Abstract
The innate and adaptive immune systems are important mechanisms for resistance to pathogens in the female lower genital tract. Lactobacilli at this site help maintain a healthy vagina by producing several factors including lactic acid. Indeed, bacterial vaginosis, a condition in which the genital microbiota is altered, is strongly associated with increased rates of a number of infections including HIV. However, the precise factors that contribute to increased rates of microbial and viral infections in bacterial vaginosis remain to be elucidated.
We have studied the effects of bacterial microbiota in the lower genital tract on innate immunity and have found that Toll-like receptor ligands and short chain fatty acids, produced by bacterial microbiota, have dramatic effects on immune function. In this review, we will discuss these results, in addition to some recent articles that we believe will enhance our understanding of how microbes might interact with the immune system.
Keywords: innate immunity, short chain fatty acids, vaginal microbiota
Introduction
The female genital tract is equipped to deal with a variety of foreign substances including spermatozoa, a fetus that is immunologically distinct from its mother, and a wide array of pathogens. These pathogens include viruses, bacteria, fungi and parasites. To add to this complexity, the various parts of the female genital tract are influenced by sex hormones during menstruation.1 All of these components act in concert to optimize the conditions for reproduction and a successful pregnancy. The female genital tract is protected against these various invaders by two inter-related mechanisms: the innate and the adaptive immune systems. The intricate interplay between the two arms of the immune system, plus their interaction with the genital tract bacterial microflora and the host epithelial cells, is ultimately responsible for the health of the lower female genital tract.2, 3
There are several layers of innate protection in the lower female genital tract. The epithelial cells covering the length of the female genital tract act as the first line of defense and a physical barrier by inhibiting the passage of pathogens and their associated particles. The epithelial cells also produce mucus, which covers the internal surface of the vagina and cervix and serves to trap infectious agents.4, 5 Moreover, the presence of several antimicrobial proteins (such as defensins) in the mucus helps combat many pathogens before they gain entry into the epithelial layer of the genital tract.6
The epithelial cells further help protect against pathogens by expressing many receptors known to be important in immune responses, including a number of Toll-like receptors (TLRs), MD-2, as well as major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. These molecules help recognize, process and initiate cellular immune responses to obliterate pathogens. When activated, epithelial cells can also produce a variety of cytokines and chemokines such as TNFα, G-CSF, GM-CSF, IL-6 and IL-8, to help recruit immune cells, induce their differentiation/activation and develop successful immune responses.1, 2
If the protection afforded by the epithelial barrier is compromised, however, pathogens encounter a second layer of innate defense consisting of specialized immune cells and their products. These cells, which include macrophages, dendritic cells, neutrophils, and natural killer cells, are dispersed throughout the female genital tract, surveying that environment. Should these cells come across pathogens, they can take up, process, and/or destroy them.1, 3
The innate immune system recognizes pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPS) through various pattern recognition receptors such as the TLR and NOD-like receptors (NLRs). The interaction between these receptors and their respective microbial ligands quickly results in the production of cytokines, chemokines, and antimicrobial products in order to slow down or stop pathogen replication and begin to eradicate the pathogen. While such actions occur quickly, they lack in specificity and memory. An antigen-specific attack is launched by the adaptive arm of the immune system, consisting of T and B cells, after the microbial antigens have been recognized, processed and presented by antigen presenting cells. The cross-talk between the innate and the adaptive immune systems, as well as the important role that T and B cells play in conferring long-term immunity in the genital tract, have been discussed elsewhere. Here, we shall focus on another crucial component of this multifaceted system: the commensal bacteria and their effect on mucosal immune responses.
