Abstract
Peroxiredoxins (Prxs) are thiol-specific antioxidant proteins that exhibit peroxidase and peroxynitrite reductase activities involved in the reduction of reactive oxygen species. The peroxiredoxin Prx4 from the large yellow croaker Pseudosciaena crocea is a typical 2-Cys Prx with an N-terminal signal peptide. We solved the crystal structure of Prx4 at 1.90 Å and revealed an N-terminal antiparallel β-sheet that contributes to the dimer interface. Deletion of this β-sheet decreased the in vitro peroxidase activity to about 50% of the wild-type. In vivo assays further demonstrated that removal of this β-sheet led to some impairment in the ability of Prx4 to negatively regulate nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activity and to perform its role in anti-bacterial immunity. These results provide new insights into the structure and function relationship of a peroxiredoxin from bony fish.
Introduction
Peroxiredoxins (Prxs) are thiol-specific antioxidant proteins that protect cells against reactive oxygen species (ROS) such as hydrogen peroxide, alkyl peroxides and peroxynitrite, through their peroxidase and peroxynitrite reductase activities [1], [2], [3], [4]. Prxs reduce peroxides with the redox-active cysteines, which distinguish them from other peroxidases that require cofactors such as metal ions or prosthetic groups [5]. Prxs have been identified in almost all organisms, normally existing in several isoforms and expressed at a relatively high level [4], [6]. Based on distinct positions of the reactive Cys residues, Prxs have been classified into three groups: typical 2-Cys, atypical 2-Cys and 1-Cys Prxs [4]. Prxs in all subfamilies, however, possess one strictly conserved cysteine called peroxidatic cysteine (CP), which is located in the N-terminal region. The reaction could be dissected into three steps. First, the sulfur atom of CP residue executes a nucleophilic attack at the O-O bond of the peroxide substrate at the cost of being oxidized into the cysteine sulfenic acid form. The second step differs in three subfamilies of Prx. For Prxs in the typical 2-Cys subfamily, dimerization is necessary for the activity. The second redox-active cysteine called resolving cysteine (CR) located in the C-terminal of another subunit attacks the cysteine sulfenic acid resulting in formation of an intermolecular disulfide bond. In contrast, for the atypical 2-Cys Prxs, the CR residue is located within the same subunit and executes the nucleophilic attack to form an intramolecular disulfide bond. This step does not occur with the 1-Cys Prxs, due to the lack of the CR residue. Finally, the oxidized Prx is regenerated by thiol-containing electron donors such as thioredoxin, glutathione, or DL-Dithiothreitol (DTT) [4], [5], [7]. For typical eukaryotic 2-Cys Prxs, the cysteine sulfenic acid reacts with a second peroxide molecule to form a cysteine sulfinic acid, which can be reversed by the sulfinic acid reductase sulfiredoxin in an ATP-dependent manner [8], [9], [10]. The activity of Prx is irreversibly lost once the cysteine sulfinic acid is further oxidized to cysteine sulfonic acid [4]. In addition to the antioxidant activity, Prxs are also involved in cell proliferation, differentiation, gene expression and intracellular signaling pathways [11], [12], [13].
Since the first crystal structure of Prx was determined in 1998 [14], a series of structures of Prxs at various redox and/or hydrogen peroxide-binding states have been reported [15], [16], [17]. All of these structures share a conserved thioredoxin fold. In all reduced Prxs, the CP residue is located in the first turn of a helix and surrounded by three highly conserved residues (Pro, Thr and Arg). Upon oxidation, the residues adjacent to CP and CR undergo significant conformational changes to form the disulfide bond in the oxidized form [15]. Moreover, the typical 2-Cys Prxs can assemble into the toroid-shaped homodecameric complexes, which are related to the redox states and/or functions [5], [18].
Human Prx4 is a typical 2-Cys Prx with an N-terminal signal peptide [19], [20]. In addition to the peroxidase activity, it also plays a role in inhibiting NF-κB function as a cytosolic molecule [21], or activating NF-κB as an extracellular factor [22]. Recently, we identified the gene of Prx4 from the large yellow croaker Pseudosciaena crocea, and found that it regulated the pro-inflammatory responses by inhibiting NF-κB activity and protected the fish against bacterial challenge [23]. Here, we report the 1.90 Å crystal structure of P. crocea Prx4 in the reduced form. Comparative structural analysis revealed an N-terminal antiparallel β-sheet, which is located at the dimeric interface and involved in the in vitro enzymatic activity and in vivo biological functions of P. crocea Prx4.
