Abstract
Background
Icosapent ethyl (IPE) is a high-purity prescription form of eicosapentaenoic acid ethyl ester approved by the US Food and Drug Administration as an adjunct to diet to reduce triglyceride (TG) levels in adult patients with severe (≥500 mg/dL) hypertriglyceridemia. In addition to TG-lowering effects, IPE also reduces non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and apolipoprotein B levels without significantly increasing low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in patients with very high TG levels ≥500 mg/dL (MARINE study) and in patients with well-controlled LDL-C and residually high TG levels 200–500 mg/dL (ANCHOR study). This analysis examined the effect of IPE on inflammatory markers in patients from MARINE and ANCHOR.
Methods
MARINE (N = 229) and ANCHOR (N = 702) were Phase III, double-blind studies that randomized hypertriglyceridemic patients to IPE 4 g/day, 2 g/day, or placebo. This analysis assessed the median placebo-adjusted percentage change from baseline in markers representing various stages of atherosclerotic inflammation such as intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), oxidized low-density lipoprotein (Ox-LDL), lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP).
Results
Compared to placebo, IPE 4 g/day significantly decreased Ox-LDL (13 %, p < 0.0001, ANCHOR), Lp-PLA2 (14 %, p < 0.001, MARINE; 19 %, p < 0.0001, ANCHOR), and hsCRP levels (36 %, p < 0.01, MARINE; 22 %, p < 0.001, ANCHOR), but did not significantly change ICAM-1 and IL-6 levels. In the MARINE study, IPE 2 g/day did not significantly change ICAM-1, Ox-LDL, Lp-PLA2, IL-6, or hsCRP levels. Also, compared to placebo in the ANCHOR study, IPE 2 g/day significantly decreased Lp-PLA2 levels (8 %, p < 0.0001), but did not significantly change levels of other assessed inflammatory markers.
Conclusion
Compared to placebo, in hypertriglyceridemic patients, IPE 4 g/day significantly decreased Ox-LDL, Lp-PLA2, and hsCRP levels.
Introduction
Inflammation plays an important role in all stages of atherosclerosis [1]. Markers of inflammation are often used to assess cardiovascular risk, and sometimes guide decisions regarding the treatment of atherosclerotic coronary heart disease (CHD) [1, 2]. Upon vascular injury, vascular endothelial cells express vascular adhesion molecules (such as intercellular adhesion molecule-1 [ICAM-1]), that facilitate attachment of circulating leukocytes and promote vascular inflammation, which may help explain the observed association of vascular adhesion molecules with increased CHD risk [3, 4]. Concurrently, lipoprotein particles such as low-density lipoproteins (LDL) may collect within the intima, where they can undergo oxidation and create unstable oxygen free radicals and other reactive oxygen species [5]. Increased plasma concentrations of oxidized LDL (Ox-LDL) are thought to help predict future CHD events [6].
Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) is an enzyme brought into the arterial intima bound to LDL particles; it may also be produced by plaque inflammatory cells [7, 8]. Lp-PLA2 facilitates enzymatic modification of Ox-LDL particles, hydrolyzing Ox-LDL phospholipids to lysophosphatidylcholine and oxidized free fatty acids, which subsequently activate inflammatory macrophages [8]. Ox-LDL activation of macrophages can also increase interleukin-6 (IL-6), which may increase adhesion molecule expression, thus promoting vascular inflammation and potentially worsening atherosclerotic progression [9]. In clinical practice, the potential contribution of inflammation to atherosclerosis is most often assessed by C-reactive protein (CRP), an acute-phase reactant. CRP is produced by the liver and various other non-hepatic tissues such as vascular smooth muscle cells [10]. Increased CRP can be found with inflammatory diseases, as well as in overweight individuals as a response to increased IL-6 from dysfunctional adipose tissue [11]. Low-grade increases in CRP levels may also occur in response to increased inflammatory signaling from vascular macrophages associated with atherosclerosis [10]. Clinical trials have found levels of Lp-PLA2 and CRP to be higher in patients who developed CHD and ischemic stroke compared to those who did not experience these cardiovascular events [12, 13].
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) are omega-3 fatty acids found in fish oil and in supplements and prescription formulations [14]. Therapeutically, EPA and DHA lower triglyceride (TG) levels and may reduce cardiovascular events [15]. Icosapent ethyl (IPE; VascepaTM [formerly AMR101]; Amarin, Bedminster, NJ, USA) is a high-purity prescription form of EPA ethyl ester approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as an adjunct to diet to reduce TG levels in adult patients with severe (≥500 mg/dL) hypertriglyceridemia. MARINE (Multi-Center, PlAcebo-Controlled, Randomized, Double-BlINd, 12-week study with an open-label Extension) evaluated the efficacy and safety of IPE in lowering TG levels in 229 patients with very high TG levels (≥500 mg/dL and ≤2000 mg/dL). In MARINE, patients were allowed to continue with their statin therapy if they were deemed to have a high risk for CHD or CHD risk equivalents and were on a stable dose. ANCHOR evaluated the efficacy and safety of IPE in lowering TG levels in 702 statin-treated patients at high cardiovascular risk with well-controlled LDL-C and residually high TG levels (≥200 mg/dL and <500 mg/dL). In both studies, IPE 4 g/day significantly lowered TG, non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C), apolipoprotein B (apo B), very-low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (VLDL-C), and total cholesterol (TC) levels, all without significantly raising LDL-C levels [16, 17]. This current analysis describes the effects of IPE on the a priori secondary and exploratory endpoints of the circulating inflammatory markers ICAM-1, Ox-LDL, Lp-PLA2, IL-6, and high-sensitivity CRP (hsCRP) observed in MARINE and ANCHOR.