The Lower Genital Tract Bacterial Microbiome
The lower genital tract of women is colonized by commensal bacteria that can affect immune responses. Identifying the types of bacteria present at this mucosal site is therefore a critical step in understanding how immunity is affected by the microbiota. Clinical diagnostic criteria have classically divided genital bacterial microbiota into at least two large groups; microbiota that is considered to be healthy; and bacteria associated with bacterial vaginosis (BV). While healthy microbiota is dominated by Lactobacillus species, BV can be variable between women but, in most cases, consists largely of colonization by several types of anaerobic bacteria and Gardnerella vaginalis.7–9 Recent studies have largely confirmed the existence of these two groupings using molecular techniques such as direct sequencing or PCR of the 16S rRNA genes to identify and quantify the types of bacteria present since culture may skew the proportions of bacteria identified at this mucosal site.10–12 More recently, Ravel et al.13 sequenced the genital microbiota of 396 asymptomatic North American women and found there were roughly five types of bacterial communities, dominated by either Lactobacillus iners, L. crispatus, L. gasseri, L. jensenii, and a fifth group that was not dominated by lactobacilli but instead consisted of mostly anaerobes and G. vaginalis. Also recently, Hummelen et al. showed that, in a group of HIV+ African women, L. iners and G. vaginalis were the main constituents of the vaginal microbiota.14 Prevotella bivia, a pathogen known to invade epithelial cells and to cause inflammatory responses15, dominated in this cohort of African women who were also BV+. Interestingly, L. crispatus was more strongly associated with a healthy vaginal pH than L. iners in the HIV+ African cohort, although at higher frequencies L. iners also correlated with a vaginal pH of less than 4.5.14
A key feature of colonization by predominantly Lactobacillus is a relatively low pH (pH < 4.5), due to production of large amounts of lactic acid by these bacteria.16 This low pH is believed to help protect against colonization by pathogens. Lactobacilli are also thought to contribute to the health of the vagina by producing H2O2 and by competing against more pathogenic microorganisms.17–23 In contrast, bacteria in BV produce relatively little lactic acid, but make a number of immunomodulatory substances including succinate, sialydases and proteases24, as well as proinflammatory substances such as lipopolysaccharides (LPS), lipoteichoic acids (LTA) and peptidoglycans (PGN).25, 26 These microbial products can stimulate cells through TLRs or NLRs that are present on immune cells and other cells in the female lower genital tract.
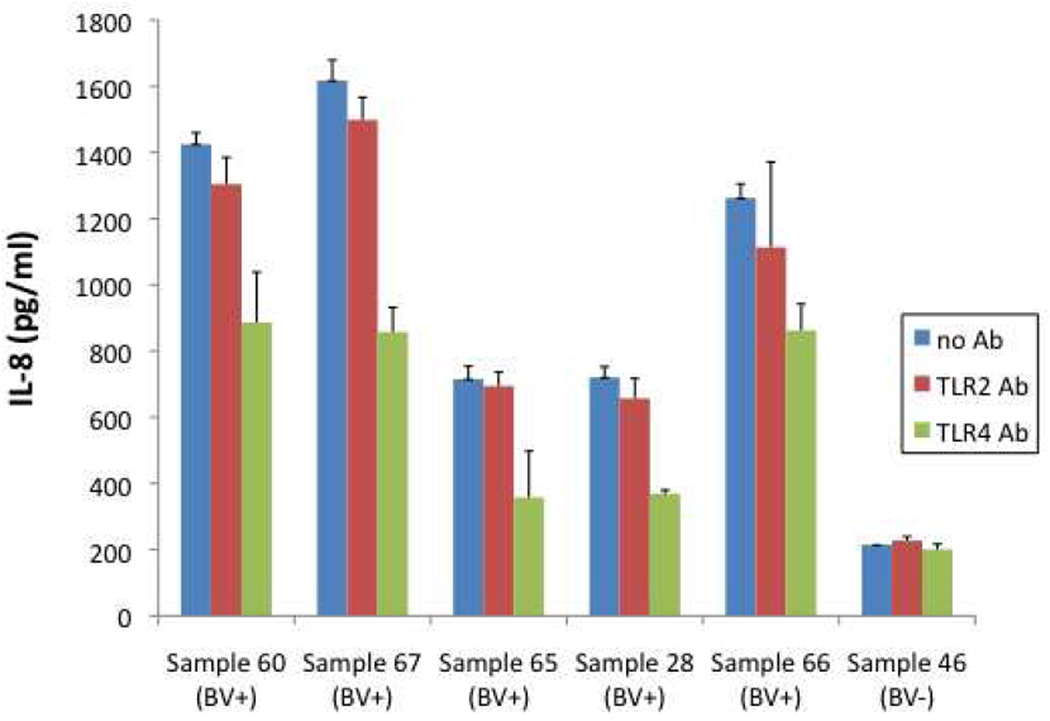
Studies by us show that substances in the mucosal fluid of women with BV can stimulate myeloid cells to secrete several cytokines including IL-8 while fluids from women with healthy microbiota are much less stimulatory (27, 28 and Fig. 1). Previous studies using cell lines expressing TLR2 showed that some of the stimulatory products in BV mucosal fluids activated cells through this receptor.28 To determine whether stimulation through either TLR2 or TLR4 was predominant, antibodies to TLR2 or TLR4 were added to cultures. Antibody to TLR2 only slightly reduced stimulation of the myeloid cell line while antibody to TLR4 reduced IL-8 production by 30–60 percent (Fig. 1). These results indicate that while there are some TLR2 ligands present in BV, stimulation through TLR4 is stronger. However, these results also suggest that TLR2 and TLR4 ligands may not account for all the stimulatory substances in BV mucosal fluids.