Materials and Methods
Ethics Statement
This study was carried out in strict accordance with the Regulations for the Administration of Affairs Concerning Experimental Animals established by the Fujian Provincial Department of Science and Technology. The experiments on this animal were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of the Third Institute of Oceanography, State Oceanic Administration. All surgery was performed under Tricaine-S anesthesia, and all efforts were made to minimize suffering.
Cloning, Expression and Purification of P. crocea Prx4
The DNA sequence encoding the mature Prx4 protein without the 29-residue signal peptide, as predicted by SignalP 3.0 Server [24] was amplified by PCR using the recombinant plasmid Prx4-pET28a (Novagen, Germany) as the template, which was constructed as previously described [23]. The PCR product was cloned into a pET28a-derived vector. This construct contained a hexahistidine (6× His) tag at the N-terminus of the recombinant protein, which was overexpressed in E. coli Rosetta (DE3) strain (Novagen, Germany) in 2× YT medium (Oxoid Ltd, England) supplemented with 34 µg/ml kanamycin and 30 µg/ml chloramphenicol. The cells were grown at 37°C to an A600 nm of 0.6 and induced with 0.2 mM isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactoside for 4 hr at 37°C. Cells were harvested by centrifugation at 4000 g for 10 min and resuspended in lysis buffer (20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.5, 200 mM NaCl). After three cycles of freezing-thawing followed by sonication, the disrupted cells were centrifuged at 16,000 g for 25 min. The supernatant containing the target protein was collected and loaded onto a Ni-NTA column (Qiagen, Germany) equilibrated with the binding buffer (20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.5, 200 mM NaCl, 14 mM β-mercaptoethanol). The target protein was eluted with 500 mM imidazole buffer and further purified by gel filtration in a Superdex™ 200 column (GE Healthcare, USA) equilibrated with the binding buffer. Fractions containing the target protein were collected and concentrated to 15 mg/mL. The purity of the protein was evaluated by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and the protein sample was stored at −80°C until use. The Prx4C113S and truncated versions of Prx4ΔN62 and Prx4ΔN67, that lacked the N-terminal 62 and 67 residues respectively, were prepared with a similar procedure.
Crystallization, Data Collection and Processing
The crystals were grown at 16°C using the hanging drop vapor-diffusion techniques. In each drop, 1 µL of the Prx4 at 15 mg/mL in the buffer of 20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.5, 50 mM NaCl, 14 mM β-mercaptoethanol, 10 mM DTT was mixed with 1 µL reservoir solution (10% polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether 5,000, 0.1 M HEPES-NaOH, pH 8.0) and equilibrated against 0.5 mL reservoir solution. Typically, crystals appeared in one day and reached the maximum size of 100×100×400 µm3 in one week. A single crystal was transferred to the cryoprotectant, which consisted of the reservoir solution plus 30% glycerol, and flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen. The X-ray diffraction data were collected at a wavelength of 0.9999 Å at the Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (SSRF) using beamline 17 U with a MX225 CCD (MARresearch, Germany). The diffraction data were indexed, integrated, and scaled with HKL2000 [25].
Structure Solution and Refinement
The crystal structure of Prx4 was determined by molecular replacement with the program MOLREP [26] using the coordinates of human truncated Prx4 (PDB code 2PN8) as the search model. The initial model was refined using the maximum likelihood method implemented in REFMAC5 [27] as part of the CCP4i [28] program suite and rebuilt interactively using the σA-weighted electron density maps with coefficients 2mFo-DFc and mFo-DFc in the program COOT [29]. Five percent of the reflections were set aside to calculate an R-free factor. Refinement finally converged to an R-factor of 19.56% and an R-free factor of 21.98% at 1.90 ? resolution. The final model was validated with the programs MOLPROBITY [30] and PROCHECK [31]. The statistics and refinement parameters are listed in Table 1. All structure figures were prepared with the program PyMol [32]. The final structure factors and coordinates of P. crocea Prx4 have been deposited in the Protein Data Bank under the accession code of 3QPM.
