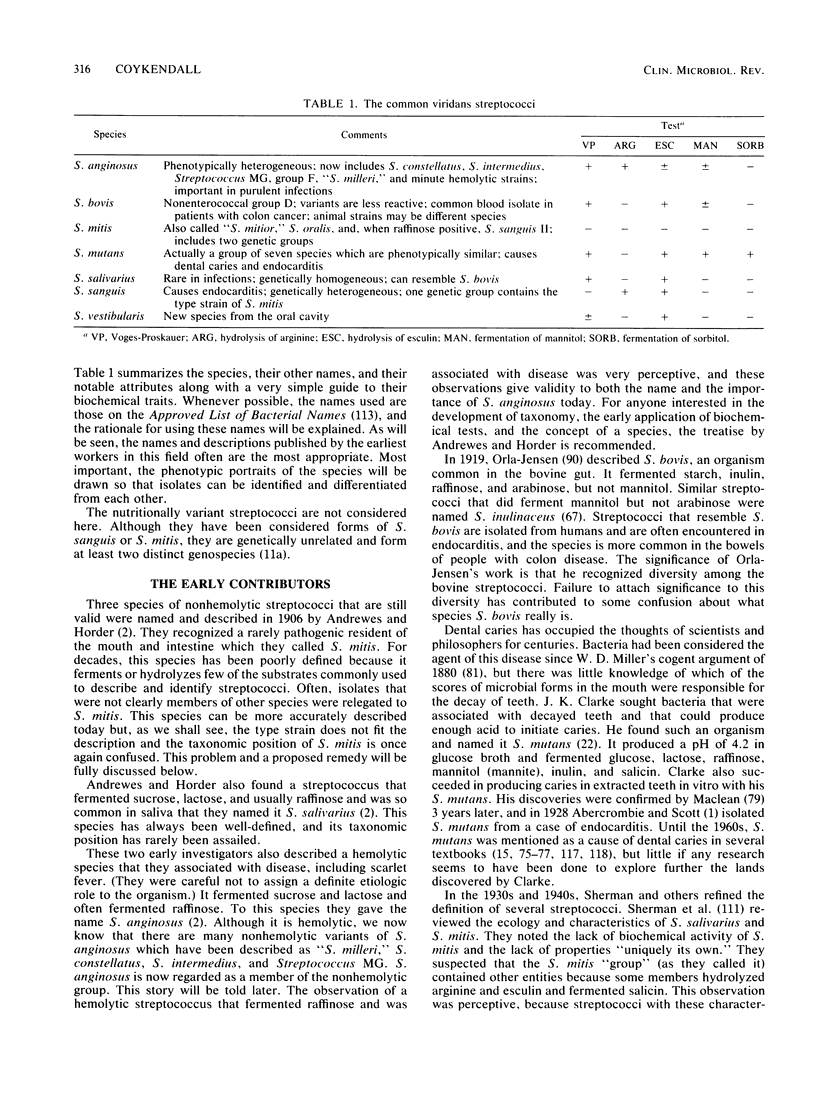
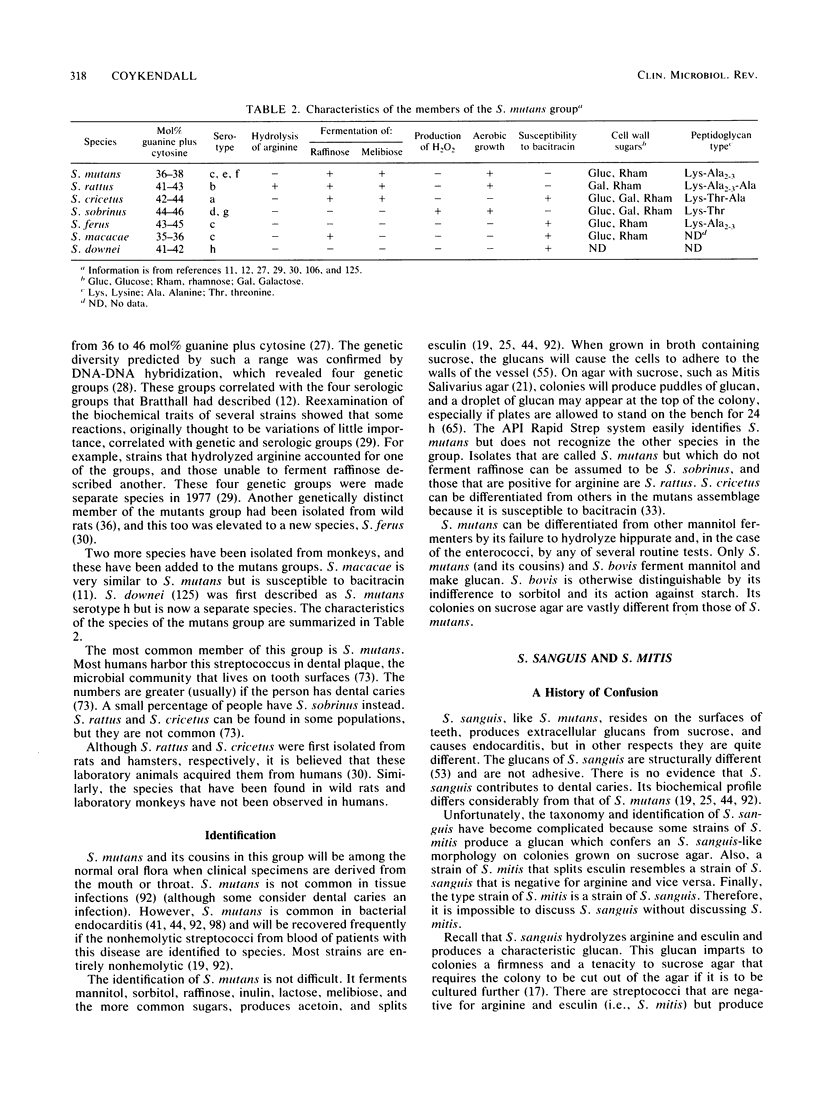
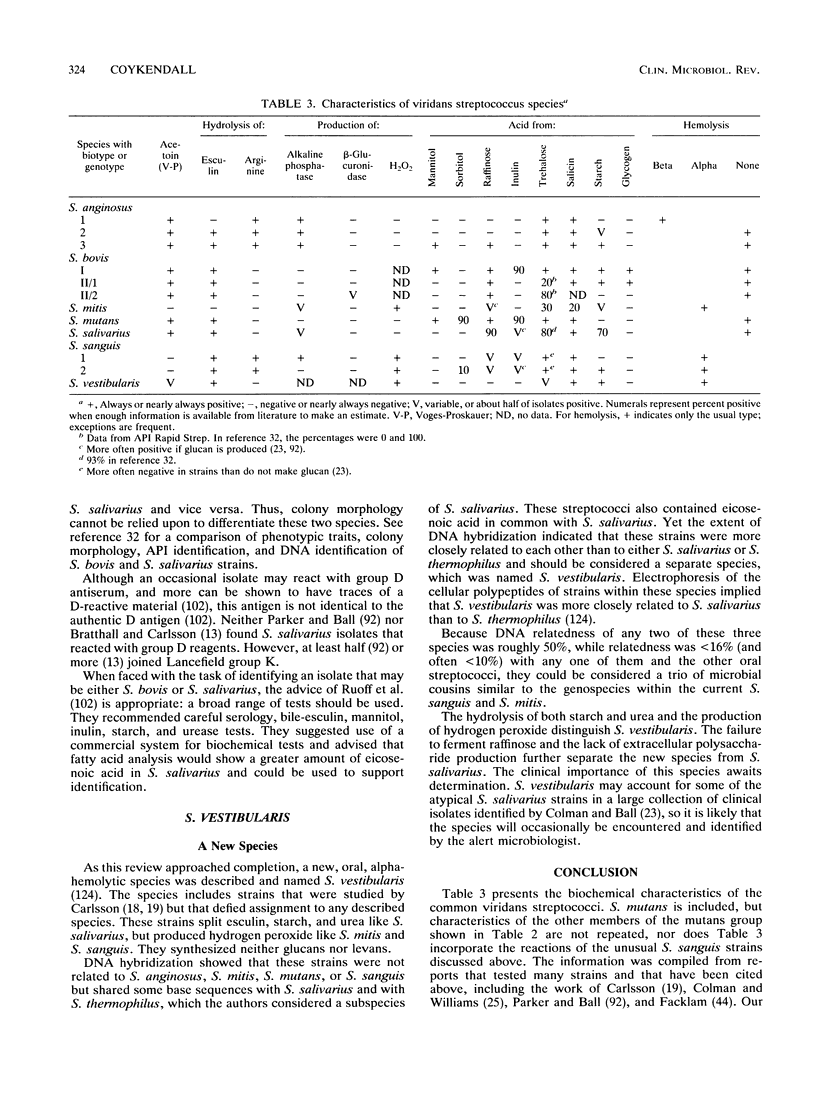
Abstract
This review traces the history of the human, nonhemolytic, or viridans, streptococci and describes improvements in their taxonomy wrought by study of their biochemical profiles and analysis of their nucleic acids. The goal was to define species on the basis of genetic relationships and to describe these species by their phenotypic characteristics so that they can be easily identified. This method has resulted in the division of some species. Streptococcus mutans has been divided into four species, two of which are common in humans. Three more mutans group species are indigenous to animals. Conversely, S. constellatus, S. intermedius, and "S. milleri" have been combined under S. anginosus. S. mitis (or "S. mitior") can be well-defined and includes S. sanguis II. There is genetic heterogeneity within S. sanguis, but the species is usually easy to identify. There is also some heterogeneity in S. bovis, but most human isolates are genetically related. Discussions of the taxonomy of these species are accompanied by descriptions of the characteristics by which these streptococci can be identified. Among these species are potential pathogens which should be suspected in cases of endocarditis and purulent infections of liver, brain, and other tissues.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appelbaum P. C., Chaurushiya P. S., Jacobs M. R., Duffett A. Evaluation of the rapid strep system for species identification of streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 May;19(5):588–591. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.5.588-591.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAILEY R. W., OXFORD A. E. A quantitative study of the production of dextran from sucrose by rumen strains of Streptococcus bovis. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Aug;19(1):130–145. doi: 10.1099/00221287-19-1-130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball L. C., Parker M. T. The cultural and biochemical characters of Streptococcus milleri strains isolated from human sources. J Hyg (Lond) 1979 Feb;82(1):63–78. doi: 10.1017/s002217240002547x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannatyne R. M., Randall C. Ecology of 350 isolates of group F Streptococcus. Am J Clin Pathol. 1977 Feb;67(2):184–186. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/67.2.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayliss R., Clarke C., Oakley C. M., Somerville W., Whitfield A. G., Young S. E. The microbiology and pathogenesis of infective endocarditis. Br Heart J. 1983 Dec;50(6):513–519. doi: 10.1136/hrt.50.6.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratthall D., Carlsson J. Oral streptococci and commercial grouping sera. Odontol Revy. 1968;19(2):205–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratthall D. Demonstration of five serological groups of streptococcal strains resembling Streptococcus mutans. Odontol Revy. 1970;21(2):143–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J. A numerical taxonomic study of human oral streptococci. Odontol Revy. 1968;19(2):137–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J. Presence of various types of non-haemolytic streptococci in dental plaque and in other sites of the oral cavity in man. Odontol Revy. 1967;18(1):55–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J. Zooglea-forming streptococci, resembling Streptococcus sanguis, isolated from dental plaque in man. Odontol Revy. 1965;16(4):348–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang G. T., Ellner P. D. Evaluation of slide agglutination methods for identifying group D streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):804–806. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.804-806.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman G., Ball L. C. Identification of streptococci in a medical laboratory. J Appl Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;57(1):1–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1984.tb02351.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman G., Williams R. E. The cell walls of streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Dec;41(3):375–387. doi: 10.1099/00221287-41-3-375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Chen K., Coykendall A. L., Wesbecher P., Herson V. C. Fatal infection in neonates of 26 weeks' gestation due to Streptococcus milleri: report of two cases. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Feb;40(2):190–193. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.2.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coykendall A. L. Base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid isolated from cariogenic streptococci. Arch Oral Biol. 1970 Apr;15(4):365–368. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(70)90063-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coykendall A. L. Genetic heterogeneity in Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 1971 Apr;106(1):192–196. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.1.192-196.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coykendall A. L., Specht P. A. DNA base sequence homologies among strains of Streptococcus sanguis. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Nov;91(1):92–98. doi: 10.1099/00221287-91-1-92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coykendall A. L., Specht P. A., Samol H. H. Streptococcus mutans in a wild, sucrose-eating rat population. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):216–219. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.216-219.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAIN J. A., NEAL A. L., SEELEY H. W. The effect of carbon dioxide on polysaccharide production by Streptococcus bovis. J Bacteriol. 1956 Aug;72(2):209–213. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.2.209-213.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drucker D. B., Melville T. H. Computer classification of streptococci, mostly of oral origin. Nature. 1969 Feb 15;221(5181):664–664. doi: 10.1038/221664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etienne J., Reverdy M. E., Mouren C., Fleurette J. Etude bactériologique de cent vingt-cinq endocardites infectieuses à streptocoque. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1982 Oct;30(8):707–710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZGERALD R. J., JORDAN H. V., STANLEY H. R. Experimental caries and gingival pathologic changes in the gnotobiotic rat. J Dent Res. 1960 Sep-Oct;39:923–935. doi: 10.1177/00220345600390052701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZGERALD R. J., KEYES P. H. Demonstration of the etiologic role of streptococci in experimental caries in the hamster. J Am Dent Assoc. 