Figure 1. Mucosal fluids from women with BV stimulate cells to secrete IL-8.
Mucosal fluids were collected from women by cervical-vaginal lavage. Lavage fluid was cleared by centrifugation, diluted and added to cultures of U937 monocytic cells along with antibodies to TLR2 and TLR4. The final dilution of fluid in cultures was 1:40. After overnight incubation, supernatants were collected and IL-8 levels measured (mean±SD of triplicate cultures).
In addition to TLR ligands, bacteria, especially anaerobes, produce large quantities of short chain fatty acids (SCFAs) in mucosal sites such as the gut29 and the female genital tract in BV (30, 31, also Fig. 2). These microbial products, which include acetic, butyric, and propionic acids, have been shown to play an important role in a wide array of immune responses, based largely on studies investigating the gut microflora. Those studies show that SCFAs modulate immune responses by inhibiting the production of proinflammatory cytokines, and by affecting immune cell migration and phagocytosis. Furthermore, these compounds are known to induce apoptosis in various cell types including neutrophils.32–38 In fact, due to its mostly anti-inflammatory effects on the immune system, butyric acid has long been used to treat inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).29
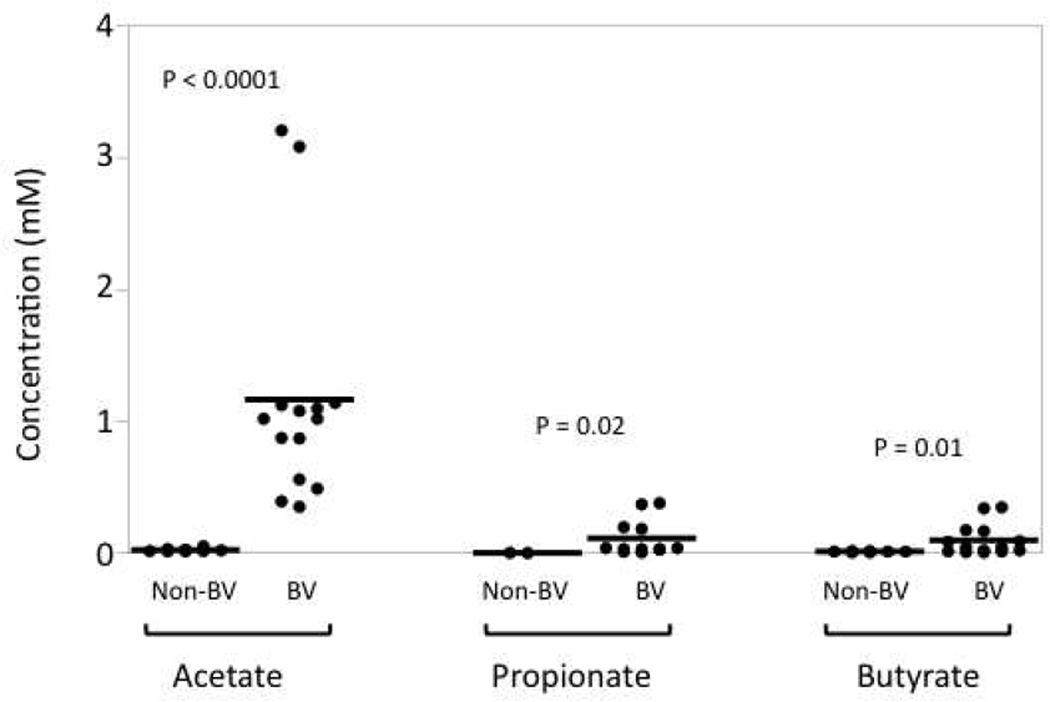
Figure 2. SCFAs are present in vaginal fluid.