Methods
Design and Patients
MARINE (NCT01047683) and ANCHOR (NCT01047501) study designs were previously published [16, 17]. Briefly, both were phase III, placebo-controlled, randomized, double-blind, multicenter studies with a 4- to 6-week lead-in period of diet, lifestyle, and medication stabilization with washout of prohibited lipid-altering medications. In both studies, eligible men and women aged >18 years with qualifying lipid levels (MARINE: TG ≥500 mg/dL and ≤2000 mg/dL; ANCHOR: TG ≥200 mg/dL and <500 mg/dL and LDL-C ≥40 mg/dL and <115 mg/dL) entered a 12-week double-blind treatment period and were randomized to receive either IPE 4 g/day, IPE 2 g/day, or matched placebo.
Statistical Analysis
The primary efficacy endpoint for MARINE and ANCHOR was the median placebo-adjusted percentage change in TG levels from baseline to study end (week 12) in the two active treatment groups. All efficacy analyses were performed on the intent-to-treat (ITT) population, defined as all randomized patients who had a baseline efficacy measurement, received ≥1 dose of study drug, and had ≥1 post-randomization efficacy measurement. The efficacy endpoints reported here include median placebo-adjusted percentage changes from baseline to week 12 in ICAM-1, Ox-LDL, Lp-PLA2, IL-6, and hsCRP levels for IPE (both doses) compared to placebo. All were exploratory variables except for Lp-PLA2, which was a secondary variable. In MARINE, inflammation-related endpoints were evaluated in nearly all patients; in ANCHOR, ICAM-1, Ox-LDL, and IL-6 were measured in approximately the first 240 patients of the ITT population.
The median difference of each variable in this analysis (percentage change from baseline) between each IPE treatment group and the placebo group was evaluated with a non-parametric test using the Hodges-Lehmann medians of the differences between treatment groups and the Wilcoxon rank-sum test (data were non-parametric in distribution). For the exploratory endpoints assessed in this analysis, a p value alpha of ≤0.05 was prespecified and no adjustments were made for multiple comparisons; adjustments were made for multiple comparisons for Lp-PLA2 as this was a prespecified secondary endpoint (the p-values were adjusted by applying Hommel’s multiple comparison procedure to control the Type I error as pre-specified in the study protocol). All statistical analyses were carried out using SAS software version 8.2 or higher (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA). Note that the two-sample Hodges-Lehmann median does not estimate the difference of the means or the difference of the medians; it estimates the median of the differences, which, if the underlying distributions are asymmetric, is a different quantity (i.e., the Hodges-Lehmann median of the differences between treatment groups does not exactly match the numerical difference between the two medians of the treatment groups).
Laboratory Measurements
Serum concentrations of ICAM-1 were measured using a Quantikine® Human sICAM-1 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA). Plasma Ox-LDL concentrations were measured with a solid-phase two-site enzyme immunoassay (Mercodia, Winston Salem, NC, USA). Serum IL-6 concentrations were measured using the Luminex fluorescent microsphere technology. Serum Lp-PLA2 and hsCRP were measured as previously described [16]. All assays were performed by Medpace Reference Laboratories (Cincinnati, OH, USA; Navi, Mumbai, India; and Leuven, Belgium) except for the Lp-PLA2 assay, which was performed by Berkeley HeartLab (Burlingame, CA, USA).
Results
Patient Characteristics
Table 1 includes the baseline demographics of patients in the randomized populations of MARINE and ANCHOR, and Table 2 lists the baseline lipid parameters in the ITT populations. Baseline demographics and lipid parameters were comparable among treatment groups within each study. A higher percentage of patients in ANCHOR (73 %) had diabetes mellitus than in MARINE (28 %), reflecting that ANCHOR was a high CHD risk population. Differences in baseline lipid parameters between the studies were reflective of the different lipid entry criteria. In MARINE, 55 % of the randomized patients were at high risk for CHD; in ANCHOR, all patients were required to have clinical CHD or CHD risk equivalents (10-year risk ≥20 %).
Table 1.
| Characteristic | MARINE | ANCHOR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPE 4 g/day (n = 77) | IPE 2 g/day (n = 76) | Placebo (n = 76) | IPE 4 g/day (n = 233) | IPE 2 g/day (n = 236) | Placebo (n = 233) | |
| Age, years [mean (SD)] | 51.9 (10.27) | 53.4 (9.34) | 53.4 (8.34) | 61.1 (10.03) | 61.8 (9.42) | 61.2 (10.05) |
| Male [n (%)] | 59 (76.6) | 58 (76.3) | 58 (76.3) | 142 (60.9) | 144 (61.0) | 145 (62.2) |
| White [n (%)] | 67 (87.0) | 67 (88.2) | 68 (89.5) | 226 (97.0) | 226 (95.8) | 224 (96.1) |
| Weight, kg [mean (SD)] | 93.2 (18.27) | 92.1 (15.57) | 93.0 (16.92) | 94.5 (18.30) | 95.5 (18.29) | 97.0 (19.14) |
| BMI, kg/m2 [mean (SD)] | 30.4 (4.29) | 30.8 (4.24) | 31.0 (4.25) | 32.7 (4.99) | 32.9 (4.98) | 33.0 (5.04) |
| Diabetes [n (%)] | 22 (28.6) | 20 (26.3) | 21 (27.6) | 171 (73.4) | 172 (72.9) | 171 (73.4) |
| Baseline TG >750 mg/dL [n (%)] | 29 (37.7) | 29 (38.2) | 32 (42.1) | NA | NA | NA |
| Statin use [n (%)]a | ||||||
| Any | 20 (26.0) | 19 (25.0) | 18 (23.7) | 233 (100) | 236 (100) | 233 (100) |
| Atorvastatin | NA | NA | NA | 44 (18.9) | 43 (18.2) | 45 (19.3) |
| Simvastatin | NA | NA | NA | 134 (57.5) | 136 (57.6) | 133 (57.1) |
| Rosuvastatin | NA | NA | NA | 55 (23.6) | 57 (24.2) | 55 (23.6) |
| Statin efficacy regimens [n (%)]b | ||||||
| Lower | NA | NA | NA | 16 (6.9) | 17 (7.2) | 15 (6.4) |
| Medium | NA | NA | NA | 148 (63.5) | 148 (62.7) | 144 (61.8) |
| Higher | NA | NA | NA | 69 (29.6) | 71 (30.1) | 74 (31.8) |
a24.9 % (57/229) of patients in the MARINE study were on statin therapy
bLower-efficacy statin regimens = simvastatin 5–10 mg; medium-efficacy statin regimens = rosuvastatin 5–10 mg, atorvastatin 10–20 mg, simvastatin 20–40 mg, simvastatin 10–20 mg + ezetimibe 5–10 mg; higher-efficacy statin regimens = rosuvastatin 20–40 mg, atorvastatin 40–80 mg, simvastatin 80 mg, simvastatin 40–80 mg + ezetimibe 5–10 mg
BMI body mass index, NA data not applicable to study design, SD standard deviation, TG triglyceride
Table 2.