Table 1. Crystal parameters, data collection and structure refinement statistics.
| Data processing | |
| Space group | C2 |
| Unit cell (Å), (°) | a = 145.12, b = 196.00, c = 51.74, α = γ = 90.00, β = 105.23 |
| Resolution range (Å) | 50.00–1.90 (1.97–1.90)a |
| Unique reflections | 108,135 (10,312) |
| Completeness (%) | 98.9 (94.2) |
| <I/σ(I)> | 12.4 (5.2) |
| Rmerge b (%) | 6.6 (21.4) |
| Redundancy | 3.5 |
| Refinement statistics | |
| Resolution range (Å) | 37.98–1.90 |
| R-factorc/R-freed (%) | 19.56/21.98 |
| Number of protein atoms | 7,784 |
| Number of water atoms | 624 |
| RMSDe bond lengths (Å) | 0.014 |
| RMSD bond angles (°) | 1.281 |
| Mean B factors (Å2) | 33.51 |
| Ramachandran plot f (residues, %) | |
| Most favored (%) | 97.41 |
| Additional allowed (%) | 2.59 |
| Outliers (%) | 0 |
| PDB entry | 3QPM |
The values in parentheses refer to statistics in the highest bin.
Rmerge = ∑hkl∑i|Ii(hkl)- <I(hkl)>|/∑hkl∑iIi(hkl), where Ii(hkl) is the intensity of an observation and <I(hkl)> is the mean value for its unique reflection; Summations are over all reflections.
R-factor = ∑h|Fo(h)-Fc(h)|/∑hFo(h), where Fo and Fc are the observed and calculated structure-factor amplitudes, respectively.
R-free was calculated with 5% of the data excluded from the refinement.
Root-mean square-deviation from ideal values.
Categories were defined by Molprobity.
Enzymatic Assays
Peroxidase activity was determined by a spectrophotometric assay that monitored the consumption of NADPH at 340 nm, as described previously [33]. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae thioredoxin Trx1 and thioredoxin reductase Trr1 were prepared as previously described [34], [35] in buffer containing 20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.0 and 100 mM NaCl. The reaction was carried out in a final volume of 200 µL reaction mix containing 50 mM HEPES-NaOH, pH 7.0, 250 µM NADPH, 3 µM Trx1, 1.5 µM Trr1, 1 µM purified Prx4 (Prx4ΔN62, Prx4ΔN67 or Prx4C113S), and 50 µM H2O2. Following the reaction triggered by the addition of H2O2, the consumption of NADPH was monitored for 3 min, with a step of 15 sec at room temperature with a DU800 spectrophotometer (Beckman Coulter, Fullerton, CA, USA). All assays were repeated three times.
Fish Culture, Protein Injection, and Sample Preparation
Large yellow croakers with an average weight of 100 g were purchased from a mariculture farm in Lianjiang, Fujian, China. After acclimatization in an aerated seawater tank for three days, four groups of 30 fish each were injected intramuscularly with purified Prx4, Prx4ΔN62, Prx4ΔN67 and Prx4C113S protein (100 µg/100 g fish) or sterile 0.85% NaCl (100 µL/100 g fish), respectively. The 0.85% NaCl-injected group served as a negative control. Spleen tissues were collected from six fish in each group at different times after injection (0, 12, 24, 48 and 72 hr) and then flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen. Three pooled samples from each treatment were subjected to electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA). All experiments were repeated three times.
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) and Bacterial Challenge Experiments
EMSA was performed as described previously [23]. In the bacterial challenge experiments, five groups of 50 large yellow croakers each were injected intramuscularly as follows: (1) Prx4 protein (100 µg/100 g fish), (2) Prx4ΔN62 protein (100 µg/100 g fish), (3) Prx4ΔN67 protein (100 µg/100 g fish), (4) Prx4C113S protein (100 µg/100 g fish) and (5) 0.85% NaCl (100 µL/100 g fish). Twelve hours after injection, fish were infected with mixed bacteria (5×106 cfu/mL of Vibrio alginolyticus, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and Aeromonas hydrophila) at a dose of 200 µL/100 g fish. Mortality was monitored for 5 days after injection.
