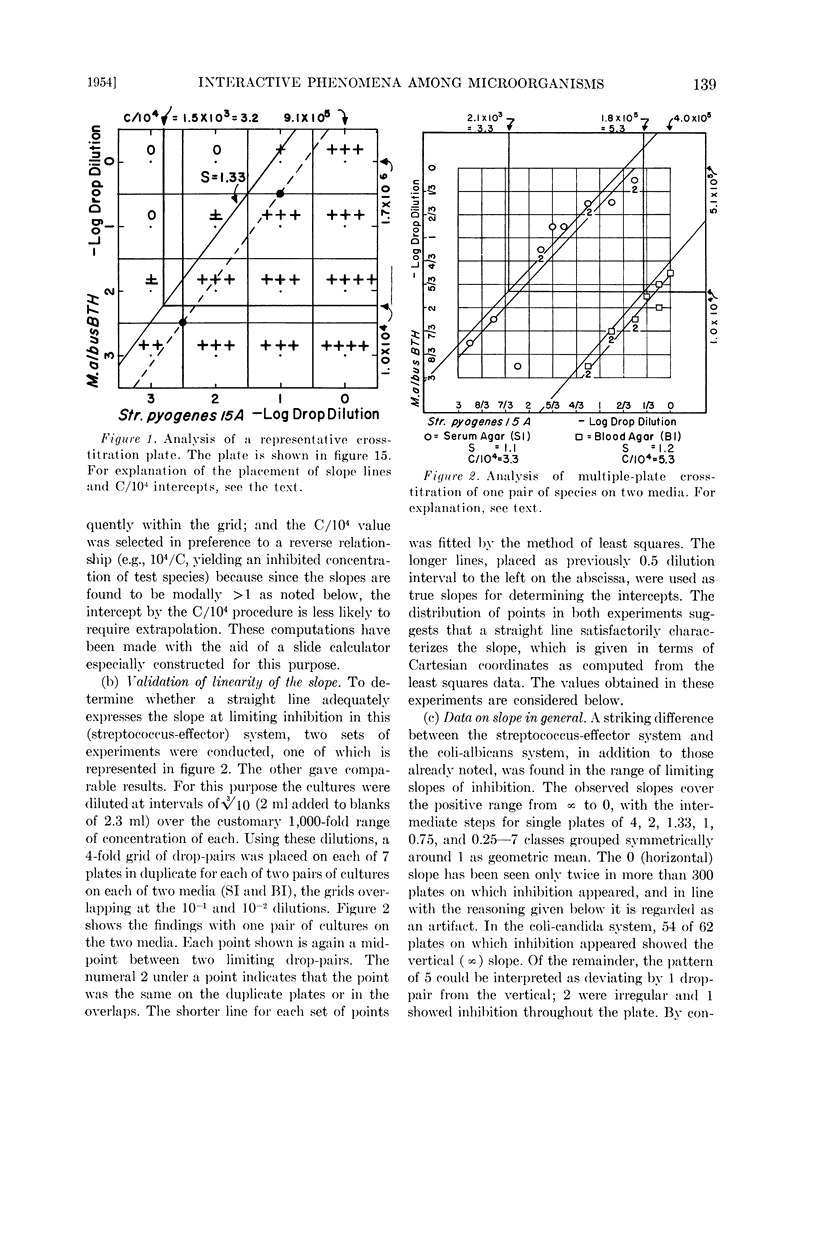
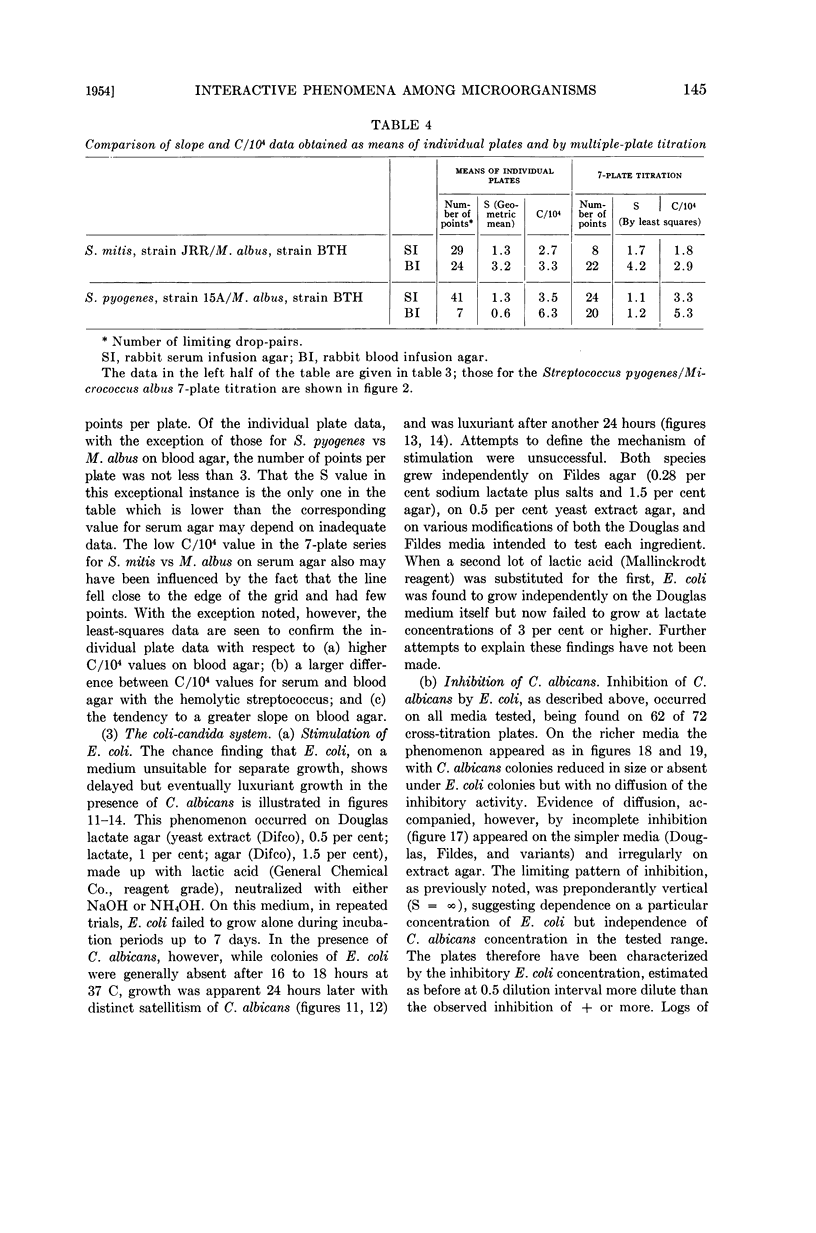
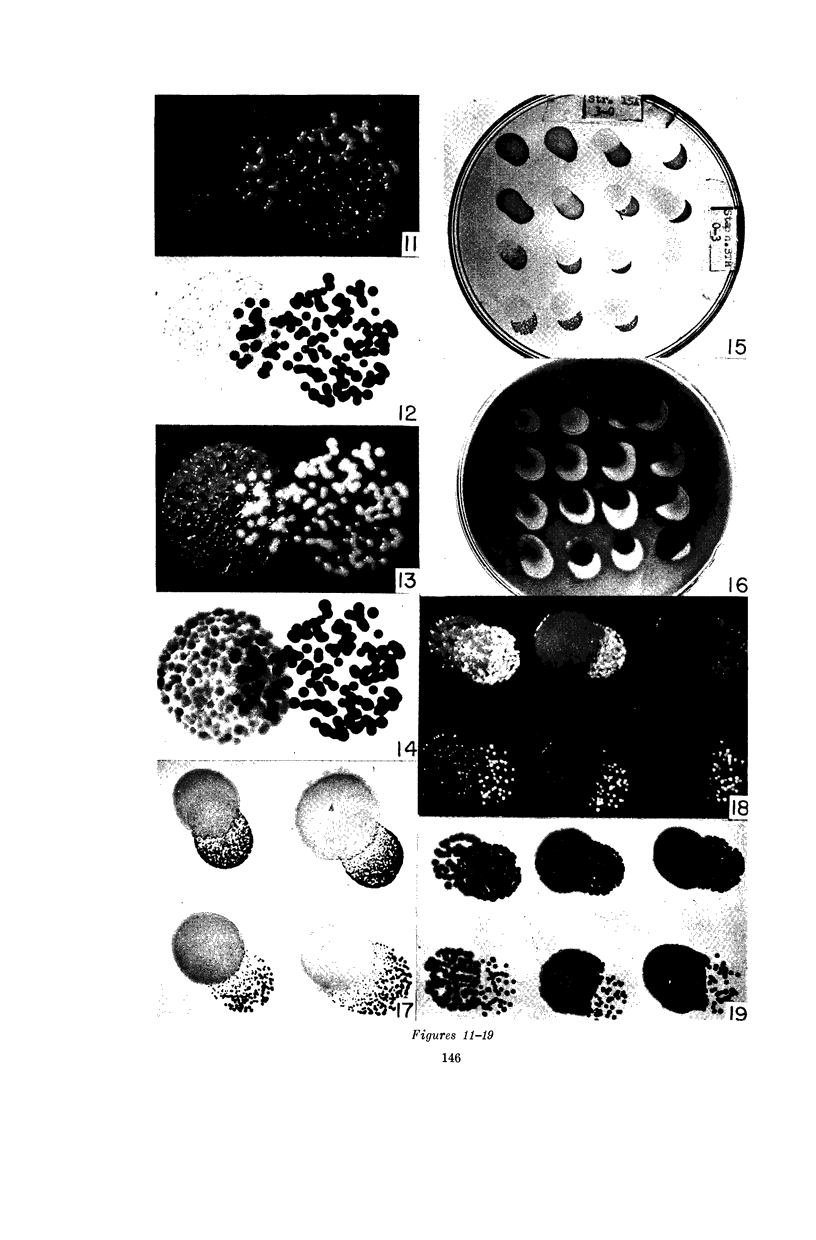
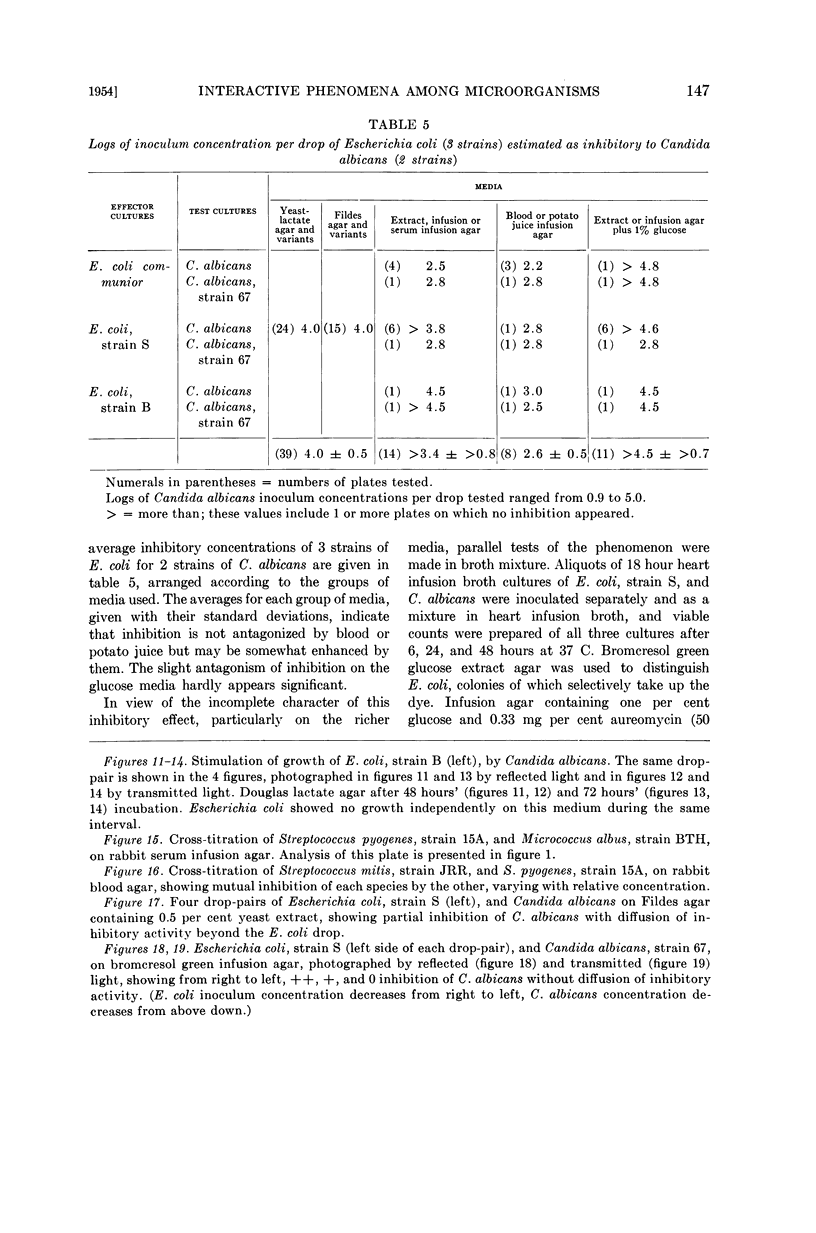
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANNEAR D. I., DORMAN D. C. Hydrogen peroxide accumulation during growth of the pneumococcus. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1952 Apr;30(2):191–195. doi: 10.1038/icb.1952.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANNEAR D. I., HAYES L. Mixed bacterial growth. I. Enumeration of the viable organisms in mixed populations of a viridans Streptococcus and Staphylococcus albus. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1950 Mar;28(2):181–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANNEAR D. I. Mixed bacterial growth. III. Studies on the mixed growths of a viridans streptococcus, a diphtheroid and Staphylococcus albus. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1951 Mar;29(2):93–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGER U. Zur Frage der antibakteriellen Wirkung des Speichels. Z Hyg Infektionskr. 