Vaginal fluids were collected from women with or without BV by cervical-vaginal lavage. The levels of acetate, propionate, and butyrate were measured by gas chromatography. P-values are given comparing non-BV and BV for each SCFA.
SCFAs are readily taken up by both nonionic diffusion and active transport by cells.29 More recently, GPR43, a member of the G-protein-coupled receptor family, was shown to bind SCFAs.39, 40 Interestingly, GPR43 is expressed on the surface of innate immune cells including neutrophils and monocytes,37, 39, 41, 42 highlighting the important role that the SCFA and GPR43 interactions may play in innate immune responses.
Our own research, among others, confirm the presence of many SCFAs in the lower genital mucosa. The SCFAs at this site include acetic, propionic, isobutyric, n-butyric, and isovaleric acids (Fig. 2 and30, 31, 43). In fact, we find that the concentration of acetic acid in cervical-vaginal lavage (CVL) samples can be as high as 3 mM (Fig. 2). Given that during the lavage the mucosal fluid is diluted an average of 40 fold, the concentration of acetic acid may reach as high as 120 mM in the lower genital tract. Our data also show that various SCFAs are found at significantly higher concentrations in BV+ women when compared to non-BV women (Fig. 2), which is not surprising given that BV is characterized by the outgrowth of mostly anaerobic bacteria. Despite their abundance in the genital tract, however, the SCFAs’ role in modulating immune responses in the genital mucosa is not well understood.
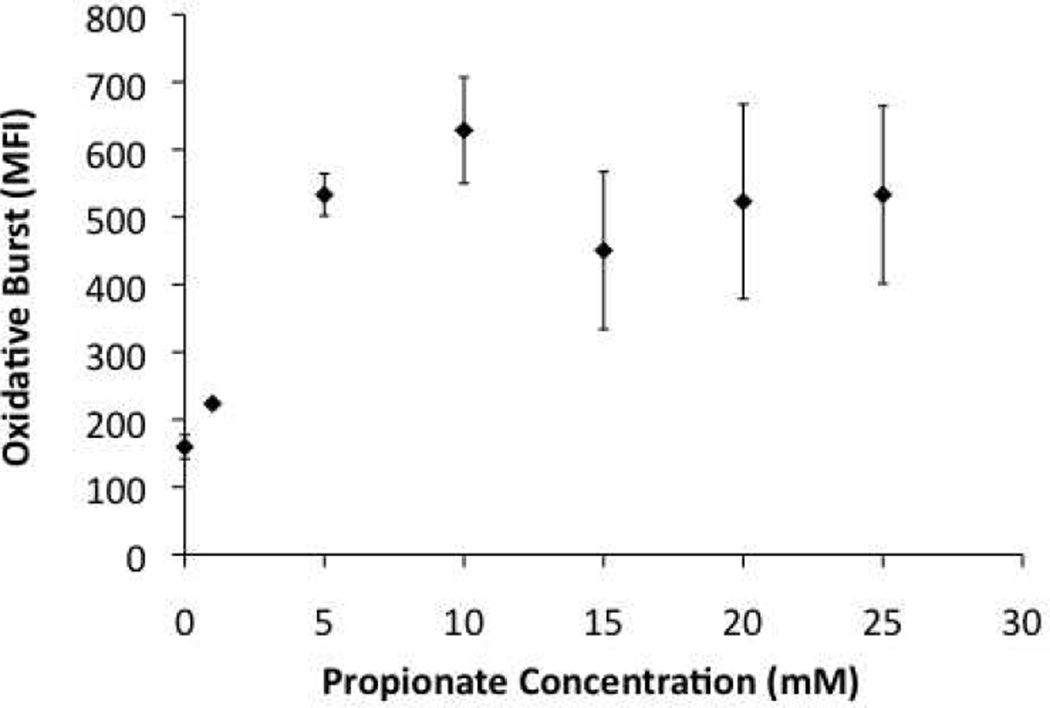
