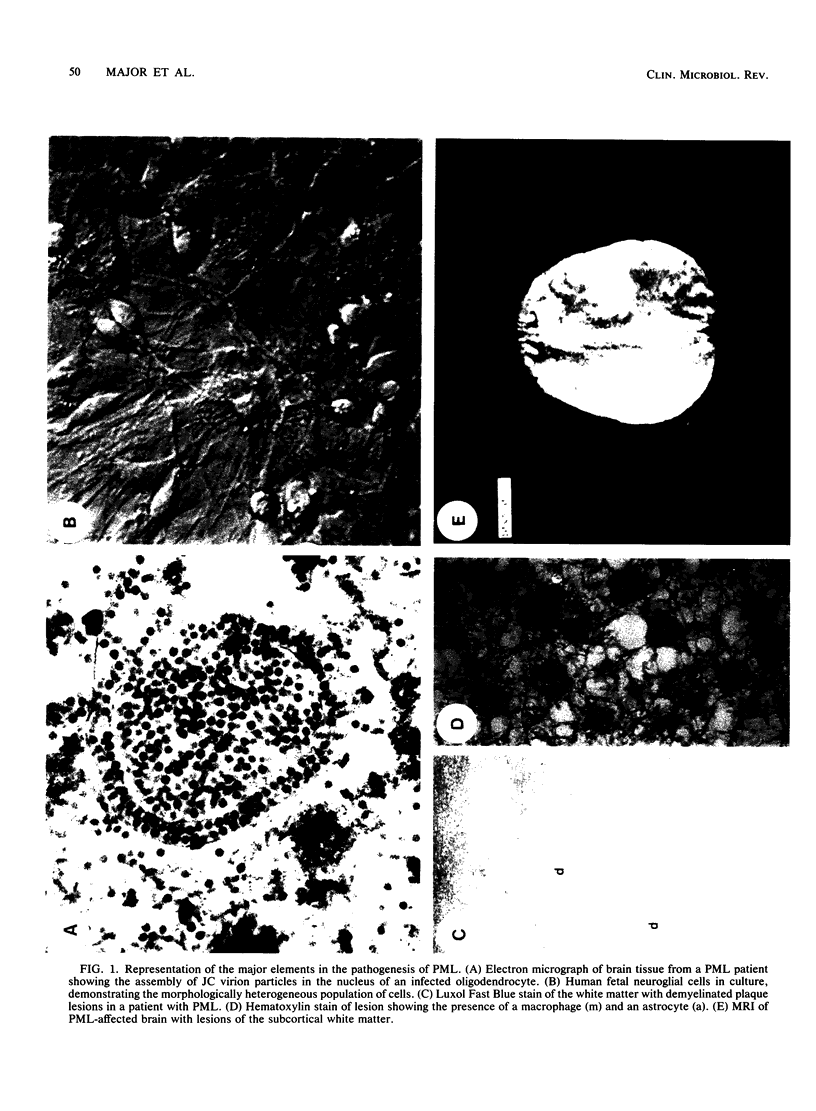
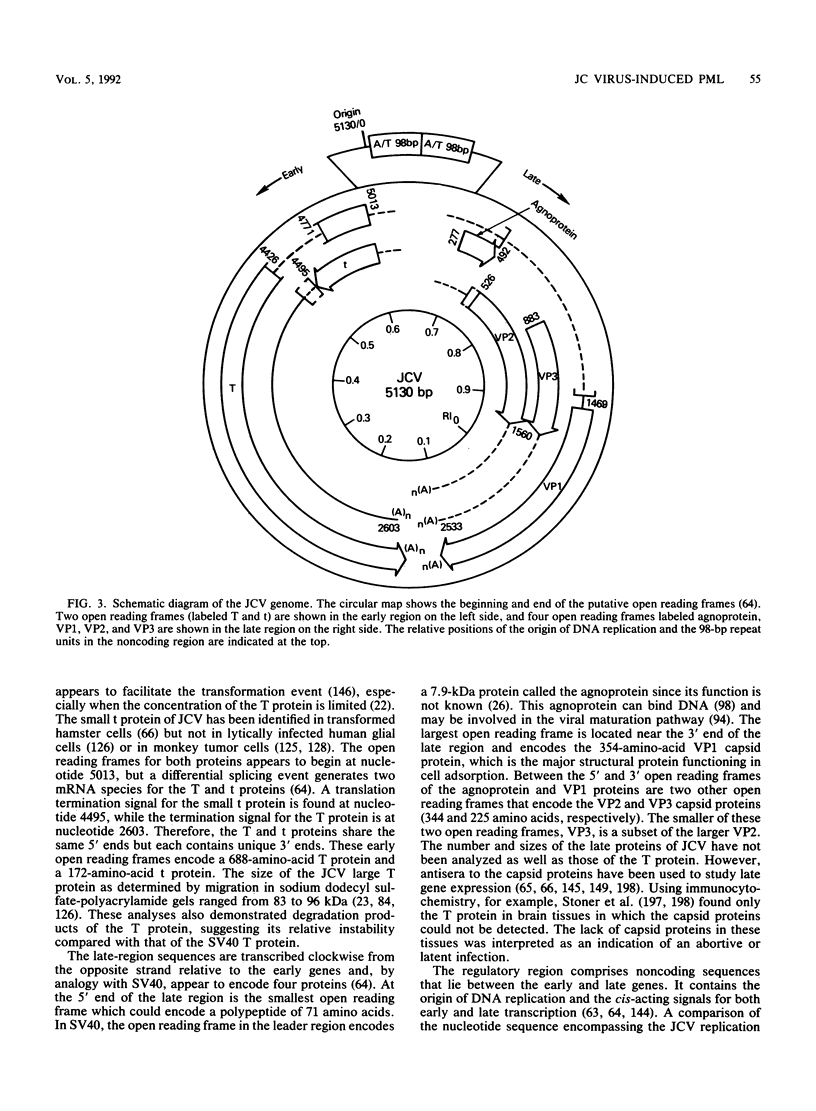
Abstract
Studies of the pathogenesis and molecular biology of JC virus infection over the last two decades have significantly changed our understanding of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, which can be described as a subacute viral infection of neuroglial cells that probably follows reactivation of latent infection rather than being the consequence of prolonged JC virus replication in the brain. There is now sufficient evidence to suggest that JC virus latency occurs in kidney and B cells. However, JC virus isolates from brain or kidney differ in the regulatory regions of their viral genomes which are controlled by host cell factors for viral gene expression and replication. DNA sequences of noncoding regions of the viral genome display a certain heterogeneity among isolates from brain and kidney. These data suggest that an archetypal strain of JC virus exists whose sequence is altered during replication in different cell types. The JC virus regulatory region likely plays a significant role in establishing viral latency and must be acted upon for reactivation of the virus. A developing hypothesis is that reactivation takes place from latently infected B lymphocytes that are activated as a result of immune suppression. JC virus enters the brain in the activated B cell. Evidence for this mechanism is the detection of JC virus DNA in peripheral blood lymphocytes and infected B cells in the brains of patients with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Once virus enters the brain, astrocytes as well as oligodendrocytes support JC virus multiplication. Therefore, JC virus infection of neuroglial cells may impair other neuroglial functions besides the production and maintenance of myelin. Consequently our increased understanding of the pathogenesis of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy suggests new ways to intervene in JC virus infection with immunomodulation therapies. Perhaps along with trials of nucleoside analogs or interferon administration, this fatal disease, for which no consensus of antiviral therapy exists, may yield to innovative treatment protocols.
