Figure 1. .
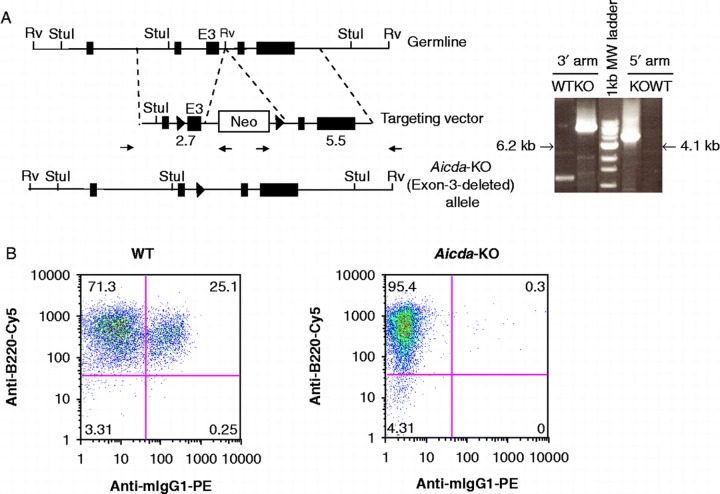
Generation and functional characterization of Aicda deficient mice. A) Gene targeting strategy used to delete the catalytic domain (exon-3) of Aicda locus. The structure of the AID domains is shown in top. The location of the homology arms in the targeting vector is indicated. The schematic of targeting construct used to delete the catalytic domain of AID (exon-3) is shown in the middle. The solid triangles represent Cre recombination sites and the Neomycin cassette was subsequently removed by expression of Cre-recombinase. Representative WT or KO PCR products using 3′ or 5′ arm analysis at the Aicda locus is shown in the right panel. The size of Aicda KO PCR product is indicated and corresponds to the modified locus. Notice that one primer is located in the Neomycin cassette and therefore only detects the targeted Aicda locus. B) FACS analysis of LPS/IL4 stimulated WT or AID KO B cells in vitro. Percentage of IgM or IgG1 are indicated in each quadrant. B220-FITC is used as a B-cell marker.