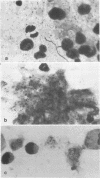
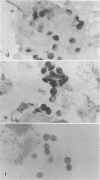
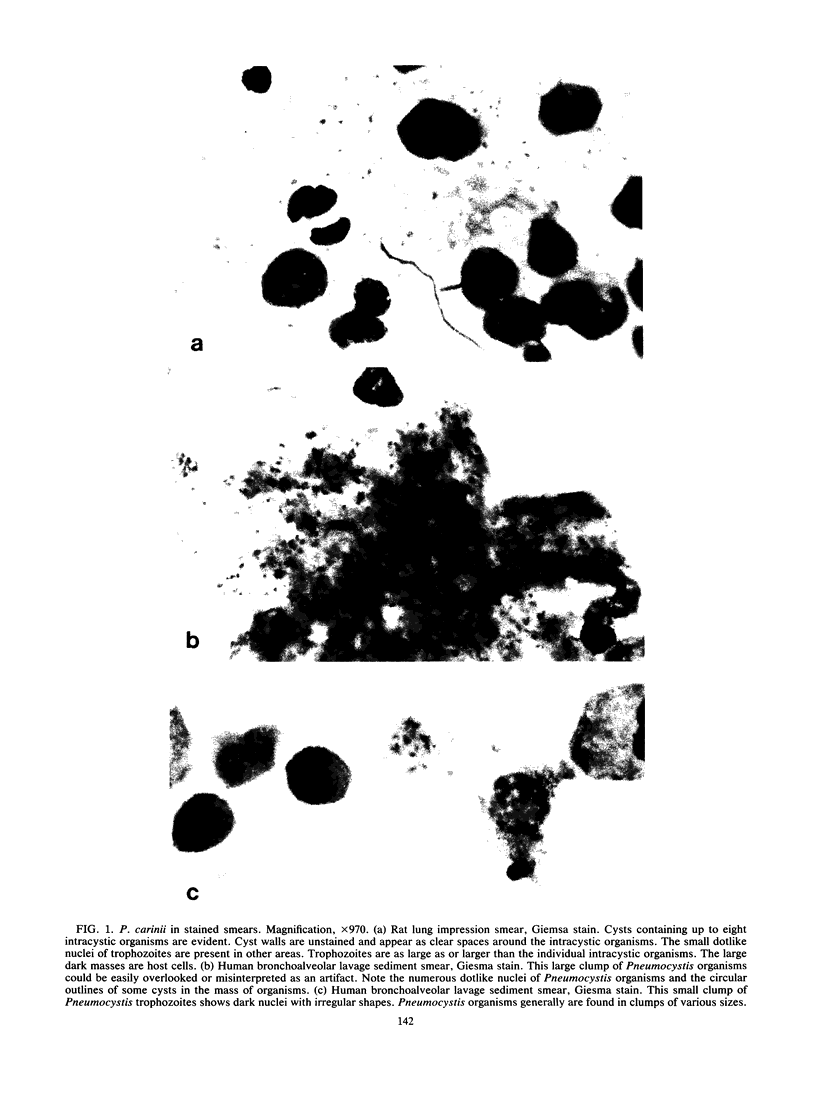
Abstract
Pneumocystis carinii has been recognized as a cause of pneumonia in immunocompromised patients for over 40 years. Until the 1980s, Pneumocystis pneumonia (pneumocystosis) was most often seen in patients undergoing chemotherapy for malignancy or transplantation. Infection could be prevented by trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole prophylaxis; thus, it was an uncommon clinical problem. With the onset of the AIDS epidemic, Pneumocystis pneumonia has become a major problem in the United States because it develops in approximately 80% of patients with AIDS and because almost two-thirds of patients have adverse reactions to anti-Pneumocystis drugs. Thus, physicians and laboratories in any community may be called upon to diagnose and provide care for patients with Pneumocystis pneumonia. The classification of the organism is currently controversial, but it is either a protozoan or a fungus. P. carinii appears to be acquired during childhood by inhalation and does not cause clinical disease in healthy persons but remains latent. If the person becomes immunosuppressed, the latent infection may become activated and lead to clinical disease. Damage of type I pneumocytes by Pneumocystis organisms leads to the foamy alveolar exudate which is characteristic of the disease. Diagnosis is established by morphologic demonstration of Pneumocystis organisms in material from the lungs. Current efforts to find better anti-Pneumocystis drugs should provide more effective therapy and prophylaxis.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abd A. G., Nierman D. M., Ilowite J. S., Pierson R. N., Jr, Bell A. L., Jr Bilateral upper lobe Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in a patient receiving inhaled pentamidine prophylaxis. Chest. 1988 Aug;94(2):329–331. doi: 10.1378/chest.94.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allegra C. J., Chabner B. A., Tuazon C. U., Ogata-Arakaki D., Baird B., Drake J. C., Masur H. Treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia with trimetrexate in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Semin Oncol. 1988 Apr;15(2 Suppl 2):46–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allegra C. J., Kovacs J. A., Drake J. C., Swan J. C., Chabner B. A., Masur H. Activity of antifolates against Pneumocystis carinii dihydrofolate reductase and identification of a potent new agent. J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):926–931. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amundson D. E., Murray K. M., Brodine S., Oldfield E. C. High-dose corticosteroid therapy for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. South Med J. 1989 Jun;82(6):711-4, 718. doi: 10.1097/00007611-198906000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen R., Boedicker M., Ma M., Goldstein E. J. Adverse reactions associated with pentamidine isethionate in AIDS patients: recommendations for monitoring therapy. Drug Intell Clin Pharm. 1986 Nov;20(11):862–868. doi: 10.1177/106002808602001108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awen C. F., Baltzan M. A. Systemic dissemination of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Can Med Assoc J. 1971 May 8;104(9):809–812. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballantine T. V., Grosfeld J. L., Knapek R. M., Baehner R. L. Interstitial pneumonitis in the immunologically suppressed child: an urgent surgical condition. J Pediatr Surg. 1977 Aug;12(4):501–508. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(77)90186-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandt P. D., Blank N., Castellino R. A. Needle diagnosis of pneumonitis. Value in high-risk patients. JAMA. 1972 Jun 19;220(12):1578–1580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett R. N., Hull J. G., Vortel V., Schwarz J. Pneumocystis carinii in lymph nodes and spleen. Arch Pathol. 1969 Aug;88(2):175–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrio J. L., Suarez M., Rodriguez J. L., Saldana M. J., Pitchenik A. E. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia presenting as cavitating and noncavitating solitary pulmonary nodules in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Nov;134(5):1094–1096. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.5.1094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barron T. F., Birnbaum N. S., Shane L. B., Goldsmith S. J., Rosen M. J. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia studied by gallium-67 scanning. Radiology. 1985 Mar;154(3):791–793. doi: 10.1148/radiology.154.3.3871532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett M. S., Durkin M. M., Jay M. A., Queener S. F., Smith J. W. Sources of rats free of latent Pneumocystis carinii. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1794–1795. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1794-1795.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett M. S., Verbanac P. A., Smith J. W. Cultivation of Pneumocystis carinii with WI-38 cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Dec;10(6):796–799. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.6.796-799.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baselski V. S., Robison M. K., Pifer L. W., Woods D. R. Rapid detection of Pneumocystis carinii in bronchoalveolar lavage samples by using Cellufluor staining. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):393–394. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.393-394.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beautyman W. Pneumocystis carinii is an endogenous liposomally modified mitochondrion. Med Hypotheses. 1983 Mar;10(3):281–289. doi: 10.1016/0306-9877(83)90115-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigby T. D., Margolskee D., Curtis J. L., Michael P. F., Sheppard D., Hadley W. K., Hopewell P. C. The usefulness of induced sputum in the diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Apr;133(4):515–518. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.133.4.515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggar R. J. The clinical features of HIV infection in Africa. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Dec 6;293(6560):1453–1454. doi: 10.1136/bmj.293.6560.1453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleiweiss I. J., Jagirdar J. S., Klein M. J., Siegel J. L., Krellenstein D. J., Gribetz A. R., Strauchen J. A. Granulomatous Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in three patients with the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Chest. 1988 Sep;94(3):580–583. doi: 10.1378/chest.94.3.580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenfeld W., Basgoz N., Owen W. F., Jr, Schmidt D. M. Granulomatous pulmonary lesions in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and Pneumocystis carinii infection. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Sep 15;109(6):505–507. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-6-505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenfeld W., Kovacs J. A. Use of a monoclonal antibody to detect Pneumocystis carinii in induced sputum and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid by immunoperoxidase staining. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1988 Dec;112(12):1233–1236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenfeld W., Mandrell R. E., Jarvis G. A., Griffiss J. M. Localization of host immunoglobulin G to the surface of Pneumocystis carinii. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):456–463. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.456-463.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenfeld W., Wagar E., Hadley W. K. Use of the transbronchial biopsy for diagnosis of opportunistic pulmonary infections in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Am J Clin Pathol. 1984 Jan;81(1):1–5. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/81.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowling M. C., Smith I. M., Wescott S. L. A rapid staining procedure for Pneumocystis carinii. Am J Med Technol. 1973 Jul;39(7):267–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradburne R. M., Ettensohn D. B., Opal S. M., McCool F. D. Relapse of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in the upper lobes during aerosol pentamidine prophylaxis. Thorax. 1989 Jul;44(7):591–593. doi: 10.1136/thx.44.7.591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzosko W. J., Krawczyński K., Madaliński K., Nowoslawski A. Immunopathologic aspects of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in infants as revealed by immunofluorescence and electron microscopy. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1976 Oct;43:163–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buff D. D., Greenberg S. D., Leong P., Palumbo F. S. Thymoma, Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia, and AIDS. N Y State J Med. 1988 May;88(5):276–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHALVARDJIAN A. M., GRAWE L. A. A NEW PROCEDURE FOR THE IDENTIFICATION OF PNEUMOCYSTIS CARINII CYSTS IN TISSUE SECTIONS AND SMEARS. J Clin Pathol. 1963 Jul;16:383–384. doi: 10.1136/jcp.16.4.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CSILLAG A., BRANDSTEIN L. The role of a Blastomyces in the aetiology of interstitial plasmocytic pneumonia of the premature infant. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1954;2(1-2):179–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter T. R., Cooper P. H., Petri W. A., Jr, Kim C. K., Walzer P. D., Guerrant R. L. Pneumocystis carinii infection of the small intestine in a patient with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Am J Clin Pathol. 1988 May;89(5):679–683. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/89.5.679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chusid M. J., Heyrman K. A. An outbreak of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia at a pediatric hospital. Pediatrics. 1978 Dec;62(6):1031–1035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Climent C., Lasala G., Vélez R., Baldizón C., Santaella M. L. Acquired immuno deficiency syndrome (AIDS): experience in the Puerto Rico Medical Center. Bol Asoc Med P R. 1985 Feb;77(2):50–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. L., Dodek P. M., Golden J. A., Luce J. M., Golden E., Gold W. M., Murray J. F. Correlation between serial pulmonary function tests and fiberoptic bronchoscopy in patients with Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia and the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Mar;129(3):491–493. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.129.3.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulman C. U., Greene I., Archibald R. W. Cutaneous pneumocystosis. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Mar;106(3):396–398. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-3-396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruickshank B. Pulmonary granulomatous pneumocystosis following renal transplantation. Report of a case. Am J Clin Pathol. 1975 Mar;63(3):384–390. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/63.3.384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushion M. T., Walzer P. D. Growth and serial passage of Pneumocystis carinii in the A549 cell line. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):245–251. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.245-251.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLorenzo L. J., Maguire G. P., Wormser G. P., Davidian M. M., Stone D. J. Persistence of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Evaluation of therapy by follow-up transbronchial lung biopsy. Chest. 1985 Jul;88(1):79–83. doi: 10.1378/chest.88.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domingo J., Waksal H. W. Wright's stain in rapid diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii. Am J Clin Pathol. 1984 Apr;81(4):511–514. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/81.4.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doppman J. L., Geelhoed G. W., De Vita V. T. Atypical radiographic features in Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Radiology. 1975 Jan;114(1):39–44. doi: 10.1148/114.1.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelson P. J., Metroka C. E., Friedman-Kien A. Dapsone, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Dec;103(6 ):963–963. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-6-963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman J. C., Kovacs J. A., Masur H., Santi D. V., Elwood H. J., Sogin M. L. Ribosomal RNA sequence shows Pneumocystis carinii to be a member of the fungi. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):519–522. doi: 10.1038/334519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elvin K. M., Lumbwe C. M., Luo N. P., Björkman A., Källenius G., Linder E. Pneumocystis carinii is not a major cause of pneumonia in HIV infected patients in Lusaka, Zambia. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1989 Jul-Aug;83(4):553–555. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(89)90290-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng R. H., Bishburg E., Smith S. M. Evidence for destruction of lung tissues during Pneumocystis carinii infection. Arch Intern Med. 1987 Apr;147(4):746–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelberg L. A., Lerner C. W., Tapper M. L. Clinical features of Pneumocystis pneumonia in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Oct;130(4):689–694. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.4.689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felegie T. P., Pasculle A. W., Dekker A. Recognition of Pneumocystis carinii by gram stain in impression smears of lung tissue. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1190–1191. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1190-1191.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenelon L. E., Keane C. T., Bakir M., Temperley I. J. A cluster of Pneumocystis carinii infections in children. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Dec 14;291(6510):1683–1683. doi: 10.1136/bmj.291.6510.1683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleury J., Escudier E., Pocholle M. J., Carre C., Bernaudin J. F. Cell population obtained by bronchoalveolar lavage in Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. Acta Cytol. 1985 Sep-Oct;29(5):721–726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Follansbee S. E., Busch D. F., Wofsy C. B., Coleman D. L., Gullet J., Aurigemma G. P., Ross T., Hadley W. K., Drew W. L. An outbreak of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in homosexual men. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 1):705–713. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fossieck B. E., Jr, Spagnolo S. V. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis in patients with lung cancer. Chest. 1980 Nov;78(5):721–722. doi: 10.1378/chest.78.5.721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K., Bartlett M. S., Smith J. W. RNA homology and the reclassification of Pneumocystis. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990 Jan-Feb;13(1):1–2. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(90)90045-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K., Good J. T., Shultz J. A. Latent Pneumocystis infection of rats, relapse, and chemotherapy. Lab Invest. 1966 Oct;15(10):1559–1577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K. Pneumocystis jiroveci n. sp. from man: morphology, physiology, and immunology in relation to pathology. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1976 Oct;43:13–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman B. A., Wenglin B. D., Hyland R. N., Rifkind D. Roentgenographically atypical Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1975 Jan;111(1):89–96. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1975.111.1.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frissen P. H., Stronkhorst A., Eeftinck Schattenkerk J. K., Danner S. A. Fansidar and Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Apr;108(4):638–639. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-108-4-638_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuta T., Ueda K., Fujiwara K., Yamanouchi K. Cellular and humoral immune responses of mice subclinically infected with Pneumocystis carinii. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):544–548. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.544-548.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAJDUSEK D. C. Pneumocystis carinii; etiologic agent of interstitial plasma cell pneumonia of premature and young infants. Pediatrics. 1957 Apr;19(4 Pt 1):543–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garay S. M., Greene J. Prognostic indicators in the initial presentation of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Chest. 1989 Apr;95(4):769–772. doi: 10.1378/chest.95.4.769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghali V. S., Garcia R. L., Skolom J. Fluorescence of Pneumocystis carinii in Papanicolaou smears. Hum Pathol. 1984 Oct;15(10):907–909. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(84)80118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill V. J., Evans G., Stock F., Parrillo J. E., Masur H., Kovacs J. A. Detection of Pneumocystis carinii by fluorescent-antibody stain using a combination of three monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;25(10):1837–1840. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.10.1837-1840.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetz O., Peller P. Pneumocystis-carinii-Pneumonien. Med Klin. 1974 Nov 1;69(44):1774–1778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden J. A., Sjoerdsma A., Santi D. V. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia treated with alpha-difluoromethylornithine. A prospective study among patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. West J Med. 1984 Nov;141(5):613–623. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman J. L., Tashkin D. P. Pneumocystis with normal chest X-ray film and arterial oxygen tension. Early diagnosis in a patient with the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Arch Intern Med. 1983 Oct;143(10):1981–1982. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1983.00350100165029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordin F. M., Simon G. L., Wofsy C. B., Mills J. Adverse reactions to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Apr;100(4):495–499. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-4-495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosey L. L., Howard R. M., Witebsky F. G., Ognibene F. P., Wu T. C., Gill V. J., MacLowry J. D. Advantages of a modified toluidine blue O stain and bronchoalveolar lavage for the diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Nov;22(5):803–807. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.5.803-807.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb M. S., Knight S., Mitsuyasu R., Weisman J., Roth M., Young L. S. Prophylaxis of Pneumocystis carinii infection in AIDS with pyrimethamine-sulfadoxine. Lancet. 1984 Aug 18;2(8399):398–399. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90560-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gransden W. R., Brown P. M. Pneumocystis pneumonia and disseminated toxoplasmosis in a male homosexual. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 May 21;286(6378):1614–1614. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6378.1614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryzan S., Paradis I. L., Zeevi A., Duquesnoy R. J., Dummer J. S., Griffith B. P., Hardesty R. L., Trento A., Nalesnik M. A., Dauber J. H. Unexpectedly high incidence of Pneumocystis carinii infection after lung-heart transplantation. Implications for lung defense and allograft survival. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Jun;137(6):1268–1274. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.6.1268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ham E. K., Greenberg D., Reynolds R. C., Singer D. B. Ultrastructure of Pneumocystis carinii. Exp Mol Pathol. 1971 Jun;14(3):362–372. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(71)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haron E., Bodey G. P., Luna M. A., Dekmezian R., Elting L. Has the incidence of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in cancer patients increased with the AIDS epidemic? Lancet. 1988 Oct 15;2(8616):904–905. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92498-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartz J. W., Geisinger K. R., Scharyj M., Muss H. B. Granulomatous pneumocystosis presenting as a solitary pulmonary nodule. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1985 May;109(5):466–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendley J. O., Weller T. H. Activation and transmission in rats of infection with Pneumocystis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Sep;137(4):1401–1404. doi: 10.3181/00379727-137-35798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodson E. M., Springthorpe B. J. Medical problems in refugee children evacuated from South Vietnam. Med J Aust. 1976 Nov 13;2(20):747–749. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1976.tb128274.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffer P. Gallium and infection. J Nucl Med. 1980 May;21(5):484–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann B., Odum N., Platz P., Ryder L. P., Svejgaard A., Nielsen P. B., Holten-Andersen W., Gerstoft J., Nielsen J. O., Mojon M. Humoral responses to Pneumocystis carinii in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and in immunocompromised homosexual men. J Infect Dis. 1985 Oct;152(4):838–840. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.4.838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holten-Andersen W., Kolmos H. J. Comparison of methenamine silver nitrate and Giemsa stain for detection of Pneumocystis carinii in bronchoalveolar lavage specimens from HIV infected patients. APMIS. 1989 Aug;97(8):745–747. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1989.tb00472.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong S. T., Steele P. E., Cushion M. T., Walzer P. D., Stringer S. L., Stringer J. R. Pneumocystis carinii karyotypes. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Aug;28(8):1785–1795. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.8.1785-1795.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopewell P. C. Diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 1988 Jun;2(2):409–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Feldman S., Sanyal S. K. Treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Can Med Assoc J. 1975 Jun 14;112(13 Spec No):47–50. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Gigliotti F. Nomenclature for Pneumocystis carinii. J Infect Dis. 1988 Mar;157(3):432–433. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.3.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Gray V. L., Gutteridge W. E., Latter V. S., Pudney M. Efficacy of a hydroxynaphthoquinone, 566C80, in experimental Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Feb;34(2):225–228. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.2.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Kuhn S., Chaudhary S., Feldman S., Verzosa M., Aur R. J., Pratt C., George S. L. Successful chemoprophylaxis for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. N Engl J Med. 1977 Dec 29;297(26):1419–1426. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197712292972602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., McNabb P. C., Makres T. D., Feldman S. Efficacy of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole in the prevention and treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Mar;5(3):289–293. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.3.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T. Pneumocystis carinii: taxing taxonomy. Eur J Epidemiol. 1989 Sep;5(3):265–269. doi: 10.1007/BF00144824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ieki R., Furuta T., Asano S., Mori S., Kudoh S., Kimura H., Takaku F. Effect of recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on Pneumocystis carinii infection in nude mice. Jpn J Exp Med. 1989 Apr;59(2):51–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JIROVEC O., VANEK J. Zur Morphologie der Pneumocystis carinii und zur Pathogenese der Pneumocystis-Pneumonie. Zentralbl Allg Pathol. 1954 Nov 20;92(10-11):424–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe H. S., Abrams D. I., Ammann A. J., Lewis B. J., Golden J. A. Complications of co-trimoxazole in treatment of AIDS-associated Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in homosexual men. Lancet. 1983 Nov 12;2(8359):1109–1111. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90627-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe J. P., Maki D. G. Lung biopsy in immunocompromised patients: one institution's experience and an approach to management of pulmonary disease in the compromised host. Cancer. 1981 Sep 1;48(5):1144–1153. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19810901)48:5<1144::aid-cncr2820480518>3.0.co;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins R., Myerowitz R. L., Kavic T., Slasky S. Diagnostic yield of transbronchoscopic biopsies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1979 Dec;72(6):926–930. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/72.6.926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jules-Elysee K. M., Stover D. E., Zaman M. B., Bernard E. M., White D. A. Aerosolized pentamidine: effect on diagnosis and presentation of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Ann Intern Med. 1990 May 15;112(10):750–757. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-112-10-750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagawa F. T., Kirsch C. M., Yenokida G. G., Levine M. L. Serum lactate dehydrogenase activity in patients with AIDS and Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. An adjunct to diagnosis. Chest. 1988 Nov;94(5):1031–1033. doi: 10.1378/chest.94.5.1031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay R., DuBois R. E. Clindamycin/primaquine therapy and secondary prophylaxis against Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in patients with AIDS. South Med J. 1990 Apr;83(4):403–404. doi: 10.1097/00007611-199004000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch M., Heizmann W. Problems in the detection of Pneumocystis carinii by indirect immunofluorescence. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990 Jan;9(1):58–59. doi: 10.1007/BF01969543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Allegra C. J., Kennedy S., Swan J. C., Drake J., Parrillo J. E., Chabner B., Masur H. Efficacy of trimetrexate, a potent lipid-soluble antifolate, in the treatment of rodent Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988 Nov;39(5):491–496. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1988.39.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Halpern J. L., Swan J. C., Moss J., Parrillo J. E., Masur H. Identification of antigens and antibodies specific for Pneumocystis carinii. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 15;140(6):2023–2031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Masur H. Prophylaxis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia: an update. J Infect Dis. 1989 Nov;160(5):882–886. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.5.882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Ng V. L., Masur H., Leoung G., Hadley W. K., Evans G., Lane H. C., Ognibene F. P., Shelhamer J., Parrillo J. E. Diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia: improved detection in sputum with use of monoclonal antibodies. N Engl J Med. 1988 Mar 10;318(10):589–593. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198803103181001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer E. L., Sanger J. J., Garay S. M., Greene J. B., Tiu S., Banner H., McCauley D. I. Gallium-67 scans of the chest in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Nucl Med. 1987 Jul;28(7):1107–1114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre C. R., Sulzer A. J., Norman L. G. Serial propagation of Pneumocystis carinii in cell line cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1204–1206. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1204-1206.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leigh T. R., Parsons P., Hume C., Husain O. A., Gazzard B., Collins J. V. Sputum induction for diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Lancet. 1989 Jul 22;2(8656):205–206. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90382-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leoung G. S., Mills J., Hopewell P. C., Hughes W., Wofsy C. Dapsone-trimethoprim for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Jul;105(1):45–48. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-105-1-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidman C., Ortqvist A., Lundbergh P., Julander I., Bergdahl S. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in Stockholm, Sweden: treatment, outcome, one-year-follow-up and pyrimethamine prophylaxis. Scand J Infect Dis. 1989;21(4):381–387. doi: 10.3109/00365548909167441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limper A. H., Martin W. J., 2nd Pneumocystis carinii: inhibition of lung cell growth mediated by parasite attachment. J Clin Invest. 1990 Feb;85(2):391–396. doi: 10.1172/JCI114451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limper A. H., Offord K. P., Smith T. F., Martin W. J., 2nd Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Differences in lung parasite number and inflammation in patients with and without AIDS. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Nov;140(5):1204–1209. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.5.1204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y. C., Tomashefski J. F., Jr, Tomford J. W., Green H. Necrotizing Pneumocystis carinii vasculitis associated with lung necrosis and cavitation in a patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1989 May;113(5):494–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. G., Smith J. S., Meier J. L. Attachment of Pneumocystis carinii to rat pneumocytes. Lab Invest. 1986 Jun;54(6):609–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas S. B. AIDS in Africa--clinicopathological aspects. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1988;82(6):801–802. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(88)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luce J. M., Stover D. E. Controversies in pulmonary medicine. Presumed Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia should be treated empirically in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Oct;138(4):1076–1077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren B., Cotton R., Lundgren J. D., Edman J. C., Kovacs J. A. Identification of Pneumocystis carinii chromosomes and mapping of five genes. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1705–1710. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1705-1710.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macher A. M., Bardenstein D. S., Zimmerman L. E., Steigman C. K., Pastore L., Poretz D. M., Eron L. J. Pneumocystis carinii choroiditis in a male homosexual with AIDS and disseminated pulmonary and extrapulmonary P. carinii infection. N Engl J Med. 1987 Apr 23;316(17):1092–1092. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198704233161715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahan C. T., Sale G. E. Rapid methenamine silver stain for Pneumocystis and fungi. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1978 Jul;102(7):351–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. J., 2nd, Smith T. F., Sanderson D. R., Brutinel W. M., Cockerill F. R., 3rd, Douglas W. W. Role of bronchoalveolar lavage in the assessment of opportunistic pulmonary infections: utility and complications. Mayo Clin Proc. 1987 Jul;62(7):549–557. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)62292-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masur H. Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare: another scourge for individuals with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. JAMA. 1982 Dec 10;248(22):3013–3013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean I., Lucas C. R., Mashford M. L., Harman P. J. Modified trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole doses in Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Lancet. 1987 Oct 10;2(8563):857–858. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuwissen J. H., Tauber I., Leeuwenberg A. D., Beckers P. J., Sieben M. Parasitologic and serologic observations of infection with Pneumocystis in humans. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jul;136(1):43–49. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan S. A., Luce J. M., Golden J., Stulbarg M., Hopewell P. C. Transbronchial biopsy without fluoroscopy in patients with diffuse roentgenographic infiltrates and the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Feb;137(2):486–488. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.2.486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery A. B., Debs R. J., Luce J. M., Corkery K. J., Turner J., Brunette E. N., Lin E. T., Hopewell P. C. Aerosolised pentamidine as sole therapy for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Lancet. 1987 Aug 29;2(8557):480–483. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91794-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery A. B., Debs R. J., Luce J. M., Corkery K. J., Turner J., Brunette E. N., Lin E. T., Hopewell P. C. Selective delivery of pentamidine to the lung by aerosol. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Feb;137(2):477–478. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.2.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery A. B., Debs R. J., Luce J. M., Corkery K. J., Turner J., Hopewell P. C. Aerosolized pentamidine as second line therapy in patients with AIDS and Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Chest. 1989 Apr;95(4):747–750. doi: 10.1378/chest.95.4.747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mottin D., Denis M., Dombret H., Rossert J., Mayaud C., Akoun G. Role for steroids in treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in AIDS. Lancet. 