Full text
PDF


















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASTROM K. E., MANCALL E. L., RICHARDSON E. P., Jr Progressive multifocal leuko-encephalopathy; a hitherto unrecognized complication of chronic lymphatic leukaemia and Hodgkin's disease. Brain. 1958 Mar;81(1):93–111. doi: 10.1093/brain/81.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed S., Rappaport J., Tada H., Kerr D., Khalili K. A nuclear protein derived from brain cells stimulates transcription of the human neurotropic virus promoter, JCVE, in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13899–13905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aksamit A. J., Major E. O., Ghatak N. R., Sidhu G. S., Parisi J. E., Guccion J. G. Diagnosis of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy by brain biopsy with biotin labeled DNA:DNA in situ hybridization. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1987 Sep;46(5):556–566. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198709000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aksamit A. J., Mourrain P., Sever J. L., Major E. O. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: investigation of three cases using in situ hybridization with JC virus biotinylated DNA probe. Ann Neurol. 1985 Oct;18(4):490–496. doi: 10.1002/ana.410180412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aksamit A. J., Sever J. L., Major E. O. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: JC virus detection by in situ hybridization compared with immunohistochemistry. Neurology. 1986 Apr;36(4):499–504. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.4.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amemiya K., Traub R., Durham L., Major E. O. Interaction of a nuclear factor-1-like protein with the regulatory region of the human polyomavirus JC virus. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):7025–7032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amirhaeri S., Wohlrab F., Major E. O., Wells R. D. Unusual DNA structure in the regulatory region of the human papovavirus JC virus. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):922–931. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.922-931.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews C. A., Daniel R. W., Shah K. V. Serologic studies of papovavirus infections in pregnant women and renal transplant recipients. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1983;105:133–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arthur R. R., Beckmann A. M., Li C. C., Saral R., Shah K. V. Direct detection of the human papovavirus BK in urine of bone marrow transplant recipients: comparison of DNA hybridization with ELISA. J Med Virol. 1985 May;16(1):29–36. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890160105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arthur R. R., Dagostin S., Shah K. V. Detection of BK virus and JC virus in urine and brain tissue by the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jun;27(6):1174–1179. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.6.1174-1179.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arthur R. R., Shah K. V., Charache P., Saral R. BK and JC virus infections in recipients of bone marrow transplants. J Infect Dis. 1988 Sep;158(3):563–569. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.3.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assouline J. G., Major E. O. Human fetal Schwann cells support JC virus multiplication. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):1002–1006. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.1002-1006.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer W. R., Turel A. P., Jr, Johnson K. P. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and cytarabine. Remission with treatment. JAMA. 1973 Oct 8;226(2):174–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann A. M., Shah K. V. Propagation and primary isolation of JCV and BKV in urinary epithelial cell cultures. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1983;105:3–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger J. R., Kaszovitz B., Post M. J., Dickinson G. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy associated with human immunodeficiency virus infection. A review of the literature with a report of sixteen cases. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Jul;107(1):78–87. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-1-78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger J. R., Mucke L. Prolonged survival and partial recovery in AIDS-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Neurology. 1988 Jul;38(7):1060–1065. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.7.1060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bikel I., Montano X., Agha M. E., Brown M., McCormack M., Boltax J., Livingston D. M. SV40 small t antigen enhances the transformation activity of limiting concentrations of SV40 large T antigen. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90435-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollag B., Chuke W. F., Frisque R. J. Hybrid genomes of the polyomaviruses JC virus, BK virus, and simian virus 40: identification of sequences important for efficient transformation. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):863–872. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.863-872.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch E. P., Cancilla P. A., Cornell S. H. Letter: Computerized tomography in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Arch Neurol. 1976 Mar;33(3):216–216. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1976.00500030072019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Radonovich M., Vodkin M., Natarajan V., Thoren M., Das G., Janik J., Salzman N. P. Site-specific base substitution and deletion mutations that enhance or suppress transcription of the SV40 major late RNA. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):625–633. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90318-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenan M., Parish C. R. Modification of lymphocyte migration by sulfated polysaccharides. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Apr;16(4):423–430. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks B. R., Walker D. L. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Neurol Clin. 1984 May;2(2):299–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P., Tsai T., Gajdusek D. C. Seroepidemiology of human papovaviruses. Discovery of virgin populations and some unusual patterns of antibody prevalence among remote peoples of the world. Am J Epidemiol. 1975 Oct;102(4):331–340. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckman R., Wiltshaw E. Letter: Progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy successfully treated with cytosine arabinoside. Br J Haematol. 1976 Sep;34(1):153–158. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1976.tb00184.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budka H., Shah K. V. Papovavirus antigens in paraffin sections of PML brains. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1983;105:299–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAVANAGH J. B., GREENBAUM D., MARSHALL A. H., RUBINSTEIN L. J. Cerebral demyelination associated with disorders of the reticuloendothelial system. Lancet. 1959 Oct 10;2(7102):524–529. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)91774-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTENSEN E., FOG M. A case of Schilder's disease in an adult with remarks to the etiology and pathogenesis. Acta Psychiatr Neurol Scand. 1955;30(1-2):141–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1955.tb06054.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Weekly clinicopathological exercises. Case 19-1972. N Engl J Med. 1972 May 11;286(19):1047–1054. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197205112861909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaigne P., Rondot P., Escourolle R., Ribadeau dumas J. L., Cathala F., Hauw J. J. Leucoencéphalopathie multifocale progressive et "gliomes" multiples. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1974 Sep-Oct;130(9-10):379–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celada A., Shiga M., Imagawa M., Kop J., Maki R. A. Identification of a nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence of the I-A beta gene. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3995–4002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesters P. M., Heritage J., McCance D. J. Persistence of DNA sequences of BK virus and JC virus in normal human tissues and in diseased tissues. J Infect Dis. 1983 Apr;147(4):676–684. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.4.676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Baldwin A. S., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. Human CCAAT-binding proteins have heterologous subunits. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90483-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuke W. F., Walker D. L., Peitzman L. B., Frisque R. J. Construction and characterization of hybrid polyomavirus genomes. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):960–971. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.960-971.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. V., Gardner S. D., Field A. M. Human polyomavirus infection in renal allograft recipients. Br Med J. 1973 Aug 18;3(5876):371–375. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5876.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. V., Wolfendale M. R., Daniel R. A., Dhanjal N. K., Gardner S. D., Gibson P. E., Field A. M. A prospective study of human polyomavirus infection in pregnancy. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jul;142(1):1–8. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conomy J. P., Beard N. S., Matsumoto H., Roessmann U. Cytarabine treatment of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Clinical course and detection of virus-like particles after antiviral chemotherapy. JAMA. 1974 Sep 2;229(10):1313–1316. doi: 10.1001/jama.229.10.1313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conomy J. P., Weinstein M. A., Agamanolis D., Holt W. S. Computed tomography in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1976 Oct;127(4):663–665. doi: 10.2214/ajr.127.4.663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway B., Halliday W. C., Brunham R. C. Human immunodeficiency virus-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: apparent response to 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 May-Jun;12(3):479–482. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.3.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. D. Current concepts. B lymphocytes. Normal development and function. N Engl J Med. 1987 Dec 3;317(23):1452–1456. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198712033172306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham M. E., Kishore P. R., Rengachary S. S., Preskorn S. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy presenting as focal mass lesion in the brain. Surg Neurol. 1977 Dec;8(6):448–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel R., Shah K., Madden D., Stagno S. Serological Investigation of the possibility of congenital transmission of papovavirus JC. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):319–321. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.319-321.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson D. M. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in myasthenia gravis. Ann Neurol. 1982 Feb;11(2):218–219. doi: 10.1002/ana.410110227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Bollekens J., Staub A., Benoist C., Mathis D. A multiplicity of CCAAT box-binding proteins. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):863–872. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90513-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson N., Bernards R., Friend S. H., Gooding L. R., Hassell J. A., Major E. O., Pipas J. M., Vandyke T., Harlow E. Large T antigens of many polyomaviruses are able to form complexes with the retinoblastoma protein. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1353–1356. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1353-1356.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dörries K., Johnson R. T., ter Meulen V. Detection of polyoma virus DNA in PML-brain tissue by (in situ) hybridization. J Gen Virol. 1979 Jan;42(1):49–57. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-42-1-49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dörries K., Loeber G., Meixensberger J. Association of polyomaviruses JC, SV40, and BK with human brain tumors. Virology. 1987 Sep;160(1):268–270. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90071-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dörries K. Progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy: analysis of JC virus DNA from brain and kidney tissue. Virus Res. 1984 Jan;1(1):25–38. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(84)90032-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan J. D., Ring B. L., Reding M. J., Wells I. C., Shuman R. M. Reticulum cell sarcoma and progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy following renal transplantation. Transplantation. 1980;29(1):84–86. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198001000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder G. A., Major E. O. Early appearance of type II astrocytes in developing human fetal brain. Brain Res. 1988 Jul 1;470(1):146–150. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(88)90211-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Embrey J. R., Silva F. G., Helderman J. H., Peters P. C., Sagalowsky A. I. Long-term survival and late development of bladder cancer in renal transplant patient with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Urol. 1988 Mar;139(3):580–581. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)42533-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell D. F. The EEG in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1969 Feb;26(2):200–205. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(69)90211-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigenbaum L., Khalili K., Major E., Khoury G. Regulation of the host range of human papovavirus JCV. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3695–3698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- First annual meeting of the Society for Experimental Neuropathology. October 1, 1988, Philadelphia, PA. Abstracts. Ann Neurol. 1988 Sep;24(3):471–482. doi: 10.1002/ana.410240330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaegstad T., Sundsfjord A., Arthur R. R., Pedersen M., Traavik T., Subramani S. Amplification and sequencing of the control regions of BK and JC virus from human urine by polymerase chain reaction. Virology. 1991 Feb;180(2):553–560. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90069-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fresa K. L., Karjalainen H. E., Tevethia S. S. Sensitivity of simian virus 40-transformed C57BL/6 mouse embryo fibroblasts to lysis by murine natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 15;138(4):1215–1220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisque R. J., Bream G. L., Cannella M. T. Human polyomavirus JC virus genome. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):458–469. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.458-469.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisque R. J., Martin J. D., Padgett B. L., Walker D. L. Infectivity of the DNA from four isolates of JC virus. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):476–482. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.476-482.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisque R. J. Regulatory sequences and virus-cell interactions of JC virus. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1983;105:41–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisque R. J., Rifkin D. B., Walker D. L. Transformation of primary hamster brain cells with JC virus and its DNA. J Virol. 1980 Jul;35(1):265–269. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.1.265-269.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner S. D., Field A. M., Coleman D. V., Hulme B. New human papovavirus (B.K.) isolated from urine after renal transplantation. Lancet. 1971 Jun 19;1(7712):1253–1257. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91776-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner S. D., MacKenzie E. F., Smith C., Porter A. A. Prospective study of the human polyomaviruses BK and JC and cytomegalovirus in renal transplant recipients. J Clin Pathol. 1984 May;37(5):578–586. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.5.578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner S. D. Prevalence in England of antibody to human polyomavirus (B.k.). Br Med J. 1973 Jan 13;1(5845):77–78. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5845.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gendelman H. E., Friedman R. M., Joe S., Baca L. M., Turpin J. A., Dveksler G., Meltzer M. S., Dieffenbach C. A selective defect of interferon alpha production in human immunodeficiency virus-infected monocytes. J Exp Med. 1990 Nov 1;172(5):1433–1442. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.5.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gendelman H. E., Phelps W., Feigenbaum L., Ostrove J. M., Adachi A., Howley P. M., Khoury G., Ginsberg H. S., Martin M. A. Trans-activation of the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat sequence by DNA viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9759–9763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber M. A., Shah K. V., Thung S. N., Zu Rhein G. M. Immunohistochemical demonstration of common antigen of polyomaviruses in routine histologic tissue sections of animals and man. Am J Clin Pathol. 1980 Jun;73(6):795–797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Lebowitz P., Frisque R. J., Gluzman Y. Identification of a promoter component involved in positioning the 5' termini of simian virus 40 early mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):100–104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GiaRusso M. H., Koeppen A. H. Atypical progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and primary cerebral malignant lymphoma. J Neurol Sci. 1978 Feb;35(2-3):391–398. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(78)90019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y., Sambrook J. F., Frisque R. J. Expression of early genes of origin-defective mutants of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3898–3902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenlee J. E., Keeney P. M. Immunoenzymatic labelling of JC papovavirus T antigen in brains of patients with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Acta Neuropathol. 1986;71(1-2):150–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00687977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenlee J. E. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Curr Clin Top Infect Dis. 1989;10:140–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinnell B. W., Martin J. D., Padgett B. L., Walker D. L. Is progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy a chronic disease because of defective interfering particles or temperature-sensitive mutants of JC virus? J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1143–1150. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1143-1150.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinnell B. W., Padgett B. L., Walker D. L. Comparison of infectious JC virus DNAs cloned from human brain. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):299–308. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.299-308.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinnell B. W., Padgett B. L., Walker D. L. Distribution of nonintegrated DNA from JC papovavirus in organs of patients with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Infect Dis. 1983 Apr;147(4):669–675. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.4.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss P., Dhar R., Khoury G. Simian virus 40 tandem repeated sequences as an element of the early promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):943–947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilleux M. H., Steiner R. E., Young I. R. MR imaging in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1986 Nov-Dec;7(6):1033–1035. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haggerty S., Walker D. L., Frisque R. J. JC virus-simian virus 40 genomes containing heterologous regulatory signals and chimeric early regions: identification of regions restricting transformation by JC virus. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2180–2190. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2180-2190.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho K., Garancis J. C., Paegle R. D., Gerber M. A., Borkowski W. J. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and malignant lymphoma of the brain in a patient with immunosuppressive therapy. Acta Neuropathol. 1980;52(1):81–83. doi: 10.1007/BF00687233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan T. F., Padgett B. L., Walker D. L., Borden E. C., McBain J. A. Rapid detection and identification of JC virus and BK virus in human urine by using immunofluorescence microscopy. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Feb;11(2):178–183. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.2.178-183.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn G. V., Bastian F. O., Moake J. L. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: failure of response to transfer factor and cytarabine. Neurology. 1978 Aug;28(8):794–797. doi: 10.1212/wnl.28.8.794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou-Jong M. H., Larsen S. H., Roman A. Role of the agnoprotein in regulation of simian virus 40 replication and maturation pathways. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):937–939. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.937-939.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houff S. A., Katz D., Kufta C. V., Major E. O. A rapid method for in situ hybridization for viral DNA in brain biopsies from patients with AIDS. AIDS. 1989 Dec;3(12):843–845. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198912000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houff S. A., Major E. O., Katz D. A., Kufta C. V., Sever J. L., Pittaluga S., Roberts J. R., Gitt J., Saini N., Lux W. Involvement of JC virus-infected mononuclear cells from the bone marrow and spleen in the pathogenesis of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. N Engl J Med. 1988 Feb 4;318(5):301–305. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198802043180507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howley P. M., Khoury G., Takemoto K. K., Martin M. A. Polynucleotide sequences common to the genomes of simian virus 40 and the human papovaviruses JC and BK. Virology. 1976 Aug;73(1):303–307. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howley P. M., Rentier-Delrue F., Heilman C. A., Law M. F., Chowdhury K., Israel M. A., Takemoto K. K. Cloned human polyomavirus JC DNA can transform human amnion cells. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):878–882. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.878-882.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoyama Y., Webster H. D., Sternberger N. H., Richardson E. P., Jr, Walker D. L., Quarles R. H., Padgett B. L. Distribution of papovavirus, myelin-associated glycoprotein, and myelin basic protein in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy lesions. Ann Neurol. 1982 Apr;11(4):396–407. doi: 10.1002/ana.410110414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay G., Nomura S., Anderson C. W., Khoury G. Identification of the SV40 agnogene product: a DNA binding protein. Nature. 1981 May 28;291(5813):346–349. doi: 10.1038/291346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones H. R., Jr, Hedley-Whyte E. T., Freidberg S. R., Kelleher J. E., Jr, Krolikowski J. Primary cerebellopontine progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy diagnosed premortem by cerebellar biopsy. Ann Neurol. 1982 Feb;11(2):199–202. doi: 10.1002/ana.410110218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy P. G., Fok-Seang J. Studies on the development, antigenic phenotype and function of human glial cells in tissue culture. Brain. 1986 Dec;109(Pt 6):1261–1277. doi: 10.1093/brain/109.6.1261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney S., Natarajan V., Salzman N. P. Mapping 5' termini of JC virus late RNA. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):216–219. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.216-219.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney S., Natarajan V., Selzer G., Salzman N. P. Mapping 5' termini of JC virus early RNAs. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):651–654. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.651-654.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney S., Natarajan V., Strike D., Khoury G., Salzman N. P. JC virus enhancer-promoter active in human brain cells. Science. 