Results
The Overall Structure and Active Site
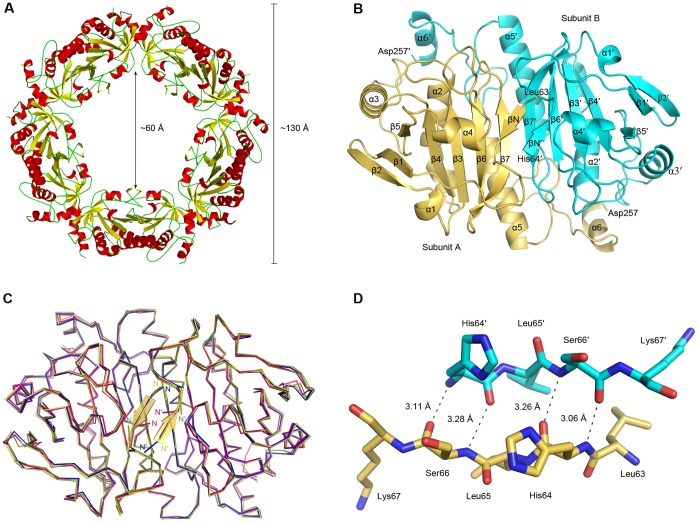
The P. crocea Prx4 also assembles into a toroid-shaped homodecameric complex as other typical 2-Cys Prxs [5], both in the crystal structure and in the solution as indicated by gel filtration (data not shown). Each asymmetric unit contains five subunits, two pairs of dimers and a monomer. Symmetric processing enables us to define a decamer (pentamer of dimers), with an inner diameter of ∼60 Å and an outer diameter of ∼130 Å ( Fig. 1A ). The basic unit of functional P. crocea Prx4 is a homodimer ( Fig. 1B ). The final structural model of this basic functional unit spans 389 residues (Leu63–Asp257 in subunit A, and His64′–Asp257′ in subunit B). The 33 N-terminal residues (Glu30–Ser62) and the three C-terminal residues (Lys258–Lys260) are not fitted into the final model due to the weak electron density, implying a high degree of structural flexibility of these regions. The core structure adopts a typical thioredoxin fold, which is composed of five β-strands (β3, β4, β5, β6 and β7) and four α-helices (α2, α3, α4 and α5). The C-terminal protrusion (Gly231–Asp257), which was comprised of helix α6 and a long loop succeeding helix α5, interacts with the core domain (Leu63–His230) of the other subunit and contributes considerably to the dimeric interface. In addition, the pair of N-terminal βN strands forms a short antiparallel β-sheet, packing against the β-sheet of β7–β7′.
Figure 1. Structure and comparison of P. crocea Prx4.
A The homodecameric structure. B The dimeric structure. Subunits A and B are colored in orange and cyan, respectively. All secondary structures are labeled sequentially. C Superposition of P. crocea Prx4 (orange), H. sapiens Prx4 (blue), R. norvegicus Prx1 (hotpink), and T. cruzi TryP (green). D Hydrogen bonds of the antiparallel β-sheet. Atoms N and O are colored in blue and red, respectively, in both subunits. Atom C is colored in orange and cyan in subunit A and B, respectively.
Similar to previously determined Prx structures, the CP residue Cys113 is located in the first turn of helix α2 and is surrounded by three highly conserved residues Pro106, Thr110 and Arg189. The distance between the sulphur atoms of CP (Cys113) and CR (Cys234′) in the other subunit of the homodimer is approximately 14 Å. Thus, as proposed previously [15], large conformational changes are required in order for P. crocea Prx4 to form the intermolecular disulfide bond between CP and CR.
Structural Comparison of P. crocea Prx4 and Other Typical 2-Cys Prxs
Superposition of the P. crocea Prx4 dimer on the human Prx4 (PDB code, 3TJK) [36], Rattus norvegicus Prx1 (2Z9S) [37], and Trypanosoma cruzi TryP (1UUL) [38] yields overall root mean square deviations of 0.41 Å, 0.59 Å and 0.60 Å over 389, 378 and 378 Cα atoms, respectively. These 2-Cys Prxs share a similar overall structure ( Fig. 1C ). The most significant difference is within the N-terminal region. Similar to human Prx4 (3TJK), P. crocea Prx4 also possesses an antiparallel β-sheet located at the dimer interface ( Fig. 1C ). This β-sheet is stabilized via four main-chain hydrogen bonds ( Fig. 1D ).
The Deletion of N-terminal β-sheet Affected the Peroxidase Activity of Prx4
To determine whether the residues of the N-terminal β-strand (Leu63–Lys67) are necessary for the peroxidase activity of Prx4, we constructed two truncated versions of Prx4, referred to as Prx4ΔN62 (residues Leu63–Lys260) and Prx4ΔN67 (residues Ala68–Lys260). Using thioredoxin system (Trx1-Trr1-NADPH) as the electron donor, the reaction velocity of Prx4ΔN62 is about two times that of Prx4ΔN67, and is almost the same as that of Prx4 ( Fig. 2 ). As could be expected, the C113S mutant abolishes the peroxidase activity. These results indicated that the N-terminal β-strand (residues Leu63–Lys67) contributed to the enzymatic activity of P. crocea Prx4.
Figure 2. Peroxidase activity assays.
