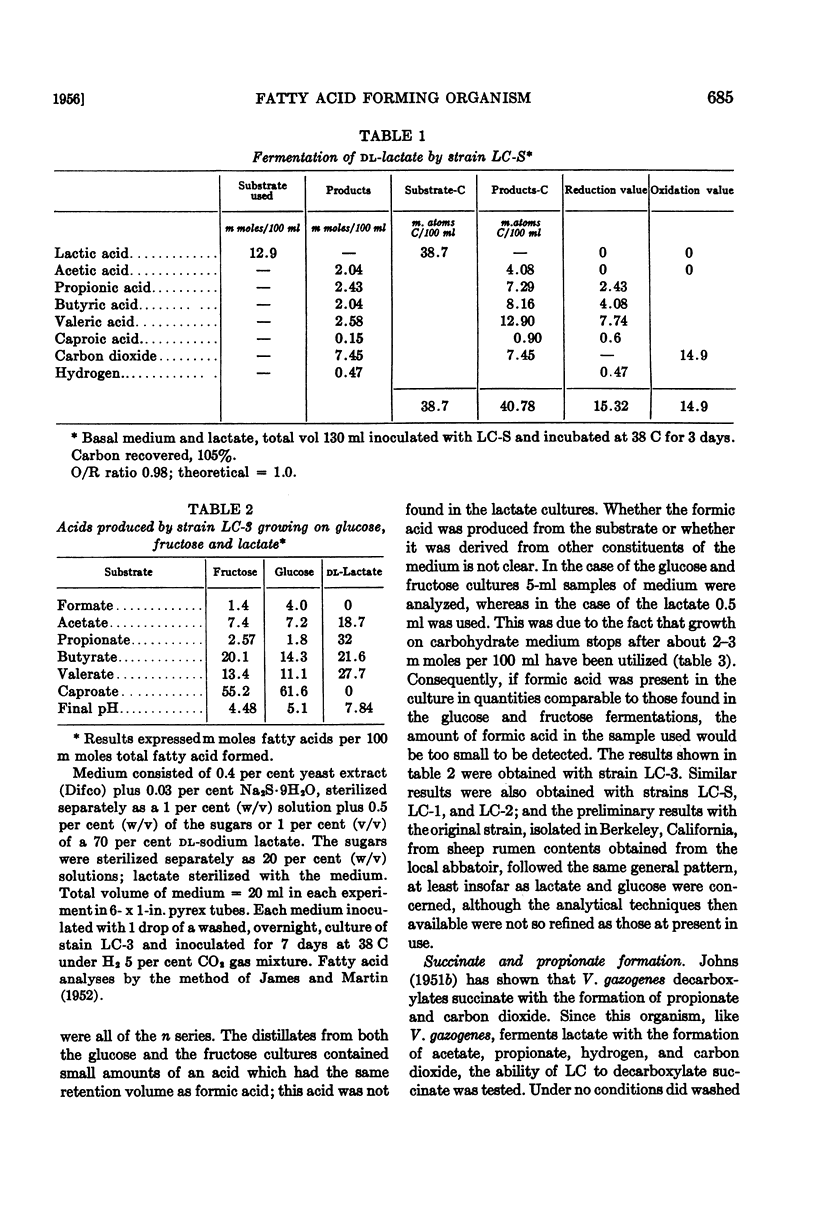
Full text
PDF







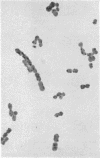
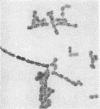
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANNISON E. F. Studies on the volatile fatty acids of sheep blood with special reference to formic acid. Biochem J. 1954 Dec;58(4):670–680. doi: 10.1042/bj0580670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker H. A., Taha S. M. Clostridium kluyverii, an Organism Concerned in the Formation of Caproic Acid from Ethyl Alcohol. J Bacteriol. 1942 Mar;43(3):347–363. doi: 10.1128/jb.43.3.347-363.1942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delwiche E. A. Mechanism of Propionic Acid Formation by Propionibacterium pentosaceum. J Bacteriol. 1948 Dec;56(6):811–820. doi: 10.1128/jb.56.6.811-820.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EL-SHAZLY K. Degradation of protein in the rumen of the sheep. I. Some volatile fatty acids, including branched-chain isomers, found in vivo. Biochem J. 1952 Aug;51(5):640–647. doi: 10.1042/bj0510640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELSDEN S. R., LEWIS D. The production of fatty acids by a gram-negative coccus. Biochem J. 1953 Aug;55(1):183–189. doi: 10.1042/bj0550183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsden S. R. The application of the silica gel partition chromatogram to the estimation of volatile fatty acids. Biochem J. 1946;40(2):252–256. doi: 10.1042/bj0400252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foubert E. L., Douglas H. C. Studies on the Anaerobic Micrococci: I. Taxonomic Considerations. J Bacteriol. 1948 Jul;56(1):25–34. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUHTANEN C. N., GALL L. S. Rumen organisms. II. Two lactate utilizers and six miscellaneous types. J Bacteriol. 1953 May;65(5):554–559. doi: 10.1128/jb.65.5.554-559.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNGATE R. E., DOUGHERTY R. W., BRYANT M. P., CELLO R. M. Microbiological and physiological changes associated with acute indigestion in sheep. Cornell Vet. 1952 Oct;42(4):423–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAMES A. T., MARTIN A. J. P. Gas-liquid partition chromatography; the separation and micro-estimation of volatile fatty acids from formic acid to dodecanoic acid. Biochem J. 1952 Mar;50(5):679–690. doi: 10.1042/bj0500679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNS A. T. Isolation of a bacterium, producing propionic acid, from the rumen of sheep. J Gen Microbiol. 