1984 Dec 14;226(4680):1337–1339. doi: 10.1126/science.6095453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kepes J. J., Chou S. M., Price L. W., Jr Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy with 10-year survival in a patient with nontropical sprue. Report of a case with unusual light and electron microscopic features. Neurology. 1975 Nov;25(11):1006–1012. doi: 10.1212/wnl.25.11.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalili K., Feigenbaum L., Khoury G. Evidence for a shift in 5'-termini of early viral RNA during the lytic cycle of JC virus. Virology. 1987 Jun;158(2):469–472. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90224-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalili K., Rappaport J., Khoury G. Nuclear factors in human brain cells bind specifically to the JCV regulatory region. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1205–1210. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02932.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyosawa M., Bosley T. M., Alavi A., Gupta N., Rhodes C. H., Chawluk J., Kushner M., Savino P. J., Sergott R. C., Schatz N. J. Positron emission tomography in a patient with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Neurology. 1988 Dec;38(12):1864–1867. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.12.1864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight R. S., Hyman N. M., Gardner S. D., Gibson P. E., Esiri M. M., Warlow C. P. Progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy and viral antibody titres. J Neurol. 1988 Nov;235(8):458–461. doi: 10.1007/BF00314247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krempien B., Kolkmann F. W., Schiemer H. G., Mayer P. Uber die progressive multifokale Leukoencephalopathie. Beitrag zur Differentialdiagnose mit elektronmikroskopischen und cytophometrischen Untersuchungen. Virchows Arch A Pathol Pathol Anat. 1972;355(2):158–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp L. B., Lipton R. B., Swerdlow M. L., Leeds N. E., Llena J. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: clinical and radiographic features. Ann Neurol. 1985 Apr;17(4):344–349. doi: 10.1002/ana.410170407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law M. F., Martin J. D., Takemoto K. K., Howley P. M. The colinear alignment of the genomes of papovaviruses JC, BK, and SV40. Virology. 1979 Jul 30;96(2):576–587. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90113-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecatsas G., Prozesky O. W., van Wyk J., Els H. J. Papova virus in urine after renal transplantation. Nature. 1973 Feb 2;241(5388):343–344. doi: 10.1038/241343a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledoux S., Libman I., Robert F., Just N. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy with gray matter involvement. Can J Neurol Sci. 1989 May;16(2):200–202. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100028912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. D., Cottingham K. L., Campbell R. J., Moore G. K., Gyorkey F., Ashizawa T., Goldman A. M. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol. 1986 Apr;19(4):399–401. doi: 10.1002/ana.410190419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton R. B., Krupp L., Horoupian D., Hershkovitz S., Arezzo J. C., Kurtzberg D. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy of the posterior fossa in an AIDS patient: clinical, radiographic and evoked potential findings. Eur Neurol. 1988;28(5):258–261. doi: 10.1159/000116280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeber G., Dörries K. DNA rearrangements in organ-specific variants of polyomavirus JC strain GS. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1730–1735. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1730-1735.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- London W. T., Houff S. A., Madden D. L., Fuccillo D. A., Gravell M., Wallen W. C., Palmer A. E., Sever J. L., Padgett B. L., Walker D. L. Brain tumors in owl monkeys inoculated with a human polyomavirus (JC virus). Science. 1978 Sep 29;201(4362):1246–1249. doi: 10.1126/science.211583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- London W. T., Houff S. A., McKeever P. E., Wallen W. C., Sever J. L., Padgett B. L., Walker D. L. Viral-induced astrocytomas in squirrel monkeys. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1983;105:227–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch K. J., Frisque R. J. Factors contributing to the restricted DNA replicating activity of JC virus. Virology. 1991 Jan;180(1):306–317. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90035-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch K. J., Frisque R. J. Identification of critical elements within the JC virus DNA replication origin. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5812–5822. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5812-5822.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Major E. O., Amemiya K., Elder G., Houff S. A. Glial cells of the human developing brain and B cells of the immune system share a common DNA binding factor for recognition of the regulatory sequences of the human polyomavirus, JCV. J Neurosci Res. 1990 Dec;27(4):461–471. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490270405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Major E. O., Matsumura P. Human embryonic kidney cells: stable transformation with an origin-defective simian virus 40 DNA and use as hosts for human papovavirus replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):379–382. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Major E. O., Miller A. E., Mourrain P., Traub R. G., de Widt E., Sever J. Establishment of a line of human fetal glial cells that supports JC virus multiplication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1257–1261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Major E. O., Mourrain P., Cummins C. JC virus-induced owl monkey glioblastoma cells in culture: biological properties associated with the viral early gene product. Virology. 1984 Jul 30;136(2):359–367. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90172-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Major E. O., Traub R. G. JC virus T protein during productive infection in human fetal brain and kidney cells. Virology. 1986 Jan 15;148(1):221–225. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90418-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Major E. O., Vacante D. A. Human fetal astrocytes in culture support the growth of the neurotropic human polyomavirus, JCV. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1989 Jul;48(4):425–436. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198907000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Major E. O., Vacante D. A., Traub R. G., London W. T., Sever J. L. Owl monkey astrocytoma cells in culture spontaneously produce infectious JC virus which demonstrates altered biological properties. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1435–1441. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1435-1441.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandl C. W., Frisque R. J. Characterization of cells transformed by the human polyomavirus JC virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Aug;67(Pt 8):1733–1739. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-8-1733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandl C., Walker D. L., Frisque R. J. Derivation and characterization of POJ cells, transformed human fetal glial cells that retain their permissivity for JC virus. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):755–763. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.755-763.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mark A. S., Atlas S. W. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in patients with AIDS: appearance on MR images. Radiology. 1989 Nov;173(2):517–520. doi: 10.1148/radiology.173.2.2798883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marriott P. J., O'Brien M. D., Mackenzie I. C., Janota I. Progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy: remission with cytarabine. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975 Mar;38(3):205–209. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.38.3.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. D., Brackmann K. H., Grinnell B. W., Frisque R. J., Walker D. L., Green M. Recombinant JC viral DNA: verification and physical map of prototype. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Nov 16;109(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91567-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. D., Frisque R. J., Padgett B. L., Walker D. L. Restriction endonuclease cleavage map of the DNA of JC virus. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):846–855. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.846-855.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. D., King D. M., Slauch J. M., Frisque R. J. Differences in regulatory sequences of naturally occurring JC virus variants. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):306–311. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.306-311.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. D., Padgett B. L., Walker D. L. Characterization of tissue culture-induced heterogeneity in DNAs of independent isolates of JC virus. J Gen Virol. 1983 Oct;64(Pt 10):2271–2280. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-10-2271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda M., Jona M., Yasui K., Nagashima K. Genetic characterization of JC virus Tokyo-1 strain, a variant oncogenic in rodents. Virus Res. 1987 Apr;7(2):159–168. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(87)90077-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller N. R., McKeever P. E., London W., Padgett B. L., Walker D. L., Wallen W. C. Brain tumors of owl monkeys inoculated with JC virus contain the JC virus genome. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):848–856. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.848-856.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamura T., Furuno A., Yoshiike K. DNA rearrangement in the control region for early transcription in a human polyomavirus JC host range mutant capable of growing in human embryonic kidney cells. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):750–756. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.750-756.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamura T., Jikuya H., Soeda E., Yoshiike K. Genomic structure of human polyoma virus JC: nucleotide sequence of the region containing replication origin and small-T-antigen gene. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):73–79. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.73-79.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamura T., Yoshiike K., Takemoto K. K. Characterization of JC papovavirus adapted to growth in human embryonic kidney cells. J Virol. 1980 Aug;35(2):498–504. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.2.498-504.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers C., Frisque R. J., Arthur R. R. Direct isolation and characterization of JC virus from urine samples of renal and bone marrow transplant patients. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4445–4449. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4445-4449.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Rio D. C., Robbins A. K., Tjian R. SV40 gene expression is modulated by the cooperative binding of T antigen to DNA. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):373–384. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mázló M., Tariska I. Are astrocytes infected in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)? Acta Neuropathol. 1982;56(1):45–51. doi: 10.1007/BF00691181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mázló M., Tariska I. Morphological demonstration of the first phase of polyomavirus replication in oligodendroglia cells of human brain in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML). Acta Neuropathol. 1980;49(2):133–143. doi: 10.1007/BF00690753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäntyjärvi R. A., Meurman O. H., Vihma L., Berglund B. A human papovavirus (B.K.), biological properties and seroepidemiology. Ann Clin Res. 1973 Oct;5(5):283–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagashima K., Yasui K., Kimura J., Washizu M., Yamaguchi K., Mori W. Induction of brain tumors by a newly isolated JC virus (Tokyo-1 strain). Am J Pathol. 1984 Sep;116(3):455–463. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nandi A., Das G., Salzman N. P. Characterization of a surrogate TATA box promoter that regulates in vitro transcription of the simian virus 40 major late gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):591–594. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Riordan T., Daly P. A., Hutchinson M., Shattock A. G., Gardner S. D. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy-remission with cytarabine. J Infect. 1990 Jan;20(1):51–54. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(90)92324-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohsumi S., Motoi M., Ogawa K. Induction of undifferentiated tumors by JC virus in the cerebrum of rats. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1986 Jun;36(6):815–825. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1986.tb03116.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. E., Robertson S. M., Padgett B. L., ZuRhein G. M., Walker D. L., Weisblum B. Comparison of JC and BK human papovaviruses with simian virus 40: restriction endonuclease digestion and gel electrophoresis of resultant fragments. J Virol. 1974 Mar;13(3):614–622. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.3.614-622.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett B. L., Rogers C. M., Walker D. L. JC virus, a human polyomavirus associated with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: additional biological characteristics and antigenic relationships. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):656–662. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.656-662.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett B. L., Walker D. L. Prevalence of antibodies in human sera against JC virus, an isolate from a case of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Infect Dis. 1973 Apr;127(4):467–470. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.4.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett B. L., Walker D. L. Virologic and serologic studies of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1983;105:107–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett B. L., Walker D. L., ZuRhein G. M., Eckroade R. J., Dessel B. H. Cultivation of papova-like virus from human brain with progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy. Lancet. 1971 Jun 19;1(7712):1257–1260. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91777-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett B. L., Walker D. L., ZuRhein G. M., Hodach A. E., Chou S. M. JC Papovavirus in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jun;133(6):686–690. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.6.686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett B. L., Walker D. L., ZuRhein G. M., Varakis J. N. Differential neurooncogenicity of strains of JC virus, a human polyoma virus, in newborn Syrian hamsters. Cancer Res. 1977 Mar;37(3):718–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parr J., Horoupian D. S., Winkelman A. C. Cerebellar form of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML). Can J Neurol Sci. 1979 May;6(2):123–128. doi: 10.1017/s031716710011950x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters A. C., Versteeg J., Bots G. T., Boogerd W., Vielvoye G. J. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: immunofluorescent demonstration of simian virus 40 antigen in CSF cells and response to cytarabine therapy. Arch Neurol. 1980 Aug;37(8):497–501. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1980.00500570045006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portegies P., Algra P. R., Hollak C. E., Prins J. M., Reiss P., Valk J., Lange J. M. Response to cytarabine in progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy in AIDS. Lancet. 1991 Mar 16;337(8742):680–681. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92504-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post M. J., Sheldon J. J., Hensley G. T., Soila K., Tobias J. A., Chan J. C., Quencer R. M., Moskowitz L. B. Central nervous system disease in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: prospective correlation using CT, MR imaging, and pathologic studies. Radiology. 