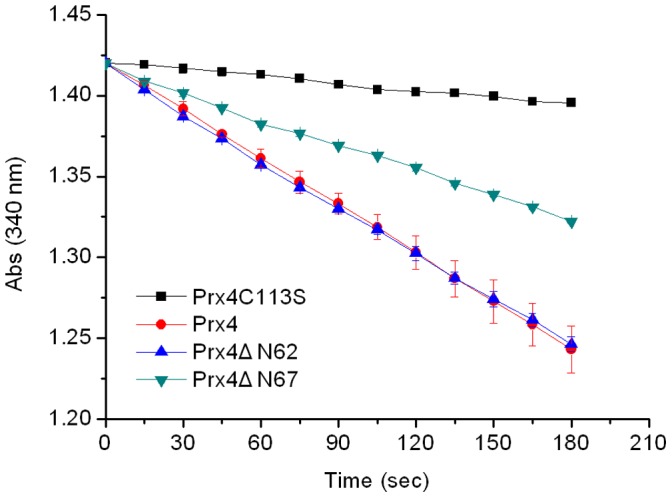
Assays were performed with Prx4 (red circles), Prx4ΔN62 (blue triangles), Prx4ΔN67 (cyan inverted triangles) and Prx4C113S (black squares).
Importance of the N-terminal β-sheet for the Negative Regulation of NF-κB Activity
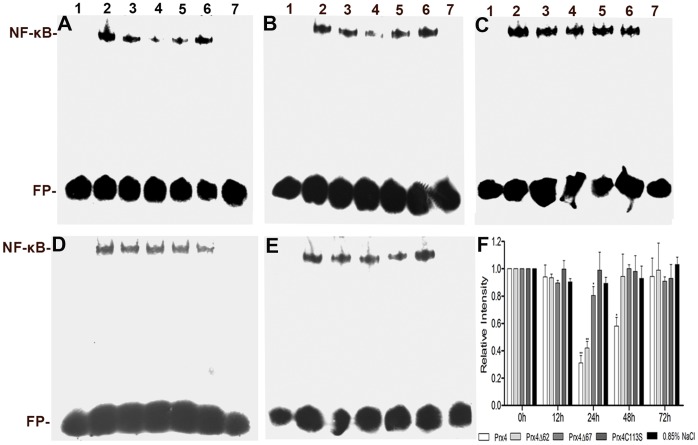
Previous studies have showed that P. crocea Prx4 negatively regulates NF-κB activity, thus modulating pro-inflammatory responses [23]. To determine whether the missing N-terminal β-sheet affects the function of P. crocea Prx4, Prx4ΔN62, Prx4ΔN67 and Prx4C113S were injected into P. crocea, and EMSA was performed to detect the NF-κB activity in spleen tissues of fish from each treatment group. In Prx4ΔN62-injected fish, the NF-κB activity was significantly decreased (−2.5-fold) at 24 hr after administration, similar to that in Prx4-injected fish ( Fig. 3A ), indicating that Prx4ΔN62 negatively regulated activation of NF-κB. In Prx4ΔN67-injected fish, however, NF-κB activity in the spleens remained virtually a little down-regulated (−1.25-fold) at 24 hr, similar to that in the Prx4C113S-injected fish (−1.11-fold) and 0.85% NaCl-injected fish (negative control), indicating that Prx4ΔN67, missing the N-terminal β-sheet, has a decreased ability to downregulate NF-κB activity ( Fig. 3B, C and D ). These results suggest the involvement of the N-terminal β-sheet of P. crocea Prx4 in the negative regulation of NF-κB activity.
Figure 3. Effects of Prx4, Prx4ΔN62, Prx4ΔN67 and Prx4C113S protein on NF-κB activation.
EMSA of NF-κB activity in nuclear extracts of spleen tissues from large yellow croakers injected with A Prx4, B Prx4ΔN62 protein, C Prx4ΔN67 protein, D Prx4C113S protein and E 0.85% NaCl (as a control). Lane 1 contains probe incubated without nuclear extracts; Lanes 2–6 contain nuclear extracts of spleen tissues collected at 0, 12, 24, 48, and 72 h post-injection; Lane 7 contains 100-fold excess of unlabeled oligonucleotide used to compete for binding. F Quantitation of relative activity of NF-κB was performed with a TANON GIS Image System Ver.3.73.