| Lipid parameter (mg/dL) | MARINE | ANCHOR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPE 4 g/day (IQR) (n = 77) | IPE 2 g/day (IQR) (n = 76) | Placebo (IQR) (n = 76) | IPE 4 g/day (IQR) (n = 233) | IPE 2 g/day (IQR) (n = 236) | Placebo (IQR) (n = 233) | |
| TG | 679.5 (265.3) (n = 76) | 656.5 (303.5) (n = 73) | 703.0 (426.5) (n = 75) | 264.8 (93.0) (n = 226) | 254.0 (92.5) (n = 234) | 259.0 (81.0) (n = 227) |
| LDL-C | 90.5 (42.5) (n = 76) | 84.0 (58.0) (n = 73) | 86.0 (58.0) (n = 75) | 82.0 (25.0) (n = 225) | 82.0 (24.0) (n = 233) | 84.0 (27.0) (n = 226) |
| Non-HDL-C | 225.0 (89.5) (n = 76) | 210.0 (75.0) (n = 73) | 229.0 (85.0) (n = 75) | 128.0 (32.0) (n = 226) | 128.0 (33.0) (n = 234) | 128.0 (34.0) (n = 227) |
| TC | 253.5 (86.5) (n = 76) | 236.0 (79.0) (n = 73) | 256.0 (97.0) (n = 75) | 167.0 (38.0) (n = 226) | 169.0 (34.0) (n = 234) | 168.0 (38.0) (n = 227) |
| HDL-C | 26.5 (10.0) (n = 76) | 26.0 (6.0) (n = 73) | 27.0 (8.0) (n = 75) | 37.0 (12.0) (n = 226) | 38.0 (13.0) (n = 234) | 39.0 (12.0) (n = 227) |
Data are presented as median (interquartile range [IQR])
HDL-C high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, LDL-C low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, TC total cholesterol, TG triglyceride
Circulating Markers of Inflammation
Compared to placebo, IPE 4 g/day significantly decreased several circulating markers of inflammation (Fig. 1 and Table 3). In ANCHOR, IPE significantly decreased Ox-LDL (13 %; p < 0.0001) and Lp-PLA2 levels (19 %; p < 0.0001 [17]), and in MARINE, IPE significantly decreased Lp-PLA2 levels (14 %; p < 0.001 [16]). IPE 2 g/day did not significantly decrease levels of these markers of inflammation, except for Lp-PLA2, for which IPE 2 g/day produced a significant reduction in ANCHOR (8.0 %; p < 0.0001 [17]). Baseline hsCRP levels were elevated in all groups (ranging from 1.8 to 2.2 mg/L; Table 3). IPE 4 g/day significantly decreased hsCRP levels by 36 % (p < 0.01) in MARINE and by 22 % (p < 0.001) [17] in ANCHOR. IPE did not cause significant changes in ICAM-1 or IL-6 levels.
Fig. 1.
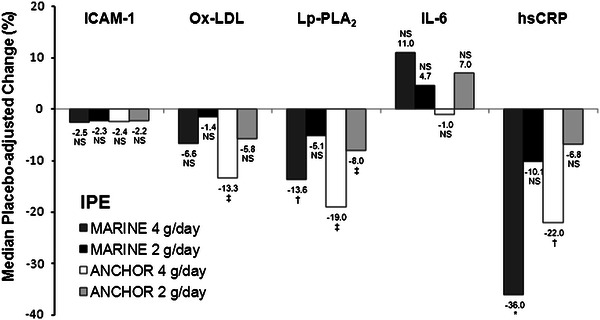
Median placebo-adjusted percentage change from baseline to week 12 in levels of inflammatory markers (intent-to-treat population). Lp-PLA2 data for MARINE from Bays et al. [16], Lp-PLA2 and hsCRP data for ANCHOR from Ballantyne et al [17]. P values for Lp-PLA2 were adjusted for multiple comparisons. hsCRP high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, ICAM-1 intercellular adhesion molecule-1, IL-6 interleukin-6, IPE icosapent ethyl, Lp-PLA 2 lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2, NS not significant, Ox-LDL oxidized low-density lipoprotein. *p < 0.01; † p < 0.001; ‡ p < 0.0001 vs. placebo
Table 3.
