Abstract
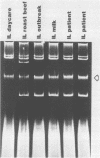
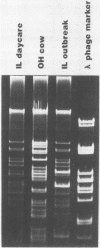
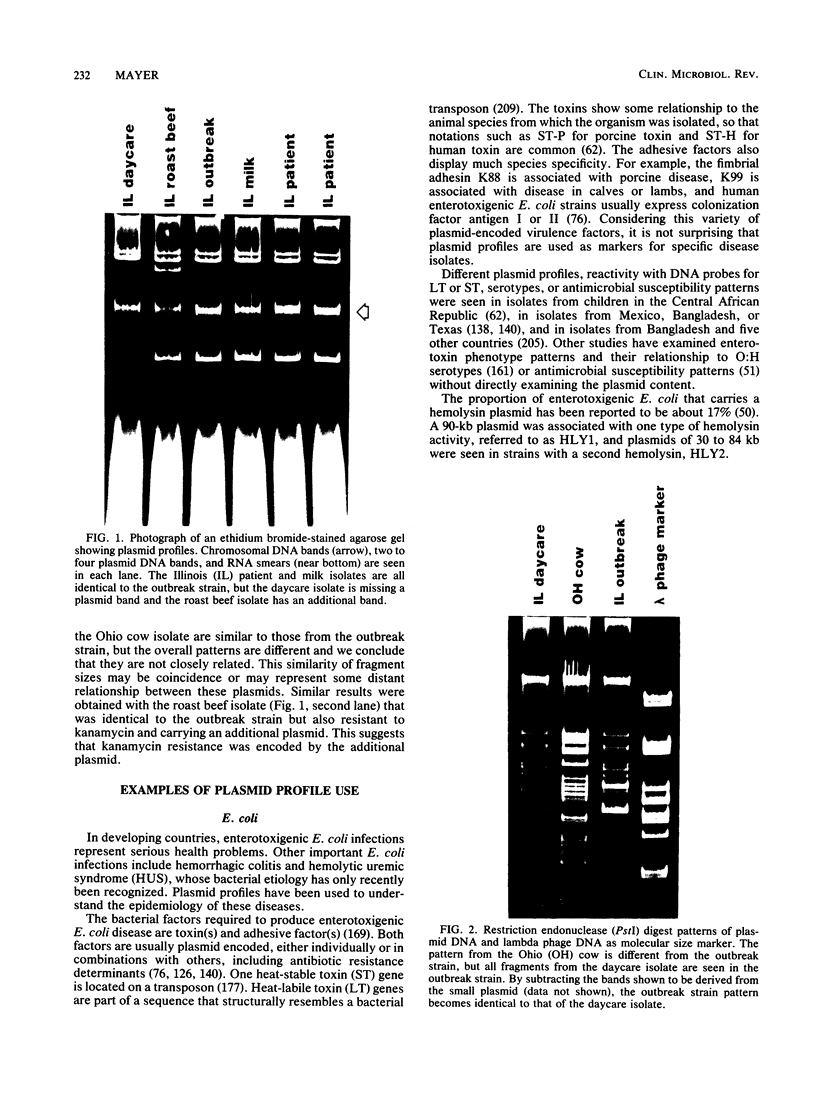
Plasmids are circular deoxyribonucleic acid molecules that exist in bacteria, usually independent of the chromosome. The study of plasmids is important to medical microbiology because plasmids can encode genes for antibiotic resistance or virulence factors. Plasmids can also serve as markers of various bacterial strains when a typing system referred to as plasmid profiling, or plasmid fingerprinting is used. In these methods partially purified plasma deoxyribonucleic acid species are separated according to molecular size by agarose gel electrophoresis. In a second procedure, plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid which has been cleaved by restriction endonucleases can be separated by agarose gel electrophoresis and the resulting pattern of fragments can be used to verify the identity of bacterial isolates. Because many species of bacteria contain plasmids, plasmid profile typing has been used to investigate outbreaks of many bacterial diseases and to trace inter- and intra-species spread of antibiotic resistance.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham L. J., Wales A. J., Rood J. I. Worldwide distribution of the conjugative Clostridium perfringens tetracycline resistance plasmid, pCW3. Plasmid. 1985 Jul;14(1):37–46. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90030-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler J. L., Anderson R. L., Boring J. R., 3rd, Nahmias A. J. A protracted hospital-associated outbreak of salmonellosis due to a multiple-antibiotic-resistant strain of Salmonella indiana. J Pediatr. 1970 Dec;77(6):970–975. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(70)80079-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki T., Takahashi A. Class D tetracycline resistance determinants of R plasmids from the fish pathogens Aeromonas hydrophila, Edwardsiella tarda, and Pasteurella piscicida. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Aug;31(8):1278–1280. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.8.1278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer G. L., Coughter J. P., Johnston J. L. Plasmid-encoded trimethoprim resistance in staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 May;29(5):733–740. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.5.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer G. L., Johnston J. L. Self-transmissible plasmids in staphylococci that encode resistance to aminoglycosides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jul;24(1):70–77. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.1.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer G. L., Karchmer A. W., Vishniavsky N., Johnston J. L. Plasmid-pattern analysis for the differentiation of infecting from noninfecting Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jun;149(6):913–920. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.6.913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer G. L., Mayhall C. G. Comparison of epidemiological markers used in the investigation of an outbreak of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):395–399. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.395-399.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer G. L., Vishniavsky N., Stiver H. G. Plasmid pattern analysis of Staphylococcal epidermidis isolates from patients with prosthetic valve endocarditis. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):627–632. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.627-632.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Garon C. F. Linear plasmids of the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi have covalently closed ends. Science. 1987 Jul 24;237(4813):409–411. doi: 10.1126/science.3603026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bawdon R. E., Crane L. R., Palchaudhuri S. Antibiotic resistance in anaerobic bacteria: molecular biology and clinical aspects. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Nov-Dec;4(6):1075–1095. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.6.1075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beverley S. M., Ismach R. B., Pratt D. M. Evolution of the genus Leishmania as revealed by comparisons of nuclear DNA restriction fragment patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):484–488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanson G. S., Khakhria R., Pagnutti D. Plasmid profiles of value in differentiating Salmonella muenster isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jun;17(6):1159–1160. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.6.1159-1160.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidwell J. L., Lewis D. A., Reeves D. S. A rapid single colony lysate method for the selective visualization of plasmids in Enterobacteriaceae, including Serratia marcescens. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8(6):481–485. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.6.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorvatn B., Lund V., Kristiansen B. E., Korsnes L., Spanne O., Lindqvist B. Applications of restriction endonuclease fingerprinting of chromosomal DNA of Neisseria meningitidis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):763–765. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.763-765.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bopp C. A., Birkness K. A., Wachsmuth I. K., Barrett T. J. In vitro antimicrobial susceptibility, plasmid analysis, and serotyping of epidemic-associated Campylobacter jejuni. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):4–7. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.4-7.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury W. C., Marko M. A., Hennessy J. N., Penner J. L. Occurrence of plasmid DNA in serologically defined strains of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):460–463. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.460-463.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury W. C., Murray R. G., Mancini C., Morris V. L. Bacterial chromosomal restriction endonuclease analysis of the homology of Bacteroides species. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):24–28. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.24-28.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury W. C., Pearson A. D., Marko M. A., Congi R. V., Penner J. L. Investigation of a Campylobacter jejuni outbreak by serotyping and chromosomal restriction endonuclease analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Mar;19(3):342–346. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.3.342-346.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A., Vickers R. M., Elder E. M., Lema M., Garrity G. M. Plasmid and surface antigen markers of endemic and epidemic Legionella pneumophila strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Aug;16(2):230–235. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.2.230-235.