1986 Jan;158(1):141–148. doi: 10.1148/radiology.158.1.3940372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preskorn S. H., Watanabe I. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: cerebral mass lesions. Surg Neurol. 1979 Sep;12(3):231–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. W., Nielsen S., Horten B., Rubino M., Padgett B., Walker D. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: a burnt-out case. Ann Neurol. 1983 May;13(5):485–490. doi: 10.1002/ana.410130503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON E. P., Jr Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. N Engl J Med. 1961 Oct 26;265:815–823. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196110262651701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand K. H., Johnson K. P., Rubinstein L. J., Wolinsky J. S., Penney J. B., Walker D. L., Padgett B. L., Merigan T. C. Adenine arabinoside in the treatment of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: use of virus-containing cells in the urine to assess response to therapy. Ann Neurol. 1977 May;1(5):458–462. doi: 10.1002/ana.410010509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymondjean M., Cereghini S., Yaniv M. Several distinct "CCAAT" box binding proteins coexist in eukaryotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):757–761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rentier-Delrue F., Lubiniecki A., Howley P. M. Analysis of JC virus DNA purified directly from human progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy brains. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):761–769. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.761-769.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes R. H., Ward J. M., Walker D. L., Ross A. A. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and retroviral encephalitis in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1988 Dec;112(12):1207–1213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson E. P., Jr, Johnson P. C. Atypical progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy with plasma-cell infiltrates. Acta Neuropathol Suppl. 1975;Suppl 6:247–250. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-08456-4_43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson E. P., Jr, Webster H. D. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: its pathological features. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1983;105:191–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rockwell D., Ruben F. L., Winkelstein A., Mendelow H. Absence of imune deficiencies in a case of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Am J Med. 1976 Sep;61(3):433–436. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90383-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal N., Kress M., Gruss P., Khoury G. BK viral enhancer element and a human cellular homolog. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):749–755. doi: 10.1126/science.6314501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rziha H. J., Bornkamm G. W., zur Hausen H. BK virus: I. Seroepidemiologic studies and serologic response to viral infection. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1978 Jul 4;165(2):73–81. doi: 10.1007/BF02122742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIDMAN R. L., DICKIE M. M., APPEL S. H. MUTANT MICE (QUAKING AND JIMPY) WITH DEFICIENT MYELINATION IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Science. 1964 Apr 17;144(3616):309–311. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3616.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxton C. R., Gailiunas P., Jr, Helderman J. H., Farkas R. A., McCoy R., Diehl J., Sagalowsky A., Murphy F. K., Ross E. D., Silva F. R. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in a renal transplant recipient. Increased diagnostic sensitivity of computed tomographic scanning by double-dose contrast with delayed films. Am J Med. 1984 Aug;77(2):333–337. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90715-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlitt M., Morawetz R. B., Bonnin J., Chandra-Sekar B., Curtiss J. J., Diethelm A. G., Jr, Whelchel J. D., Whitley R. J. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: three patients diagnosed by brain biopsy, with prolonged survival in two. Neurosurgery. 1986 Apr;18(4):407–414. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198604000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidbauer M., Budka H., Shah K. V. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) in AIDS and in the pre-AIDS era. A neuropathological comparison using immunocytochemistry and in situ DNA hybridization for virus detection. Acta Neuropathol. 1990;80(4):375–380. doi: 10.1007/BF00307690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider A., Papendick U., Gissmann L., De Villiers E. M. Interferon treatment of human genital papillomavirus infection: importance of viral type. Int J Cancer. 1987 Nov 15;40(5):610–614. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910400506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafran B., Roke M. E., Barr R. M., Cairncross J. G. Contrast enhancing lesions in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: a clinicopathological correlation. Can J Neurol Sci. 1987 Nov;14(4):600–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapshak P., Tourtellotte W. W., Wolman M., Verity N., Verity M. A., Schmid P., Syndulko K., Bedows E., Boostanfar R., Darvish M. Search for virus nucleic acid sequences in postmortem human brain tissue using in situ hybridization technology with cloned probes: some solutions and results on progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and subacute sclerosing panencephalitis tissue. J Neurosci Res. 1986;16(1):281–301. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490160124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shein H. M. Propagation of human fetal spongioblasts and astrocytes in dispersed cell cultures. Exp Cell Res. 1965 Dec;40(3):554–569. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(65)90234-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sima A. A., Finkelstein S. D., McLachlan D. R. Multiple malignant astrocytomas in a patient with spontaneous progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Ann Neurol. 1983 Aug;14(2):183–188. doi: 10.1002/ana.410140205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J. A., Khoury G., Jay G., Howley P. M., Scangos G. A. Early regions of JC virus and BK virus induce distinct and tissue-specific tumors in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8288–8292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J. A., Scangos G. A., Cork L., Jay G., Khoury G. The early region of human papovavirus JC induces dysmyelination in transgenic mice. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):13–18. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90855-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. R., Sima A. A., Salit I. E., Gentili F. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: failure of cytarabine therapy. Neurology. 1982 Feb;32(2):200–203. doi: 10.1212/wnl.32.2.200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogos V., Bussolino F., Pilia E., Torelli S., Gremo F. Acetylcholine-induced production of platelet-activating factor by human fetal brain cells in culture. J Neurosci Res. 1990 Dec;27(4):706–711. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490270431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoner G. L., Ryschkewitsch C. F., Walker D. L., Soffer D., Webster H. D. A monoclonal antibody to SV40 large T-antigen labels a nuclear antigen in JC virus-transformed cells and in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) brain infected with JC virus. J Neuroimmunol. 1988 Mar;17(4):331–345. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(88)90124-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoner G. L., Ryschkewitsch C. F., Walker D. L., Webster H. D. JC papovavirus large tumor (T)-antigen expression in brain tissue of acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) and non-AIDS patients with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2271–2275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoner G. L., Soffer D., Ryschkewitsch C. F., Walker D. L., Webster H. D. A double-label method detects both early (T-antigen) and late (capsid) proteins of JC virus in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy brain tissue from AIDS and non-AIDS patients. J Neuroimmunol. 