Abstract
Bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have the potential to differentiate into a number of phenotypes, including adipocytes. Adipogenic differentiation has traditionally been performed in monolayer culture, and, while the expression of a fat-cell phenotype can be achieved, this culture method is labor and material intensive and results in only small numbers of fragile adherent cells, which are not very useful for further applications. Aggregate culture is a cell-culture technique in which cells are induced to form three-dimensional aggregates; this method has previously been used successfully, among others, to induce and study chondrogenic differentiation of MSCs. We have previously published an adaptation of the chondrogenic aggregate culture method to a 96-well plate format. Based on the success of this method, we have used the same format for the preparation of three-dimensional adipogenic cultures. The MSCs differentiate rapidly, the aggregates can be handled and processed for histologic and biochemical assays with ease, and the format offers significant savings in supplies and labor. As a differentiation assay, this method can distinguish between degrees of senescence and appears suitable for testing medium or drug formulations in a high-volume, high-throughput fashion.
1. Introduction
Much of the research on adult mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) has been done on bone-marrow-derived populations. First described by Owen and Friedenstein [1], and later more fully characterized by other groups, these cells possess, to some degree, and for a number of population doublings, the defining properties of stem cells, that is, the ability to self-renew and the potential to differentiate along one or more lineages under appropriate culture conditions [1–5]. The chondrogenic, osteogenic, and adipogenic lineages are well documented, but there are likely others [6–10]. The emerging and potentially useful properties of MSCs include their paracrine effects, which may augment the repair of damaged tissues, and their immunosuppressive abilities [11, 12]. With respect to the adipogenic lineage specifically, Mackay et al. have shown that human MSC-(hMSC-) derived adipocytes, express mRNA encoding for adipogenic transcription factors (PPARγ2, C/EBPα, and SREBP1), adipokines (adipsin, leptin, APM1, and angiotensinogen), and lipid-metabolizing agents (aP2 and LPL) by day 12 of differentiation and are thus highly analogous to subcutaneous adipocytes at this time point [13].
For most of the clinical applications envisioned, a very large number of MSCs will be required [14, 15]. Furthermore, large-scale commercialization of MSCs, where cells from single donors are expanded into thousands of individual doses for use in clinical applications, is emerging. Unfortunately, MSC numbers and differentiation potential, decrease with donor age, and their stem-cell properties are rapidly lost in in vitro culture; for example, MSCs senesce and cease proliferating in culture after a limited number of population doublings [16–18]. Even before terminal senescence, the various differentiation potentials are progressively lost [19–21]. Given that these cell properties drift over time, screening populations of MSCs for “stemness” could be an important quality control (QC) consideration, and simple high-throughput assays would be important tools for this screening [22].
Aggregate culture is a cell-culture technique in which cells are induced to self-assemble into three-dimensional tissue-like structures. It is analogous to micromass cultures and has been used successfully to induce and study chondrogenic differentiation of MSCs [23]. We recently adapted the chondrogenic aggregate culture method to a high-throughput 96-well plate format [24–29]. In this paper, we document that adipogenic differentiation can also be achieved in aggregate culture, in the same high-throughput microplate format. Thus, two differentiation potentials can now be verified simultaneously as a part of a potential stem cell QC protocol. Although differentiation of the MSCs still takes a few weeks, the labor and material savings due to the microplate format are considerable. An additional advantage is that aggregates are much less fragile than adipogenic monolayer cultures. They can be picked up and manipulated individually, which simplifies, for example, histologic processing and other assays. Longer-term, this simple, reproducible in vitro differentiation model can also be useful for drug screening or toxicology applications.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Cell culture-media and additives, specifically Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium with 1 g/L glucose (DMEM-LG) or with 4.5 g/L glucose (DMEM-HG), were from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA, USA). Fetal bovine serum was from a lot selected as described previously (Sigma Chemical Corporation, St. Louis, MO, USA). Other serum was obtained from Hyclone (Logan, UT, USA). Percoll, dexamethasone, indomethacin, insulin and methyl-isobutyl xanthine (IBMX) were all from Sigma, while ITS+ Premix (6.25 μg/mL insulin, 6.25 μg/mL transferrin, 6.25 ng/mL selenious acid, 1.25 mg/mL serum albumin, and 5.35 μg/mL linoleic acid) was from BD Biosciences (Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). Ascorbate-2-phosphate was from WAKO (Richmond, VA, USA). Other cell-culture additives were from Invitrogen. Polypropylene 96-well microplates and lids were from Phenix (Hayward, CA, USA), while all other cell-culture plasticware was from Becton-Dickinson (Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). Human recombinant transforming growth factor beta-1 (TGFβ-1) was from Peprotech (Rocky Hill, NJ, USA), while human recombinant basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF-basic) was donated by the Biological Resources Branch of the National Cancer Institute. Other reagents, unless specifically noted, were from Sigma.