Median placebo-adjusted percentage change from baseline to study end in circulating markers of inflammation (intent-to-treat populations)
| IPE 4 g/day | IPE 2 g/day | Placebo | Median placebo-adjusted % change from baseline | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline value | End-of-treatment value | Change from baseline, % | Baseline value | End-of-treatment value | Change from baseline, % | Baseline value | End-of-treatment value | Change from baseline, % | IPE 4 g/day vs placebo, p | IPE 2 g/day vs placebo, p | |
| MARINE | n = 76 | n = 73 | n = 75 | ||||||||
| ICAM-1, ng/mL (n = 75, 70, 72) |
250.0 (85.00) |
253.0 (89.00) |
−0.9 (10.69) |
255.5 (86.00) |
257.5 (102.00) |
−0.4 (12.29) |
247.5 (101.00) |
246.0 (89.50) |
2.6 (13.43) |
−2.5 0.1188 |
−2.3 0.2201 |
| Ox-LDL, U/L (n = 74, 70, 71) |
76.2 (32.30) |
74.5 (39.60) |
−6.9 (26.28) |
71.0 (29.50) |
71.9 (29.30) |
2.7 (24.19) |
76.5 (39.30) |
75.3 (37.20) |
2.5 (22.73) |
−6.6 0.0548 |
−1.4 0.6665 |
| Lp-PLA2, ng/mL (n = 73, 70, 70) [16] |
246.0 (116.00) |
201.0 (100.00) |
−17.1 (24.43) |
235.0 (106.00) |
220.5 (101.00) |
−5.1 (24.14) |
253.0 (126.00) |
256.0 (146.00) |
−2.4 (29.35) |
−13.6 0.0003 |
−5.1 0.1529 |
| IL-6, pg/mL (n = 60, 62, 61) |
2.3 (3.34) |
2.4 (3.32) |
0.3 (93.07) |
3.0 (2.78) |
3.0 (5.39) |
3.4 (76.70) |
2.5 (4.12) |
2.3 (1.85) |
5.3 (79.27) |
11.0 0.3629 |
4.7 0.6654 |
| hsCRP, mg/L (n = 75, 70, 72) |
2.2 (3.10) |
2.2 (2.90) |
−2.5 (81.19) |
2.0 (2.70) |
2.4 (3.20) |
25.1 (96.43) |
1.8 (3.05) |
2.5 (3.95) |
33.3 (80.49) |
−36.0 0.0012 |
−10.1 0.4028 |
| ANCHOR | n = 226 | n = 234 | n = 227 | ||||||||
| ICAM-1, ng/mL (n = 78, 74, 83) |
273.0 (96.00) |
270.0 (110.00) |
0.8 (13.27) |
267.0 (97.00) |
268.5 (89.00) |
0.5 (12.41) |
269.0 (122.00) |
257.0 (131.00) |
3.6 (12.07) |
−2.4 0.1888 |
−2.2 0.1944 |
| Ox-LDL, U/L (n = 78, 75, 84) |
54.0 (14.60) |
51.4 (17.50) |
−4.8 (19.63) |
54.0 (17.80) |
55.8 (22.80) |
2.6 (18.28) |
51.8 (16.80) |
59.7 (18.10) |
11.6 (28.09) |
−13.3 < 0.0001 |
−5.8 0.0946 |
| Lp-PLA2, ng/mL (n = 217, 224, 213) [17] |
180.0 (56.00) |
160.0 (57.00) |
−12.8 (18.52) |
190.0 (55.50) |
183.5 (57.50) |
−1.8 (23.11) |
185.0 (58.00) |
200.0 (71.00) |
6.7 (24.03) |
−19.0 < 0.0001 |
−8.0 < 0.0001 |
| IL-6, pg/mL (n = 78, 74, 83) |
2.7 (2.61) |
2.6 (2.08) |
3.1 (56.47) |
2.4 (2.01) |
2.7 (2.28) |
6.9 (51.85) |
3.2 (3.23) |
2.9 (2.95) |
3.3 (59.37) |
−1.0 0.9031 |
7.0 0.3643 |
| hsCRP, mg/L (n = 217, 227, 219) [17] |
2.2 (2.70) |
2.0 (3.00) |
−2.4 (62.75) |
1.9 (2.90) |
2.5 (3.40) |
10.3 (88.61) |
2.2 (4.00) |
2.6 (4.70) |
17.1 (107.99) |
−22.0 0.0005 |
−6.8 0.2894 |
Only subjects with non-missing baseline and week 12 values are included. Data are presented as median (interquartile range [IQR]) for endpoint values. p values for Lp-PLA2 were adjusted for multiple comparisons
hsCRP high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, ICAM-1 intercellular adhesion molecule-1, IL-6 interleukin-6, Lp-PLA 2 lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2, Ox-LDL oxidized low-density lipoprotein
hsCRP Statin Use Subgroup Analyses
Table 4 and Fig. 2 show that the changes from baseline for IPE 4 g/day and placebo in hsCRP in patients not treated with statins in the MARINE trial were 0.0 % and 31 %, respectively, resulting in a statistically significant placebo-adjusted reduction of 27 % (p = 0.0311). The changes from baseline in hsCRP in patients treated with statins for IPE 4 g/day and placebo were −31 and 43 %, respectively, resulting in a statistically significant placebo-adjusted reduction of 68 % (p = 0.0098). In ANCHOR, the changes from baseline in hsCRP for IPE 4 g/day and placebo in patients treated with atorvastatin were −12 and 31 %, respectively, resulting in a statistically significant placebo-adjusted reduction of 37 % (p = 0.0475). The changes from baseline in hsCRP for IPE 4 g/day and placebo in patients treated with rosuvastatin were −1.2 % and 15.2 %, respectively, resulting in a statistically significant placebo-adjusted reduction of 31 % (p = 0.0217). The changes from baseline in hsCRP for IPE 4 g/day and placebo in patients treated with simvastatin were 0.0 and 13.2 %, respectively, resulting in a statistically non-significant placebo-adjusted reduction of 13.6 % (p = 0.0755). Compared to placebo in ANCHOR, IPE 4 g/day significantly decreased hsCRP levels in patients receiving higher- (29 %, p < 0.05) and medium- (23 %, p < 0.01) but not lower-efficacy statin regimens (+4 %). However, the number of patients receiving IPE 4 g/day in the lower-efficacy statin treatment group was smaller (n = 16) than those in the medium- (n = 132) and higher- (n = 69) efficacy statin treatment groups. IPE 2 g/day did not significantly decrease hsCRP in the subgroups analyzed. Excluding the small numbers of subjects per group with hsCRP levels >10 mg/L did not alter the conclusions on hsCRP lowering.
Table 4.