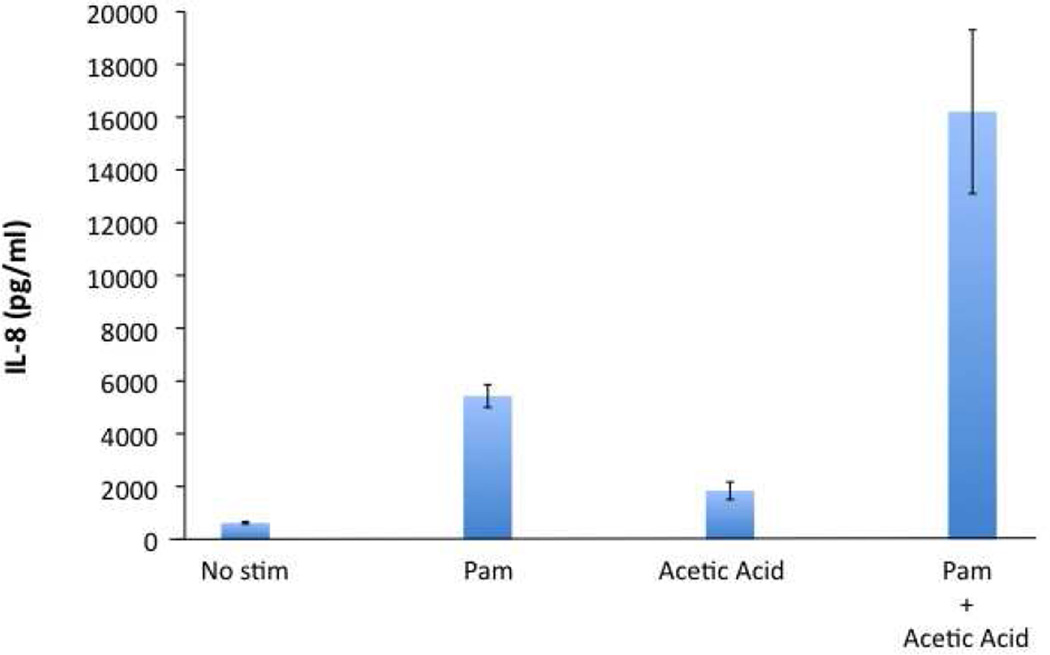
We and others have found that SCFAs can induce neutrophils to undergo an oxidative burst (Fig. 3, also37). Our data further suggest that, whereas SCFAs alone are unable to induce IL-8 production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), the production of IL-8 and TNFα (Fig. 4 and data not shown) appears to be enhanced when both SCFAs and Pam2CSK4 (a synthetic TLR2 ligand) are used to stimulate these cells. These data suggest that SCFAs, especially in combination with other microbial products, may be involved in recruitment and activation of the innate immune cells in the female genital tract. As the levels of some SCFAs have been reported to fluctuate during menstruation43, It will be interesting to investigate how various SCFAs, acting alone or in concert, might affect immune responses at different stages of menstrual cycle and what the implications of these changes are in health and disease states.
Figure 3. Propionate is a potent activator of neutrophils.
Neutrophils were isolated from the blood of healthy donors. They were subsequently loaded with 0.1 µM of dichlorofluorescin diacetate (DCFH-DA) for 15 minutes at 37°C. The oxidative burst was measured as a function of the Mean Fluorescence Intensity (MFI) by flow cytometry.
Figure 4. SCFAs enhance the ability of Pam2CSK4 to stimulate IL-8 production by PBMCs.
PBMCs were collected from healthy donors. 250,000 cells were cultured with Pam2CSK4 (Pam @ 0.1 µg/ml) and/or Acetic Acid (2 mM), as indicated. IL-8 production was measured by ELISA.