2.2. Cells and Cell Culture
2.2.1. Culture Media
MSC expansion medium was 10% FBS in DMEM-LG, either supplemented or not supplemented with 10 ng/mL FGF-2 [9, 30] (note that as in our previous studies, FGF-2 is used only in the expansion medium, not in any of the differentiation media) [30]. The adipogenic induction medium was DMEM-HG with 10% FBS, 1 μM dexamethasone, 100 μM indomethacin, 0.5 mM methyl isobutyl-xanthine (IBMX), 1.745 μM insulin, and the additional supplements listed below. Adipogenic maintenance medium was DMEM-HG with 10% FBS, and 1.745 μM insulin, and the additional supplements. The chondrogenic medium was a defined medium consisting of DMEM-HG supplemented with 1% ITS+ Premix, 37.5 μg/mL ascorbate-2-phosphate, 10−7 M dexamethasone, and 10 ng/mL TGFβ-1. Additional supplements such as L-glutamine, antibiotic antimycotic (10,000 units/mL penicillin G sodium, 10 mg/mL streptomycin sulfate, and 25 μg/mL amphotericin B in 0.85% saline), nonessential amino acids, and sodium pyruvate were added to all media at 1%.
2.2.2. Isolation and Expansion
Human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) were derived from bone-marrow aspirates obtained from 11 healthy volunteer donors at the Hematopoietic Stem Cell Core Facility of the Comprehensive Cancer Center at Case Western Reserve University. Informed consent was obtained, and an institutional review board-approved aspiration procedure was used. hMSCs were isolated as described by Haynesworth et al. [6]. Briefly, the bone-marrow samples were washed with DMEM-LG supplemented with 10% FBS from a selected lot [9]. The marrow sample was centrifuged at 500 ×g on a preformed Percoll density gradient (1.073 g/mL) to isolate the mononucleated cells. These cells were seeded at a density of 1.8 × 105 cells/cm2 in a serum-supplemented medium in 10 cm diameter plates. Nonadherent cells were removed after four days by changing the medium. At this point, and for the remainder of the expansion phase, the medium was additionally supplemented with 10 ng/mL rhFGF-2, as described previously [30]. This medium was replaced twice per week thereafter. The primary cultures were subcultured after approximately two weeks and reseeded at 5 × 103 cells/cm2 in T-175 flasks. The cells were then used at the end of the first passage. To model replicative ageing and senescence, in some cases, the cells were serially passaged and then used at the end of the third or the ninth passage. In other cases, the cells were expanded to the end of the ninth passage without FGF supplementation. All cell cultures were done at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere of 95% air and 5% CO2. Not all preparation were used for all experiments.
2.2.3. Differentiation
hMSCs were induced to differentiate into adipocytes using an adaptation of the media conditions described by Pittenger et al. [3], as modified by Mackay et al. [13]. The culture-expanded hMSCs were used at the end of the first passage, at approximately 80% confluence to prevent contact inhibition and spontaneous differentiation [31]. The MSCs were harvested by trypsinization as described previously: after a rinse with sterile Tyrode's salt solution, 0.25% Trypsin EDTA was added and the cultures returned to the incubator for 5 to 10 minutes [28]. Trypsin was then blocked using bovine calf serum, and the detached cells were centrifuged for 5 minutes at 300 ×g. The supernatant was discarded and the cells were resuspended in one of four medium formulations (I) chondrogenic medium, (II) chondrogenic medium without TGF-β1, (III) expansion medium, or (IV) adipogenic induction medium for the first few sets of experiments. For all subsequent work, only adipocyte induction medium was used.
The cells were counted using a hemacytometer and the suspension volume adjusted to a final cell density of 1.25 × 106 cells/mL. The cell suspension was mixed gently by pipetting, and then 200 μL aliquots (2.5 × 105 cells) were dispensed into the wells of an autoclave-sterilized 96-well, V Bottom, 300 μL polypropylene microplate using a repeater pipette (Eppendorf) with a large orifice tip (Fisher Scientific) to allow smooth delivery of the aliquots into the wells. These were the same plates that we had previously identified as optimal for our microplate chondrogenesis assay [28]. The plate is centrifuged for 5 minutes at 500 ×g and incubated at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere of 95% air and 5% CO2.
Twenty-four hours after seeding, any adherent aggregates were released from the bottom of the wells by aspirating and releasing 100 μL of medium back into the wells using an 8-channel pipette. The medium was changed to adipogenic induction medium on day 2 and every 2-3 days thereafter. From day 12 on adipocyte maintenance medium was used. Given the small volume of medium in each well and the number of cells in each aggregate, adherence to the medium change regimen is important.
2.3. Assays
2.3.1. Histology
For the initial aggregation medium formulation experiments, six aggregates from each group were retrieved and formalin-fixed at 1, 2, and 3 weeks after the induction of differentiation. The fixed aggregates were then sequentially infiltrated with 15 and 30% solutions of sucrose in water for 48 hours, embedded in OCT and then snap-frozen in liquid N2. Seven μm thick frozen sections were then prepared using a Leica CM1850 cryomicrotome (Leica Microsystems, Bannockburn, IL, USA). The sections were then stained for 8 minutes in Oil-Red O [32]. The Oil-Red O working solution was prepared fresh by diluting a saturated stock solution in isopropanol to 60% with water before each use [32]. The stain solution was 0.2 μm filtered immediately prior to use. Mayer's haematoxylin was used as a counterstain. Sections were then mounted in glycerin jelly and documented at 40x using a Leica DM LB2 upright microscope fitted with a SPOT-RT digital camera [33]. Individual images were then combined into a mosaic of the whole section as described previously [34].