Median placebo-adjusted percentage change from baseline to study end in high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (mg/L; intent-to-treat population subgroups)
| IPE 4 g/day | IPE 2 g/day | Placebo | Median placebo-adjusted % change from baseline | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline value | End-of-treatment value | Change from baseline, % | Baseline value | End-of-treatment value | Change from baseline, % | Baseline value | End-of-treatment value | Change from baseline, % | IPE 4 g/day vs. placebo, p | IPE 2 g/day vs. placebo, p | |
| MARINE | n = 76 | n = 73 | n = 75 | ||||||||
| Statin use | |||||||||||
| No statin (n = 56, 52, 55) |
2.2 (3.05) |
2.2 (2.55) |
0.0 (92.15) |
2.2 (2.40) |
2.5 (3.15) |
31.7 (81.50) |
1.8 (2.50) |
2.4 (3.60) |
30.8 (86.11) |
−27.4 0.0311 |
−2.7 0.8297 |
| Statin (n = 19, 18, 17) |
1.9 (3.60) |
1.3 (3.80) |
−30.6 (80.13) |
1.5 (3.30) |
1.6 (2.20) |
11.7 (169.12) |
1.8 (3.20) |
3.5 (4.10) |
42.9 (75.00) |
−67.9 0.0098 |
−33.2 0.1707 |
| ANCHOR | n = 226 | n = 234 | n = 227 | ||||||||
| Statin type | |||||||||||
| Atorvastatin (n = 38, 42, 44) |
2.1 (2.70) |
1.5 (3.00) |
−11.7 (100.00) |
1.7 (2.70) |
2.3 (3.50) |
20.1 (80.75) |
1.6 (3.55) |
2.2 (5.35) |
30.8 (117.86) |
−36.7 0.0475 |
−9.3 0.6563 |
| Rosuvastatin (n = 52, 53, 52) |
2.6 (3.05) |
1.9 (3.55) |
−1.2 (68.87) |
1.6 (1.90) |
2.0 (2.30) |
0.0 (90.95) |
2.5 (4.50) |
2.9 (6.35) |
15.2 (112.74) |
−31.4 0.0217 |
−11.0 0.3922 |
| Simvastatin (n = 127, 132, 123) |
2.2 (2.70) |
2.2 (2.80) |
0.0 (61.57) |
2.2 (3.90) |
2.7 (3.50) |
11.0 (88.18) |
2.2 (3.80) |
2.6 (3.80) |
13.2 (93.33) |
−13.6 0.0755 |
−3.8 0.6562 |
| Statin efficacy regimena | |||||||||||
| Lower (n = 16, 15, 14) |
2.1 (2.65) |
2.4 (2.45) |
11.9 (45.47) |
1.5 (2.20) |
1.7 (2.70) |
13.3 (89.74) |
2.4 (2.70) |
2.6 (1.90) |
15.7 (75.56) |
4.0 0.8843 |
10.2 0.6467 |
| Medium (n = 132, 145, 134) |
2.2 (2.95) |
1.8 (3.60) |
−7.7 (63.96) |
2.3 (4.00) |
2.6 (3.40) |
8.7 (76.67) |
2.2 (4.00) |
2.6 (5.30) |
15.3 (90.80) |
−22.8 0.0034 |
−8.3 0.2839 |
| Higher (n = 69, 67, 71) |
2.5 (2.80) |
2.0 (2.70) |
0.0 (78.97) |
1.7 (2.10) |
2.2 (3.10) |
16.7 (99.32) |
2.2 (3.30) |
2.6 (4.40) |
28.6 (124.36) |
−28.6 0.0210 |
−8.3 0.5227 |
Only subjects with non-missing baseline and week 12 values are included. Data are presented as median (interquartile range [IQR]) for endpoint values
aLower-efficacy statin regimens = simvastatin 5–10 mg; medium-efficacy statin regimens = rosuvastatin 5–10 mg, atorvastatin 10–20 mg, simvastatin 20–40 mg, simvastatin 10–20 mg + ezetimibe 5–10 mg; higher-efficacy statin regimens = rosuvastatin 20–40 mg, atorvastatin 40–80 mg, simvastatin 80 mg, simvastatin 40–80 mg + ezetimibe 5–10 mg
Fig. 2.
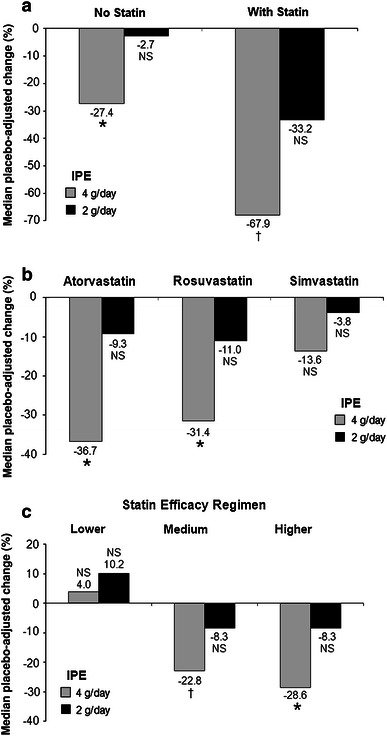
Median placebo-adjusted percentage change from baseline to week 12 in hsCRP levels for statin use subgroups (intent-to-treat population). a MARINE; b and c ANCHOR. IPE icosapent ethyl, Lower-efficacy statin regimens simvastatin 5–10 mg, medium-efficacy statin regimens rosuvastatin 5–10 mg, atorvastatin 10–20 mg, simvastatin 20–40 mg, simvastatin 10–20 mg + ezetimibe 5–10 mg, higher-efficacy statin regimens rosuvastatin 20–40 mg, atorvastatin 40–80 mg, simvastatin 80 mg, simvastatin 40–80 mg + ezetimibe 5–10 mg, NS not significant. *p < 0.05; † p < 0.01 vs. placebo
Discussion
IPE (formerly AMR101) is a high-purity prescription form of EPA ethyl ester approved by the FDA as an adjunct to diet to reduce TG levels in adult patients with severe (≥500 mg/dL) hypertriglyceridemia. MARINE evaluated IPE in patients with very high TG levels (≥500 mg/dL and ≤2000 mg/dL) with and without statin therapy [16] and ANCHOR evaluated IPE in statin-treated patients with residually high TG (≥200 mg/dL and <500 mg/dL) [17]. Both these studies demonstrated that, compared to placebo, IPE lowered TG, non-HDL-C, apo B, VLDL-C, and TC levels without significantly raising LDL-C levels [16, 17].
