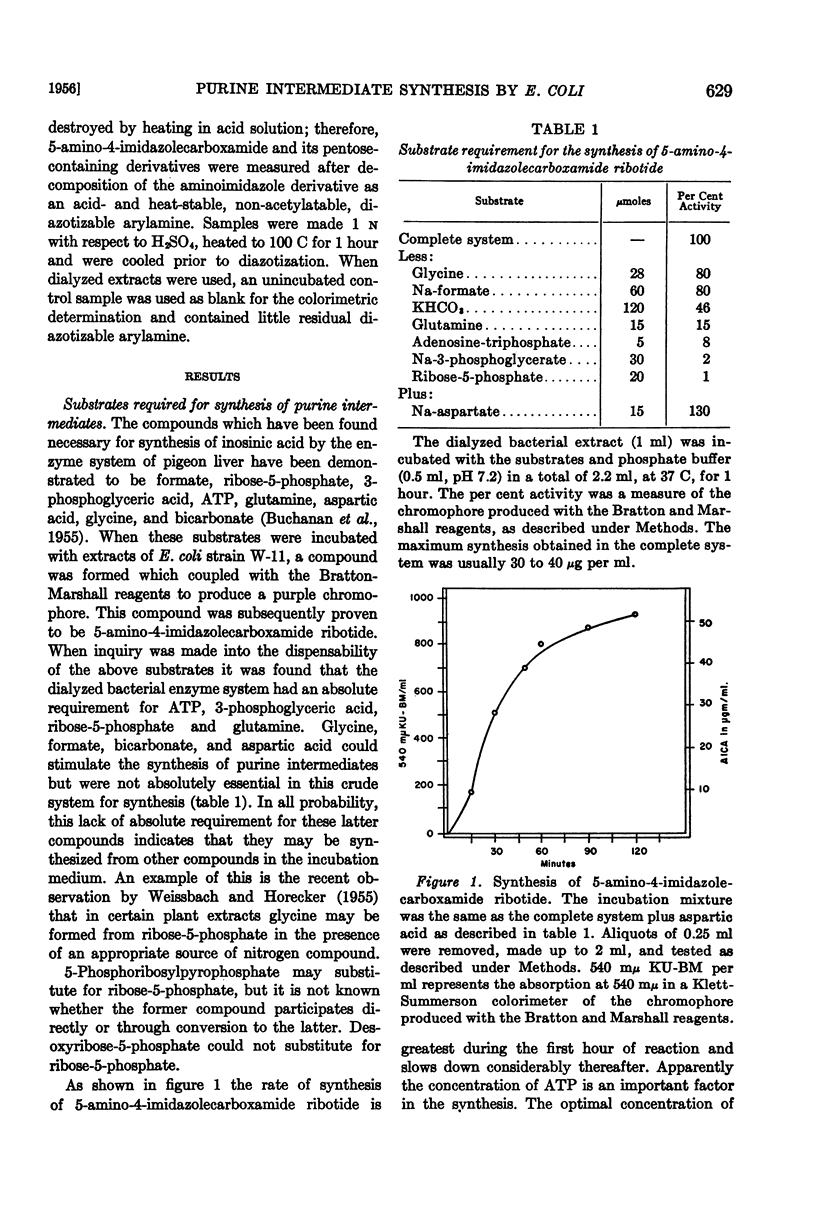
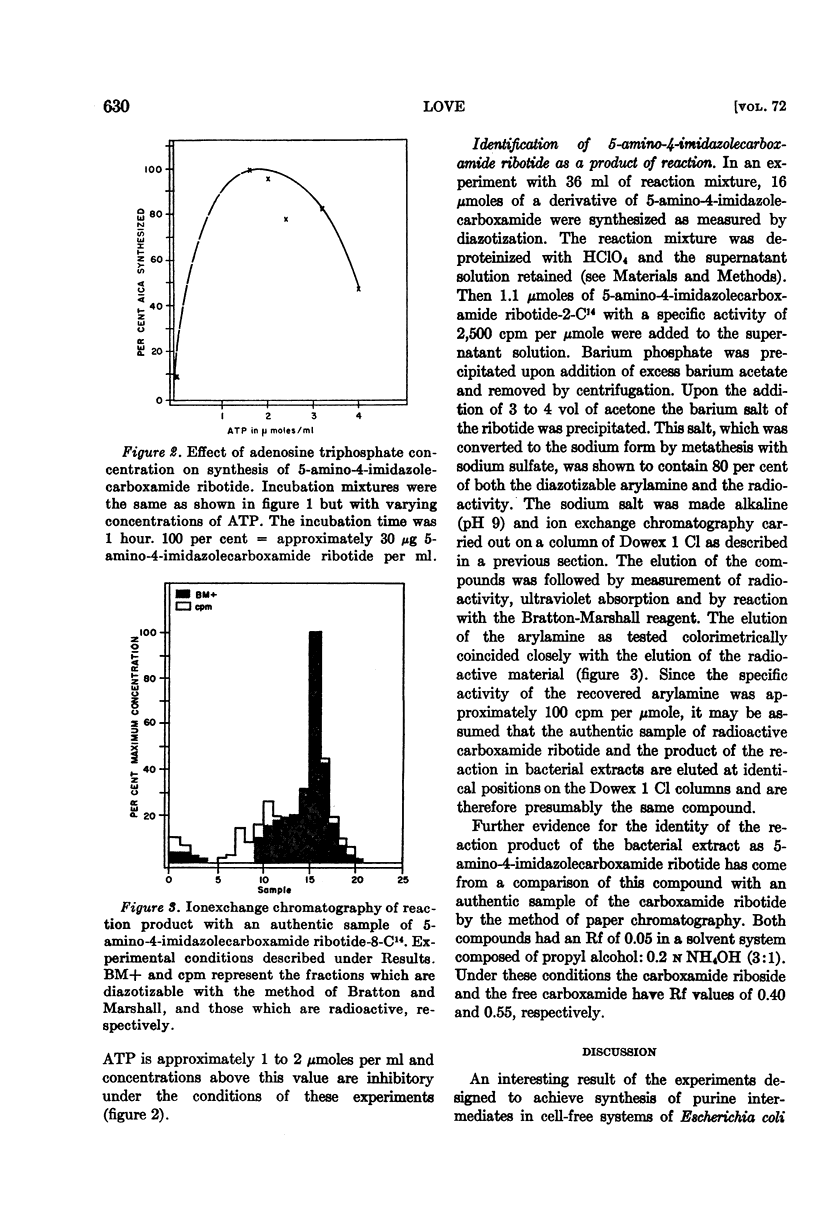
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAMS R. Incorporation of glycine-1-C14 and adenine-8-C13 in the purines of a purine-requiring yeast. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Jun;37(2):270–275. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90191-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTS J. S., CHU E. C. Studies on purine metabolism in bacteria. I. The role of p-aminobenzoic acid. J Bacteriol. 1952 Oct;64(4):537–546. doi: 10.1128/jb.64.4.537-546.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOVE S. H., GOTS J. S. Purine metabolism in bacteria. III. Accumulation of a new pentose-containing arylamine by a purine-requiring mutant of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1955 Feb;212(2):647–654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REMY C. N., REMY W. T., BUCHANAN J. M. Biosynthesis of the purines. VIII. Enzymatic synthesis and utilization of alpha-5-phosphoribosylpyrophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1955 Dec;217(2):885–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULMAN M. P., SONNE J. C., BUCHANAN J. M. Biosynthesis of the purines. I. Hypoxanthine formation in pigeon liver homogenates and extracts. J Biol Chem. 1952 May;196(2):499–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