2.3.2. Morphometry
At least ten random 40x digital images were analyzed for each aggregate in each treatment group and time point using the ImageJ software package [35]. Briefly, the total area of aggregate covered in the frame was outlined and measured. The image was then color-thresholded to segment the Oil-Red-stained components [36]. The resulting image was then converted first to 8-bit monochrome and then made binary. Particles were counted with a 50-pixel cutoff to reduce noise. The data are presented as percent area of the aggregate sections stained by Oil-Red.
2.3.3. DNA Assays
Cell numbers were determined indirectly by measuring the DNA content of the aggregates. Six aggregates were digested individually with papain as described previously [37]. The digested extract was combined with 0.1 N NaOH, incubated at room temperature for 20 minutes, and then neutralized with 0.1 N HCl in 5 M NaCl and 100 mM NaH2PO4. One hundred microliter of the neutralized mixture was combined with 100 μL of 0.7 μg/mL Hoechst 33258 dye in water. Fluorescence was read using a Tecan Genios Pro plate reader (λ ex = 360 nm, λ em = 465 nm; Tecan US, Durham NC, USA) and compared to that of a certified calf thymus DNA standard (Amersham, Piscataway, NJ, USA).
2.3.4. GPDH Assays
Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GPDH; EC 1.1.1.8) activity was measured on some aggregates that were harvested at days 0, 1, 7, 14, 21, and 28, using the TaKaRa kit (Clontech, MK426, Mountain View, CA, USA), following the manufacturer's instructions. GPDH catalyzes the reversible reaction between dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glycerol 3-phosphate with NAD as coenzyme; its activity increases during the differentiation of progenitor cells into adipocytes [38]. Briefly, 6 replicate aggregates were washed in PBS and lysed in 500 μL of the lysis buffer solution provided with the kit. A small pestle was used to help break up the aggregate as sonication did not appear to work well. Lysates were stored frozen at −20°C until processed [38]. The lysates were serially diluted with the bis-mercaptoethanol containing dilution buffer. 25 μL of the diluted samples were mixed with 100 μL of substrate at 30°C. The absorbance at 340 nm was then measured every minute for 15 minutes using a Tecan Genios Pro plate reader (Tecan Männedorf, Switzerland) and the supplied UV-transparent 96-well plate. ΔOD340 per minute was obtained from dilutions in which the change in OD proceeded linearly, using Sigmaplot software (Systat, San Jose, CA, USA). Activity was computed as prescribed in the kit protocol. Six replicate aggregates from the same donor were analyzed for DNA content, and these values were used for normalization. Confidence intervals for the ratio were estimated using Fieller's theorem.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Results
3.1.1. Aggregate Formation
Regardless of the initial culture medium used (see Section 2.2.3), hMSCs in all four treatment groups and from all donors formed aggregates within the first 24 hours. Similarly, the timing of aggregate formation was identical in P2 and P10 MSCs in these experiments, although this has not always been the case in our hands. However, in P10 cells, this was only the case in MSCs which had been expanded in FGF-2 supplemented medium; those expanded without FGF supplementation failed to form aggregates and thus were not evaluated further. Aside from those cells, there were no gross differences between treatment groups in the aspect of the aggregates. The aggregates were cohesive in that they could be released from the bottoms of the wells by a jet of medium, as described above, without dissociating. Aggregates remained cohesive through 4 weeks although they did compact over time. From the beginning of week 2 and beyond, most aggregates became sufficiently buoyant that they floated to the top of the culture medium in the microplate wells.
3.1.2. Adipogenic Differentiation
At 1 week, there were differences between the amount of lipid produced by cells initially aggregated in the 4 medium formulations (Figure 1(a)). Compared to adipogenic medium, the differences in aggregate formation in expansion medium or chondrogenic medium without TGF-β1 were not significant. By contrast, significantly less (P < 0.05) of the aggregate cross-sectional area was Oil-Red O positive in the aggregates formed in complete chondrogenic medium for the first 24 hours (group I). (One-way ANOVA, Dunn's post hoc pairwise comparisons).
Figure 1.
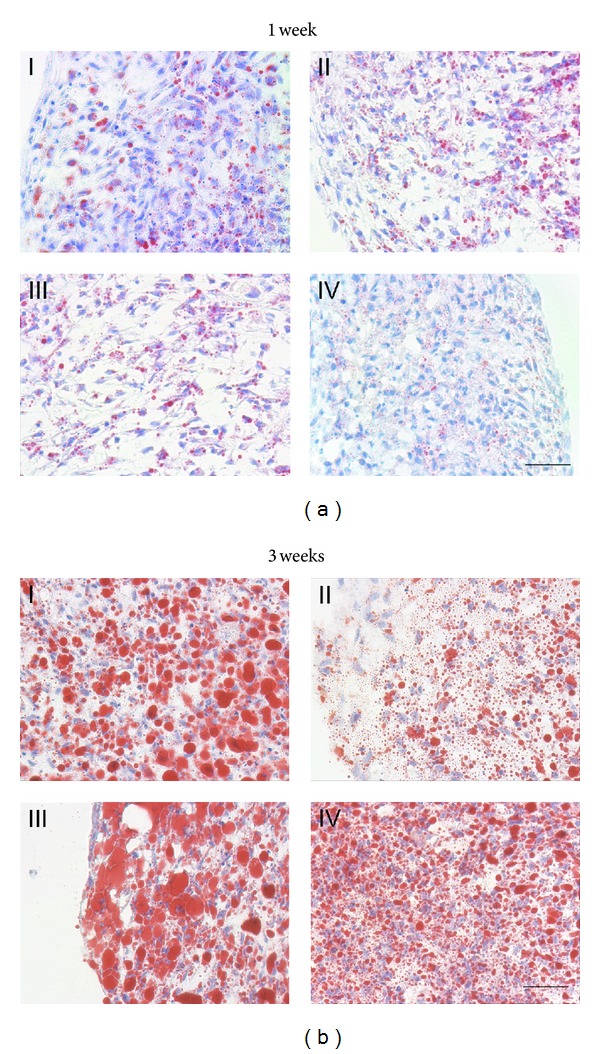
Effect of initial pelleting medium on MSC adipogenesis. Medium compositions were described in Section 2.2.3. (a): At one week (I) 3.3 ± 0.4%, (II) 7.6 ± 0.3%, (III) 6.6 ± 0.8%, and (IV) 5.8 ± 0.8% of the total cross-sectional area were Oil-red O positive (fraction of total aggregate area measured on at least 15 40x fields per condition per donor, N = 3). (b): At 3 weeks overall: (I) 50.2 ± 2.3%, (II) 28.5 ± 3%, (III) 58.6 ± 2.4%, and (IV) 47 ± 3.3% of the total cross-sectional area were Oil-red O positive. (fraction of total aggregate area measured on at least 10 40x fields per condition per donor, N = 3). Oil-Red O with hematoxylin counterstain, scale bars = 50 μm.