1960 Jul;61:9–19. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1960.0138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R., Cooksey R. C., Wortham E. C. Evaluation of commercial latex agglutination reagents for grouping streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Nov;10(5):641–646. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.5.641-646.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R. Physiological differentiation of viridans streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Feb;5(2):184–201. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.2.184-201.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R. Recognition of group D streptococcal species of human origin by biochemical and physiological tests. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Jun;23(6):1131–1139. doi: 10.1128/am.23.6.1131-1139.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R., Rhoden D. L., Smith P. B. Evaluation of the Rapid Strep system for the identification of clinical isolates of Streptococcus species. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Nov;20(5):894–898. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.5.894-898.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrow J. A., Collins M. D. DNA base composition, DNA-DNA homology and long-chain fatty acid studies on streptococcus thermophilus and Streptococcus salivarius. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Feb;130(2):357–362. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-2-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman M. L., Coykendall A. L. Variation in internal polysaccharide synthesis among Streptococcus mutans strains. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):475–479. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.475-479.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman M., Birkhed D., Coykendall A., Rizzo D. Linkage analyses of extracellular glucans from Streptococcus sanguis and Streptococcus mitior. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):907–909. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.907-909.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUTHOF O. Ueber pathogene vergrünende Streptokokken; Streptokokken-Befunde bei dentogenen Abszessen und Infiltraten im Bereich der Mundhöhle. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1956 Sep;166(7-8):553–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Nygaard M. Synthesis of insoluble dextran and its significance in the formation of gelatinous deposits by plaque-forming streptococci. Arch Oral Biol. 1968 Oct;13(10):1249–1262. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(68)90081-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossling J. Occurrence and pathogenicity of the Streptococcus milleri group. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Mar-Apr;10(2):257–285. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.2.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffar A. A., Fuselier P. A., Baker C. J. Species distribution of non-group D alpha-hemolytic streptococci in maternal genital and neonatal blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):101–103. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.101-103.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldane E. V., Haldane J. H., Digout G., West A., van Rooyen C. E. Streptococcus bovis endocarditis. Can Med Assoc J. 1974 Oct 5;111(7):678-9, 82. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Slade H. D. Biology, immunology, and cariogenicity of Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Jun;44(2):331–384. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.331-384.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handley P. S., Carter P. L., Wyatt J. E., Hesketh L. M. Surface structures (peritrichous fibrils and tufts of fibrils) found on Streptococcus sanguis strains may be related to their ability to coaggregate with other oral genera. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):217–227. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.217-227.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoppes W. L., Lerner P. I. Nonenterococcal group-D streptococcal endocarditis caused by Streptococcus bovis. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Nov;81(5):588–593. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-81-5-588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelstrup J. Extracellular polysaccharides of smooth and rough variants of Streptococcus salivarius. Scand J Dent Res. 1981 Oct;89(5):374–383. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1981.tb01696.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiel P., Skadhauge K. Studies on mannitol-fermenting strains of Streptococcus bovis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Feb;81(1):10–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02181.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. S., Catalano M. T., Edberg S. C., Casey J. I., Steigbigel N. H. Streptococcus bovis septicemia and carcinoma of the colon. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Oct;91(4):560–562. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-4-560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. S., Recco R. A., Catalano M. T., Edberg S. C., Casey J. I., Steigbigel N. H. Association of Streptococcus bovis with carcinoma of the colon. N Engl J Med. 1977 Oct 13;297(15):800–802. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197710132971503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J. Role of Streptococcus mutans in human dental decay. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):353–380. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.353-380.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr, Watson B. K., Kunz L. J. Endocarditis due to group D streptococci. Comparison of disease caused by streptococcus bovis with that produced by the enterococci. Am J Med. 1974 Aug;57(2):239–250. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90448-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V., Smibert R. M., Good I. J., Burmeister J. A., Palcanis K. G., Ranney R. R. Bacteriology of experimental gingivitis in young adult humans. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):651–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.651-667.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Roberts R. B. Streptococcus bovis bacteremia and underlying gastrointestinal disease. Arch Intern Med. 1978 Jul;138(7):1097–1099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niven C. F., Kiziuta Z., White J. C. Synthesis of a Polysaccharide from Sucrose by Streptococcus S.B.E. J Bacteriol. 1946 Jun;51(6):711–716. doi: 10.1128/jb.51.6.711-716.1946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niven C. F., Smiley K. L., Sherman J. M. The Production of Large Amounts of a Polysaccharid by Streptococcus salivarius. J Bacteriol. 