Concluding Remarks
The female genital tract is a complex and unique environment. It is equipped to promote a successful pregnancy in an ever-changing milieu affected by sex hormones and various foreign invaders. Its protection against infections hangs in balance between commensal versus pathogenic microorganisms. Given the scope of sexually transmitted diseases, and the extent to which they cause morbidity and mortality worldwide, it is crucial to elucidate factors that contribute to the health of the female genital tract. Clearly, more work needs to be done to determine what the important immune mediators are in genital mucosa, what the respective roles of epithelial and immune cells are in production of these mediators, and how the chronologic and reproductive aging impacts immune responses. Furthermore, because of the heterogeneity of microbial flora in different individuals both in health and disease states, it will be important to identify and fully investigate how these bacteria shape mucosal immune responses in the female genital tract.
Bibliography
- 1.Wira CR, Fahey JV, Ghosh M, Patel MV, Hickey DK, Ochiel DO. Sex hormone regulation of innate immunity in the female reproductive tract: the role of epithelial cells in balancing reproductive potential with protection against sexually transmitted pathogens. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2010;63:544–565. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0897.2010.00842.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wira CR, Grant-Tschudy KS, Crane-Godreau MA. Epithelial cells in the female reproductive tract: a central role as sentinels of immune protection. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2005;53:65–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0897.2004.00248.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wira CR, Fahey JV, Sentman CL, Pioli PA, Shen L. Innate and adaptive immunity in female genital tract: cellular responses and interactions. Immunol Rev. 2005;206:306–335. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2005.00287.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Iwasaki A. Antiviral immune responses in the genital tract: clues for vaccines. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10:699–711. doi: 10.1038/nri2836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Franklin RD, Kutteh WH. Characterization of immunoglobulins and cytokines in human cervical mucus: influence of exogenous and endogenous hormones. J Reprod Immunol. 1999;42:93–106. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0378(98)00086-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Valore EV, Park CH, Igreti SL, Ganz T. Antimicrobial components of vaginal fluid. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2002;187:561–568. doi: 10.1067/mob.2002.125280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sha BE, Chen HY, Wang QJ, Zariffard MR, Cohen MH, Spear GT. Utility of Amsel criteria, Nugent score, and quantitative PCR for Gardnerella vaginalis, Mycoplasma hominis, and Lactobacillus spp. for diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis in human immunodeficiency virus-infected women. J Clin Microbiol. 2005;43:4607–4612. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.9.4607-4612.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hillier SL. Diagnostic microbiology of bacterial vaginosis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1993;169:455–459. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(93)90340-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hillier SL, Krohn MA, Nugent RP, Gibbs RS. Characteristics of three vaginal flora patterns assessed by gram stain among pregnant women. Vaginal Infections and Prematurity Study Group. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1992;166:938–944. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(92)91368-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Fredricks DN, Fiedler TL, Marrazzo JM. Molecular identification of bacteria associated with bacterial vaginosis. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1899–1911. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa043802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Fredricks DN, Fiedler TL, Thomas KK, Oakley BB, Marrazzo JM. Targeted PCR for detection of vaginal bacteria associated with bacterial vaginosis. J Clin Microbiol. 2007;45:3270–3276. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01272-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Spear GT, Sikaroodi M, Zariffard MR, Landay AL, French AL, Gillevet PM. Comparison of the Diversity of the Vaginal Microbiota in HIV-Infected and HIV-Uninfected Women with or without Bacterial Vaginosis. J Infect Dis. 2008 doi: 10.1086/591942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ravel J, Gajer P, Abdo Z, Schneider GM, Koenig SS, McCulle SL, Karlebach S, Gorle R, Russell J, Tacket CO, Brotman RM, Davis CC, Ault K, Peralta L, Forney LJ. Microbes and Health Sackler Colloquium: Vaginal microbiome of reproductive-age women. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1002611107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hummelen R, Fernandes AD, Macklaim JM, Dickson RJ, Changalucha J, Gloor GB, Reid G. Deep sequencing of the vaginal microbiota of women with HIV. PLoS One. 2010;5:e12078. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Jousimies-Somer H. Recently described clinically important anaerobic bacteria: taxonomic aspects and update. Clin Infect Dis. 1997;25(Suppl 2):S78–S87. doi: 10.1086/516227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Antonio MA, Hawes SE, Hillier SL. The identification of vaginal Lactobacillus species and the demographic and microbiologic characteristics of women colonized by these species. J Infect Dis. 1999;180:1950–1956. doi: 10.1086/315109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Eschenbach DA, Davick PR, Williams BL, Klebanoff SJ, Young-Smith K, Critchlow CM, Holmes KK. Prevalence of hydrogen peroxide-producing Lactobacillus species in normal women and women with bacterial vaginosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1989;27:251–256. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.251-256.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Barrons R, Tassone D. Use of Lactobacillus probiotics for bacterial genitourinary infections in women: a review. Clin Ther. 2008;30:453–468. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2008.03.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Klebanoff SJ, Coombs RW. Viricidal effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus on human immunodeficiency virus type 1: possible role in heterosexual transmission. J Exp Med. 1991;174:289–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.1.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Martius J, Krohn MA, Hillier SL, Stamm WE, Holmes KK, Eschenbach DA. Relationships of vaginal Lactobacillus species, cervical Chlamydia trachomatis, and bacterial vaginosis to preterm birth. Obstet Gynecol. 1988;71:89–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sha BE, Zariffard MR, Wang QJ, Chen HY, Bremer J, Cohen MH, Spear GT. Female genital-tract HIV load correlates inversely with Lactobacillus species but positively with bacterial vaginosis and Mycoplasma hominis. J Infect Dis. 2005;191:25–32. doi: 10.1086/426394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Vasquez A, Jakobsson T, Ahrne S, Forsum U, Molin G. Vaginal lactobacillus flora of healthy Swedish women. J Clin Microbiol. 2002;40:2746–2749. doi: 10.1128/JCM.40.8.2746-2749.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hillier SL, Krohn MA, Klebanoff SJ, Eschenbach DA. The relationship of hydrogen peroxide-producing lactobacilli to bacterial vaginosis and genital microflora in pregnant women. Obstet Gynecol. 1992;79:369–373. doi: 10.1097/00006250-199203000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hillier SL. The vaginal microbial ecosystem and resistance to HIV. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1998;14(Suppl 1):S17–S21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mattsby-Baltzer I, Platz-Christensen JJ, Hosseini N, Rosen P. IL-1beta, IL-6, TNFalpha, fetal fibronectin, and endotoxin in the lower genital tract of pregnant women with bacterial vaginosis. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1998;77:701–706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Platz-Christensen JJ, Mattsby-Baltzer I, Thomsen P, Wiqvist N. Endotoxin and interleukin-1 alpha in the cervical mucus and vaginal fluid of pregnant women with bacterial vaginosis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1993;169:1161–1166. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(93)90274-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.St John EP, Martinson J, Simoes JA, Landay AL, Spear GT. Dendritic cell activation and maturation induced by mucosal fluid from women with bacterial vaginosis. Clin Immunol. 2007;125:95–102. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2007.06.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zariffard MR, Novak RM, Lurain N, Sha BE, Graham P, Spear GT. Induction of tumor necrosis factor- alpha secretion and toll-like receptor 2 and 4 mRNA expression by genital mucosal fluids from women with bacterial vaginosis. J Infect Dis. 2005;191:1913–1921. doi: 10.1086/429922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Roy CC, Kien CL, Bouthillier L, Levy E. Short-chain fatty acids: ready for prime time? Nutr Clin Pract. 