Abstract
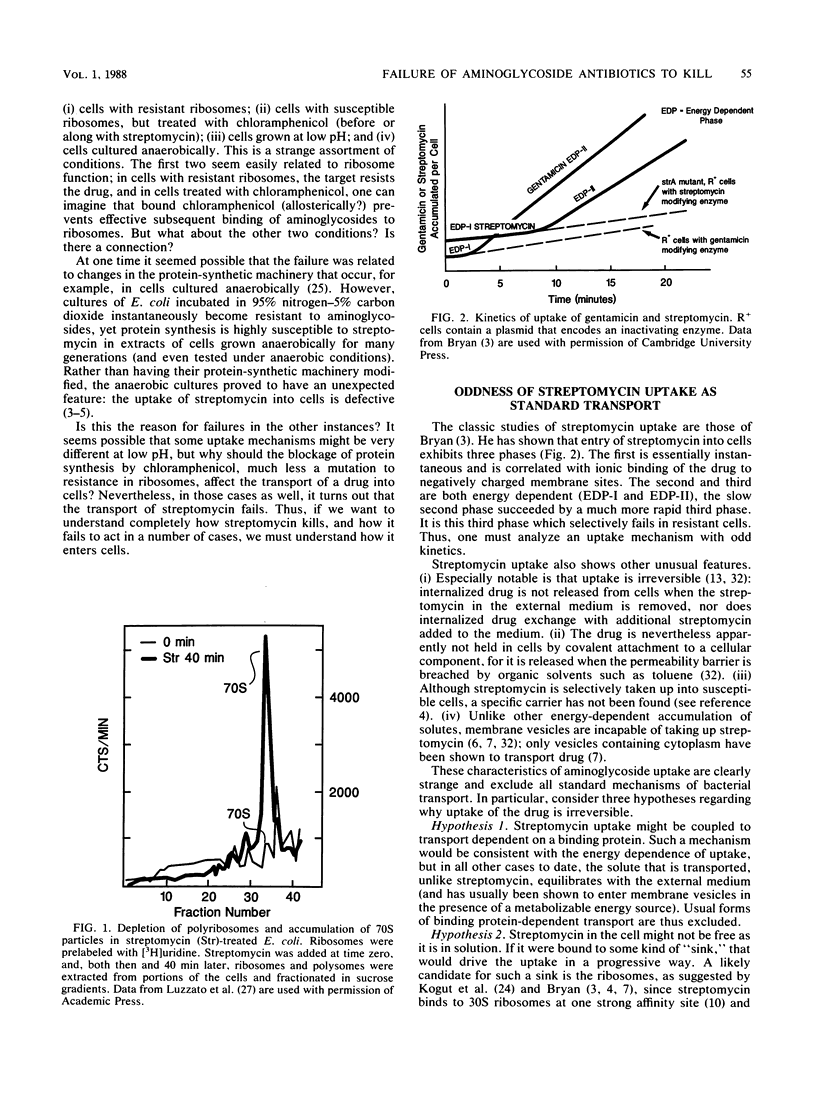
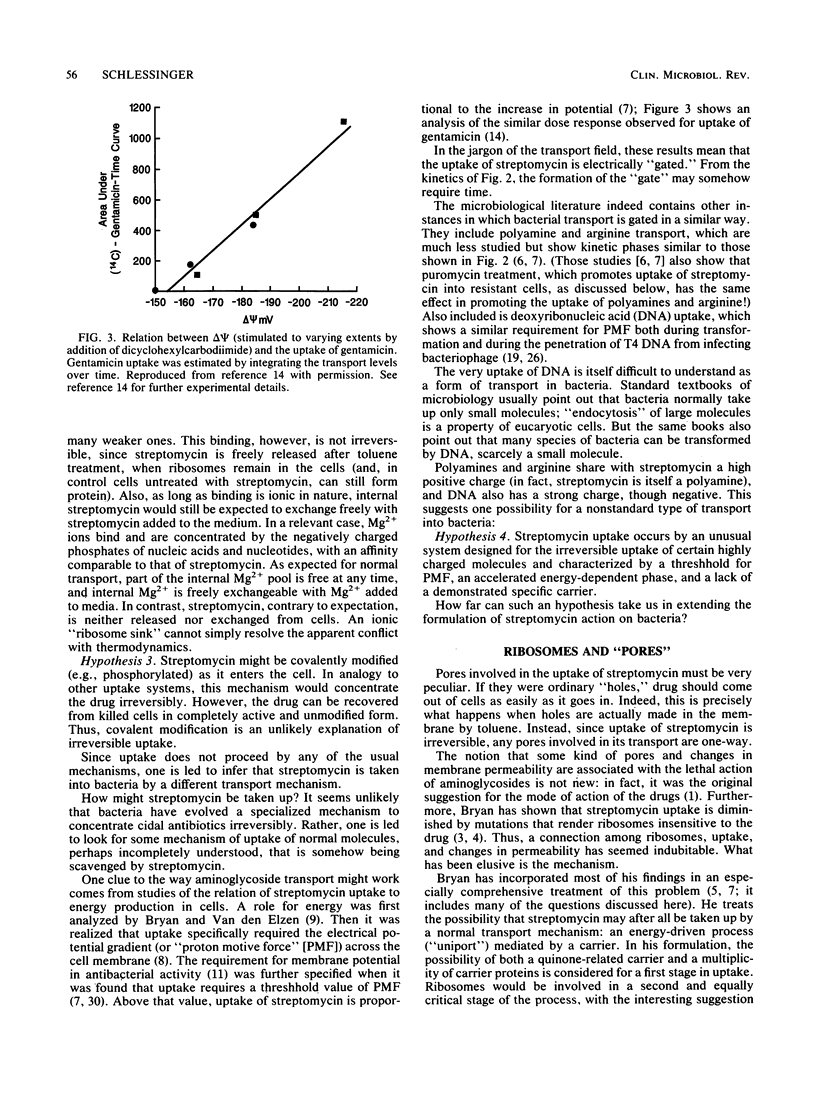
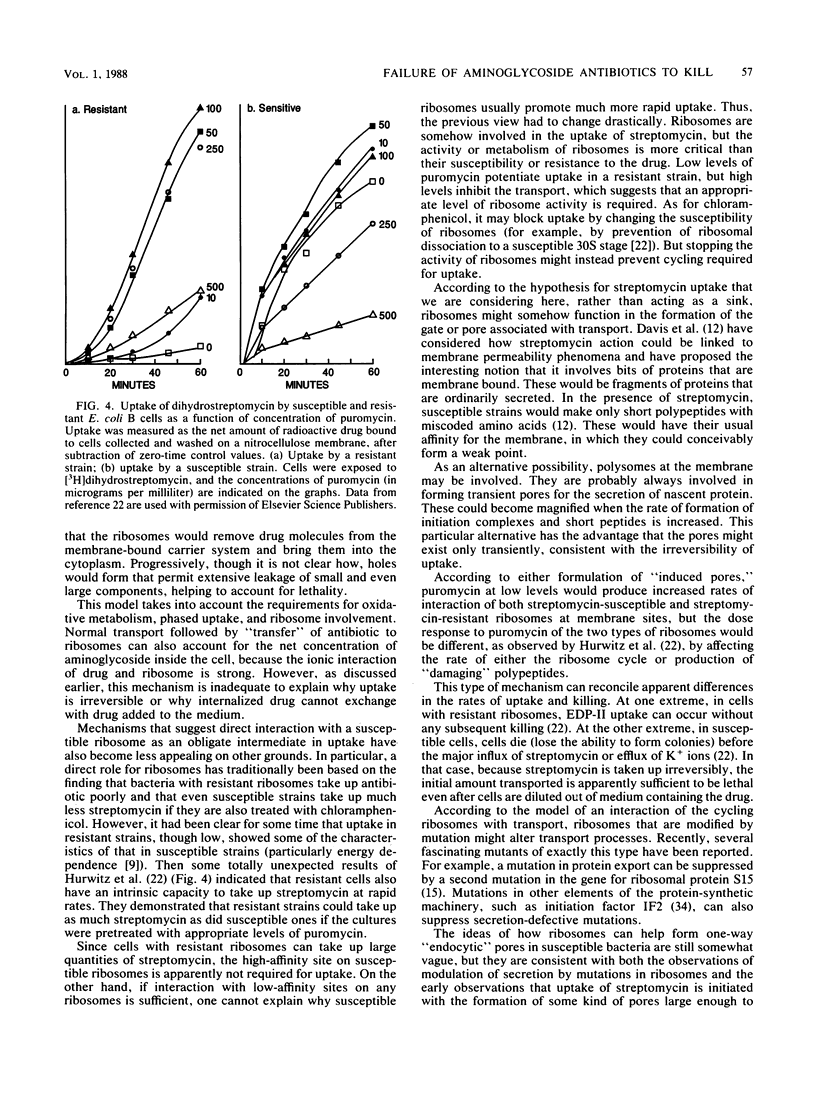
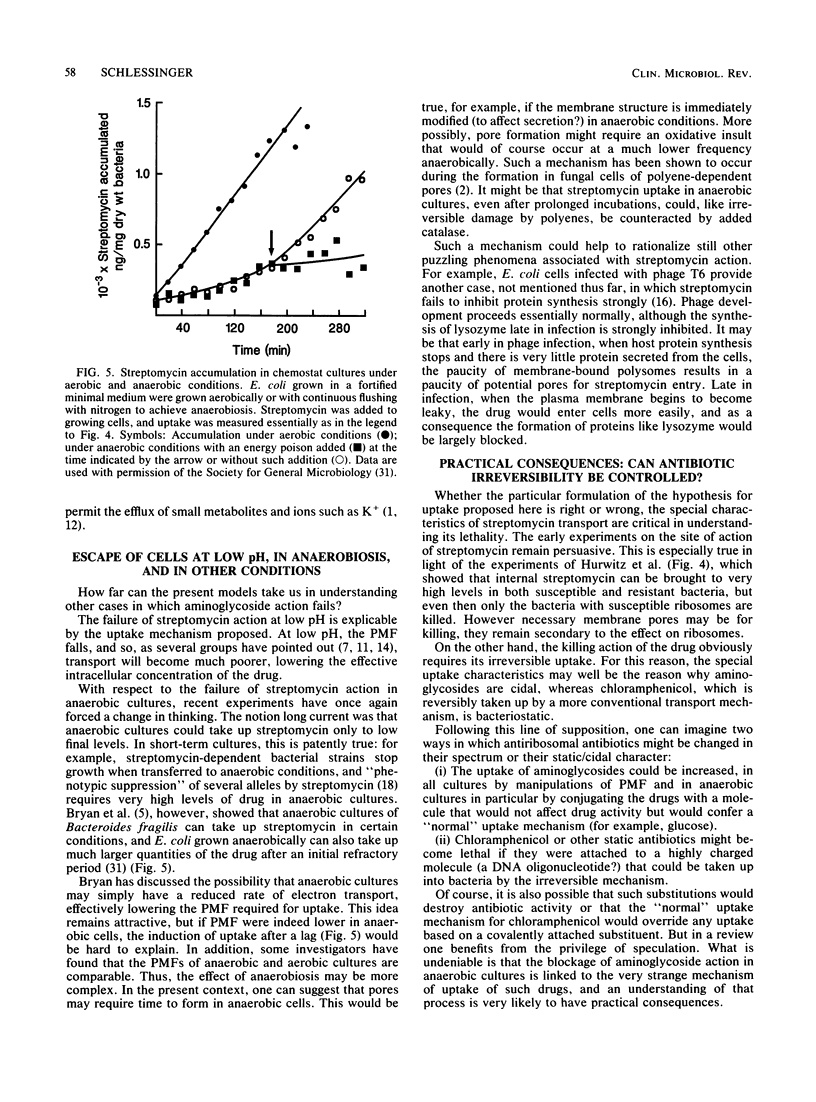
The critical inhibition of ribosome function by aminoglycosides has long been established. But the binding of drug to ribosomes is reversible: why then are aminoglycosides bactericidal? Several groups have shown that irreversible action (lethality) results from irreversible uptake into susceptible cells; conversely, resistance in cases such as anaerobiosis is associated with the failure of uptake. Oddly, the pattern of results excludes all traditional transport mechanisms; most unusual is the apparent dependence of uptake on the interaction of drug with ribosomes. A traditional view that ribosomes may function during uptake as a "sink" for aminoglycosides cannot explain all the data. Instead, the alternative is considered that cycling ribosomes at the cell membrane help to induce "one-way endocytic pores." Although no detailed mechanism is formulated, the results do suggest a way that the permeation of antibiotics might be systematically controllable to render them more cidal.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANAND N., DAVIS B. D. Damage by streptomycin to the cell membrane of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1960 Jan 2;185:22–23. doi: 10.1038/185022a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brajtburg J., Elberg S., Schwartz D. R., Vertut-Croquin A., Schlessinger D., Kobayashi G. S., Medoff G. Involvement of oxidative damage in erythrocyte lysis induced by amphotericin B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Feb;27(2):172–176. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.2.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Kowand S. K., Van Den Elzen H. M. Mechanism of aminoglycoside antibiotic resistance in anaerobic bacteria: Clostridium perfringens and Bacteroides fragilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jan;15(1):7–13. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Kwan S. Mechanisms of aminoglycoside resistance of anaerobic bacteria and facultative bacteria grown anaerobically. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl 500):1–8. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_d.