By three weeks in culture, the fraction of Oil-Red O positive area in group II aggregates was significantly (P < 0.01) less than that in the other 3 groups, which were statistically not significantly different from each other.
Having established that the cells would form aggregates in adipogenic induction medium, the remainder of the experiments were done using aggregates that were aggregated directly in this medium (Formulation IV). In P2 MSCs, after as little as 1 week of exposure to the adipogenic induction medium, the vast majority of the cells in the aggregates contained several small Oil-Red O-stained lipid droplets (Figures 1 and 2). There was a gradient in droplet size and number, with more numerous and larger drops at the periphery. Overall, about 6% of the cross-sectional area of the aggregates was Oil-Red positive at 1 week.
Figure 2.
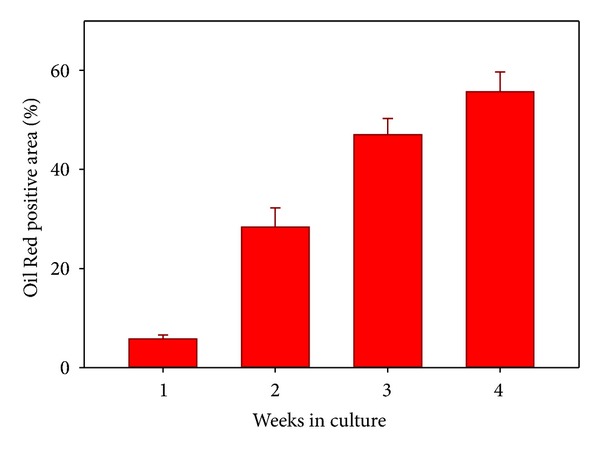
Percent of the cross-sectional area of aggregates which is stained with Oil-Red positive (donors N = 3, mean ± SD, and overall 30–60 40x fields were measured for each group). All aggregates were formed in adipogenic medium.
By two weeks, lipid droplets had increased in size and number. The size gradient from the periphery to the center of the aggregates was more apparent. At this point, about 28% of the aggregate cross section was stained with Oil-Red (Figure 2, histology not shown).
At three weeks, the trend towards larger droplets continued, and the lipid-positive component of the cross-sectional area had increased further to 47%. The trend towards larger and more abundant fat droplets continued at 4 weeks, when 56% of the cross-sectional area of the aggregates was Oil-Red positive (Figures 1(b) and 2).
In all cases, cell numbers, as reflected by DNA content decreased in a time-dependent fashion during the course of the assay (0.95 ± 0.07, 0.71 ± 0.12, 0.45 ± 0.16, and 0.22 ± 0.08 μgDNA, mean ± SD, per aggregate at weeks 1, 2, 3, and 4, resp.).
GPDH activity was below the detection limit of the assay at days 0 and 1. Activity was 11.3 mU/μg DNA by week 1 (90% CI 10.4–12.5), 35.4 mU/μg DNA by week 2 (90% CI 32–39.5), and at week 3 reached 68 mU/μg DNA (90% CI 52.2–87.9).
In MSCs expanded in FGF-2-containing medium and used to form aggregates at P10 (Figure 3), only 50–75% of the cells became Oil-Red positive and both the number and size of the lipid droplets were decreased. Further, the aggregates contracted much less than those from earlier passage cells. hMSCs expanded to P10 in the absence of FGF-2 treatment showed signs of senescence (large surface area, markedly increased doubling time, and prominent stress fibers) and failed to form aggregates at all in adipogenic induction medium.
Figure 3.