1987 Aug 29;2(8557):519–519. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91841-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy M. J., Pifer L. L., Hughes W. T. Pneumocystis carinii in vitro: A study by scanning electron microscopy. Am J Pathol. 1977 Feb;86(2):387–401. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musto L., Flanigan M., Elbadawi A. Ten-minute silver stain for Pneumocystis carinii and fungi in tissue sections. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1982 Jun;106(6):292–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naafs B. Pentamidine-induced diabetes mellitus. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1985;79(1):141–141. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(85)90267-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natale R. B., Yagoda A., Brown A., Singer C., Stover D., Bajorunas D. Combined Pneumocystis carinii and Nocardia asteroides pneumonitis in a patient with an ACTH-producing carcinoid. Cancer. 1981 Jun 15;47(12):2933–2935. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19810615)47:12<2933::aid-cncr2820471233>3.0.co;2-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neiman P. E., Thomas E. D., Reeves W. C., Ray C. G., Sale G., Lerner K. G., Buckner C. D., Clift R. A., Storb R., Weiden P. L. Opportunistic infection and interstitial pneumonia following marrow transplantation for aplastic anemia and hematologic malignancy. Transplant Proc. 1976 Dec;8(4):663–667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng V. L., Yajko D. M., McPhaul L. W., Gartner I., Byford B., Goodman C. D., Nassos P. S., Sanders C. A., Howes E. L., Leoung G. Evaluation of an indirect fluorescent-antibody stain for detection of Pneumocystis carinii in respiratory specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 May;28(5):975–979. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.5.975-979.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ognibene F. P., Gill V. J., Pizzo P. A., Kovacs J. A., Godwin C., Suffredini A. F., Shelhamer J. H., Parrillo J. E., Masur H. Induced sputum to diagnose Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in immunosuppressed pediatric patients. J Pediatr. 1989 Sep;115(3):430–433. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(89)80848-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pifer L. L., Hughes W. T., Stagno S., Woods D. Pneumocystis carinii infection: evidence for high prevalence in normal and immunosuppressed children. Pediatrics. 1978 Jan;61(1):35–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pifer L. L., Niell H. B., Morrison B. J., Counce J. D., Jr, Freeman J. M., Woods D. R., Neely C. L. Pneumocystis carinii antigenemia in adults with malignancy, infection, or pulmonary disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Nov;20(5):887–890. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.5.887-890.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pifer L. L. Serodiagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii. Chest. 1985 May;87(5):698–700. doi: 10.1378/chest.87.5.698a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus P. S., Hurwitz M. D., Kallenbach J. M., Abramowitz J. A., Zwi S. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in Johannesburg. S Afr Med J. 1987 Mar 7;71(5):289–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus P. S., Sandler M. A., Naude G. E., Kallenbach J. M., Isaacson C., Zwi S. Multiple pulmonary cavities--an unusual complication of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. S Afr Med J. 1987 Dec 19;72(12):871–872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintozzi R. L. Modified Grocott's methenamine silver nitrate method for quick staining of Pneumocystis carinii. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Aug;31(8):803–805. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.8.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poblete R. B., Rodriguez K., Foust R. T., Reddy K. R., Saldana M. J. Pneumocystis carinii hepatitis in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) Ann Intern Med. 1989 May 1;110(9):737–738. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-110-9-737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pottratz S. T., Martin W. J., 2nd Role of fibronectin in Pneumocystis carinii attachment to cultured lung cells. J Clin Invest. 1990 Feb;85(2):351–356. doi: 10.1172/JCI114445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queener S. F., Bartlett M. S., Jay M. A., Durkin M. M., Smith J. W. Activity of lipid-soluble inhibitors of dihydrofolate reductase against Pneumocystis carinii in culture and in a rat model of infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Sep;31(9):1323–1327. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.9.1323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queener S. F., Bartlett M. S., Richardson J. D., Durkin M. M., Jay M. A., Smith J. W. Activity of clindamycin with primaquine against Pneumocystis carinii in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jun;32(6):807–813. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.6.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radin D. R., Baker E. L., Klatt E. C., Balthazar E. J., Jeffrey R. B., Jr, Megibow A. J., Ralls P. W. Visceral and nodal calcification in patients with AIDS-related Pneumocystis carinii infection. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1990 Jan;154(1):27–31. doi: 10.2214/ajr.154.1.2104720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahimi S. A. Disseminated Pneumocystis carinii in thymic alymphoplasia. Arch Pathol. 1974 Mar;97(3):162–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramaswamy G., Jagadha V., Tchertkoff V. Diffuse alveolar damage and interstitial fibrosis in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patients without concurrent pulmonary infection. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1985 May;109(5):408–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao C. P., Gelfand E. W. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis in patients with hypogammaglobulinemia and intact T cell immunity. J Pediatr. 1983 Sep;103(3):410–412. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80415-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao N. A., Zimmerman P. L., Boyer D., Biswas J., Causey D., Beniz J., Nichols P. W. A clinical, histopathologic, and electron microscopic study of Pneumocystis carinii choroiditis. Am J Ophthalmol. 1989 Mar 15;107(3):218–228. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(89)90303-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raviglione M. C., Garner G. R., Mullen M. P. Pneumocystis carinii in bone marrow. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Aug 1;109(3):253–253. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-3-253_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman J. C. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in an adopted Vietnamese infant. A case of diffuse, fulminant disease, with recovery. JAMA. 1974 Dec 16;230(11):1561–1563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter W. M., Cimoch P. J. Dapsone-induced methemoglobinemia in a patient with P. carinii pneumonia and AIDS. N Engl J Med. 1987 Dec 31;317(27):1740–1741. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198712313172715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolston K. V., Rodriguez S., McRory L., Uribe-Botero G., Morice R., Mansell P. W. Diagnostic value of induced sputum in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Med. 1988 Aug;85(2):269–269. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(88)80359-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorat E., Garcia R. L., Skolom J. Diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia by cytologic examination of bronchial washings. JAMA. 1985 Oct 11;254(14):1950–1951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen P. P., Martini N., Armstrong D. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Diagnosis by lung biopsy. Am J Med. 1975 Jun;58(6):794–802. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90634-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi J. F., Dubois A., Bengler C., Arich C., Gervais C., Delage A., Janbon C. Pneumocystis carinii in bone marrow. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Jun;102(6):868–868. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-102-6-868_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi J. F., Eledjam J. J., Delage A., Bengler C., Schved J. F., Bonnafoux J. Pneumocystis carinii infection of bone marrow in patients with malignant lymphoma and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Original report of three cases. Arch Intern Med. 1990 Feb;150(2):450–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruebush T. K., 2nd, Weinstein R. A., Baehner R. L., Wolff D., Bartlett M., Gonzles-Crussi F., Sulzer A. J., Schultz M. G. An outbreak of pneumocystis pneumonia in children with acute lymphocytic leukemia. Am J Dis Child. 1978 Feb;132(2):143–148. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1978.02120270041009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruf B., Pohle H. D. Clindamycin/primaquine for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Lancet. 1989 Sep 9;2(8663):626–627. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90755-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santiago-Delpín E. A., Mora E., González Z. A., Morales-Otero L. A., Bermudez R. Factors in an outbreak of Pneumocystis carinii in a transplant unit. Transplant Proc. 1988 Feb;20(1 Suppl 1):462–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar T. K., Barker P. V., Gumaste V. V. Role of bronchial brush biopsy in AIDS with Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Chest. 1985 Apr;87(4):553–554. doi: 10.1378/chest.87.4.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattler F. R., Allegra C. J., Verdegem T. D., Akil B., Tuazon C. U., Hughlett C., Ogata-Arakaki D., Feinberg J., Shelhamer J., Lane H. C. Trimetrexate-leucovorin dosage evaluation study for treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jan;161(1):91–96. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saulsbury F. T., Bernstein M. T., Winkelstein J. A. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia as the presenting infection in congenital hypogammaglobulinemia. J Pediatr. 1979 Oct;95(4):559–561. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80766-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinella R. A., Breda S. D., Hammerschlag P. E. Otic infection due to Pneumocystis carinii in an apparently healthy man with antibody to the human immunodeficiency virus. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Mar;106(3):399–400. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-3-399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Settnes O. P., Larsen P. E. Inhibition of toluidine blue O stain for Pneumocystis carinii by additives in the diethyl ether. Am J Clin Pathol. 1979 Sep;72(3):493–494. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/72.3.493a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman B. A., Rubinstein A. Serum lactate dehydrogenase levels in adults and children with acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) and AIDS-related complex: possible indicator of B cell lymphoproliferation and disease activity. Effect of intravenous gammaglobulin on enzyme levels. Am J Med. 1985 May;78(5):728–736. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90275-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer C., Armstrong D., Rosen P. P., Schottenfeld D. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia: a cluster of eleven cases. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Jun;82(6):772–777. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-82-6-722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer F., Talavera W., Zumoff B. Elevated levels of angiotensin-converting enzyme in Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Chest. 1989 Apr;95(4):803–806. doi: 10.1378/chest.95.4.803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. A., Hirschfield L. S., Zahtz G., Siegal F. P. Pneumocystis carinii otitis media. Am J Med. 1988 Nov;85(5):745–746. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(88)80264-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobonya R. E., Barbee R. A., Wiens J., Trego D. Detection of fungi and other pathogens in immunocompromised patients by bronchoalveolar lavage in an area endemic for coccidioidomycosis. Chest. 1990 Jun;97(6):1349–1355. doi: 10.1378/chest.97.6.1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogin M. L., Edman J. C. A self-splicing intron in the small subunit rRNA gene of Pneumocystis carinii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):5349–5359. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.5349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogin M. L., Gunderson J. H., Elwood H. J., Alonso R. A., Peattie D. A. Phylogenetic meaning of the kingdom concept: an unusual ribosomal RNA from Giardia lamblia. Science. 1989 Jan 6;243(4887):75–77. doi: 10.1126/science.2911720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl-Bayliss C. M., Kalman C. M., Laskin O. L. Pentamidine-induced hypoglycemia in patients with the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1986 Mar;39(3):271–275. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1986.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoicescu V. Some aspects of the invasion mechanism in human pneumocystosis. Arch Roum Pathol Exp Microbiol. 