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Kwan S. Roles of ribosomal binding, membrane potential, and electron transport in bacterial uptake of streptomycin and gentamicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jun;23(6):835–845. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.6.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Nicas T., Holloway B. W., Crowther C. Aminoglycoside-resistant mutation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa defective in cytochrome c552 and nitrate reductase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jan;17(1):71–79. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Van Den Elzen H. M. Effects of membrane-energy mutations and cations on streptomycin and gentamicin accumulation by bacteria: a model for entry of streptomycin and gentamicin in susceptible and resistant bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Aug;12(2):163–177. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.2.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F. N., Flaks J. G. Binding of dihydrostreptomycin to Escherichia coli ribosomes: characteristics and equilibrium of the reaction. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Oct;2(4):294–307. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.4.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damper P. D., Epstein W. Role of the membrane potential in bacterial resistance to aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Dec;20(6):803–808. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.6.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. D., Chen L. L., Tai P. C. Misread protein creates membrane channels: an essential step in the bactericidal action of aminoglycosides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6164–6168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickie P., Bryan L. E., Pickard M. A. Effect of enzymatic adenylylation on dihydrostreptomycin accumulation in Escherichia coli carrying an R-factor: model explaining aminoglycoside resistance by inactivating mechanisms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Oct;14(4):569–580. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.4.