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. D., Duong Hong M. o., Rhoades E. R. Chloramphenicol-resistant Salmonella typhi in Saigon. JAMA. 1975 Jan 13;231(2):162–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner F., Margadant A., Peduzzi R., Piffaretti J. C. The plasmid pattern as an epidemiologic tool for Salmonella typhimurium epidemics: comparison with the lysotype. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jul;148(1):7–11. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman T. G., Roizman B., Nahmias A. J. Demonstration of exogenous genital reinfection with herpes simplex virus type 2 by restriction endonuclease fingerprinting of viral DNA. J Infect Dis. 1979 Sep;140(3):295–304. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.3.295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns J. L., Rubens C. E., Mendelman P. M., Smith A. L. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of a gene encoding nonenzymatic chloramphenicol resistance from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Mar;29(3):445–450. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.3.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. G., Mee B. J., Nikoletti S. M. Evolution and spread of IncFIV plasmids conferring resistance to trimethoprim. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 May;29(5):807–813. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.5.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos J., Garcia-Tornel S., Musser J. M., Selander R. K., Smith A. L. Molecular Epidemiology of multiply resistant Haemophilus influenzae type b in day care centers. J Infect Dis. 1987 Sep;156(3):483–489. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.3.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castle S. P., Nims L. J., Lapham S. C. Isolation of Salmonella enteritidis, serotype Horsham, from three American Indian Tribes. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):219–221. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.219-221.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabbert Y. A., El Solh N., Le Pors M. J., Roussel A., Witchitz J. L. Plasmid epidemics. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1979;35:27–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang B. J., Bolton S. M. Plasmids and resistance to antimicrobial agents in Aeromonas sobria and Aeromonas hydrophila clinical isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Aug;31(8):1281–1282. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.8.1281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaslus-Dancla E., Gerbaud G., Lagorce M., Lafont J. P., Courvalin P. Persistence of an antibiotic resistance plasmid in intestinal Escherichia coli of chickens in the absence of selective pressure. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 May;31(5):784–788. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.5.784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaslus-Dancla E., Gerbaud G., Martel J. L., Lagorce M., Lafont J. P., Courvalin P. Detection of a second mechanism of resistance to gentamicin in animal strains of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Aug;31(8):1274–1277. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.8.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen G. C., Lema M., Brown A. Plasmid transfer into members of the family Legionellaceae. J Infect Dis. 1984 Oct;150(4):513–516. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.4.513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Gawron-Burke C. Conjugative transposons and the dissemination of antibiotic resistance in streptococci. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:635–659. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.003223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Tauxe R. V. Drug-resistant Salmonella in the United States: an epidemiologic perspective. Science. 1986 Nov 21;234(4779):964–969. doi: 10.1126/science.3535069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Wong E. S., Falkow S. Common R-plasmids in Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis during a nosocomial Staphylococcus aureus outbreak. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Feb;21(2):210–215. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.2.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N. Transposable genetic elements and plasmid evolution. Nature. 1976 Oct 28;263(5580):731–738. doi: 10.1038/263731a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughter J. P., Johnston J. L., Archer G. L. Characterization of a staphylococcal trimethoprim resistance gene and its product. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jul;31(7):1027–1032. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.7.1027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courvalin P. M., Shaw W. V., Jacob A. E. Plasmid-mediated mechanisms of resistance to aminoglycoside-aminocyclitol antibiotics and to chloramphenicol in group D streptococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 May;13(5):716–725. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.5.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H., Olarte J., Mata L. J., Luttropp L. K., Peñaranda M. E. Characterization of an R-plasmid associated with ampicillin resistance in Shigella dysenteriae type 1 isolated from epidemics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Mar;11(3):553–558. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.3.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currier T. C., Nester E. W. Isolation of covalently closed circular DNA of high molecular weight from bacteria. Anal Biochem. 1976 Dec;76(2):431–441. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90338-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Hughes V. M., Nugent M. E., Richards H. Plasmids and transposons and their stability and mutability in bacteria isolated during an outbreak of hospital infection. Plasmid. 1979 Apr;2(2):182–196. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeBoy J. M., 2nd, Wachsmuth I. K., Davis B. R. Antibiotic resistance in Enterotoxigenic and non-enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Aug;12(2):264–270. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.2.264-270.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeBoy J. M., 2nd, Wachsmuth I. K., Davis B. R. Hemolytic activity in enterotoxigenic and non-enterotoxigenic strains of Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Aug;12(2):193–198. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.2.193-198.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowd G., Cafferkey M., Dougan G. Gentamicin and methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Dublin hospitals: molecular studies. J Med Microbiol. 1983 May;16(2):129–138. doi: 10.1099/00222615-16-2-129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H., Nakahama C., Tobin J. O., Calarco K., Beer K. B., Joly J. R., Selander R. K. Paleoepidemiologic investigation of Legionnaires disease at Wadsworth Veterans Administration Hospital by using three typing methods for comparison of legionellae from clinical and environmental sources. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jun;23(6):1121–1126. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.6.1121-1126.