Deletion of the N-terminal β-sheet Affects the Role of P. crocea Prx4 in the Anti-bacterial Immunity
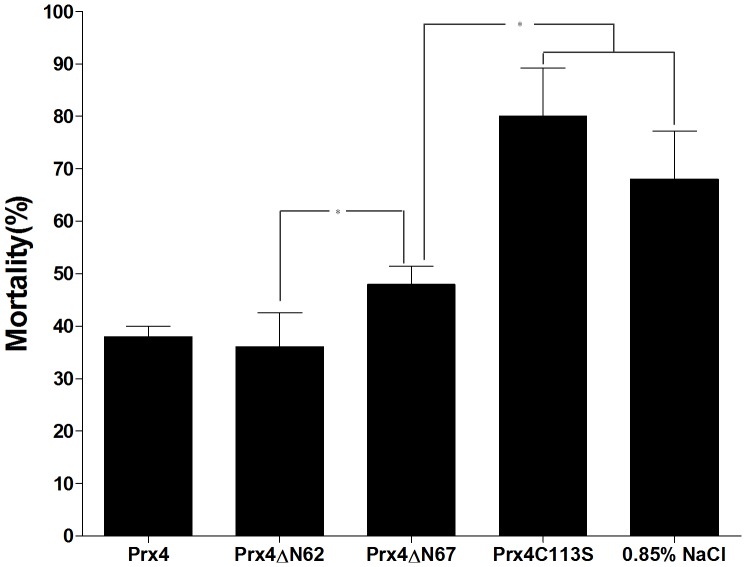
To further assess whether a lack of the N-terminal β-sheet affects the role of Prx4 in the immune response against bacterial challenge, four groups of healthy large yellow croakers were injected intramuscularly with Prx4, Prx4ΔN62, Prx4ΔN67, Prx4C113S, or 0.85% NaCl, followed by infection with the bacterial mixture. Five days after challenge, the mortality rate for the Prx4ΔN67-injected group was 48%, which was significantly higher than that of the Prx4ΔN62 and Prx4-injected group (36% and 38% mortality rate, P<0.05) ( Fig. 4 ). The mortality rate of Prx4C113S - and 0.85% NaCl-injected groups was 68% and 80% ( Fig. 4 ). These results indicated that Prx4ΔN62 possessed a higher protective effect against bacterial challenge compared to Prx4ΔN67, although Prx4ΔN67 also had a protective effect, suggesting that deletion of the N-terminal β-sheet may affect the role of this enzyme in anti-bacterial immunity in large yellow croakers.
Figure 4. The functions of the three Prx4 proteins during bacterial challenge.
Large yellow croakers were injected with Prx4, Prx4ΔN62, Prx4ΔN67, Prx4C113S or 0.85% NaCl and then challenged with a bacterial mixture. Fish mortality in each group was monitored for 5 days. The symbol * represents a significant difference in the mortality rate between the two groups injected with different proteins as indicated (P<0.05).
Discussion
In the present study, we determined the crystal structure of Prx4 from large yellow croaker, a marine fish species, for the first time. Similar to previously determined typical 2-Cys Prx structures [5], [15], P. crocea Prx4 also assembles into the toroid-shaped homodecameric complex with generally identical inner diameter and outer diameter ( Fig. 1A ). The B-type interface [15] is also adopted in P. crocea Prx4 homodimer ( Fig. 1B ). Structural superposition of P. crocea Prx4 dimer against other typical 2-Cys Prxs indicates that they share a similar overall structure. However, an extra N-terminal antiparallel β-sheet is found at the dimer interface of Prx4 proteins from P. crocea as well as H. sapiens ( Fig. 1C ). Since the basic functional unit of P. crocea Prx4 is a homodimer, this N-terminal β-sheet, which is situated at the dimer interface and involved in four main-chain hydrogen bonds ( Fig. 1D ), should be important for the peroxidase activity and biological function of this enzyme.
Several lines of evidence indicate that NF-κB activation can be controlled by ROS, such as H2O2 and superoxide [21], [39]. Prxs govern intracellular H2O2 levels via their peroxidase activity, thus regulating NF-κB activity [11], [21], [40]. Therefore, the peroxidase activity of Prxs within cells is essential for regulation of NF-κB activity. Here, we demonstrated that Prx4ΔN67, which lacks the N-terminal β-sheet, exhibits a decreased peroxidase activity compared with Prx4ΔN62 ( Fig. 2 ) and also has a decreased ability to downregulate NF-κB activity ( Fig. 3B and C ). These results indicate that deletion of the N-terminal β-sheet decreased the activity of P. crocea Prx4, which may result in influence of its function in the negative regulation of NF-κB activation due to the change of redox status within cells. Therefore, the N-terminal β-sheet may be involved in Prx4 regulation of NF-κB activation by affecting the peroxidase activity of this enzyme.