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg E. S., Mandel L. J., Kaback H. R., Miller M. H. Quantitative association between electrical potential across the cytoplasmic membrane and early gentamicin uptake and killing in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1984 Mar;157(3):863–867. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.3.863-867.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freda C. E., Cohen S. S. Streptomycin and infection of Escherichia coli by T6r+ bacteriophage. J Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;92(6):1670–1679. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.6.1670-1679.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurgo C., Apirion D., Schlessinger D. Polyribosome metabolism in Escherichia coli treated with chloramphenicol, neomycin, spectinomycin or tetracycline. J Mol Biol. 1969 Oct 28;45(2):205–220. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie C., Nomura M. Initiation of protein synthesis: a critical test of the 30S subunit model. Nature. 1968 Jul 20;219(5151):232–235. doi: 10.1038/219232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz C., Braun C. B., Rosano C. L. Role of ribosome recycling in uptake of dihydrostreptomycin by sensitive and resistant Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jan 29;652(1):168–176. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(81)90220-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOGUT M., LIGHTBROWN J. W., ISAACSON P. STREPTOMYCIN ACTION AND ANAEROBIOSIS. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 May;39:155–164. doi: 10.1099/00221287-39-2-155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwan C. N., Apirion D., Schlessinger D. Anaerobiosis-induced changes in an isoleucyl transfer ribonucleic acid and the 50S ribosomes of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1968 Jan;7(1):427–433. doi: 10.1021/bi00841a055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzzatto L., Apirion D., Schlessinger D. Polyribosome depletion and blockage of the ribosome cycle by streptomycin in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jun 14;42(2):315–335. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzzatto L., Apirion D., Schlessinger D. Streptomycin action: greater inhibition of Escherichia coli ribosome function with exogenous than with endogenous messenger ribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):206–209. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.206-209.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangiarotti G., Schlessinger D. Polyribosome metabolism in Escherichia coli. I. Extraction of polyribosomes and ribosomal subunits from fragile, growing Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1966 Sep;20(1):123–143. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mates S. M., Eisenberg E. S., Mandel L. J., Patel L., Kaback H. R., Miller M. H. Membrane potential and gentamicin uptake in Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6693–6697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muir M. E., Ballesteros M., Wallace B. J. Respiration rate, growth rate and the accumulation of streptomycin in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Oct;131(10):2573–2579. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-10-2573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols W. W., Young S. N. Respiration-dependent uptake of dihydrostreptomycin by Escherichia coli. Its irreversible nature and lack of evidence for a uniport process. Biochem J. 1985 Jun 1;228(2):505–512. doi: 10.1042/bj2280505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki M., Mizushima S., Nomura M. Identification and functional characterization of the protein controlled by the streptomycin-resistant locus in E. coli. Nature. 1969 Apr 26;222(5191):333–339. doi: 10.1038/222333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPOTTS C. R., STANIER R. Y. Mechanism of streptomycin action on bacteria: a unitary hypothesis. Nature. 1961 Nov 18;192:633–637. doi: 10.1038/192633a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiba K., Ito K., Nakamura Y., Dondon J., Grunberg-Manago M. Altered translation initiation factor 2 in the cold-sensitive ssyG mutant affects protein export in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):3001–3006. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04598.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace B. J., Davis B. D. Cyclic blockade of initiation sites by streptomycin-damaged ribosomes in Escherichia coli: an explanation for dominance of sensitivity. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 5;75(2):377–390. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



