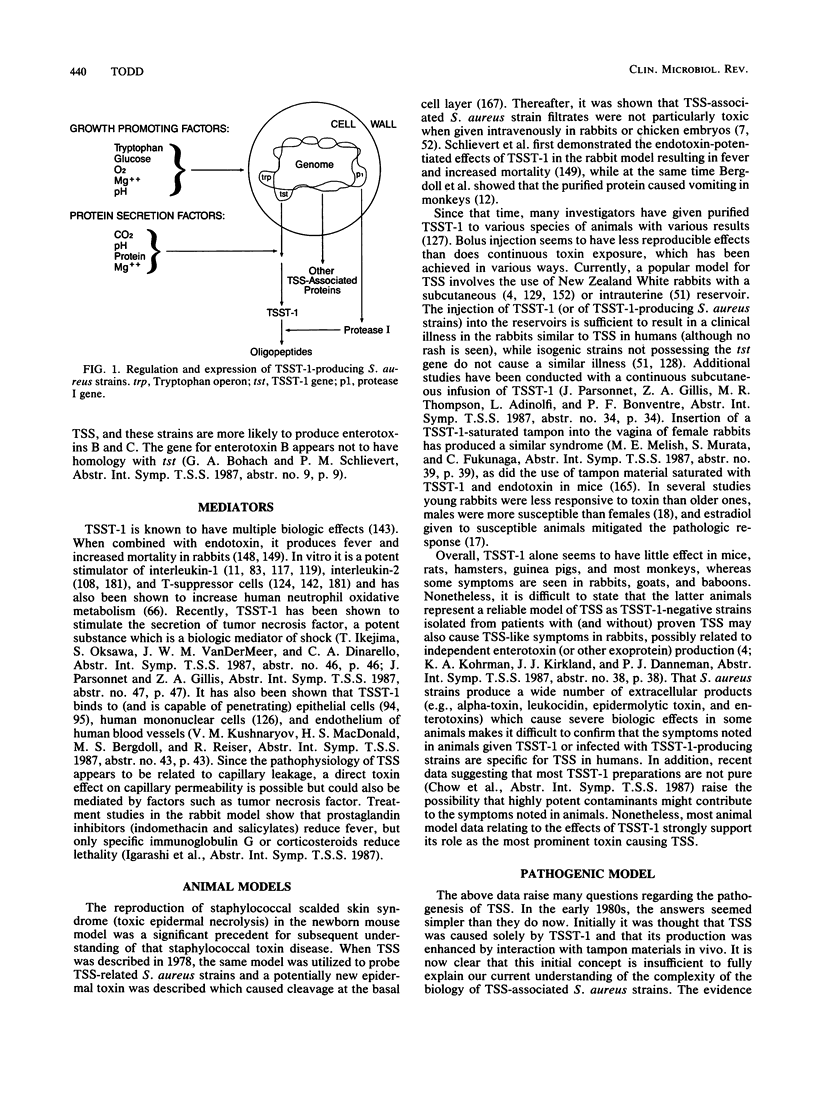
Abstract
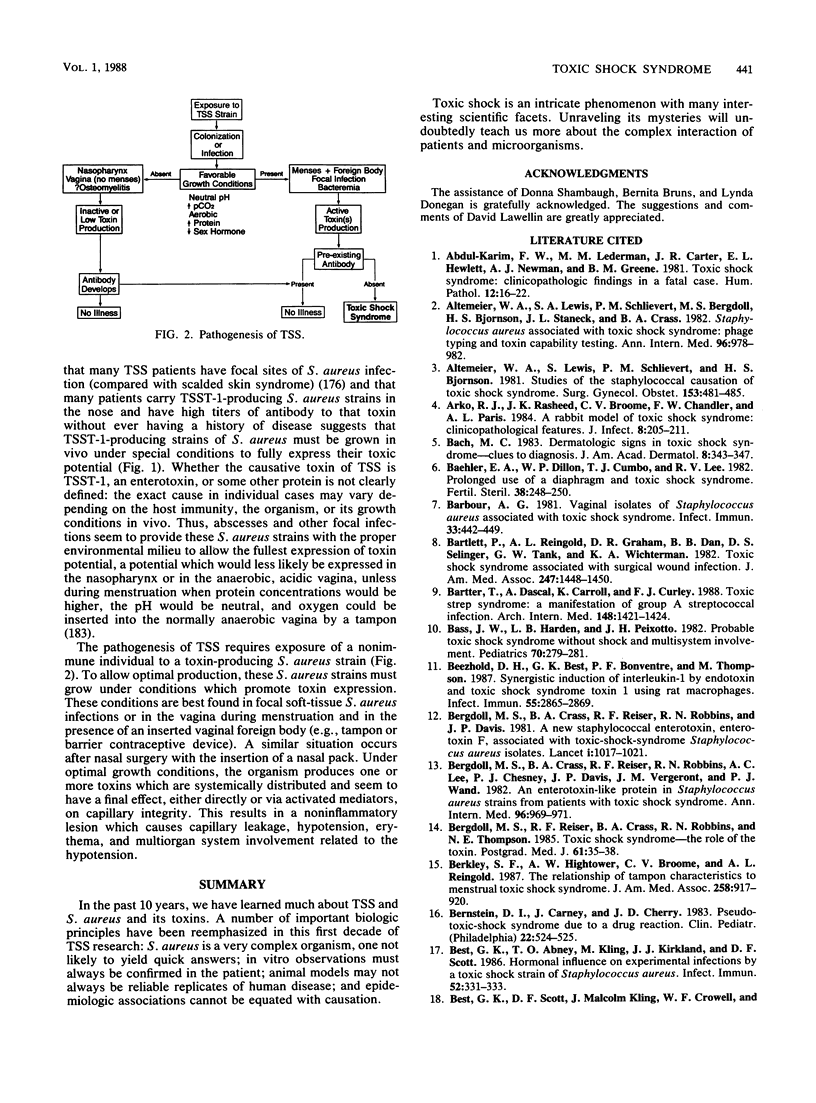
In the past 10 years, we have learned much about TSS and S. aureus and its toxins. A number of important biologic principles have been reemphasized in this first decade of TSS research: S. aureus is a very complex organism, one not likely to yield quick answers; in vitro observations must always be confirmed in the patient; animal models may not always be reliable replicates of human disease; and epidemiologic associations cannot be equated with causation. Toxic shock is an intricate phenomenon with many interesting scientific facets. Unraveling its mysteries will undoubtedly teach us more about the complex interaction of patients and microorganisms.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdul-Karim F. W., Lederman M. M., Carter J. R., Hewlett E. L., Newman A. J., Greene B. M. Toxic shock syndrome: clinicopathologic findings in a fatal case. Hum Pathol. 1981 Jan;12(1):16–22. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(81)80237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altemeier W. A., Lewis S. A., Schlievert P. M., Bergdoll M. S., Bjornson H. S., Staneck J. L., Crass B. A. Staphylococcus aureus associated with toxic shock syndrome: phage typing and toxin capability testing. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):978–982. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altemeier W. A., Lewis S., Schlievert P. M., Bjornson H. S. Studies of the staphylococcal causation of toxic shock syndrome. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1981 Oct;153(4):481–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arko R. J., Rasheed J. K., Broome C. V., Chandler F. W., Paris A. L. A rabbit model of toxic shock syndrome: clinicopathological features. J Infect. 1984 May;8(3):205–211. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(84)93859-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach M. C. Dermatologic signs in toxic shock syndrome--clues to diagnosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1983 Mar;8(3):343–347. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(83)70037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baehler E. A., Dillon W. P., Cumbo T. J., Lee R. V. Prolonged use of a diaphragm and toxic shock syndrome. Fertil Steril. 1982 Aug;38(2):248–250. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)46467-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Vaginal isolates of Staphylococcus aureus associated with toxic shock syndrome. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):442–449. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.442-449.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett P., Reingold A. L., Graham D. R., Dan B. B., Selinger D. S., Tank G. W., Wichterman K. A. Toxic shock syndrome associated with surgical wound infections. JAMA. 1982 Mar 12;247(10):1448–1450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartter T., Dascal A., Carroll K., Curley F. J. 'Toxic strep syndrome'. A manifestation of group A streptococcal infection. Arch Intern Med. 1988 Jun;148(6):1421–1424. doi: 10.1001/archinte.148.6.1421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass J. W., Harden L. B., Peixotto J. H. Probable toxic shock syndrome without shock and multisystem involvement. Pediatrics. 1982 Aug;70(2):279–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beezhold D. H., Best G. K., Bonventre P. F., Thompson M. Synergistic induction of interleukin-1 by endotoxin and toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 using rat macrophages. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):2865–2869. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.2865-2869.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergdoll M. S., Crass B. A., Reiser R. F., Robbins R. N., Davis J. P. A new staphylococcal enterotoxin, enterotoxin F, associated with toxic-shock-syndrome Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Lancet. 1981 May 9;1(8228):1017–1021. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92186-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergdoll M. S., Crass B. A., Reiser R. F., Robbins R. N., Lee A. C., Chesney P. J., Davis J. P., Vergeront J. M., Wand P. J. An enterotoxin-like protein in Staphylococcus aureus strains from patients with toxic shock syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):969–971. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergdoll M. S., Reiser R. F., Crass B. A., Robbins R. N., Thompson N. E. Toxic shock syndrome--the role of the toxin. Postgrad Med J. 1985;61 (Suppl 1):35–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkley S. F., Hightower A. W., Broome C. V., Reingold A. L. The relationship of tampon characteristics to menstrual toxic shock syndrome. JAMA. 1987 Aug 21;258(7):917–920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein D. I., Carney J., Cherry J. D. Pseudo-toxic-shock syndrome due to a drug reaction. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1983 Jul;22(7):524–525. doi: 10.1177/000992288302200715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best G. K., Abney T. O., Kling J. M., Kirkland J. J., Scott D. F. Hormonal influence on experimental infections by a toxic shock strain of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):331–333. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.331-333.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best G. K., Scott D. F., Kling J. M., Crowell W. F., Kirkland J. J. Enhanced susceptibility of male rabbits to infection with a toxic shock strain of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):727–732. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.727-732.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair J. D., Livingston D. G., Vongsnichakul R. Tampon-related toxic-shock syndrome. Histopathologic and clinical findings in a fatal case. Am J Clin Pathol. 1982 Sep;78(3):372–376. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/78.3.372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomster-Hautamaa D. A., Kreiswirth B. N., Kornblum J. S., Novick R. P., Schlievert P. M. The nucleotide and partial amino acid sequence of toxic shock syndrome toxin-1. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15783–15786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre P. F., Linnemann C., Weckbach L. S., Staneck J. L., Buncher C. R., Vigdorth E., Ritz H., Archer D., Smith B. Antibody responses to toxic-shock-syndrome (TSS) toxin by patients with TSS and by healthy staphylococcal carriers. J Infect Dis. 1984 Nov;150(5):662–666. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.5.662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre P. F., Thompson M. R., Adinolfi L. E., Gillis Z. A., Parsonnet J. Neutralization of toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 by monoclonal antibodies in vitro and in vivo. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):135–141. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.135-141.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre P. F., Weckbach L., Staneck J., Schlievert P. M., Thompson M. Production of staphylococcal enterotoxin F and pyrogenic exotoxin C by Staphylococcus aureus isolates from toxic shock syndrome-associated sources. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1023–1029. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1023-1029.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bracero L., Bowe E. Postpartum toxic shock syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1982 Jun 15;143(4):478–479. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(82)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresler M. J. Toxic shock syndrome due to occult postoperative wound infection. West J Med. 1983 Nov;139(5):710–713. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchdahl R., Levin M., Wilkins B., Gould J., Jaffe P., Matthew D. J., Dillon M. J. Toxic shock syndrome. Arch Dis Child. 1985 Jun;60(6):563–567. doi: 10.1136/adc.60.6.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson E. C. A CO2-enhanced hemolytic activity of Staphylococcus aureus associated with toxic shock syndrome: inhibition by agar. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;154(1):186–188. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.1.186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambless L. E., Greenberg B. G. Statistical methods in the study of toxic shock syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):912–917. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheek M. G., Mashchak A. C., Lau B. H. Toxic shock syndrome in a postpartum patient. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1982 Apr 1;142(7):927–928. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)32544-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesney P. J., Davis J. P., Purdy W. K., Wand P. J., Chesney R. W. Clinical manifestations of toxic shock syndrome. JAMA. 1981 Aug 14;246(7):741–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesney P. J., Jaucian R. M., McDonald R. A., Kapral F. A., Bergdoll M. S. Exfoliative dermatitis in an infant. Association with enterotoxin F-producing staphylococci. Am J Dis Child. 1983 Sep;137(9):899–901. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1983.02140350073018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesney R. W., McCarron D. M., Haddad J. G., Hawker C. D., DiBella F. P., Chesney P. J., Davis J. P. Pathogenic mechanisms of the hypocalcemia of the staphylococcal toxic-shock syndrome. J Lab Clin Med. 1983 Apr;101(4):576–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow A. W., Bartlett K. H., Percival-Smith R., Morrison B. J. Vaginal colonization with Staphylococcus aureus, positive for toxic-shock marker protein, and Escherichia coli in healthy women. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jul;150(1):80–84. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.1.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow A. W., Wittmann B. K., Bartlett K. H., Scheifele D. W. Variant postpartum toxic shock syndrome with probable intrapartum transmission to the neonate. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1984 Apr 15;148(8):1074–1079. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(84)90448-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow A. W., Wong C. K., MacFarlane A. M., Bartlett K. H. Toxic shock syndrome: clinical and laboratory findings in 30 patients. Can Med Assoc J. 1984 Feb 15;130(4):425–430. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensson B., Hedström S. A. Serological response to toxic shock syndrome toxin in Staphylococcus aureus infected patients and healthy controls. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1985 Apr;93(2):87–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1985.tb02857.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensson B., Johansson P. J., Oxelius V. A. Imbalanced serum IgG subclass pattern in toxic shock syndrome patients: deficiency of specific IgG1 and IgG4 subclass antibodies to toxic shock syndrome toxin 1. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Nov;66(2):443–449. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu M. C., Melish M. E., James J. F. Tryptophan auxotypy associated with Staphylococcus aureus that produce toxic-shock-syndrome toxin. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jun;151(6):1157–1158. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.6.1157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clyne M., De Azavedo J., Carlson E., Arbuthnott J. Production of gamma-hemolysin and lack of production of alpha-hemolysin by Staphylococcus aureus strains associated with toxic shock syndrome. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):535–539. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.535-539.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Falkow S. Protein antigens from Staphylococcus aureus strains associated with toxic-shock syndrome. Science. 1981 Feb 20;211(4484):842–844. doi: 10.1126/science.7466361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Graves L. M., Hayes P. S., Gibson R. J., Rasheed J. K., Feeley J. C. Toxic shock syndrome: modification and comparison of methods for detecting marker proteins in Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):372–375. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.372-375.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone L. A., Woodard D. R., Schlievert P. M., Tomory G. S. Clinical and bacteriologic observations of a toxic shock-like syndrome due to Streptococcus pyogenes. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 16;317(3):146–149. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707163170305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crass B. A., Bergdoll M. S. Involvement of coagulase-negative staphylococci in toxic shock syndrome. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jan;23(1):43–45. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.1.43-45.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crass B. A., Bergdoll M. S. Involvement of staphylococcal enterotoxins in nonmenstrual toxic shock syndrome. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jun;23(6):1138–1139. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.6.1138-1139.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crass B. A., Bergdoll M. S. Toxin involvement in toxic shock syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1986 May;153(5):918–926. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.5.918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. P., Chesney P. J., Wand P. J., LaVenture M. Toxic-shock syndrome: epidemiologic features, recurrence, risk factors, and prevention. N Engl J Med. 1980 Dec 18;303(25):1429–1435. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198012183032501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. P., Osterholm M. T., Helms C. M., Vergeront J. M., Wintermeyer L. A., Forfang J. C., Judy L. A., Rondeau J., Schell W. L. Tri-state toxic-shock syndrome study. II. Clinical and laboratory findings. J Infect Dis. 1982 Apr;145(4):441–448. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.4.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. P., Vergeront J. M. The effect of publicity on the reporting of toxic-shock syndrome in Wisconsin. J Infect Dis. 1982 Apr;145(4):449–457. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.4.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeYoung P., Martyn J., Wass H., Harth L., Crichton E., Reynolds C. Toxic shock syndrome associated with a contraceptive diaphragm. Can Med Assoc J. 1982 Oct 1;127(7):611–612. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donawa M. E., Schmid G. R., Osterholm M. T. Toxic shock syndrome: chronology of state and federal epidemiologic studies and regulatory decision-making. Public Health Rep. 1984 Jul-Aug;99(4):342–350. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornan K. J., Thompson D. M., Conn A. R., Wittmann B. K., Stiver H. G., Chow A. W. Toxic shock syndrome in the postoperative patient. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1982 Jan;154(1):65–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbaum D. J., Wood C., Abuabara F., Morhenn V. B. Bullae in a patient with toxic shock syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1984 Feb;10(2 Pt 1):267–272. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(84)70035-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher C. J., Jr, Horowitz B. Z., Nolan S. M. The clinical spectrum of toxic shock syndrome. West J Med. 1981 Sep;135(3):175–182. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher C. J., Jr, Horowitz Z., Albertson T. E. Cardiorespiratory failure in toxic shock syndrome: effect of dobutamine. Crit Care Med. 1985 Mar;13(3):160–165. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198503000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. F., Goodpasture H. C., Peterie J. D., Voth D. W. Toxic shock syndrome in menstruating women. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Feb;94(2):156–163. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-2-156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedell S., Mercer L. J. Nonmenstrual toxic shock syndrome. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 1986 Jun;41(6):336–341. doi: 10.1097/00006254-198606000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galea P., Goel K. M. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS) in children. Scott Med J. 1987 Feb;32(1):28–29. doi: 10.1177/003693308703200115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbe P. L., Arko R. J., Reingold A. L., Graves L. M., Hayes P. S., Hightower A. W., Chandler F. W., Broome C. V. Staphylococcus aureus isolates from patients with nonmenstrual toxic shock syndrome. Evidence for additional toxins. JAMA. 1985 May 3;253(17):2538–2542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetz M. B., Proctor R. A., Reiser R. F., Bergdoll M. S. Effect of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin F on human neutrophil oxidative metabolism. J Infect Dis. 1983 Oct;148(4):764–764. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.4.764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S. L., LaPeter K. S. Evidence for postpartum toxic-shock syndrome in a mother-infant pair. Am J Med. 1982 Jan;72(1):169–172. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90605-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson T. L., Swinger G. L., Booth A. L., Hutcheson R. H., Jr, Schaffner W. Survey of tampon use and toxic shock syndrome, Tennessee, 1979 to 1981. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1982 Jun 15;143(4):369–374. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(82)90074-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey M., Horwitz R. I., Feinstein A. R. Diagnostic bias and toxic shock syndrome. Am J Med. 1984 Mar;76(3):351–360. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90651-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey M., Horwitz R. I., Feinstein A. R. Toxic shock and tampons. Evaluation of the epidemiologic evidence. JAMA. 1982 Aug 20;248(7):840–846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes P. S., Graves L. M., Feeley J. C., Hancock G. A., Cohen M. L., Reingold A. L., Broome C. V., Hightower A. W. Production of toxic-shock-associated protein(s) in Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from 1956 through 1982. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jul;20(1):43–46. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.1.43-46.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward J., Vergeront J. M., Stolz-LaVerriere S. J., Bohn M. J., Davis J. P. A hospital discharge code review of toxic shock syndrome in Wisconsin. Am J Epidemiol. 1986 May;123(5):876–883. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helgerson S. D., Foster L. R. Toxic shock syndrome in Oregon: epidemiologic findings. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):909–911. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helgerson S. D., Mallery B. L., Foster L. R. Toxic shock syndrome in Oregon. Risk of recurrence. JAMA. 1984 Dec 28;252(24):3402–3404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland K. T., Ingham E., Eady E. A., Gowland G. Toxic shock syndrome: the effect of solid phase materials on the physiology of Staphylococcus aureus. Postgrad Med J. 1985;61 (Suppl 1):39–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz R. I., Feinstein A. R., Harvey M. R. Case-control research. Temporal precedence and other problems of the exposure-disease relationship. Arch Intern Med. 1984 Jun;144(6):1257–1259. doi: 10.1001/archinte.144.6.1257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull H. F., Mann J. M., Sands C. J., Gregg S. H., Kaufman P. W. Toxic shock syndrome related to nasal packing. Arch Otolaryngol. 1983 Sep;109(9):624–626. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1983.00800230060015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz R. M., Ackerman A. B. Cutaneous pathology of the toxic shock syndrome. Am J Dermatopathol. 1985 Dec;7(6):563–578. doi: 10.1097/00000372-198512000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz R. M., Rivera H. P., Gooch M. H., Slama T. G., Handt A., Weiss J. Toxic shock syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis? Case reports showing clinical similarity and histologic separation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1982 Aug;7(2):246–254. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(82)70114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde L. Toxic shock syndrome associated with diaphragm use. J Fam Pract. 1983 Mar;16(3):616-7, 620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi H., Fujikawa H., Shingaki M., Bergdoll M. S. Latex agglutination test for staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome toxin 1. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):509–512. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.509-512.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikejima T., Dinarello C. A., Gill D. M., Wolff S. M. Induction of human interleukin-1 by a product of Staphylococcus aureus associated with toxic shock syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1984 May;73(5):1312–1320. doi: 10.1172/JCI111334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Immerman R. P., Greenman R. L. Toxic shock syndrome associated with pyomyositis caused by a strain of Staphylococcus aureus that does not produce toxic-shock-syndrome toxin-1. J Infect Dis. 1987 Sep;156(3):505–507. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.3.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson J. A., Kasworm E. M., Crass B. A., Bergdoll M. S. Nasal carriage of toxigenic Staphylococcus aureus and prevalence of serum antibody to toxic-shock-syndrome toxin 1 in Utah. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):356–359. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson J. A., Kasworm E. M. Toxic shock syndrome after nasal surgery. Case reports and analysis of risk factors. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1986 Mar;112(3):329–332. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1986.03780030093019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahler R. C., Boyce J. M., Bergdoll M. S., Lockwood W. R., Taylor M. R. Toxic shock syndrome associated with TSST-1 producing coagulase-negative staphylococci. Am J Med Sci. 1986 Nov;292(5):310–312. doi: 10.1097/00000441-198611000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapral F. A. Epidermal toxin production by Staphylococcus aureus strains from patients with toxic shock syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):972–974. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehrberg M. W., Latham R. H., Haslam B. T., Hightower A., Tanner M., Jacobson J. A., Barbour A. G., Noble V., Smith C. B. Risk factors for staphylococcal toxic-shock syndrome. Am J Epidemiol. 1981 Dec;114(6):873–879. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreiswirth B. N., Löfdahl S., Betley M. J., O'Reilly M., Schlievert P. M., Bergdoll M. S., Novick R. P. The toxic shock syndrome exotoxin structural gene is not detectably transmitted by a prophage. Nature. 1983 Oct 20;305(5936):709–712. doi: 10.1038/305709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreiswirth B. N., Novick R. P., Schlievert P. M., Bergdoll M. Genetic studies on Staphylococcal strains from patients with toxic shock syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):974–977. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreiswirth B. N., O'Reilly M., Novick R. P. Genetic characterization and cloning of the toxic shock syndrome exotoxin. Surv Synth Pathol Res. 1984;3(1):73–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreiswirth B. N., Schlievert P. M., Novick R. P. Evaluation of coagulase-negative staphylococci for ability to produce toxic shock syndrome toxin 1. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;25(10):2028–2029. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.10.2028-2029.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushnaryov V. M., Bergdoll M. S., MacDonald H. S., Vellinga J., Reiser R. Study of staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome toxin in human epithelial cell culture. J Infect Dis. 1984 Oct;150(4):535–545. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.4.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushnaryov V. M., MacDonald H. S., Reiser R., Bergdoll M. S. Staphylococcal toxic shock toxin specifically binds to cultured human epithelial cells and is rapidly internalized. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):566–571. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.566-571.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanes S. F., Poole C., Dreyer N. A., Lanza L. L. Toxic shock syndrome, contraceptive methods, and vaginitis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1986 May;154(5):989–991. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(86)90734-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langmuir A. D., Worthen T. D., Solomon J., Ray C. G., Petersen E. The Thucydides syndrome. A new hypothesis for the cause of the plague of Athens. N Engl J Med. 1985 Oct 17;313(16):1027–1030. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198510173131618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lansdell L. W., Taplin D., Aldrich T. E. Recovery of Staphylococcus aureus from multiple body sites in menstruating women. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):307–310. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.307-310.