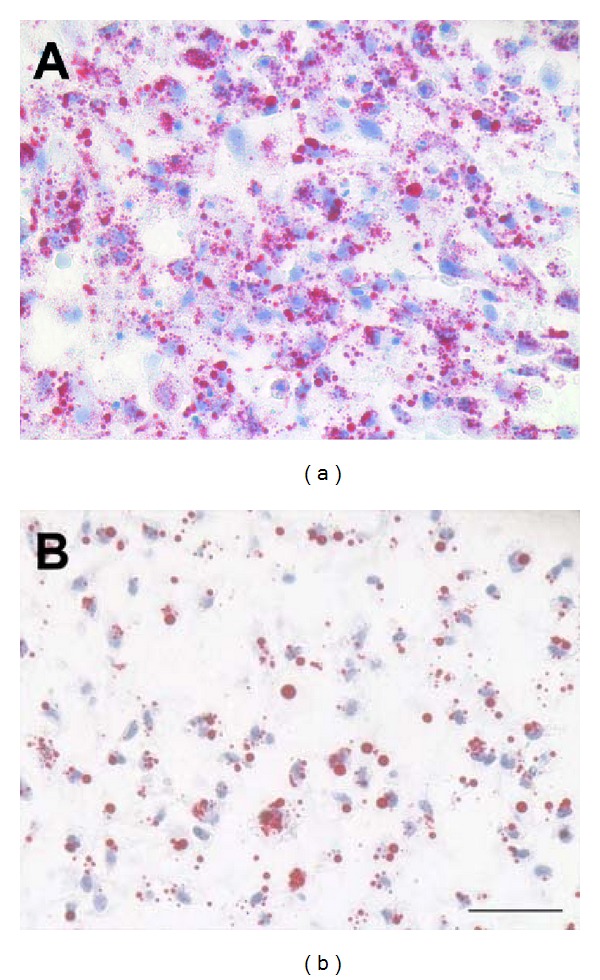
Adipogenic differentiation of hMSCs in aggregate culture at two weeks, illustrating the loss of adipogenic differentiation potential with serial expansion in culture. The cells in both Figures are from the same donor preparation and were expanded using the identical medium formulation. (a): 2nd passage cells; (b): 10th passage cells. On average, passage 10 aggregates had slightly less than half the Oil Red positive area of passage 2 aggregates (P < 0.01, 2 donor preparations, 100 40x fields were measured) frozen section, Oil red-O with haematoxylin counterstain. Original magnification: 40x, scale bar: 50 μm.
3.2. Discussion
Stem cells are generally defined as having the ability to both self-renew through mitosis and to, under appropriate conditions, differentiate and acquire specialized phenotypes [39]. Stem cell-based tissue engineering and regenerative medicine applications or drug-type cell preparations as used for, for example, graft-versus-host disease, require very large number of cells, which makes extensive and usually rapid in vitro subcultivation a requirement. There is, thus, an incentive to maximize the number of cells that can be obtained from a single marrow preparation. Although hMSCs can be expanded to a significant (but nonetheless finite) number of population doublings in culture and can differentiate into a number of mesenchymal phenotypes, both proliferative and differentiation capacities are highly variable [40]. They depend in part on identifiable factors such as the age or health of the donor, the frequency of MSCs in the marrow, the marrow-harvest protocol, and the culture conditions used, but also on yet unexplained donor-to-donor differences [8, 20, 41–44]. In in vitro culture, at least, as it is currently practiced, the cells progressively fail in both of the defining “stemness” criteria as they drift and senesce [18, 20, 45, 46]. With respect to proliferation, while there are sporadic reports of 30–40 population doublings (109–1012: 1 expansion), preparations grown under comparable conditions frequently cease proliferating after only 4-5 population doublings (50 : 1 expansion) [8, 17, 20, 42]. Well before they lose the ability to proliferate, mesenchymal stem cells also progressively lose the ability to differentiate. The loss of differentiation potentials appears to be a function of passage number, or more importantly, population doubling number [30]. Chondrogenic potential is lost early; the ability to differentiate into adipocytes [20] is more durable, and osteogenic potential is maintained the longest, suggesting this may be the default lineage for bone-marrow-derived MSCs [8, 17, 18, 20, 45, 46]. Given these findings, it does not appear unreasonable to assume that other emerging, and potentially beneficial, properties of MSCs are also lost during extended in vitro expansion.
To warrant describing a culture-expanded cell population as mesenchymal stem cells, QC becomes mandatory. Considerations should include documenting the cells' actual differentiation potential at the passage at which they are used in addition to their proliferative potential or cell surface marker expression. Screening techniques based on proxy assays, such as flow cytometry or PCR, may be rapid but may not always be accurate predictors of actual differentiation ability in, for example, tissue engineering applications. Conventional differentiation assays remain cumbersome; we have therefore been adapting MSC differentiation protocols into high-throughput screening assays.
3.2.1. Screening Assays
Adipogenic differentiation of human MSCs was first described by Pittenger in 1999 [3]. Adipocyte culture is traditionally done in monolayer because of buoyancy even as the so-called ceiling culture or modifications thereof [47, 48]. The latter is a relatively complex and time-, space-, and resource-intensive culture method but works well for MSCs [13]. It results in only small numbers of adherent cells per culture surface area, and these are quite fragile and thus not very useful for further applications.
Aggregate culture is a simple cell-culture technique in which cells are induced to form three-dimensional tissue structures. It is analogous to micromass cultures and has been used successfully to induce and study chondrogenic differentiation of MSCs [23]. As originally described, individual 15ml conical tubes were used for each aggregate, which was quite cumbersome; we have previously published a high-throughput 96-well plate modification of the chondrogenic aggregate culture method [28, 29]. In this study, we used the same 96-well format as for chondrogenic cultures for the preparation of three-dimensional adipogenic cultures, eliminating the need for fastidious monolayer culture methods. The aggregates are nonadherent and can be handled easily. Histological, biochemical, and enzymatic assays can easily be performed, as described previously.