1951 May;5(2):317–325. doi: 10.1099/00221287-5-2-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNS A. T. The mechanism of propionic acid formation by Clostridium propionicum. J Gen Microbiol. 1952 Feb;6(1-2):123–127. doi: 10.1099/00221287-6-1-2-123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNS A. T. The mechanism of propionic acid formation by Veillonella gazogenes. J Gen Microbiol. 1951 May;5(2):326–336. doi: 10.1099/00221287-5-2-326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNS A. T. The mechanism of propionic acid formation by propionibacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1951 May;5(2):337–345. doi: 10.1099/00221287-5-2-337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOHLMILLER E. F., Jr, GEST H. A comparative study of the light and dark fermentations of organic acids by Rhodo-spirillum rubrum. J Bacteriol. 1951 Mar;61(3):269–282. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.3.269-282.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs H. A. The role of fumarate in the respiration of Bacterium coli commune. Biochem J. 1937 Nov;31(11):2095–2124. doi: 10.1042/bj0312095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS D., ELSDEN S. R. The fermentation of L-threonine, L-serine, L-cysteine and acrylic acid by a gram-negative coccus. Biochem J. 1955 Aug;60(4):683–692. doi: 10.1042/bj0600683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY G. E., TRUANT J. P. The morphology, cell structure, and taxonomic affinities of the Moraxella. J Bacteriol. 1954 Jan;67(1):13–22. doi: 10.1128/jb.67.1.13-22.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyle V., Baldwin E., Scarisbrick R. Separation and estimation of saturated C(2)-C(8) fatty acids by buffered partition columns. Biochem J. 1948;43(2):308–317. doi: 10.1042/bj0430308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STADTMAN E. R. Functional group of coenzyme A and its metabolic relations, especially in the fatty acid cycle: Discussion. Fed Proc. 1953 Sep;12(3):692–693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winzler R. J. AZIDE INHIBITION OF ANAEROBIC ASSIMILATION OF GLUCOSE BY YEAST AND ITS APPLICATION TO THE DETERMINATION OF FERMENTABLE SUGAR. Science. 1944 Apr 21;99(2573):327–328. doi: 10.1126/science.99.2573.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]