Compared to placebo in MARINE, IPE 4 g/day substantially decreased hsCRP levels more in the statin-treated patients (68 %) than in patients not receiving statin therapy (27 %) (Table 4). Compared to placebo in ANCHOR, IPE 4 g/day decreased hsCRP levels by 37, 31, and 14 % in patients taking atorvastatin, rosuvastatin, and simvastatin, respectively. In ANCHOR, IPE 4 g/day significantly decreased median placebo-adjusted Ox-LDL levels by 13 % (p < 0.0001). In MARINE and ANCHOR, respectively, IPE 4 g/day significantly decreased median placebo-adjusted Lp-PLA2 by 14 % (p < 0.001) [16] and 19 % (p < 0.0001) [17] and hsCRP levels by 36 % (p < 0.01) and 22 % (p < 0.001) [17]. IPE did not significantly change ICAM-1 or IL-6. Statins are known to decrease hsCRP levels [18, 19], and subjects in both MARINE and ANCHOR who received statin therapy were on stable therapy prior to administration of IPE. Thus, the effects of IPE on inflammatory markers in this study were in addition to effects already achieved with statins. It is of interest that in ANCHOR, IPE decreased hsCRP more in higher-efficacy statin regimens.
Prior reports of EPA and/or DHA effects on LDL oxidation [20, 21] or CRP [22–30] are inconsistent. As is standard for reporting efficacy in placebo-controlled clinical trials, and as per the statistical analyses defined for this study, all measured efficacy parameters including hsCRP and Ox-LDL were in comparison to placebo. Placebo-adjusted comparisons between groups were based upon median values, because TG and the other measured parameters are commonly non-parametric, especially when evaluated in patients with high or very high TG levels. Despite variability inherent in these non-parametric parameters, the data shown in Tables 3 and 4 support that IPE 4 g/day (the dose approved for clinical use) consistently decreased or resulted in no change from baseline in hsCRP or Ox-LDL, and significantly decreased hsCRP relative to the placebo groups. Compared to placebo, IPE 4 g/day consistently decreased hsCRP in patients treated with or without statins, and among different statins and different statin doses. The only exception was seen in patients receiving lower-efficacy statin regimens, for whom IPE 4 g/day resulted in a mild increase in hsCRP, which was not statistically significant and was numerically lower than the increase seen with placebo. Some reports suggest consumption of omega-3 fatty acids has little effect on Lp-PLA2 levels in healthy patients [31, 32]. However, the data in this analysis are consistent with the prior finding that when 4 g per day of a prescription omega-3 fatty acid (containing both EPA and DHA) were added to stable statin therapy in hypertriglyceridemic patients, Lp-PLA2 levels were decreased [33].
Clinically, the degree by which LDL particles bind to and are internalized by LDL receptors may be somewhat dependent upon the LDL particle oxidation. Circulating LDL particles with minimal oxidative modification may continue to be recognized and internalized by body tissue (such as liver) LDL receptors, while extensively oxidized LDL particles may be less able to bind to LDL receptors [34]. Conversely, oxidized LDL particles may undergo preferential uptake by macrophage scavenger receptors, which are not regulated by cellular cholesterol content [34]. In the subendothelial space, the cholesterol-laden macrophages may be transformed into foam cells, which are commonly found within atherosclerotic lesions [34]. The net result is that the decreased recognition of circulatory Ox-LDL by LDL receptors may contribute to increased circulating LDL-C levels, while the increased uptake of Ox-LDL by subendothelial macrophages may promote accumulation and death of foam cells, endothelial toxicity, and promotion of atherogenesis.
Given that other omega-3 fatty acid therapies of EPA and DHA in hypertriglyceridemic patients may (substantially) increase LDL-C levels [35, 36], the lack of LDL-C increases in MARINE and ANCHOR may be explained by the lack of DHA in IPE. It is possible that the decrease in LDL oxidation with IPE (albeit a non-significant reduction in MARINE) observed in this analysis may increase LDL receptor recognition and may play a role in the lack of rise in LDL-C levels in MARINE and perhaps contribute to the decrease in LDL-C levels found in ANCHOR.
The potential clinical significance of the anti-inflammatory effects of IPE may be supported by JELIS (Japan EPA Lipid Intervention Study), wherein administration of 1.8 g/day of >98 % EPA ethyl ester (Mochida Pharmaceuticals, Tokyo, Japan) reduced major coronary events in Japanese hypercholesterolemic patients receiving statin therapy [37] despite only marginal differences in LDL-C, HDL-C, and TG levels between the EPA + statin and statin-alone groups [37, 38]. Possible mechanisms wherein omega-3 fatty acids may reduce CHD include anti-inflammatory effects [15].
Limitations of this analysis include that: (i) all endpoints were exploratory, with the exception of Lp-PLA2, which was a secondary endpoint in both studies; (ii) patients were not selected based upon elevated baseline inflammatory marker levels, which may have limited the ability to detect significant changes in some inflammatory markers (e.g., IL-6 and ICAM-1); and (iii) ICAM-1, Ox-LDL, and IL-6 were measured in a subset of the ANCHOR ITT population and thus may lack statistical power to detect significant changes. Additionally, neither MARINE nor ANCHOR were of a design, or of sufficient size, to assess cardiovascular disease outcomes. To this end, the ongoing REDUCE-IT (Reduction of Cardiovascular Events with EPA – Intervention Trial; NCT01492361) will evaluate whether IPE in combination with statin therapy is superior to statin therapy alone in the reduction of long-term cardiovascular events in approximately 8,000 high-risk patients with mixed dyslipidemia.