We had expected that it might be necessary to induce aggregate formation pharmacologically, hence the trials using chondrogenic medium with and without TGF-β1 for 24 hours. Somewhat surprisingly, however, the cells formed cohesive aggregates regardless of the initial culture conditions tested. This demonstrates that, on the one hand, three-dimensional aggregation and adipogenic differentiation can be triggered in adipogenic medium directly. On the other hand, for QC purposes, a dual lineage screen can be set up easily as the aggregates in a batch of 96-well plates could be set up from the same cell suspension in chondrogenic medium and then switched to adipogenic medium the next day, thereby eliminating several steps in the setup protocol. Admittedly, there was less lipid deposited in the cells which were initially formed in complete chondrogenic medium, at 1 week (Figure 1(a)), but this difference disappeared by 3 (Figure 1(b)) and 4 weeks (not shown). The cells aggregated in chondrogenic medium, but without TGF-β, fared the worst in the long term (Figure 1(b)).
We, and others, have shown previously that human MSCs can be expanded for a far greater number of population doublings in the presence of FGF-2 than without [30]. The effects of FGF-2 supplementation have not only been documented with respect to the retention of proliferative capacity, but also to differentiation capacity [14, 30, 49]. At a basic level, histologic and biochemical analysis can be used in this differentiation assay to easily discriminate between vigorous adipogenic differentiation at P2 and P4, reduced differentiation in FGF-2-treated P10 cells, and nonexistent differentiation in MSCs expanded to P10 without FGF supplementation using histology.
3.2.2. Other Potential Applications
The goal in developing this method was to establish a rapid screening assay for adipogenic potential. Rapid, in the context of this assay, refers to the time commitment required to set up, maintain, and optionally manipulate the cultures. A reasonable number of replicate aggregate cultures, for example, 5–10, can be established by diverting 1-2 × 106 cells. However, a typical MSC preparation can yield 100–250 × 106 cells at the end of passage 1 and 10 times that at the end of passage 2, so it is possible and practical to establish hundreds to thousands of these small-scale adipogenic assays simultaneously from a single marrow aspirate. As, for example, Mackay et al. have shown that human MSC- (hMSC-) derived adipocytes express transcription factors, adipokines, and lipid-metabolizing agents typical of adipose tissue, this approach then has implications for drug, growth factor, and toxicology assays [13]. The medium composition experiments shown here exemplify the type of experiment that can be done easily and in a very compact format. Compared to culture methods like ceiling cultures, the culture medium is readily accessible. Time savings increase with the number of parallel samples for example, for a full 96-well plate, we estimate a 90% reduction in the time needed for common cell-culture tasks such as medium changes compared to cultures done in flasks. Harvesting the cells for assays is done by aspirating the aggregate using a wide-orifice pipet tip. In the future, robotic manipulations and sampling methods can be utilized, further decreasing labor. Although we have not yet explored this possibility, this approach could potentially be developed for use as injectable autologous fat for small-scale applications in cosmetic surgery, for example, not only cosmetic applications in ageing, but also defect-filling after tumor surgery, infections, full-thickness burns, cachexia in AIDS or tumor patients, and so forth. A viable autologous tissue as a filler has clear advantages over the injection of a more-or-less inert foreign substance, but not all patients (burns) actually have fat tissue that is amenable to harvesting. As noted, the aggregates can be handled easily, the large surface to volume area of the individual aggregates mitigates mass-transport issues during culture and provides space for vascular invasion after implantation. Scale-up for larger applications may require a structural scaffold [50]. Combined with MSC cryopreservation, it is possible to envisage multiple implantations over time from a single bone-marrow aspirate, which is not currently possible using autologous native fat.
4. Conclusions
In summary, we present a simple method for the establishment and maintenance of large numbers of three-dimensional adipogenic MSC cultures. For general screening of the differentiation potential of MSCs for quality control purposes, both chondrogenic and adipogenic aggregate culture assays can now be done in the same convenient 96-well plate high-throughput format. The method has implications for the refinement of medium formulations, and for adipotropic drug screening, and is sensitive enough to track the loss of adipogenic differentiation potential of cultured MSCs over time. Compared to conventional cell culture, there are significant reductions in labor, space requirements, plasticware, and media costs; further, the use of emerging robotic manipulators would allow for industrial scale-up. To our knowledge, this is also the first practical example of scaffold-free tissue engineering of adipose tissue.
Conflict of Interests
The authors affirm that they have no financial or other conflict of interests.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health (R01-AR50208, JFW, P01-AR053622, JFW & LAS) as well as the Center for Stem Cells and Regenerative Medicine (CSCRM, LAS). Cells were provided by the Hematopoietic Stem Cell Core Facility at CWRU. The authors thank Ms. Margie Harris for the preparation of the human bone-marrow samples.