1941 Apr;41(4):479–484. doi: 10.1128/jb.41.4.479-484.1941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyvad B., Kilian M. Microbiology of the early colonization of human enamel and root surfaces in vivo. Scand J Dent Res. 1987 Oct;95(5):369–380. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1987.tb01627.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORLAND F. J., BLAYNEY J. R., HARRISON R. W., REYNIERS J. A., TREXLER P. C., ERVIN R. F., GORDON H. A., WAGNER M. Experimental caries in germfree rats inoculated with enterococci. J Am Dent Assoc. 1955 Mar;50(3):259–272. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1955.0061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. T., Ball L. C. Streptococci and aerococci associated with systemic infection in man. J Med Microbiol. 1976 Aug;9(3):275–302. doi: 10.1099/00222615-9-3-275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier L. L., Jr, Coyle M., Petersdorf R. Dextran production as a possible virulence factor in streptococcal endocarditis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1978 Jul;158(3):415–420. doi: 10.3181/00379727-158-40216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price T., French G. L., Talsania H., Phillips I. Differentiation of Streptococcus sanguis and S. mitior by whole-cell rhamnose content and possession of arginine dihydrolase. J Med Microbiol. 1986 May;21(3):189–197. doi: 10.1099/00222615-21-3-189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez-Ronda C. H. Adherence of glucan-positive and glucan-negative streptococcal strains to normal and damaged heart valves. J Clin Invest. 1978 Oct;62(4):805–814. doi: 10.1172/JCI109192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravreby W. D., Bottone E. J., Keusch G. T. Group D streptococcal bacteremia, with emphasis on the incidence and presentation of infectious due to Streptococcus bovis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Dec 27;289(26):1400–1403. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197312272892605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. G., Silva E., McCormack W. M. Association of Streptococcus bovis bacteremia with bowel disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;17(4):696–697. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.4.696-697.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. B., Krieger A. G., Schiller N. L., Gross K. C. Viridans streptococcal endocarditis: the role of various species, including pyridoxal-dependent streptococci. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 Nov-Dec;1(6):955–966. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.6.955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoff K. L., Ferraro M. J., Holden J., Kunz L. J. Identification of Streptococcus bovis and Streptococcus salivarius in clinical laboratories. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;20(2):223–226. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.2.223-226.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoff K. L., Ferraro M. J. Hydrolytic enzymes of "Streptococcus milleri". J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1645–1647. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1645-1647.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoff K. L., Ferraro M. J. Presumptive identification of "Streptococcus milleri" in 5 h. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Sep;24(3):495–497. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.3.495-497.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoff K. L., Kunz L. J. Use of the Rapid STREP system for identification of viridans streptococcal species. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1138–1140. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1138-1140.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoff K. L. Streptococcus anginosus ("Streptococcus milleri"): the unrecognized pathogen. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jan;1(1):102–108. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.1.102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheld W. M., Valone J. A., Sande M. A. Bacterial adherence in the pathogenesis of endocarditis. Interaction of bacterial dextran, platelets, and fibrin. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1394–1404. doi: 10.1172/JCI109057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer K. H., Kandler O. Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):407–477. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.407-477.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman J. M., Niven C. F., Smiley K. L. Streptococcus salivarius and Other Non-hemolytic Streptococci of the Human Throat. J Bacteriol. 1943 Mar;45(3):249–263. doi: 10.1128/jb.45.3.249-263.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman J. M. THE STREPTOCOCCI. Bacteriol Rev. 1937 Dec;1(1):3–97. doi: 10.1128/br.1.1.3-97.1937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer R. C., Nanayakarra C. S., Coup A. J. Fulminant neonatal sepsis due to Streptococcus milleri. J Infect. 1982 Jan;4(1):88–89. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(82)91394-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spigelblatt L., Saintonge J., Chicoine R., Laverdière M. Changing pattern of neonatal streptococcal septicemia. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1985 Jan-Feb;4(1):56–58. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198501000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenover F. C. Diagnostic deoxyribonucleic acid probes for infectious diseases. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jan;1(1):82–101. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.1.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillotson G. S. An evaluation of the API-20 STREP system. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Apr;35(4):468–472. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.4.468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITTENBURY R. HYDROGEN PEROXIDE FORMATION AND CATALASE ACTIVITY IN THE LACTIC ACID BACTERIA. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Apr;35:13–26. doi: 10.1099/00221287-35-1-13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. C., Niven C. F., Jr Streptococcus S.B.E.: A Streptococcus Associated with Subacute Bacterial Endocarditis. J Bacteriol. 1946 Jun;51(6):717–722. doi: 10.1128/jb.51.6.717-722.1946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Houte J., de Moor C. E., Jansen H. M. Synthesis of iodophilic polysaccharide by human oral streptococci. Arch Oral Biol. 1970 Mar;15(3):263–266. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(70)90084-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