NF-κB is clearly one of the most important regulators of pro-inflammatory response, as synthesis of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and chemokines, is mediated by NF-κB [41]. Studies have shown that P. crocea Prx4 may regulate pro-inflammatory responses by inhibiting NF-κB activity and protected fish against bacterial challenge [23]. In this study, Prx4ΔN67 missing the N-terminal β-sheet has a decreased ability to downregulate NF-κB activity, thus having lower potential to modulate pro-inflammatory response as compared with Prx4ΔN62. This may result in a higher mortality rate for the Prx4ΔN67-injected fish (48% mortality rate) than that for Prx4ΔN62-injected fish (36% mortality rate) in bacterial challenge experiments ( Fig. 4 ).
In summary, we determined the 1.90 Å crystal structure of P. crocea Prx4 and identified an antiparallel β-sheet at the N-terminus. This β-sheet, which contributes to the dimer interface, is involved not only in the peroxidase activity of P. crocea Prx4 but also in the negative regulation of NF-κB activity and anti-bacterial immunity.
Funding Statement
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31125027, 30870490 and 31001131), the National Basic Research Program of China (2012CB114402 and 2006CB910202), and the Nation ‘863’ Project of China (2012AA092202). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1. Jacobson FS, Morgan RW, Christman MF, Ames BN (1989) An alkyl hydroperoxide reductase from Salmonella typhimurium involved in the defense of DNA against oxidative damage. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem 264: 1488–1496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Chae HZ, Chung SJ, Rhee SG (1994) Thioredoxin-dependent peroxide reductase from yeast. J Biol Chem 269: 27670–27678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Bryk R, Griffin P, Nathan C (2000) Peroxynitrite reductase activity of bacterial peroxiredoxins. Nature 407: 211–215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Wood ZA, Schröder E, Robin Harris J, Poole LB (2003) Structure, mechanism and regulation of peroxiredoxins. Trends Biochem Sci 28: 32–40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Barranco-Medina S, Lazaro JJ, Dietz KJ (2009) The oligomeric conformation of peroxiredoxins links redox state to function. FEBS Lett 583: 1809–1816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Hall A, Karplus PA, Poole LB (2009) Typical 2-Cys peroxiredoxins–structures, mechanisms and functions. FEBS J 276: 2469–2477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Pérez-Ruiz JM, Spinola MC, Kirchsteiger K, Moreno J, Sahrawy M, et al. (2006) Rice NTRC is a high-efficiency redox system for chloroplast protection against oxidative damage. Plant Cell 18: 2356–2368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Biteau B, Labarre J, Toledano MB (2003) ATP-dependent reduction of cysteine-sulphinic acid by S. cerevisiae sulphiredoxin. Nature 425: 980–984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Budanov AV, Sablina AA, Feinstein E, Koonin EV, Chumakov PM (2004) Regeneration of peroxiredoxins by p53-regulated sestrins, homologs of bacterial AhpD. Science 304: 596–600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Jönsson TJ, Lowther WT (2007) The peroxiredoxin repair proteins. Subcell Biochem 44: 115–141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Fujii J, Ikeda Y (2002) Advances in our understanding of peroxiredoxin, a multifunctional, mammalian redox protein. Redox Rep 7: 123–130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Kim H, Lee TH, Park ES, Suh JM, Park SJ, et al. (2000) Role of peroxiredoxins in regulating intracellular hydrogen peroxide and hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in thyroid cells. J Biol Chem 275: 18266–18270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Wen ST, Van Etten RA (1997) The PAG gene product, a stress-induced protein with antioxidant properties, is an Abl SH3-binding protein and a physiological inhibitor of c-Abl tyrosine kinase activity. Genes Dev 11: 2456–2467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Choi HJ, Kang SW, Yang CH, Rhee SG, Ryu SE (1998) Crystal structure of a novel human peroxidase enzyme at 2.0 Å resolution. Nat Struct Biol 5: 400–406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Karplus PA, Hall A (2007) Structural survey of the peroxiredoxins. Subcell Biochem 44: 41–60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Nakamura T, Kado Y, Yamaguchi T, Matsumura H, Ishikawa K, et al. (2010) Crystal structure of peroxiredoxin from Aeropyrum pernix K1 complexed with its substrate, hydrogen peroxide. J Biochem 147: 109–115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Hall A, Nelson K, Poole LB, Karplus PA (2011) Structure-based insights into the catalytic power and conformational dexterity of peroxiredoxins. Antioxid Redox Signal 15: 795–815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Parsonage D, Youngblood DS, Sarma GN, Wood ZA, Karplus PA, et al. (2005) Analysis of the link between enzymatic activity and oligomeric state in AhpC, a bacterial