References
- 1.Owen M, Friedenstein AJ. Stromal stem cells: marrow-derived osteogenic precursors. Ciba Foundation Symposium. 1988;136:42–60. doi: 10.1002/9780470513637.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Pittenger MF, Mosca JD, McIntosh KR. Human mesenchymal stem cells: progenitor cells for cartilage, bone, fat and stroma. Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology. 2000;251:3–11. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-57276-0_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284(5411):143–147. doi: 10.1126/science.284.5411.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Crisan M, Yap S, Casteilla L, et al. A perivascular origin for mesenchymal stem cells in multiple human organs. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;3(3):301–313. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2008.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Halleux C, Sottile V, Gasser JA, Seuwen K. Multi-lineage potential of human mesenchymal stem cells following clonal expansion. Journal of Musculoskeletetal and Neuronal Interactions. 2001;2(1):71–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Haynesworth SE, Goshima J, Goldberg VM, Caplan AI. Characterization of cells with osteogenic potential from human marrow. Bone. 1992;13(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/8756-3282(92)90364-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Haynesworth SE, Baber MA, Caplan AI. Cytokine expression by human marrow-derived mesenchymal progenitor cells in vitro: effects of dexamethasone and IL-1 alpha. Journal of Cellular Physiology. 1996;166(3):585–592. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(199603)166:3<585::AID-JCP13>3.0.CO;2-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bruder SP, Jaiswal N, Haynesworth SE. Growth kinetics, self-renewal, and the osteogenic potential of purified human mesenchymal stem cells during extensive subcultivation and following cryopreservation. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry. 1997;64(2):278–294. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-4644(199702)64:2<278::aid-jcb11>3.0.co;2-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lennon DP, Haynesworth SE, Bruder SP, Jaiswal N, Caplan AI. Human and animal mesenchymal progenitor cells from bone marrow: identification of serum for optimal selection and proliferation. In Vitro Cellular and Developmental Biology. 1996;32(10):602–611. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Solchaga L, Goldberg VM, Mishra R, Caplan A, Welter J. FGF-2 modifies the gene expression profile of bone marrow-derived human mesenchymal stem cells. Transactions of the Orthopaedic Research Society. 2004;29:p. 777. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Auletta JJ, Zale EA, Welter JF, Solchaga LA. Fibroblast growth factor-2 enhances expansion of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells without diminishing their immunosuppressive potential. Stem Cells International. 2011;2011:10 pages. doi: 10.4061/2011/235176.235176 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Caplan AI, Correa D. The MSC: an injury drugstore. Cell Stem Cell. 2011;9(1):11–15. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2011.06.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mackay DL, Tesar PJ, Liang LN, Haynesworth SE. Characterizing medullary and human mesenchymal stem cell-derived adipocytes. Journal of Cellular Physiology. 2006;207(3):722–728. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Solchaga LA, Penick K, Goldberg VM, Caplan AI, Welter JF. Fibroblast growth factor-2 enhances proliferation and delays loss of chondrogenic potential in human adult bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Engineering A. 2010;16(3):1009–1019. doi: 10.1089/ten.tea.2009.0100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kebriaei P, Isola L, Bahceci E, et al. Adult human mesenchymal stem cells added to corticosteroid therapy for the treatment of acute graft-versus-host disease. Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation. 2009;15(7):804–811. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2008.03.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mets T, Verdonk G. Variations in the stromal cell population of human bone marrow during aging. Mechanisms of Ageing and Development. 1981;15(1):41–49. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(81)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Baxter MA, Wynn RF, Jowitt SN, Wraith JE, Fairbairn LJ, Bellantuono I. Study of telomere length reveals rapid aging of human marrow stromal cells following in vitro expansion. Stem Cells. 2004;22(5):675–682. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.22-5-675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Banfi A, Bianchi G, Notaro R, Luzzatto L, Cancedda R, Quarto R. Replicative aging and gene expression in long-term cultures of human bone marrow stromal cells. Tissue Engineering. 2002;8(6):901–910. doi: 10.1089/107632702320934001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mets T, Verdonk G. In vitro aging of human bone marrow derived stromal cells. Mechanisms of Ageing and Development. 1981;16(1):81–89. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(81)90035-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Digirolamo CM, Stokes D, Colter D, Phinney DG, Class R, Prockop DJ. Propagation and senescence of human marrow stromal cells in culture: a simple colony-forming assay identifies samples with the greatest potential to propagate and differentiate. British Journal of Haematology. 1999;107(2):275–281. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.1999.01715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Banfi A, Muraglia A, Dozin B, Mastrogiacomo M, Cancedda R, Quarto R. Proliferation kinetics and differentiation potential of ex vivo expanded human bone marrow stromal cells: implications for their use in cell therapy. Experimental Hematology. 2000;28(6):707–715. doi: 10.1016/s0301-472x(00)00160-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315–317. doi: 10.1080/14653240600855905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Johnstone B, Hering TM, Caplan AI, Goldberg VM, Yoo JU. In vitro chondrogenesis of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal progenitor cells. Experimental Cell Research. 1998;238(1):265–272. doi: 10.1006/excr.1997.3858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Holtzer H, Abbott J, Lash J, Holtzer S. The loss of phenotypic traits by differentiated cells in vitro, I. Dedifferentiation of cartilage cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1960;46(12):1533–1542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.12.1533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Manning WK, Bonner WM. Isolation and culture of chondrocytes from human adult articular cartilage. Arthritis & Rheumatism. 