Conclusion
This follow-up analysis of MARINE and ANCHOR examined the placebo-adjusted effects of IPE (a high-purity prescription form of EPA ethyl ester approved by the FDA as an adjunct to diet to reduce TG levels in adult patients with severe [≥500 mg/dL] hypertriglyceridemia) on inflammatory markers associated with cardiovascular disease and atherosclerosis in hypertriglyceridemic patients. In addition to the previously reported favorable lipid effects of IPE [16, 17], this analysis showed that IPE 4 g/day significantly decreased Ox-LDL, Lp-PLA2, and hsCRP levels and thus may offer a combination of beneficial lipid and anti-inflammatory effects.
Acknowledgments
MARINE and ANCHOR were sponsored and designed by Amarin Pharma Inc., Bedminster, NJ, USA, and conducted by Medpace, Inc., Cincinnati, OH, USA, with funding from Amarin Pharma Inc. Editorial assistance was provided by Peloton Advantage, LLC, Parsippany, NJ, and funded by Amarin Pharma Inc. Dr Harold Bays (Principal Investigator) wrote the first draft of this report, with subsequent drafts revised and edited by the other authors, who vouch for the accuracy and completeness of the data and approved the final version for submission.
Dr Bays has received research grants from Amarin Pharma, Inc., Alere, Amgen, Ardea, Arena, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, California Raisin Board, Cargill, Eisai, Esperion, Essentialis, Forest, Gilead, Given, GlaxoSmithKline, High Point Pharmaceuticals, Hoffmann-LaRoche, Home Access, Johnson and Johnson, Merck, Micropharma, Novartis, NovoNordisk, Omthera, Orexigen, Pfizer Inc, Shionogi, Stratum Nutrition, Takeda, TIMI, Traanstech Pharma, Trygg, TWI Bio, Vivus, and Xoma. He has received honoraria as a consultant and/or speaker for Amarin Pharma, Inc., Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Catabasis, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Merck & Co., Pfizer Inc, and Vivus.
Dr Ballantyne has received research grants from Abbott Laboratories, Amarin Pharma, Inc., AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, diaDexus, GlaxoSmithKline, Kowa Pharmaceuticals America, Inc., Merck & Co., Novartis, Roche, Sanofi-Synthelabo, Takeda, the National Institutes of Health, the American Diabetes Association, and the American Heart Association; speakers bureau fees from Abbott, GlaxoSmithKline, and Merck & Co.; honoraria from Abbott, Amarin Pharma, Inc., AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck & Co., Sanofi-Synthelabo, and Takeda; and has provided consultancy services for Abbott, Adnexus, Amylin, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Esperion, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Idera Pharma, Kowa, Novartis, Omthera, Resverlogix, Roche, Sanofi-Synthelabo, and Takeda. Drs Braeckman, Stirtan, and Soni are employees of Amarin Pharma, Inc., for which Drs Soni, Braeckman, and Stirtan are stock shareholders.
References
- 1.Libby P, Okamoto Y, Rocha VZ, et al. Inflammation in atherosclerosis: transition from theory to practice. Circ J. 2010;74(2):213–220. doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-09-0706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Davidson MH, Ballantyne CM, Jacobson TA, et al. Clinical utility of inflammatory markers and advanced lipoprotein testing: advice from an expert panel of lipid specialists. J Clin Lipidol. 2011;5:338–367. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2011.07.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hwang SJ, Ballantyne CM, Sharrett AR, et al. Circulating adhesion molecules VCAM-1, ICAM-1, and E-selectin in carotid atherosclerosis and incident coronary heart disease cases: the Atherosclerosis Risk In Communities (ARIC) study. Circulation. 1997;96(12):4219–4225. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.96.12.4219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lawson C, Wolf S. ICAM-1 signaling in endothelial cells. Pharmacol Rep. 2009;61(1):22–32. doi: 10.1016/s1734-1140(09)70004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Levitan I, Volkov S, Subbaiah PV. Oxidized LDL: diversity, patterns of recognition, and pathophysiology. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2010;13(1):39–75. doi: 10.1089/ars.2009.2733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Meisinger C, Baumert J, Khuseyinova N, et al. Plasma oxidized low-density lipoprotein, a strong predictor for acute coronary heart disease events in apparently healthy, middle-aged men from the general population. Circulation. 2005;112(5):651–657. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.529297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Toth PP, McCullough PA, Wegner MS, et al. Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2: role in atherosclerosis and utility as a cardiovascular biomarker. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2010;8(3):425–438. doi: 10.1586/erc.10.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Corson MA, Jones PH, Davidson MH. Review of the evidence for the clinical utility of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 as a cardiovascular risk marker. Am J Cardiol. 2008;101(12A):41F–50F. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2008.04.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Schuett H, Luchtefeld M, Grothusen C, et al. How much is too much? Interleukin-6 and its signalling in atherosclerosis. Thromb Haemost. 2009;102(2):215–222. doi: 10.1160/TH09-05-0297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Nystrom T. C-reactive protein: a marker or a player? Clin Sci (Lond) 2007;113(2):79–81. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 11.Bays HE. Adiposopathy is “sick fat” a cardiovascular disease? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;57(25):2461–2473. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.02.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ballantyne CM, Hoogeveen RC, Bang H, et al. Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, and risk for incident coronary heart disease in middle-aged men and women in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Circulation. 2004;109(7):837–842. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000116763.91992.F1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ballantyne CM, Hoogeveen RC, Bang H, et al. Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, and risk for incident ischemic stroke in middle-aged men and women in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Arch Intern Med. 2005;165(21):2479–2484. doi: 10.1001/archinte.165.21.2479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bays HE. Safety considerations with omega-3 fatty acid therapy. Am J Cardiol. 2007;99(6A):35C–43C. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2006.11.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bays H. Fish oils in the treatment of dyslipidemia and cardiovascular disease. In: Kwiterovich PO, editor. The Johns Hopkins textbook of dyslipidemia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wolters Kluwer; 2010. pp. 245–257. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bays HE, Ballantyne CM, Kastelein JJ, et al. Eicosapentaenoic acid ethyl ester (AMR101) therapy in patients with very high triglyceride levels (from the Multi-center, plAcebo-controlled, Randomized, double-blINd, 12-week study with an open-label Extension [MARINE] trial) Am J Cardiol. 2011;108(5):682–690. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2011.04.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ballantyne CM, Bays HE, Kastelein JJ, et al. A phase 3, multicenter, placebo-controlled, randomized, double-blind, 12-week study to evaluate the effect of two doses of AMR101 on fasting serum triglycerides and other lipid parameters in statin-treated patients with persistent high triglycerides (≥200 and <500 mg/dL): the ANCHOR study. Am J Cardiol. 2012;110(7):984–992. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2012.05.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ridker PM, Rifai N, Clearfield M, et al. Measurement of C-reactive protein for the targeting of statin therapy in the primary prevention of acute coronary events. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(26):1959–1965. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200106283442601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ridker PM, Danielson E, Fonseca FA, et al. Rosuvastatin to prevent vascular events in men and women with elevated C-reactive protein. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(21):2195–2207. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0807646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Garrido-Sanchez L, Garcia-Fuentes E, Rojo-Martinez G, et al. Inverse relation between levels of anti-oxidized-LDL antibodies and eicosapentanoic acid (EPA) Br J Nutr. 2008;100(3):585–589. doi: 10.1017/S0007114508921723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mesa MD, Buckley R, Minihane AM, et al. Effects of oils rich in eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids on the oxidizability and thrombogenicity of low-density lipoprotein. Atherosclerosis. 2004;175(2):333–343. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2004.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Watanabe E, Sobue Y, Sano K, et al. Eicosapentaenoic acid for the prevention of recurrent atrial fibrillation. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2011;16(4):373–378. doi: 10.1111/j.1542-474X.2011.00465.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Mori TA, Woodman RJ, Burke V, et al. Effect of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid on oxidative stress and inflammatory markers in treated-hypertensive type 2 diabetic subjects. Free Radic Biol Med. 2003;35(7):772–781. doi: 10.1016/S0891-5849(03)00407-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Satoh N, Shimatsu A, Kotani K, et al. Highly purified eicosapentaenoic acid reduces cardio-ankle vascular index in association with decreased serum amyloid A-LDL in metabolic syndrome. Hypertens Res. 2009;32(11):1004–1008. doi: 10.1038/hr.2009.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Satoh N, Shimatsu A, Kotani K, et al. Purified eicosapentaenoic acid reduces small dense LDL, remnant lipoprotein particles, and C-reactive protein in metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Care. 2007;30(1):144–146. doi: 10.2337/dc06-1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kelley DS, Siegel D, Fedor DM, et al. DHA supplementation decreases serum C-reactive protein and other markers of inflammation in hypertriglyceridemic men. J Nutr. 2009;139(3):495–501. doi: 10.3945/jn.108.100354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Micallef MA, Munro IA, Garg ML. An inverse relationship between plasma n-3 fatty acids and C-reactive protein in healthy individuals. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2009;63(9):1154–1156. doi: 10.1038/ejcn.2009.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bloomer RJ, Larson DE, Fisher-Wellman KH, et al. Effect of eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acid on resting and exercise-induced inflammatory and oxidative stress biomarkers: a randomized, placebo controlled, cross-over study. Lipids Health Dis. 2009;8:36. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-8-36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chan DC, Watts GF, Barrett PH, et al. Effect of atorvastatin and fish oil on plasma high-sensitivity C-reactive protein concentrations in individuals with visceral obesity. Clin Chem. 2002;48(6 Pt 1):877–883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Skulas-Ray AC, Kris-Etherton PM, Harris WS, et al. Dose-response effects of omega-3 fatty acids on triglycerides, inflammation, and endothelial function in healthy persons with moderate hypertriglyceridemia. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011;93(2):243–252. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.110.003871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Pedersen MW, Koenig W, Christensen JH, et al. The effect of marine n-3 fatty acids in different doses on plasma concentrations of Lp-PLA2 in healthy adults. Eur J Nutr. 2009;48(1):1–5. doi: 10.1007/s00394-008-0758-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Nelson TL, Hokanson JE, Hickey MS. Omega-3 fatty acids and lipoprotein associated phospholipase A(2) in healthy older adult males and females. Eur J Nutr. 2011;50(3):185–193. doi: 10.1007/s00394-010-0126-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Davidson MH, Maki KC, Bays H, et al. Effects of prescription omega-3 ethyl esters on lipoprotein particle concentrations, apolipoproteins AI and CIII, and lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 mass in statin-treated subjects with hypertriglyceridemia. J Clin Lipidol. 2009;3(5):332–340. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2009.08.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Glass CK, Witztum JL. Atherosclerosis: the road ahead. Cell. 2001;104(4):503–516. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00238-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Bays HE, Tighe AP, Sadovsky R, et al. Prescription omega-3 fatty acids and their lipid effects: physiologic mechanisms of action and clinical implications. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2008;6(3):391–409. doi: 10.1586/14779072.6.3.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Bays H. Rationale for prescription omega-3-acid ethyl ester therapy for hypertriglyceridemia: a primer for clinicians. Drugs Today (Barc) 2008;44(3):205–246. doi: 10.1358/dot.2008.44.3.1166387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Yokoyama M, Origasa H, Matsuzaki M, et al. Effects of eicosapentaenoic acid on major coronary events in hypercholesterolaemic patients (JELIS): a randomised open-label, blinded endpoint analysis. Lancet. 2007;369(9567):1090–1098. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Itakura H, Yokoyama M, Matsuzaki M, et al. Relationships between plasma fatty acid composition and coronary artery disease. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2011;18(2):99–107. doi: 10.5551/jat.5876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