1952;133(5):371–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEWAR M. R., PARFITT G. J. Research note on the preparation of tomato peptone agar medium. Br Dent J. 1951 Mar 20;90(6):150–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS H. C. On the occurrence of the lactate fermenting anaerobe, Micrococcus lactilyticus, in human saliva. J Dent Res. 1950 Jun;29(3):304–306. doi: 10.1177/00220345500290030801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS C. A., SMITH W. M., JOHNSTON E. A., GIBLETT E. R. Bacterial flora of the normal human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1950 Oct;15(4):305–324. doi: 10.1038/jid.1950.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALBERT S. P., SWICK L., SONN C. Characteristics of antibiotic-producing strains of the ocular bacterial flora. J Immunol. 1953 Apr;70(4):400–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEGEMANN F. Weitere Untersuchungsergebnisse über die Natur des von menschlichen Speichelkokken erzeugten antibakteriellen Stoffes. Z Hyg Infektionskr. 1950;131(4):355–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HESSELTINE C. W., HAUCK M., HAGEN M. T., BOHONOS N. Isolation and growth of yeasts in the presence of aureomycin. J Bacteriol. 1952 Jul;64(1):55–61. doi: 10.1128/jb.64.1.55-61.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod J. W., Gordon J. Production of Hydrogen Peroxide by Bacteria. Biochem J. 1922;16(4):499–506. doi: 10.1042/bj0160499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxford A. E. Diplococcin, an anti-bacterial protein elaborated by certain milk streptococci. Biochem J. 1944;38(2):178–182. doi: 10.1042/bj0380178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSEBURY T., CLARK A. R., MACDONALD J. B., O'CONNELL D. C. Studies of fusospirochetal infection. III. Further studies of a guinea pig passage strain of fusospirochetal infection, including the infectivity of sterile exudate filtrates, of mixed cultures through ten transfers, and of recombined pure cultures. J Infect Dis. 1950 Nov-Dec;87(3):234–248. doi: 10.1093/infdis/87.3.234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STREPTOZYME, a lytic enzyme from lactic streptococci. Nature. 1951 Oct 6;168(4275):607–607. doi: 10.1038/168607a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON R., JOHNSON A. The inhibitory action of saliva on the diphtheria bacillus: hydrogen peroxide, the inhibitory agent produced by salivary streptococci. J Infect Dis. 1951 Jan-Feb;88(1):81–85. doi: 10.1093/infdis/88.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R., Shibuya M. The Inhibitory Action of Saliva on the Diphtheria Bacillus: The Antibiotic Effect of Salivary Streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1946 Jun;51(6):671–684. doi: 10.1128/jb.51.6.671-684.1946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHEATER D. M., HIRSCH A., MATTICK A. T. R. Possible identity of lactobacillin with hydrogen peroxide produced by lactobacilli. Nature. 1952 Oct 11;170(4328):623–624. doi: 10.1038/170623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]