1967;10(3):235–239. doi: 10.1002/art.1780100309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kato Y, Iwamoto M, Koike T, Suzuki F, Takano Y. Terminal differentiation and calcification in rabbit chondrocyte cultures grown in centrifuge tubes: regulation by transforming growth factor β and serum factors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1988;85(24):9552–9556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ballock RT, Reddi AH. Thyroxine is the serum factor that regulates morphogenesis of columnar cartilage from isolated chondrocytes in chemically defined medium. Journal of Cell Biology. 1994;126(5):1311–1318. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.5.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Penick KJ, Solchaga LA, Welter JF. High-throughput aggregate culture system to assess the chondrogenic potential of mesenchymal stem cells. BioTechniques. 2005;39(5):687–691. doi: 10.2144/000112009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Welter JF, Solchaga LA, Penick KJ. Simplification of aggregate culture of human mesenchymal stem cells as a chondrogenic screening assay. BioTechniques. 2007;42(6):732–737. doi: 10.2144/000112451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Solchaga LA, Penick K, Porter JD, Goldberg VM, Caplan AI, Welter JF. FGF-2 enhances the mitotic and chondrogenic potentials of human adult bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Journal of Cellular Physiology. 2005;203(2):398–409. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Solchaga LA, Welter JF, Lennon DP, Caplan AI. Generation of pluripotent stem cells and their differentiation to the chondrocytic phenotype. Methods in Molecular Medicine. 2004;100:53–68. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-810-2:053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lillie R, Ashburn L. Supersaturated solutions of fat stains in dilute isopropanol for demonstration of acute fatty degeneration not shown by Herxheimer’s technique. Archives of Pathology. 1943;36:432–440. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Luna LG. Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Manual of Histological Staining Methodsed. 3rd edition. New York, NY, USA: McGraw-Hill; 1968. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Solchaga L, Penick K, Welter J. A “manual” mosaicking approach to generating large, high-resolution digital images of histological sections. Proceedings of the Royal Microscopical Society. 2004;39:313–320. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nature Methods. 2012;9:671–675. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Landini G. “Threshold Color”, in: Image J Plugins, 2012, http://www.dentistry.bham.ac.uk/landinig/software/software.html.
- 37.Ponticiello MS, Schinagl RM, Kadiyala S, Barry FP. Gelatin-based resorbable sponge as a carrier matrix for human mesenchymal stem cells in cartilage regeneration therapy. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research. 2000;52(2):246–255. doi: 10.1002/1097-4636(200011)52:2<246::aid-jbm2>3.0.co;2-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sottile V, Seuwen K. A high-capacity for adipogenic differentiation. Analytical Biochemistry. 2001;293(1):124–128. doi: 10.1006/abio.2001.5121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lagasse E, Shizuru JA, Uchida N, Tsukamoto A, Weissman IL. Toward regenerative medicine. Immunity. 2001;14(4):425–436. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(01)00123-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Minguell JJ, Erices A, Conget P. Mesenchymal stem cells. Experimental Biology and Medicine. 2001;226(6):507–520. doi: 10.1177/153537020122600603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Galotto M, Berisso G, Delfino L, et al. Stromal damage as consequence of high-dose chemo/radiotherapy in bone marrow transplant recipients. Experimental Hematology. 1999;27(9):1460–1466. doi: 10.1016/s0301-472x(99)00076-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Phinney DG, Kopen G, Righter W, Webster S, Tremain N, Prockop DJ. Donor variation in the growth properties and osteogenic potential of human marrow stromal cells. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry. 1999;75(3):424–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Blazsek I, Delmas Marsalet B, Legras S, Marion S, Machover D, Misset JL. Large scale recovery and characterization of stromal cell-associated primitive haemopoietic progenitor cells from filter-retained human bone marrow. Bone Marrow Transplantation. 1999;23(7):647–657. doi: 10.1038/sj.bmt.1701616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Koc ON, Peters C, Aubourg P, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells remain host-derived despite successful hematopoietic engraftment after allogeneic transplantation in patients with lysosomal and peroxisomal storage diseases. Experimental Hematology. 1999;27(11):1675–1681. doi: 10.1016/s0301-472x(99)00101-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Conget PA, Minguell JJ. Phenotypical and functional properties of human bone marrow mesenchymal progenitor cells. Journal of Cellular Physiology. 1999;181:67–73. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(199910)181:1<67::AID-JCP7>3.0.CO;2-C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Pittenger MF, Mbalaviele G, Black M, Mosca JD, Marshak DR. Mesenchymal stem cells. In: Koller MR, Palsson BO, Masters JRW, editors. Primary Mesenchymal Cells. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 2001. pp. 189–207. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Sugihara H, Yonemitsu N, Miyabara S, Yun K. Primary cultures of unilocular fat cells: characteristics of growth in vitro and changes in differentiation properties. Differentiation. 1986;31(1):42–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1986.tb00381.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Zhang HH, Kumar S, Barnett AH, Eggo MC. Ceiling culture of mature human adipocytes: use in studies of adipocyte functions. Journal of Endocrinology. 2000;164(2):119–128. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1640119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Tsutsumi S, Shimazu A, Miyazaki K, et al. Retention of multilineage differentiation potential of mesenchymal cells during proliferation in response to FGF. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2001;288(2):413–419. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.5777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Tsuji W, Inamoto T, Yamashiro H, et al. Adipogenesis induced by human adipose tissue-derived stem cells. Tissue Engineering A. 2009;15(1):83–93. doi: 10.1089/ten.tea.2007.0297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