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elwell L. P., Inamine J. M., Minshew B. H. Common plasmid specifying tobramycin resistance found in two enteric bacteria isolated from burn patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Feb;13(2):312–317. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.2.312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elwell L. P., Roberts M., Mayer L. W., Falkow S. Plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase production in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Mar;11(3):528–533. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.3.528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar W. E., Jr Investigation of nosocomial infections by plasmid analysis. Clin Invest Med. 1983;6(3):213–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar W. E., Jr Molecular analysis of plasmids in epidemiologic investigation. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jul;148(1):1–6. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garon C. F., Petersen L. L. An improved method for the isolation of supercoiled DNA molecules using ion-exchange column chromatography. Gene Anal Tech. 1987 Jan-Feb;4(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0735-0651(87)90006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelmi M., Foresti I., Ravizzola G., Bonfanti C., Verardi R., Caruso A., Turano A. Antibiotic resistances and plasmids in Staphylococcus aureus from Italian hospitals. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Mar;23(2):111–118. doi: 10.1099/00222615-23-2-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georges M. C., Wachsmuth I. K., Birkness K. A., Moseley S. L., Georges A. J. Genetic probes for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from childhood diarrhea in the Central African Republic. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):199–202. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.199-202.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie M. T., May J. W., Skurray R. A. Antibiotic susceptibilities and plasmid profiles of nosocomial methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a retrospective study. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Jun;17(3):295–310. doi: 10.1099/00222615-17-3-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein F. W., Chumpitaz J. C., Guevara J. M., Papadopoulou B., Acar J. F., Vieu J. F. Plasmid-mediated resistance to multiple antibiotics in Salmonella typhi. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):261–266. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotuzzo E., Morris J. G., Jr, Benavente L., Wood P. K., Levine O., Black R. E., Levine M. M. Association between specific plasmids and relapse in typhoid fever. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1779–1781. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1779-1781.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouby A., Bourg G., Ramuz M. Previously undescribed 6.6-kilobase R plasmid in penicillinase-producing Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jun;29(6):1095–1097. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.6.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin H. G., Foster T. J., Falkiner F. R., Carr M. E., Coleman D. C. Molecular analysis of multiple-resistance plasmids transferred from gram-negative bacteria isolated in a urological unit. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Sep;28(3):413–418. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.3.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimont F., Grimont P. A. Ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene restriction patterns as potential taxonomic tools. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Sep-Oct;137B(2):165–175. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiney D. G., Jr, Hasegawa P., Davis C. E. Expression in Escherichia coli of cryptic tetracycline resistance genes from bacteroides R plasmids. Plasmid. 1984 May;11(3):248–252. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(84)90031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Márquez J., Freire M., Segade F. A simple procedure for large-scale purification of plasmid DNA. Gene. 1987;54(2-3):255–259. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90494-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadfield T. L., Monson M. H., Wachsmuth I. K. An outbreak of antibiotic-resistant Salmonella enteritidis in Liberia, West Africa. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):790–795. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handsfield H. H., Totten P. A., Fennel C. L., Falkow S., Holmes K. K. Molecular epidemiology of Haemophilus ducreyi infections. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Sep;95(3):315–318. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-95-3-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. B., Olsen R. H. Isolation of large bacterial plasmids and characterization of the P2 incompatibility group plasmids pMG1 and pMG5. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):227–238. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.227-238.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. R., Wachsmuth I. K., Davis B. R., Cohen M. L. High-molecular-weight plasmid correlates with Escherichia coli enteroinvasiveness. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):1295–1298. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.1295-1298.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartstein A. I., Valvano M. A., Morthland V. H., Fuchs P. C., Potter S. A., Crosa J. H. Antimicrobic susceptibility and plasmid profile analysis as identity tests for multiple blood isolates of coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Apr;25(4):589–593. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.4.589-593.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkey P. M., Bennett P. M., Hawkey C. A. Cryptic plasmids in hospital isolates of Providencia stuarti. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Oct;18(2):277–284. doi: 10.1099/00222615-18-2-277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg S. D., Osterholm M. T., Senger K. A., Cohen M. L. Drug-resistant Salmonella from animals fed antimicrobials. N Engl J Med. 1984 Sep 6;311(10):617–622. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198409063111001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg S. D., Schell W. L., Fanning G. R., Wachsmuth I. K., Hickman-Brenner F. W., Blake P. A., Brenner D. J., Farmer J. J., 3rd Aeromonas intestinal infections in the United States. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Nov;105(5):683–689. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-105-5-683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg S. D., Wachsmuth I. K., Hickman-Brenner F. W., Blake P. A., Farmer J. J., 3rd Plesiomonas enteric infections in the United States. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Nov;105(5):690–694. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-105-5-690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook E. W., 3rd, Judson F. N., Handsfield H. H., Ehret J. M., Holmes K. K., Knapp J. S. Auxotype/serovar diversity and antimicrobial resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae in two mid-sized American cities. Sex Transm Dis. 1987 Jul-Sep;14(3):141–146. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198707000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hächler H., Berger-Bächi B., Kayser F. H. Genetic characterization of a Clostridium difficile erythromycin-clindamycin resistance determinant that is transferable to Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jul;31(7):1039–1045. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.7.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hächler H., Kayser F. H., Berger-Bächi B. Homology of a transferable tetracycline resistance determinant of Clostridium difficile with Streptococcus (Enterococcus) faecalis transposon Tn916. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jul;31(7):1033–1038. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.7.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe H. W., Sweeney H. M., Nathan C., Weinstein R. A., Kabins S. A., Cohen S. Identity and interspecific transfer of gentamicin-resistance plasmids in Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jun;141(6):738–747. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.6.738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn G., Bialasiewicz A. A., Blenk H. Evaluation of plasmids in tetracycline resistant strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Ureaplasma urealyticum in a case of severe urethritis. Eur J Epidemiol. 1985 Dec;1(4):294–300. doi: 10.1007/BF00237105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson A. F., Bremner D. A., Bergquist P. L., Lane H. E. Characterization of plasmids from antibiotic-resistant Shigella isolates by agarose gell electrophoresis. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Jul;113(1):73–81. doi: 10.1099/00221287-113-1-73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John J. F., Jr, McKee K. T., Jr, Twitty J. A., Schaffner W. Molecular epidemiology of sequential nursery epidemics caused by multiresistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Pediatr. 1983 Jun;102(6):825–830. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John J. F., Jr, McNeill W. F. Characteristics of Serratia marcescens containing a plasmid coding for gentamicin resistance in nosocomial infections. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jun;143(6):810–817. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.6.810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John J. F., Jr, Sharbaugh R. J., Bannister E. R. Enterobacter cloacae: bacteremia, epidemiology, and antibiotic resistance. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Jan-Feb;4(1):13–28. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. H., Grossman L. I. Electrophoresis of DNA in agarose gels. Optimizing separations of conformational isomers of double- and single-stranded DNAs. Biochemistry. 1977 Sep 20;16(19):4217–4225. doi: 10.1021/bi00638a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler C., Neumaier P. S., Wolf W. Recognition sequences of restriction endonucleases and methylases--a review. Gene. 1985;33(1):1–102. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90119-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinashi H., Shimaji M., Sakai A. Giant linear plasmids in Streptomyces which code for antibiotic biosynthesis genes. 1987 Jul 30-Aug 5Nature. 328(6129):454–456. doi: 10.1038/328454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp J. S., Holmes K. K., Bonin P., Hook E. W., 3rd Epidemiology of gonorrhea: distribution and temporal changes in auxotype/serovar classes of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Sex Transm Dis. 1987 Jan-Mar;14(1):26–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp J. S., Zenilman J. M., Biddle J. W., Perkins G. H., DeWitt W. E., Thomas M. L., Johnson S. R., Morse S. A. Frequency and distribution in the United States of strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae with plasmid-mediated, high-level resistance to tetracycline. J Infect Dis. 1987 Apr;155(4):819–822. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.4.819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopecko D. J., Washington O., Formal S. B. Genetic and physical evidence for plasmid control of Shigella sonnei form I cell surface antigen. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):207–214. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.207-214.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotarski S. F., Merriwether T. L., Tkalcevic G. T., Gemski P. Genetic studies of kanamycin resistance in Campylobacter jejuni. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Aug;30(2):225–230. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.2.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuijper E. J., Oudbier J. H., Stuifbergen W. N., Jansz A., Zanen H. C. Application of whole-cell DNA restriction endonuclease profiles to the epidemiology of Clostridium difficile-induced diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Apr;25(4):751–753. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.4.751-753.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert T., Gerbaud G., Trieu-Cuot P., Courvalin P. Structural relationship between the genes encoding 3'-aminoglycoside phosphotransferases in Campylobacter and in gram-positive cocci. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1985 Sep-Oct;136B(2):135–150. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(85)80040-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampson B. C., von David W., Parisi J. T. Novel mechanism for plasmid-mediated erythromycin resistance by pNE24 from Staphylococcus epidermidis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):653–658. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langenberg W., Rauws E. A., Widjojokusumo A., Tytgat G. N., Zanen H. C. Identification of Campylobacter pyloridis isolates by restriction endonuclease DNA analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Sep;24(3):414–417. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.3.414-417.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclercq R., Carlier C., Duval J., Courvalin P. Plasmid-mediated resistance to lincomycin by inactivation in Staphylococcus haemolyticus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Sep;28(3):421–424. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.3.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. C., Cleary P. P., Gerding D. N. More than one DNA sequence encodes the 2''-O-adenylyltransferase phenotype. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Apr;31(4):667–670. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.4.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. C., Gerding D. N., Cleary P. P. Hospital distribution, persistence, and reintroduction of related gentamicin R plasmids. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Apr;29(4):654–659. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.4.654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. C., Gerding D. N., Cleary P. P. Plasmid macroevolution in a nosocomial environment: demonstration of a persistent molecular polymorphism and construction of a cladistic phylogeny on the basis of restriction data. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;194(1-2):173–178. doi: 10.1007/BF00383513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Xu J. G., Kaper J. B., Lior H., Prado V., Tall B., Nataro J., Karch H., Wachsmuth K. A DNA probe to identify enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli of O157:H7 and other serotypes that cause hemorrhagic colitis and hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):175–182. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locksley R. M., Cohen M. L., Quinn T. C., Tompkins L. S., Coyle M. B., Kirihara J. M., Counts G. W. Multiply antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: introduction, transmission, and evolution of nosocomial infection. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Sep;97(3):317–324. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-3-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon B. R., Gillespie M. T., Byrne M. E., May J. W., Skurray R. A. Plasmid-mediated resistance to gentamicin in Staphylococcus aureus: the involvement of a transposon. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Mar;23(2):101–110. doi: 10.1099/00222615-23-2-101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon B. R., Iuorio J. L., May J. W., Skurray R. A. Molecular epidemiology of multiresistant Staphylococcus aureus in Australian hospitals. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Feb;17(1):79–89. doi: 10.1099/00222615-17-1-79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons R. W., Samples C. L., DeSilva H. N., Ross K. A., Julian E. M., Checko P. J. An epidemic of resistant Salmonella in a nursery. Animal-to-human spread. JAMA. 1980 Feb 8;243(6):546–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher W. E., Plouffe J. F., Para M. F. Plasmid profiles of clinical and environmental isolates of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Dec;18(6):1422–1423. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.6.1422-1423.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahony D. E., Stringer M. F., Borriello S. P., Mader J. A. Plasmid analysis as a means of strain differentiation in Clostridium perfringens. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jul;25(7):1333–1335. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.7.1333-1335.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz S. M., Veazey J. M., Jr, Macrina F. L., Mayhall C. G., Lamb V. A. Sequential outbreaks of infection due to Klebsiella pneumoniae in a neonatal intensive care unit: implication of a conjugative R plasmid. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jul;142(1):106–112. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.1.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martel A. Y., Gosselin P., Ouellette M., Roy P. H., Bergeron M. G. Isolation and molecular characterization of beta-lactamase-producing Haemophilus parainfluenzae from the genital tract. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jun;31(6):966–968. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.6.966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Suárez J. V., Baquero F., Reig M., Pérez-Díaz J. C. Transferable plasmid-linked chloramphenicol acetyltransferase conferring high-level resistance in Bacteroides uniformis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jul;28(1):113–117. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.1.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer K. H., Hopkins J. D., Gilleece E. S., Chao L., O'Brien T. F. Molecular evolution, species distribution, and clinical consequences of an endemic aminoglycoside resistance plasmid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Apr;29(4):628–633. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.4.628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo M. S., Cook W. L., Schlitzer R. L., Ward M. A., Wilson L. A., Ahearn D. G. Antibiograms, serotypes, and plasmid profiles of Pseudomonas aeruginosa associated with corneal ulcers and contact lens wear. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Sep;24(3):372–376. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.3.372-376.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazaitis A. J., Maas R., Maas W. K. Structure of a naturally occurring plasmid with genes for enterotoxin production and drug resistance. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):97–105. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.97-105.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan J. E., Jr, Terry P. M., Huang T. S., Houk C. L., Davies J. Nosocomial infections with gentamicin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: plamid analysis as an epidemiologic tool. J Infect Dis. 1979 Dec;140(6):864–872. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.6.864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner P. S., Falkinham J. O., 3rd Plasmid DNA profiles as epidemiological markers for clinical and environmental isolates of Mycobacterium avium, Mycobacterium intracellulare, and Mycobacterium scrofulaceum. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):325–331. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickelsen P. A., Plorde J. J., Gordon K. P., Hargiss C., McClure J., Schoenknecht F. D., Condie F., Tenover F. C., Tompkins L. S. Instability of antibiotic resistance in a strain of Staphylococcus epidermidis isolated from an outbreak of prosthetic valve endocarditis. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jul;152(1):50–58. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.1.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mingrone M. G., Fantasia M., Figura N., Guglielmetti P. Characteristics of Yersinia enterocolitica isolated from children with diarrhea in Italy. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jul;25(7):1301–1304. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.7.1301-1304.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley H. L., Chippendale G. R., Fraiman M. H., Tenney J. H., Warren J. W. Variable phenotypes of Providencia stuartii due to plasmid-encoded traits. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Nov;22(5):851–853. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.5.851-853.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. G., Jr, Lin F. Y., Morrison C. B., Gross R. J., Khabbaz R., Maher K. O., Rowe B., Israel E., Libonati J. P. Molecular epidemiology of neonatal meningitis due to Citrobacter diversus: a study of isolates from hospitals in Maryland. J Infect Dis. 1986 Sep;154(3):409–414. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.3.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. A., Johnson S. R., Biddle J. W., Roberts M. C. High-level tetracycline resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae is result of acquisition of streptococcal tetM determinant. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):664–670. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mucha D. K., Farrand S. K. Diversity of determinants encoding carbenicillin, gentamicin, and tobramycin resistance in nosocomial Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Aug;30(2):281–289. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.2.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E., Halebian S., Kwok R. Y., Cheng W. C., Finegold S. M., Anselmo C. R., Gerding D. N., Peterson L. R. Bacterial agglutination and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for typing Clostridium difficile. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):267–271. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E., Church D. A., Wanger A., Zscheck K., Levison M. E., Ingerman M. J., Abrutyn E., Mederski-Samoraj B. Comparison of two beta-lactamase-producing strains of Streptococcus faecalis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Dec;30(6):861–864. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.6.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E., Evans D. J., Jr, Penãranda M. E., Evans D. G. CFA/I-ST plasmids: comparison of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) of serogroups O25, O63, O78, and O128 and mobilization from an R factor-containing epidemic ETEC isolate. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):566–570. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.566-570.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E., Moellering R. C., Jr In-vivo acquisition of two different types of aminoglycoside resistance by a single strain of Klebsiella pneumoniae causing severe infection. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Feb;96(2):176–180. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-2-176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E., Tsao J. Comparison of CFA/I:ST plasmids of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1987 Aug;156(2):398–401. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.2.398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muytjens H. L., Zanen H. C., Sonderkamp H. J., Kollée L. A., Wachsmuth I. K., Farmer J. J., 3rd Analysis of eight cases of neonatal meningitis and sepsis due to Enterobacter sakazakii. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):115–120. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.115-120.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M., Sato S., Ohya T., Suzuki S., Ikeda S. Plasmid profile analysis in epidemiological studies of animal Salmonella typhimurium infection in Japan. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Feb;23(2):360–365. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.2.360-365.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nassif X., Sansonetti P. J. Correlation of the virulence of Klebsiella pneumoniae K1 and K2 with the presence of a plasmid encoding aerobactin. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):603–608. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.603-608.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Newland J. W., Miller S. F., Holmes R. K., Smith H. W., Formal S. B. Shiga-like toxin-converting phages from Escherichia coli strains that cause hemorrhagic colitis or infantile diarrhea. Science. 1984 Nov 9;226(4675):694–696. doi: 10.1126/science.6387911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien T. F., Hopkins J. D., Gilleece E. S., Medeiros A. A., Kent R. L., Blackburn B. O., Holmes M. B., Reardon J. P., Vergeront J. M., Schell W. L. Molecular epidemiology of antibiotic resistance in salmonella from animals and human beings in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1982 Jul 1;307(1):1–6. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198207013070101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan R. J., Rousset K. M., Harkess N. K., Murray M. L., Lewis A. C., Williams W. L. Analysis of increasing antibiotic resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae relative to changes in chemotherapy. J Infect Dis. 1978 Sep;138(3):293–298. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.3.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odelson D. A., Rasmussen J. L., Smith C. J., Macrina F. L. Extrachromosomal systems and gene transmission in anaerobic bacteria. Plasmid. 1987 Mar;17(2):87–109. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(87)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olarte J., Galindo E. Salmonella typhi resistant to chloramphenicol, ampicillin, and other antimicrobial agents: strains isolated during an extensive typhoid fever epidemic in Mexico. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Dec;4(6):597–601. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.6.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsvik O., Sørum H., Birkness K., Wachsmuth K., Fjølstad M., Lassen J., Fossum K., Feeley J. C. Plasmid characterization of Salmonella typhimurium transmitted from animals to humans. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Sep;22(3):336–338. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.3.336-338.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouellette M., Gerbaud G., Lambert T., Courvalin P. Acquisition by a Campylobacter-like strain of aphA-1, a kanamycin resistance determinant from members of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jul;31(7):1021–1026. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.7.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrott P. L., Terry P. M., Whitworth E. N., Frawley L. W., Coble R. S., Wachsmuth I. K., McGowan J. E., Jr Pseudomonas aeruginosa peritonitis associated with contaminated poloxamer-iodine solution. Lancet. 1982 Sep 25;2(8300):683–685. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90712-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips I. Beta-lactamase-producing, penicillin-resistant gonococcus. Lancet. 1976 Sep 25;2(7987):656–657. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92466-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmids and plasmid-associated determinants of Yersinia enterocolitica pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):775–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.775-782.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prado D., Murray B. E., Cleary T. G., Pickering L. K. Limitations of using the plasmid pattern as an epidemiological tool for clinical isolates of Shigella sonnei. J Infect Dis. 1987 Feb;155(2):314–316. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.2.314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prevot M. H., Andremont A., Sancho-Garnier H., Tancrede C. Epidemiology of intestinal colonization by members of the family Enterobacteriaceae resistant to cefotaxime in a hematology-oncology unit. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Dec;30(6):945–947. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.6.945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid A. J., Amyes S. G. Plasmid penicillin resistance in Vibrio cholerae: identification of new beta-lactamase SAR-1. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Aug;30(2):245–247. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.2.