1977 Jul-Dec;36(3-4):301–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telzak E. E., Cote R. J., Gold J. W., Campbell S. W., Armstrong D. Extrapulmonary Pneumocystis carinii infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 May-Jun;12(3):380–386. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.3.380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toma E., Fournier S., Poisson M., Morisset R., Phaneuf D., Vega C. Clindamycin with primaquine for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Lancet. 1989 May 13;1(8646):1046–1048. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92446-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger P. D., Rosenblum M., Krown S. E. Disseminated Pneumocystis carinii infection in a patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Hum Pathol. 1988 Jan;19(1):113–116. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(88)80327-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vavra J., Kucera K. Pneumocystis carinii delanoë, its ultrastructure and ultrastructural affinities. J Protozool. 1970 Aug;17(3):463–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1970.tb04715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINSLOW D. J., HATHAWAY B. M. Pulmonary pneumocystosis and cryptococcosis; report of a case of mixed infection in a United States male adult. Am J Clin Pathol. 1959 Apr;31(4):337–342. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/31.4.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield A. E., Hopkin J. M., Burns J., Hipkiss J. B., Stewart T. J., Moxon E. R. Cloning of DNA from Pneumocystis carinii. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):859–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield A. E., Pixley F. J., Banerji S., Sinclair K., Miller R. F., Moxon E. R., Hopkin J. M. Detection of Pneumocystis carinii with DNA amplification. Lancet. 1990 Aug 25;336(8713):451–453. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker A. N., Garner R. E., Horst M. N. Immunocytochemical detection of chitin in Pneumocystis carinii. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):412–415. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.412-415.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walmsley S., Salit I. E., Brunton J. The possible role of corticosteroid therapy for pneumocystis pneumonia in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1988;1(4):354–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Linke M. J. A comparison of the antigenic characteristics of rat and human Pneumocystis carinii by immunoblotting. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2257–2265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waskin H., Stehr-Green J. K., Helmick C. G., Sattler F. R. Risk factors for hypoglycemia associated with pentamidine therapy for Pneumocystis pneumonia. JAMA. 1988 Jul 15;260(3):345–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe J., Hori H., Tanabe K., Nakamura Y. Phylogenetic association of Pneumocystis carinii with the 'Rhizopoda/Myxomycota/Zygomycota group' indicated by comparison of 5S ribosomal RNA sequences. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Jan 15;32(2-3):163–167. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts J. C., Chandler F. W. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. The nature and diagnostic significance of the methenamine silver-positive "intracystic bodies". Am J Surg Pathol. 1985 Oct;9(10):744–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheat L. J., Connolly-Stringfield P., Kohler R. B., Frame P. T., Gupta M. R. Histoplasma capsulatum polysaccharide antigen detection in diagnosis and management of disseminated histoplasmosis in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Med. 1989 Oct;87(4):396–400. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(89)80820-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. V., Haddad Z. H., Brunner E., Sainz C. Desensitization to trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole in patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome and Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Ann Allergy. 1989 Mar;62(3):177–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witebsky F. G., Andrews J. W., Gill V. J., MacLowry J. D. Modified toluidine blue O stain for Pneumocystis carinii: further evaluation of some technical factors. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Apr;26(4):774–775. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.4.774-775.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff L. J., Bartlett M. S., Baehner R. L., Grosfeld J. L., Smith J. W. The causes of interstitial pneumonitis in immunocompromised children: an aggressive systematic approach to diagnosis. Pediatrics. 1977 Jul;60(1):41–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolfenden J. M., Carrasquillo J. A., Larson S. M., Simmons J. T., Masur H., Smith P. D., Shelhamer J. H., Ognibene F. P. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: Ga-67 citrate imaging. Radiology. 1987 Feb;162(2):383–387. doi: 10.1148/radiology.162.2.3492009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoganathan T., Lin H., Buck G. A. An electrophoretic karyotype and assignment of ribosomal genes to resolved chromosomes of Pneumocystis carinii. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Nov;3(11):1473–1480. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00132.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneda K., Walzer P. D. Attachment of Pneumocystis carinii to type I alveolar cells studied by freeze-fracture electron microscopy. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):812–815. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.812-815.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoo O. H., Choi H. S., Cucco R. A., Desmond E., Lesser M. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: diagnosis using minilavage samples. South Med J. 1989 Jul;82(7):829–832. doi: 10.1097/00007611-198907000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S. Management of opportunistic infections complicating the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Med Clin North Am. 1986 May;70(3):677–692. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)30946-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziefer A., Abramowitz J. A. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in HIV-positive and HIV-negative patients. An epidemiological, clinical and histopathological study of 18 patients. S Afr Med J. 1989 Oct 7;76(7):308–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuger A., Wolf B. Z., el-Sadr W., Simberkoff M. S., Rahal J. J. Pentamidine-associated fatal acute pancreatitis. JAMA. 1986 Nov 7;256(17):2383–2385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Rio C., Guarner J., Honig E. G., Slade B. A. Sputum examination in the diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1988 Dec;112(12):1229–1232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]