2006;21:351–366. doi: 10.1177/0115426506021004351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Al-Mushrif S, Eley A, Jones BM. Inhibition of chemotaxis by organic acids from anaerobes may prevent a purulent response in bacterial vaginosis. J Med Microbiol. 2000;49:1023–1030. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-49-11-1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Chaudry AN, Travers PJ, Yuenger J, Colletta L, Evans P, Zenilman JM, Tummon A. Analysis of vaginal acetic acid in patients undergoing treatment for bacterial vaginosis. J Clin Microbiol. 2004;42:5170–5175. doi: 10.1128/JCM.42.11.5170-5175.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Tedelind S, Westberg F, Kjerrulf M, Vidal A. Anti-inflammatory properties of the short-chain fatty acids acetate and propionate: a study with relevance to inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13:2826–2832. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i20.2826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Cavaglieri CR, Nishiyama A, Fernandes LC, Curi R, Miles EA, Calder PC. Differential effects of short-chain fatty acids on proliferation and production of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines by cultured lymphocytes. Life Sci. 2003;73:1683–1690. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(03)00490-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Segain JP, Raingeard de la Bletiere D, Bourreille A, Leray V, Gervois N, Rosales C, Ferrier L, Bonnet C, Blottiere HM, Galmiche JP. Butyrate inhibits inflammatory responses through NFkappaB inhibition: implications for Crohn's disease. Gut. 2000;47:397–403. doi: 10.1136/gut.47.3.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Luhrs H, Kudlich T, Neumann M, Schauber J, Melcher R, Gostner A, Scheppach W, Menzel TP. Butyrate-enhanced TNFalpha-induced apoptosis is associated with inhibition of NF-kappaB. Anticancer Res. 2002;22:1561–1568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Luhrs H, Gerke T, Muller JG, Melcher R, Schauber J, Boxberge F, Scheppach W, Menzel T. Butyrate inhibits NF-kappaB activation in lamina propria macrophages of patients with ulcerative colitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2002;37:458–466. doi: 10.1080/003655202317316105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Maslowski KM, Vieira AT, Ng A, Kranich J, Sierro F, Yu D, Schilter HC, Rolph MS, Mackay F, Artis D, Xavier RJ, Teixeira MM, Mackay CR. Regulation of inflammatory responses by gut microbiota and chemoattractant receptor GPR43. Nature. 2009;461:1282–1286. doi: 10.1038/nature08530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Cox MA, Jackson J, Stanton M, Rojas-Triana A, Bober L, Laverty M, Yang X, Zhu F, Liu J, Wang S, Monsma F, Vassileva G, Maguire M, Gustafson E, Bayne M, Chou CC, Lundell D, Jenh CH. Short-chain fatty acids act as antiinflammatory mediators by regulating prostaglandin E(2) and cytokines. World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15:5549–5557. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.5549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Le Poul E, Loison C, Struyf S, Springael JY, Lannoy V, Decobecq ME, Brezillon S, Dupriez V, Vassart G, Van Damme J, Parmentier M, Detheux M. Functional characterization of human receptors for short chain fatty acids and their role in polymorphonuclear cell activation. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:25481–25489. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M301403200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Brown AJ, Goldsworthy SM, Barnes AA, Eilert MM, Tcheang L, Daniels D, Muir AI, Wigglesworth MJ, Kinghorn I, Fraser NJ, Pike NB, Strum JC, Steplewski KM, Murdock PR, Holder JC, Marshall FH, Szekeres PG, Wilson S, Ignar DM, Foord SM, Wise A, Dowell SJ. The Orphan G protein-coupled receptors GPR41 and GPR43 are activated by propionate and other short chain carboxylic acids. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:11312–11319. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M211609200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Sina C, Gavrilova O, Forster M, Till A, Derer S, Hildebrand F, Raabe B, Chalaris A, Scheller J, Rehmann A, Franke A, Ott S, Hasler R, Nikolaus S, Folsch UR, Rose-John S, Jiang HP, Li J, Schreiber S, Rosenstiel P. G protein-coupled receptor 43 is essential for neutrophil recruitment during intestinal inflammation. J Immunol. 2009;183:7514–7522. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hirasawa A, Hara T, Katsuma S, Adachi T, Tsujimoto G. Free fatty acid receptors and drug discovery. Biol Pharm Bull. 2008;31:1847–1851. doi: 10.1248/bpb.31.1847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Preti G, Huggins GR. The Human vagina. In: Hafez ESE, Evans TN, editors. The Human Vagina. Amsterdam ; New York: Elsevier North-Holland Biomedical Press; 1978. pp. 151–166. [Google Scholar]