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis M. H., Matos D. P., de Castro A. F., Toledo M. R., Trabulsi L. R. Relationship among enterotoxigenic phenotypes, serotypes, and sources of strains in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):24–27. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.24-27.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley L. W., Cohen M. L. Plasmid profiles and salmonella epidemiology. Lancet. 1982 Mar 6;1(8271):573–573. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92088-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley L. W., DiFerdinando G. T., Jr, DeMelfi T. M., Cohen M. L. Evaluation of isolated cases of salmonellosis by plasmid profile analysis: introduction and transmission of a bacterial clone by precooked roast beef. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jul;148(1):12–17. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.1.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M. C., Hillier S. L., Hale J., Holmes K. K., Kenny G. E. Tetracycline resistance and tetM in pathogenic urogenital bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):810–812. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotger R., García-Valdés E., Trallero E. P. Characterization of a beta-lactamase-specifying plasmid isolated from Eikenella corrodens and its relationship to a commensal Neisseria plasmid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Sep;30(3):508–509. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.3.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubens C. E., Farrar W. E., Jr, McGee Z. A., Schaffner W. Evolution of a plasmid mediating resistance to multiple antimicrobial agents during a prolonged epidemic of nosocomial infections. J Infect Dis. 1981 Feb;143(2):170–181. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.2.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan C. A., Nickels M. K., Hargrett-Bean N. T., Potter M. E., Endo T., Mayer L., Langkop C. W., Gibson C., McDonald R. C., Kenney R. T. Massive outbreak of antimicrobial-resistant salmonellosis traced to pasteurized milk. JAMA. 1987 Dec 11;258(22):3269–3274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Human diarrheal disease caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:333–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski P. L., Peterson B. C., Gerding D. N., Cleary P. P. Physical characterization of ten R plasmids obtained from an outbreak of nosocomial Klebsiella pneumoniae infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Apr;15(4):616–624. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.4.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagara H., Mochizuki A., Okamura N., Nakaya R. Antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli with special reference to plasmid profiles of Japanese clinical isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 May;31(5):713–719. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.5.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Kopecko D. J., Formal S. B. Involvement of a plasmid in the invasive ability of Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):852–860. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.852-860.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaberg D. R., Rubens C. E., Alford R. H., Farrar W. E., Schaffner W., McGee Z. A. Evolution of antimicrobial resistance and nosocomial infection. Lessons from the Vanderbilt experience. Am J Med. 1981 Feb;70(2):445–448. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90786-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaberg D. R., Tompkins L. S., Falkow S. Use of agarose gel electrophoresis of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid to fingerprint gram-negative bacilli. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jun;13(6):1105–1108. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.6.1105-1108.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serwold-Davis T. M., Groman N. B. Mapping and cloning of Corynebacterium diphtheriae plasmid pNG2 and characterization of its relatedness to plasmids from skin coryneforms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jul;30(1):69–72. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So M., Heffron F., McCarthy B. J. The E. coli gene encoding heat stable toxin is a bacterial transposon flanked by inverted repeats of IS1. Nature. 1979 Feb 8;277(5696):453–456. doi: 10.1038/277453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sox T. E., Mohammed W., Sparling P. F. Transformation-derived Neisseria gonorrhoeae plasmids with altered structure and function. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):510–518. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.510-518.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spika J. S., Waterman S. H., Hoo G. W., St Louis M. E., Pacer R. E., James S. M., Bissett M. L., Mayer L. W., Chiu J. Y., Hall B. Chloramphenicol-resistant Salmonella newport traced through hamburger to dairy farms. A major persisting source of human salmonellosis in California. N Engl J Med. 1987 Mar 5;316(10):565–570. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198703053161001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacket C. O., Dominguez L. B., Fisher H. J., Cohen M. L. An outbreak of multiple-drug-resistant Salmonella enteritis from raw milk. JAMA. 1985 Apr 12;253(14):2058–2060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacket C. O., Shahid N., Huq M. I., Alim A. R., Cohen M. L. Usefulness of plasmid profiles for differentiation of Shigella isolates in Bangladesh. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;20(2):300–301. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.2.300-301.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi S., Nagano Y. Rapid procedure for isolation of plasmid DNA and application to epidemiological analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):608–613. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.608-613.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tantulavanich S., Olexy V. M., Prasad T. R., Bird T. J., Talanda-Fath C., Grieble H. G., Farrand S. K. An R plasmid of broad host-range, coding for resistance to nine antimicrobial agents endemic in Gram-negative nosocomial isolates. J Med Microbiol. 1981 Nov;14(4):371–380. doi: 10.1099/00222615-14-4-371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E., Chumpitaz J. C., Goldstein F. Variability of IncHI1 plasmids from Salmonella typhi with special reference to Peruvian plasmids encoding resistance to trimethoprim and other antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Sep;28(3):452–455. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.3.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E., Garner R. S., Allan B. J. Characterization of tetracycline resistance plasmids from Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Dec;24(6):930–935. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.6.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. N., Wachsmuth I. K., Shangkuan Y. H., Schmidt E. V., Barrett T. J., Schrader J. S., Scherach C. S., McGee H. B., Feldman R. A., Brenner D. J. Salmonellosis associated with marijuana: a multistate outbreak traced by plasmid fingerprinting. N Engl J Med. 1982 May 27;306(21):1249–1253. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198205273062101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenover F. C. Studies of antimicrobial resistance genes using DNA probes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 May;29(5):721–725. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.5.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenover F. C., Williams S., Gordon K. P., Harris N., Nolan C., Plorde J. J. Utility of plasmid fingerprinting for epidemiological studies of Campylobacter jejuni infections. J Infect Dis. 1984 Feb;149(2):279–279. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.2.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenover F. C., Williams S., Gordon K. P., Nolan C., Plorde J. J. Survey of plasmids and resistance factors in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jan;27(1):37–41. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thakker-Varia S., Jenssen W. D., Moon-McDermott L., Weinstein M. P., Dubin D. T. Molecular epidemiology of macrolides-lincosamides-streptogramin B resistance in Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 May;31(5):735–743. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.5.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R., Hughes S. G., Broda P. Plasmid identification using specific endonucleases. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;133(2):141–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00264835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmis K., Winkler U. Isolation of covalently closed circular deoxyribonucleic acid from bacteria which produce exocellular nuclease. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jan;113(1):508–509. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.1.508-509.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins L. S., Plorde J. J., Falkow S. Molecular analysis of R-factors from multiresistant nosocomial isolates. J Infect Dis. 1980 May;141(5):625–636. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.5.625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins L. S., Troup N., Labigne-Roussel A., Cohen M. L. Cloned, random chromosomal sequences as probes to identify Salmonella species. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;154(1):156–162. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.1.156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Totten P. A., Vidal L., Baldwin J. N. Penicillin and tetracycline resistance plasmids in Staphylococcus epidermidis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Sep;20(3):359–365. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.3.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H., Spohr M., Bauer D. Chemotherapeutic efficacy of cefotaxime and failure of fosfomycin in murine Salmonella typhimurium infection. Chemotherapy. 1984;30(3):148–157. doi: 10.1159/000238261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Embden J. D., Dessens-Kroon M., Van Klingeren B. A new beta-lactamase plasmid in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Feb;15(2):247–250. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.2.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Nhieu G. T., Goldstein F. W., Pinto M. E., Acar J. F., Collatz E. Transfer of amikacin resistance by closely related plasmids in members of the family Enterobacteriaceae isolated in Chile. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 May;29(5):833–837. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.5.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. G., Davis B. R., Wachsmuth I. K., Riley L. W., Remis R. S., Sokolow R., Morris G. K. Laboratory investigation of hemorrhagic colitis outbreaks associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):512–520. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.512-520.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams W. W., Mariano J., Spurrier M., Donnell H. D., Jr, Breckenridge R. L., Jr, Anderson R. L., Wachsmuth I. K., Thornsberry C., Graham D. R., Thibeault D. W. Nosocomial meningitis due to Citrobacter diversus in neonates: new aspects of the epidemiology. J Infect Dis. 1984 Aug;150(2):229–235. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.2.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willshaw G. A., Smith H. R., Anderson E. S. Application of agarose gel electrophoresis to the characterization of plasmid DNA in drug-resistant enterobacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Sep;114(1):15–25. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-1-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willshaw G. A., Smith H. R., McConnell M. M., Barclay E. A., Krnjulac J., Rowe B. Genetic and molecular studies of plasmids coding for colonization factor antigen I and heat-stable enterotoxin in several escherichia coli serotypes. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):858–868. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.858-868.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. R., Skinner S. E., Shaw W. V. Analysis of two chloramphenicol resistance plasmids from Staphylococcus aureus: insertional inactivation of Cm resistance, mapping of restriction sites, and construction of cloning vehicles. Plasmid. 1981 May;5(3):245–258. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woloj M., Tolmasky M. E., Roberts M. C., Crosa J. H. Plasmid-encoded amikacin resistance in multiresistant strains of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from neonates with meningitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Feb;29(2):315–319. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.2.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Honda T., Miwatani T., Yokota T. A virulence plasmid in Escherichia coli enterotoxigenic for humans: intergenetic transfer and expression. J Infect Dis. 1984 Nov;150(5):688–698. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.5.688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Yokota T. Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin genes are flanked by repeated deoxyribonucleic acid sequences. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):850–860. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.850-860.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zervos M. J., Mikesell T. S., Schaberg D. R. Heterogeneity of plasmids determining high-level resistance to gentamicin in clinical isolates of Streptococcus faecalis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jul;30(1):78–81. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.1.78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ketel R. J., ter Schegget J., Zanen H. C. Molecular epidemiology of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):362–364. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.362-364.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Bodman S. B., Shaw P. D. Conservation of plasmids among plant-pathogenic Pseudomonas syringae isolates of diverse origins. Plasmid. 1987 May;17(3):240–247. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(87)90032-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]