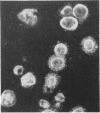
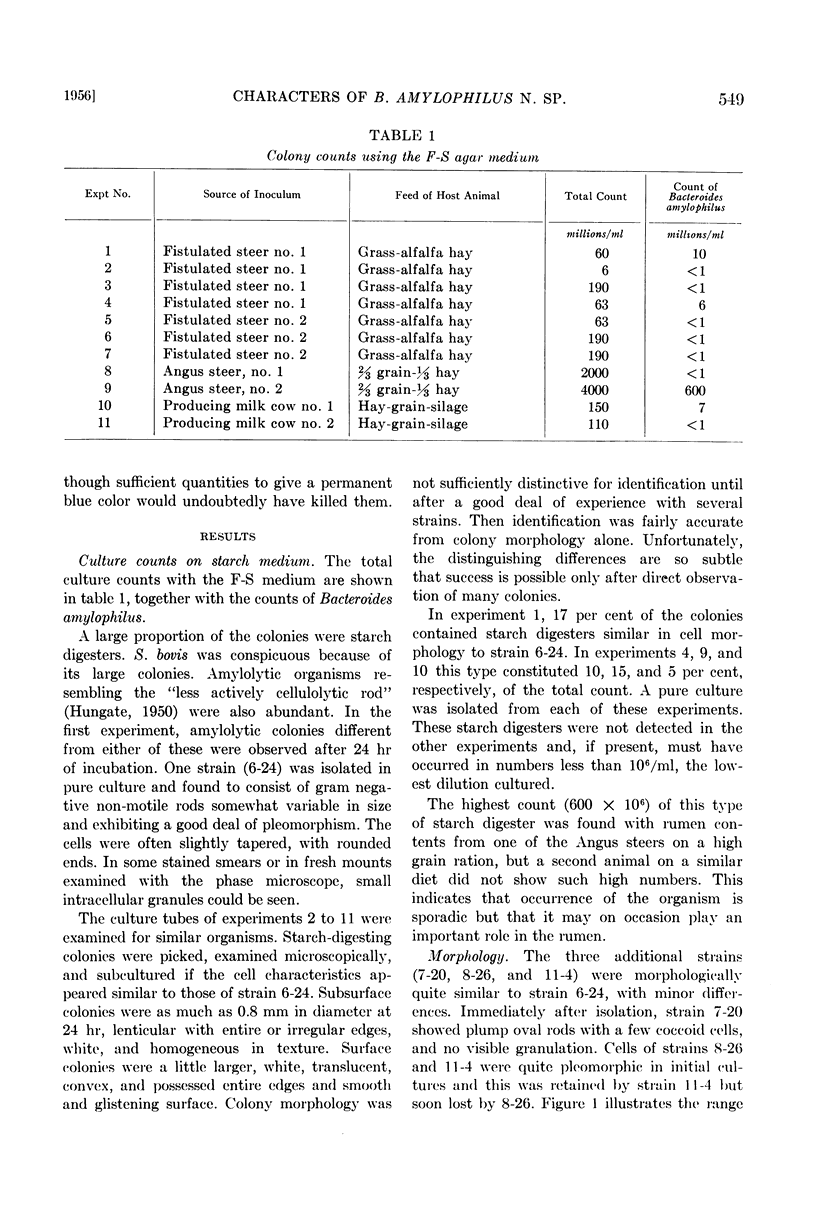
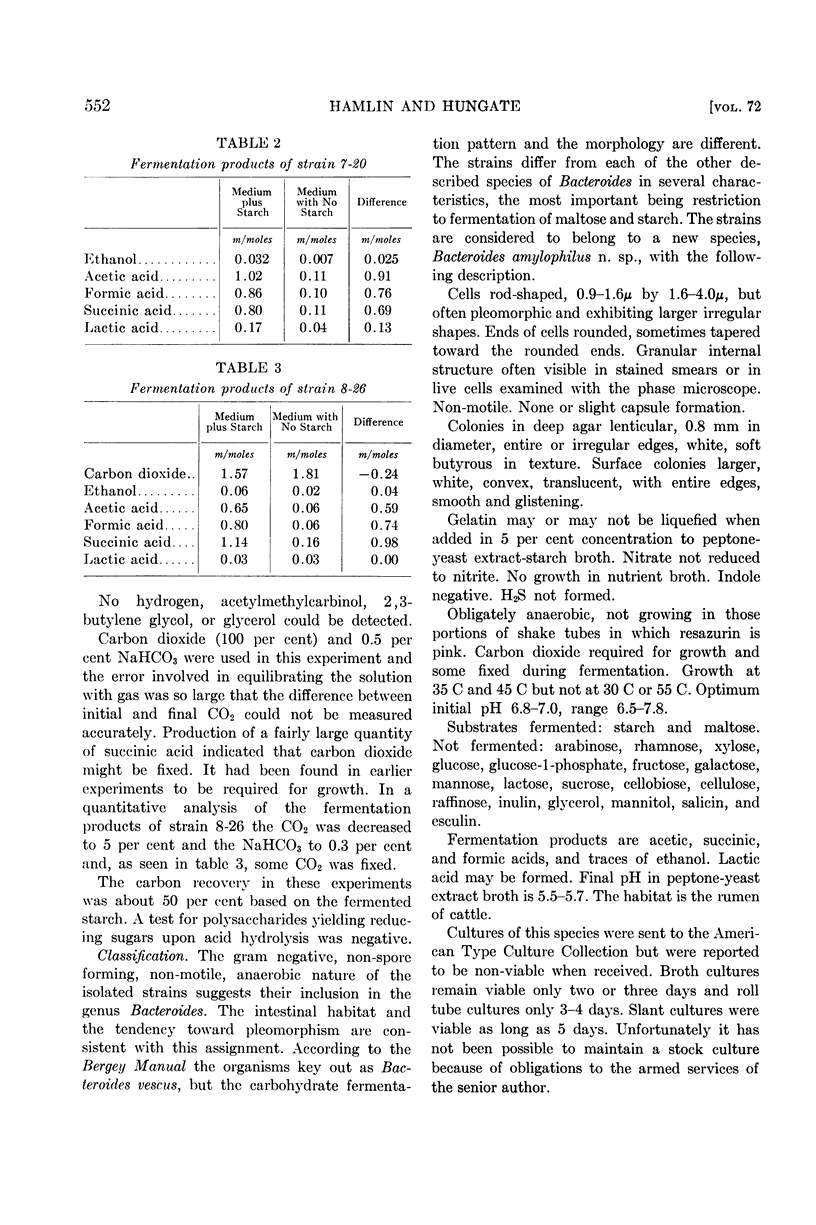
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GUTIERREZ J. Experiments on the culture and physiology of holotriches from the bovine rumen. Biochem J. 1955 Jul;60(3):516–522. doi: 10.1042/bj0600516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOBSON P. N., MANN S. O. Some factors affecting the formation of iodophilic polysaccharide in group D streptococci from the rumen. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Dec;13(3):420–435. doi: 10.1099/00221287-13-3-420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUHTANEN C. N., GALL L. S. Rumen organisms. I. Curved rods and a related rod type. J Bacteriol. 1953 May;65(5):548–553. doi: 10.1128/jb.65.5.548-553.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUHTANEN C. N., GALL L. S. Rumen organisms. II. Two lactate utilizers and six miscellaneous types. J Bacteriol. 1953 May;65(5):554–559. doi: 10.1128/jb.65.5.554-559.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNGATE R. E., DOUGHERTY R. W., BRYANT M. P., CELLO R. M. Microbiological and physiological changes associated with acute indigestion in sheep. Cornell Vet. 1952 Oct;42(4):423–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACPHERSON M. J. Isolation and identification of amylolytic Streptococci from the rumen of the sheep. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1953 Jul;66(1):95–102. doi: 10.1002/path.1700660113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUGDEN B., OXFORD A. E. Some cultural studies with holotrich ciliate protozoa of the sheep's rumen. J Gen Microbiol. 1952 Aug;7(1-2):145–153. doi: 10.1099/00221287-7-1-2-145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]