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkin S. M., Williams D. N., Osterholm M. T., Tofte R. W., Posalaky Z. Toxic shock syndrome: clinical, laboratory, and pathologic findings in nine fatal cases. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):858–864. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latham R. H., Kehrberg M. W., Jacobson J. A., Smith C. B. Toxic shock syndrome in Utah: a case-control and surveillance study. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):906–908. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. C., Crass B. A., Bergdoll M. S. Investigation by syringe method of effect of tampons on production in vitro of toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 by Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jan;25(1):87–90. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.1.87-90.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnemann C. C., Jr, Knarr D. Increasing incidence of toxic shock syndrome in the 1970s. Am J Public Health. 1986 May;76(5):566–567. doi: 10.2105/ajph.76.5.566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loch E. G., Crass B. A., Bergdoll M. S. Staphylococcus aureus--toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 antibody titers in serum of German women. Arch Gynecol. 1986;237(4):229–233. doi: 10.1007/BF02133785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald K. L., Osterholm M. T., Hedberg C. W., Schrock C. G., Peterson G. F., Jentzen J. M., Leonard S. A., Schlievert P. M. Toxic shock syndrome. A newly recognized complication of influenza and influenzalike illness. JAMA. 1987 Feb 27;257(8):1053–1058. doi: 10.1001/jama.257.8.1053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz L. E., Hightower A. W., Broome C. V., Reingold A. L. Toxic shock syndrome. Evaluation of national surveillance data using a hospital discharge survey. JAMA. 1987 Jul 3;258(1):75–78. doi: 10.1001/jama.258.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIvor M. E., Levin M. L. Treatment of recurrent toxic shock syndrome with oral contraceptive agents. Md State Med J. 1982 Sep;31(9):56–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna U. G., Meadows J. A., 3rd, Brewer N. S., Wilson W. R., Perrault J. Toxic shock syndrome, a newly recognized disease entity. Report of 11 cases. Mayo Clin Proc. 1980 Nov;55(11):663–672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Micusan V. V., Mercier G., Bhatti A. R., Reiser R. F., Bergdoll M. S., Oth D. Production of human and murine interleukin-2 by toxic shock syndrome toxin-1. Immunology. 1986 Jun;58(2):203–208. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. T., Parsonnet J., Tsai Y. C., Kendrick M., Hickman R. K., Kaśs E. H. Control of production of toxic-shock-syndrome toxin-1 (TSST-1) by magnesium ion. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jun;151(6):1158–1161. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.6.1158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison V. A., Oldfield E. C., 3rd Postoperative toxic shock syndrome. Arch Surg. 1983 Jul;118(7):791–794. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1983.01390070003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notermans S., van Leeuwen W. J., Dufrenne J., Tips P. D. Serum antibodies to enterotoxins produced by Staphylococcus aureus with special reference to enterotoxin F and toxic shock syndrome. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1055–1060. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1055-1060.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterholm M. T., Davis J. P., Gibson R. W., Forfang J. C., Stolz S. J., Vergeront J. M. Toxic shock syndrome: relation to catamenial products, personal health and hygiene, and sexual practices. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):954–958. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterholm M. T., Davis J. P., Gibson R. W., Mandel J. S., Wintermeyer L. A., Helms C. M., Forfang J. C., Rondeau J., Vergeront J. M. Tri-state toxic-state syndrome study. I. Epidemiologic findings. J Infect Dis. 1982 Apr;145(4):431–440. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.4.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterholm M. T., Forfang J. C. Surveillance of toxic shock syndrome in Minnesota: comments on national surveillance. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):887–890. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterholm M. T., Forfang J. C. Toxic-shock syndrome in Minnesota: results of an active-passive surveillance system. J Infect Dis. 1982 Apr;145(4):458–464. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.4.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris A. L., Herwaldt L. A., Blum D., Schmid G. P., Shands K. N., Broome C. V. Pathologic findings in twelve fatal cases of toxic shock syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):852–857. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsonnet J., Gillis Z. A., Pier G. B. Induction of interleukin-1 by strains of Staphylococcus aureus from patients with nonmenstrual toxic shock syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;154(1):55–63. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsonnet J., Harrison A. E., Spencer S. E., Reading A., Parsonnet K. C., Kass E. H. Nonproduction of toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 by coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1370–1372. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1370-1372.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsonnet J., Hickman R. K., Eardley D. D., Pier G. B. Induction of human interleukin-1 by toxic-shock-syndrome toxin-1. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):514–522. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. R. Epidemiologic comparisons of incidence of toxic shock syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):891–891. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Schlievert P. M., Conroy W., Kelly J. A., Spika J., Quie P. G. Protection against staphylococcal pyrogenic exotoxin type C-enhanced endotoxin lethality with methylprednisolone and IgG. J Infect Dis. 1983 Feb;147(2):358–358. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.2.358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petitti D. B., Reingold A., Chin J. The incidence of toxic shock syndrome in Northern California. 