1988 Sep;19(3):223–236. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(88)90004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoner G. L., Walker D. L., Webster H. D. Age distribution of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Acta Neurol Scand. 1988 Oct;78(4):307–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1988.tb03661.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada H., Lashgari M., Rappaport J., Khalili K. Cell type-specific expression of JC virus early promoter is determined by positive and negative regulation. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):463–466. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.463-466.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada H., Rappaport J., Lashgari M., Amini S., Wong-Staal F., Khalili K. Trans-activation of the JC virus late promoter by the tat protein of type 1 human immunodeficiency virus in glial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3479–3483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto K. K., Howley P. M., Miyamura T. JC human papovavirus replication in human amnion cells. J Virol. 1979 Apr;30(1):384–389. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.1.384-389.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura T., Inoue T., Nagata K., Mikoshiba K. Enhancer of human polyoma JC virus contains nuclear factor I-binding sequences; analysis using mouse brain nuclear extracts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 15;157(2):419–425. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80265-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarsy D., Holden E. M., Segarra J. M., Calabresi P., Feldman R. G. 5-Iodo-2'-deoxyuridine (IUDR; NSC-39661) given intraventricularly in the treatment of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Cancer Chemother Rep. 1973 Feb;57(1):73–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashiro K., Doi S., Moriwaka F., Maruo Y., Nomura M. Progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy with magnetic resonance imaging verification and therapeutic trials with interferon. J Neurol. 1987 Aug;234(6):427–429. doi: 10.1007/BF00314091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telenti A., Aksamit A. J., Jr, Proper J., Smith T. F. Detection of JC virus DNA by polymerase chain reaction in patients with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Infect Dis. 1990 Oct;162(4):858–861. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.4.858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trapp B. D., Small J. A., Pulley M., Khoury G., Scangos G. A. Dysmyelination in transgenic mice containing JC virus early region. Ann Neurol. 1988 Jan;23(1):38–48. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyring S. K., Cauda R., Ghanta V., Hiramoto R. Activation of natural killer cell function during interferon-alpha treatment of patients with condyloma acuminatum is predictive of clinical response. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 1988 Apr-Jun;2(2):63–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vacante D. A., Traub R., Major E. O. Extension of JC virus host range to monkey cells by insertion of a simian virus 40 enhancer into the JC virus regulatory region. Virology. 1989 Jun;170(2):353–361. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90425-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varakis J., ZuRhein G. M., Padgett B. L., Walker D. L. Induction of peripheral neuroblastomas in Syrian hamsters after injection as neonates with JC virus, a human polyoma virus. Cancer Res. 1978 Jun;38(6):1718–1722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazeux R., Cumont M., Girard P. M., Nassif X., Trotot P., Marche C., Matthiessen L., Vedrenne C., Mikol J., Henin D. Severe encephalitis resulting from coinfections with HIV and JC virus. Neurology. 1990 Jun;40(6):944–948. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.6.944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. L., Padgett B. L. The epidemiology of human polyomaviruses. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1983;105:99–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. L., Padgett B. L., ZuRhein G. M., Albert A. E., Marsh R. F. Human papovavirus (JC): induction of brain tumors in hamsters. Science. 1973 Aug 17;181(4100):674–676. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4100.674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallen W. C., London W. T., Traub R. G., Peterson K. E., Witzel N. L. Antibody responses to JC virus-associated antigens by tumor-bearing owl monkeys. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1983;105:261–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weck P. K., Buddin D. A., Whisnant J. K. Interferons in the treatment of genital human papillomavirus infections. Am J Med. 1988 Aug 29;85(2A):159–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner L. P., Herndon R. M., Narayan O., Johnson R. T. Further studies of a simian virus 40-like virus isolated from human brain. J Virol. 1972 Jul;10(1):147–149. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.1.147-149.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner L. P., Narayan O., Penney J. B., Jr, Herndon R. M., Feringa E. R., Tourtellotte W. W., Johnson R. T. Papovavirus of JC type in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Rapid identification and subsequent isolation. Arch Neurol. 1973 Jul;29(1):1–3. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490250019001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley C. A., Grafe M., Kennedy C., Nelson J. A. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and JC virus in acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) patients with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Acta Neuropathol. 1988;76(4):338–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00686970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willoughby E., Price R. W., Padgett B. L., Walker D. L., Dupont B. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML): in vitro cell-mediated immune responses to mitogens and JC virus. Neurology. 1980 Mar;30(3):256–262. doi: 10.1212/wnl.30.3.256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolinsky J. S., Johnson K. P., Rand K., Merigan T. C. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: clinical pathological correlates and failure of a drug trial in two patients. Trans Am Neurol Assoc. 1976;101:81–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wroblewska Z., Wellish M., Gilden D. Growth of JC virus in adult human brain cell cultures. Arch Virol. 1980;65(2):141–148. doi: 10.1007/BF01317325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Kitamura T., Sugimoto C., Ueki T., Aso Y., Hara K., Taguchi F. Isolation of a possible archetypal JC virus DNA sequence from nonimmunocompromised individuals. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3139–3143. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3139-3143.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshiike K., Miyamura T., Chan H. W., Takemoto K. K. Two defective DNAs of human polyomavirus JC adapted to growth in human embryonic kidney cells. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):395–401. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.395-401.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZURHEIN G., CHOU S. M. PARTICLES RESEMBLING PAPOVA VIRUSES IN HUMAN CEREBRAL DEMYELINATING DISEASE. Science. 1965 Jun 11;148(3676):1477–1479. doi: 10.1126/science.148.3676.1477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zochodne D. W., Kaufmann J. C. Prolonged progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy without immunosuppression. Can J Neurol Sci. 1987 Nov;14(4):603–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zu Rhein G. M. Association of papova-virions with a human demyelinating disease (progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy). Prog Med Virol. 1969;11:185–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zu Rhein G. M. Polyoma-like virions in a human demyelinating disease. Acta Neuropathol. 1967 Mar 6;8(1):57–68. doi: 10.1007/BF00686650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zu Rhein G. M., Varakis J. N. Perinatal induction of medulloblastomas in Syrian golden hamsters by a human polyoma virus (JC). Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1979 May;(51):205–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]