peroxiredoxin. Biochemistry 44: 10583–10592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Okado-Matsumoto A, Matsumoto A, Fujii J, Taniguchi N (2000) Peroxiredoxin IV is a secretable protein with heparin-binding properties under reduced conditions. J Biochem 127: 493–501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Wong CM, Chun AC, Kok KH, Zhou Y, Fung PC, et al. (2000) Characterization of human and mouse peroxiredoxin IV: evidence for inhibition by Prx-IV of epidermal growth factor- and p53-induced reactive oxygen species. Antioxid Redox Signal 2: 507–518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Jin DY, Chae HZ, Rhee SG, Jeang KT (1997) Regulatory role for a novel human thioredoxin peroxidase in NF-kappaB activation. J Biol Chem 272: 30952–30961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Haridas V, Ni J, Meager A, Su J, Yu GL, et al. (1998) TRANK, a novel cytokine that activates NF-kappa B and c-Jun N-terminal kinase. J Immunol 161: 1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Yu S, Mu Y, Ao J, Chen X (2010) Peroxiredoxin IV regulates pro-inflammatory responses in large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) and protects against bacterial challenge. J Proteome Res 9: 1424–1436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Emanuelsson O, Brunak S, von Heijne G, Nielsen H (2007) Locating proteins in the cell using TargetP, SignalP and related tools. Nat Protoc 2: 953–971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Otwinowski Z, Minor W (1997) Processing of X-ray diffraction data collected in oscillation mode. Methods Enzymol 276: 307–326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Vagin A, Teplyakov A (2010) Molecular replacement with MOLREP. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 66: 22–25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Murshudov GN, Vagin AA, Dodson EJ (1997) Refinement of macromolecular structures by the maximum-likelihood method. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 53: 240–255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Collaborative (1994) The CCP4 suite: programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 50: 760–763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Emsley P, Cowtan K (2004) Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 60: 2126–2132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Chen VB, Arendall WB 3rd, Headd JJ, Keedy DA, Immormino RM, et al (2010) MolProbity: all-atom structure validation for macromolecular crystallography. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 66: 12–21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Laskowski RA, MacArthur MW, Moss DS, Thornton JM (1993) Procheck - a program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J Appl Crystallogr 26: 283–291. [Google Scholar]
- 32.DeLano W The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System. DeLano Scientific LLC, San Carlos, CA, USA. Available: http://wwwpymolorg.
- 33. Kim JA, Park S, Kim K, Rhee SG, Kang SW (2005) Activity assay of mammalian 2-cys peroxiredoxins using yeast thioredoxin reductase system. Anal Biochem 338: 216–223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Zhang Y, Bao R, Zhou CZ, Chen Y (2008) Expression, purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of thioredoxin Trx1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 64: 323–5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Zhang Z, Bao R, Zhang Y, Yu J, Zhou CZ, et al. (2009) Crystal structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cytoplasmic thioredoxin reductase Trr1 reveals the structural basis for species-specific recognition of thioredoxin. Biochim Biophys Acta 1794: 124–128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Cao Z, Tavender TJ, Roszak AW, Cogdell RJ, Bulleid NJ (2011) Crystal Structure of Reduced and of Oxidized Peroxiredoxin IV Enzyme Reveals a Stable Oxidized Decamer and a Non-disulfide-bonded Intermediate in the Catalytic Cycle. J Biol Chem 286: 42257–42266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Matsumura T, Okamoto K, Iwahara S, Hori H, Takahashi Y, et al. (2008) Dimer-oligomer interconversion of wild-type and mutant rat 2-Cys peroxiredoxin: disulfide formation at dimer-dimer interfaces is not essential for decamerization. J Biol Chem 283: 284–293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Piñeyro MD, Pizarro JC, Lema F, Pritsch O, Cayota A, et al. (2005) Crystal structure of the tryparedoxin peroxidase from the human parasite Trypanosoma cruzi . J Struct Biol 150: 11–22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Asehnoune K, Strassheim D, Mitra S, Kim JY, Abraham E (2004) Involvement of reactive oxygen species in Toll-like receptor 4-dependent activation of NF-kappa B. J Immunol. 172: 2522–2529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Hofmann B, Hecht HJ, Flohé L (2002) Peroxiredoxins. Biol Chem 383: 347–364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Tak PP, Firestein GS (2001) NF-kappaB: a key role in inflammatory diseases. J Clin Invest 107: 7–11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]