1972 through 1983. JAMA. 1986 Jan 17;255(3):368–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petitti D., D'Agostino R. B., Oldman M. J. Nonmenstrual toxic shock syndrome. Methodologic problems in estimating incidence and delineating risk factors. J Reprod Med. 1987 Jan;32(1):10–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poindexter N. J., Schlievert P. M. Binding of toxic-shock-syndrome toxin-1 to human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):122–129. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poindexter N. J., Schlievert P. M. Suppression of immunoglobulin-secreting cells from human peripheral blood by toxic-shock-syndrome toxin-1. J Infect Dis. 1986 Apr;153(4):772–779. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.4.772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poindexter N. J., Schlievert P. M. Toxic-shock-syndrome toxin 1-induced proliferation of lymphocytes: comparison of the mitogenic response of human, murine, and rabbit lymphocytes. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jan;151(1):65–72. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quimby F., Nguyen H. T. Animal studies of toxic shock syndrome. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1985;12(1):1–44. doi: 10.3109/10408418509104424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasheed J. K., Arko R. J., Feeley J. C., Chandler F. W., Thornsberry C., Gibson R. J., Cohen M. L., Jeffries C. D., Broome C. V. Acquired ability of Staphylococcus aureus to produce toxic shock-associated protein and resulting illness in a rabbit model. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):598–604. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.598-604.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves M. W., Arko R. J., Chandler F. W., Bridges N. B. Affinity purification of staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 and its pathologic effects in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):431–439. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.431-439.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves M. W., Pine L., Feeley J. C., Wells D. E. Presence of toxic shock toxin in toxic shock and other clinical strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):590–597. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.590-597.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reingold A. L., Dan B. B., Shands K. N., Broome C. V. Toxic-shock syndrome not associated with menstruation. A review of 54 cases. Lancet. 1982 Jan 2;1(8262):1–4. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92552-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reingold A. L., Hargrett N. T., Dan B. B., Shands K. N., Strickland B. Y., Broome C. V. Nonmenstrual toxic shock syndrome: a review of 130 cases. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):871–874. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reingold A. L., Hargrett N. T., Shands K. N., Dan B. B., Schmid G. P., Strickland B. Y., Broome C. V. Toxic shock syndrome surveillance in the United States, 1980 to 1981. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):875–880. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reingold A. L. Toxic shock in the United States of America: epidemiology. Postgrad Med J. 1985;61 (Suppl 1):23–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiser R. F., Hinzman S. J., Bergdoll M. S. Production of toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 by Staphylococcus aureus restricted to endogenous air in tampons. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1450–1452. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1450-1452.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiser R. F., Robbins R. N., Khoe G. P., Bergdoll M. S. Purification and some physicochemical properties of toxic-shock toxin. Biochemistry. 1983 Aug 2;22(16):3907–3912. doi: 10.1021/bi00285a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington K. M., Buller R. S., Kelly J. R. Effect of the Today contraceptive sponge on growth and toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 production by Staphylococcus aureus. Obstet Gynecol. 1987 Apr;69(4):563–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritz H. L., Kirkland J. J., Bond G. G., Warner E. K., Petty G. P. Association of high levels of serum antibody to staphylococcal toxic shock antigen with nasal carriage of toxic shock antigen-producing strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):954–958. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.954-958.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins R. N., Reiser R. F., Hehl G. L., Bergdoll M. S. Production of toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 by Staphylococcus aureus as determined by tampon disk-membrane-agar method. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1446–1449. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1446-1449.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosene K. A., Copass M. K., Kastner L. S., Nolan C. M., Eschenbach D. A. Persistent neuropsychological sequelae of toxic shock syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):865–870. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlech W. F., 3rd, Shands K. N., Reingold A. L., Dan B. B., Schmid G. P., Hargrett N. T., Hightower A., Herwaldt L. A., Neill M. A., Band J. D. Risk factors for development of toxic shock syndrome. Association with a tampon brand. JAMA. 1982 Aug 20;248(7):835–839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M. Alteration of immune function by staphylococcal pyrogenic exotoxin type C: possible role in toxic-shock syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1983 Mar;147(3):391–398. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.3.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M. Biological properties of toxic shock syndrome exotoxin. Surv Synth Pathol Res. 1984;3(1):54–62. doi: 10.1159/000156915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M., Blomster D. A., Kelly J. A. Toxic shock syndrome Staphylococcus aureus: effect of tampons on toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 production. Obstet Gynecol. 1984 Nov;64(5):666–671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M., Blomster D. A. Production of staphylococcal pyrogenic exotoxin type C: influence of physical and chemical factors. J Infect Dis. 1983 Feb;147(2):236–242. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.2.236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M. Effect of magnesium on production of toxic-shock-syndrome toxin-1 by Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):618–620. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M., Kelly J. A. Staphylococcal pyrogenic exotoxin type C: further characterization. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):982–986. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M., Osterholm M. T., Kelly J. A., Nishimura R. D. Toxin and enzyme characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from patients with and without toxic shock syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):937–940. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M., Shands K. N., Dan B. B., Schmid G. P., Nishimura R. D. Identification and characterization of an exotoxin from Staphylococcus aureus associated with toxic-shock syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):509–516. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutzer S. E., Fischetti V. A., Zabriskie J. B. Toxic shock syndrome and lysogeny in Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1983 Apr 15;220(4594):316–318. doi: 10.1126/science.6220467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. F., Kling J. M., Best G. K. Immunological protection of rabbits infected with Staphylococcus aureus isolates from patients with toxic shock syndrome. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):441–444. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.441-444.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. F., Kling J. M., Kirkland J. J., Best G. K. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from patients with toxic shock syndrome, using polyethylene infection chambers in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):383–387. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.383-387.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands K. N., Schmid G. P., Dan B. B., Blum D., Guidotti R. J., Hargrett N. T., Anderson R. L., Hill D. L., Broome C. V., Band J. D. Toxic-shock syndrome in menstruating women: association with tampon use and Staphylococcus aureus and clinical features in 52 cases. N Engl J Med. 1980 Dec 18;303(25):1436–1442. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198012183032502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierks M. R., Reilly P. J. Application of cross-linked carboxymethyl cellulose degradation by beta-glucosidase and vaginal microbes to toxic shock syndrome. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Sep;50(3):634–637. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.3.634-637.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smirniotopoulos T. T., Maheswaran V. Early attenuation of Toxic Shock syndrome with intravenous nafcillin sodium. W V Med J. 1983 Mar;79(3):52–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smirniotopoulos T. T. Update on toxic shock syndrome. Recognizing and treating the mild case. Postgrad Med. 1983 Oct;74(4):369–372. doi: 10.1080/00325481.1983.11698481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solino Noleto A. L., da Costa Cesar E., Bergdoll M. S. Antibodies to staphylococcal enterotoxins and toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 in sera of patients and healthy people in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Nov;24(5):809–811. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.5.809-811.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperber S. J., Francis J. B. Toxic shock syndrome during an influenza outbreak. JAMA. 1987 Feb 27;257(8):1086–1087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stallones R. A. A review of the epidemiologic studies of toxic shock syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):917–920. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolz S. J., Davis J. P., Vergeront J. M., Crass B. A., Chesney P. J., Wand P. J., Bergdoll M. S. Development of serum antibody to toxic shock toxin among individuals with toxic shock syndrome in Wisconsin. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):883–889. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thek J., Braun B. J., Skiendzielewski J. J. The spectrum of toxic shock syndrome. Am J Emerg Med. 1983 Jul;1(1):30–34. doi: 10.1016/0735-6757(83)90035-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas S. W., Baird I. M., Frazier R. D. Toxic shock syndrome following submucous resection and rhinoplasty. JAMA. 1982 May 7;247(17):2402–2403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tierno P. M., Jr, Hanna B. A., Davies M. B. Growth of toxic-shock-syndrome strain of Staphylococcus aureus after enzymic degradation of 'Rely' tampon component. Lancet. 1983 Mar 19;1(8325):615–618. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91794-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tierno P. M., Jr, Hanna B. A. In vitro amplification of toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 by intravaginal devices. Contraception. 1985 Feb;31(2):185–194. doi: 10.1016/0010-7824(85)90033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tierno P. M., Jr, Malloy V., Matias J. R., Hanna B. A. Effects of toxic shock syndrome Staphylococcus aureus, endotoxin and tampons in a mouse model. Clin Invest Med. 1987 Mar;10(2):64–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toback J., Fayerman J. W. Toxic shock syndrome following septorhinoplasty. Implications for the head and neck surgeon. Arch Otolaryngol. 1983 Sep;109(9):627–629. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1983.00800230063016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. K., Franco-Buff A., Lawellin D. W., Vasil M. L. Phenotypic distinctiveness of Staphylococcus aureus strains associated with toxic shock syndrome. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):339–344. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.339-344.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. K. Pathogenesis of toxic shock syndrome: clinical-bacteriological correlates. Surv Synth Pathol Res. 1984;3(1):63–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. K., Ressman M., Caston S. A., Todd B. H., Wiesenthal A. M. Corticosteroid therapy for patients with toxic shock syndrome. JAMA. 1984 Dec 28;252(24):3399–3402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. K. Staphylococcal toxin syndromes. Annu Rev Med. 1985;36:337–347. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.36.020185.002005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. K., Todd B. H., Franco-Buff A., Smith C. M., Lawellin D. W. Influence of focal growth conditions on the pathogenesis of toxic shock syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1987 Apr;155(4):673–681. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.4.673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. K. Toxic shock syndrome--scientific uncertainty and the public media. Pediatrics. 1981 Jun;67(6):921–923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. K. Toxic shock syndrome: a perspective through the looking glass. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):839–842. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. K., Wiesenthal A. M., Ressman M., Caston S. A., Hopkins R. S. Toxic shock syndrome. II. Estimated occurrence in Colorado as influenced by case ascertainment methods. Am J Epidemiol. 1985 Nov;122(5):857–867. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J., Fishaut M., Kapral F., Welch T. Toxic-shock syndrome associated with phage-group-I Staphylococci. Lancet. 1978 Nov 25;2(8100):1116–1118. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92274-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tofte R. W., Williams D. N. Clinical and laboratory manifestations of toxic shock syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):843–847. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tofte R. W., Williams D. N. Toxic shock syndrome. Evidence of a broad clinical spectrum. JAMA. 1981 Nov 13;246(19):2163–2167. doi: 10.1001/jama.246.19.2163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tofte R. W., Williams D. N. Toxic shock syndrome: clinical and laboratory features in 15 patients. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Feb;94(2):149–156. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-2-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama T., Kamagata Y., Yan X. J., Kohno M., Yoshioka M., Fujikawa H., Igarashi H., Okubo M., Awano F., Saito-Taki T. Study of the biological activities of toxic shock syndrome toxin-1: II. Induction of the proliferative response and the interleukin 2 production by T cells from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells stimulated with the toxin. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Jun;68(3):638–647. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergeront J. M., Stolz S. J., Crass B. A., Nelson D. B., Davis J. P., Bergdoll M. S. Prevalence of serum antibody to staphylococcal enterotoxin F among Wisconsin residents: implications for toxic-shock syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1983 Oct;148(4):692–698. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.4.692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner G., Bohr L., Wagner P., Petersen L. N. Tampon-induced changes in vaginal oxygen and carbon dioxide tensions. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1984 Jan 15;148(2):147–150. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(84)80165-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch T. R., Beekman R. A. Toxic shock syndrome in the male. A clinical reminder. N Y State J Med. 1982 Oct;82(11):1585–1586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston W. L., Todd J. K. Toxic-shock syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1981 Apr;4(4):478–480. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(81)80263-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield J. W., Valenti W. M., Magnussen C. R. Toxic shock syndrome in the puerperium. JAMA. 1981 Oct 16;246(16):1806–1807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick M. R., Bahn R. C., McKenna U. G. Toxic shock syndrome. A fatal case with autopsy findings. Mayo Clin Proc. 1982 Sep;57(9):583–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesenthal A. M., Ressman M., Caston S. A., Todd J. K. Toxic shock syndrome. I. Clinical exclusion of other syndromes by strict and screening definitions. Am J Epidemiol. 1985 Nov;122(5):847–856. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesenthal A. M., Todd J. K. Toxic shock syndrome in children aged 10 years or less. Pediatrics. 1984 Jul;74(1):112–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. D. Toxic shock syndrome and diaphragm use. J Adolesc Health Care. 1983 Dec;4(4):290–291. doi: 10.1016/s0197-0070(83)80015-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zettergren J. G., Leifer M. J., Nakashima H., Wuepper K. D. Human mononuclear leukocyte transglutaminase activity is enhanced by streptococcal erythrogenic toxin and a staphylococcal mitogenic factor associated with toxic shock syndrome. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Dec 20;802(3):385–389. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90354-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Azavedo J. C., Arbuthnott J. P. Toxicity of staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):314–317. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.314-317.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Azavedo J. C., Foster T. J., Hartigan P. J., Arbuthnott J. P., O'Reilly M., Kreiswirth B. N., Novick R. P. Expression of the cloned toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 gene (tst) in vivo with a rabbit uterine model. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):304–309. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.304-309.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Azavedo J. C., Lucken R. N., Arbuthnott J. P. Effect of toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 on chicken embryos. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):710–712. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.710-712.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Nooij M. P., van Leeuwen W. J., Notermans S. Enterotoxin production by strains of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from clinical and non-clinical specimens with special reference to enterotoxin F and toxic shock syndrome. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Dec;89(3):499–505. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400071060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Saxe M. J., Wieneke A. A., de Azevedo J., Arbuthnott J. P. Staphylococci associated with toxic shock syndrome in the United Kingdom. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):991–996. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



