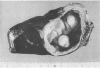
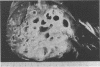
Abstract
Echinococcosis is an infectious disease of humans caused by the larval (metacestode) stage of the cestode species Echinococcus granulosus (cystic echinococcosis or hydatid disease) or Echinococcus multilocularis (alveolar echinococcosis or alveolar hydatid disease). Clinical manifestations depend primarily on localization and size of hepatic lesions and may include hepatomegaly, obstructive jaundice, or cholangitis. Prognostically, alveolar echinococcosis is considered similar to liver malignancies, including a lethality rate of 90% for untreated cases. Diagnosis is based on imaging techniques coupled with immunodiagnostic procedures. Antibody detection tests for E. multilocularis have markedly improved with the use of affinity-purified Em2 antigen and recombinant antigen II/3-10 in enzyme immunoassays. Antigens of corresponding quality for E. granulosus are still unavailable. The detection of circulating antigens and immune complexes in the sera of patients with cystic echinococcosis, the demonstration of in vitro lymphocyte proliferation in response to stimulation with Echinococcus antigens, and the discrimination of serum immunoglobulin isotype activity to various Echinococcus antigens in both cystic and alveolar echinococcosis have been suggested for diagnostic purposes as well as for monitoring patients after treatment. New diagnostic molecular tools include DNA probes for Southern hybridization tests and polymerase chain reaction for the amplification of E. multilocularis and E. granulosus species-specific DNA fragments.
Full text
PDF




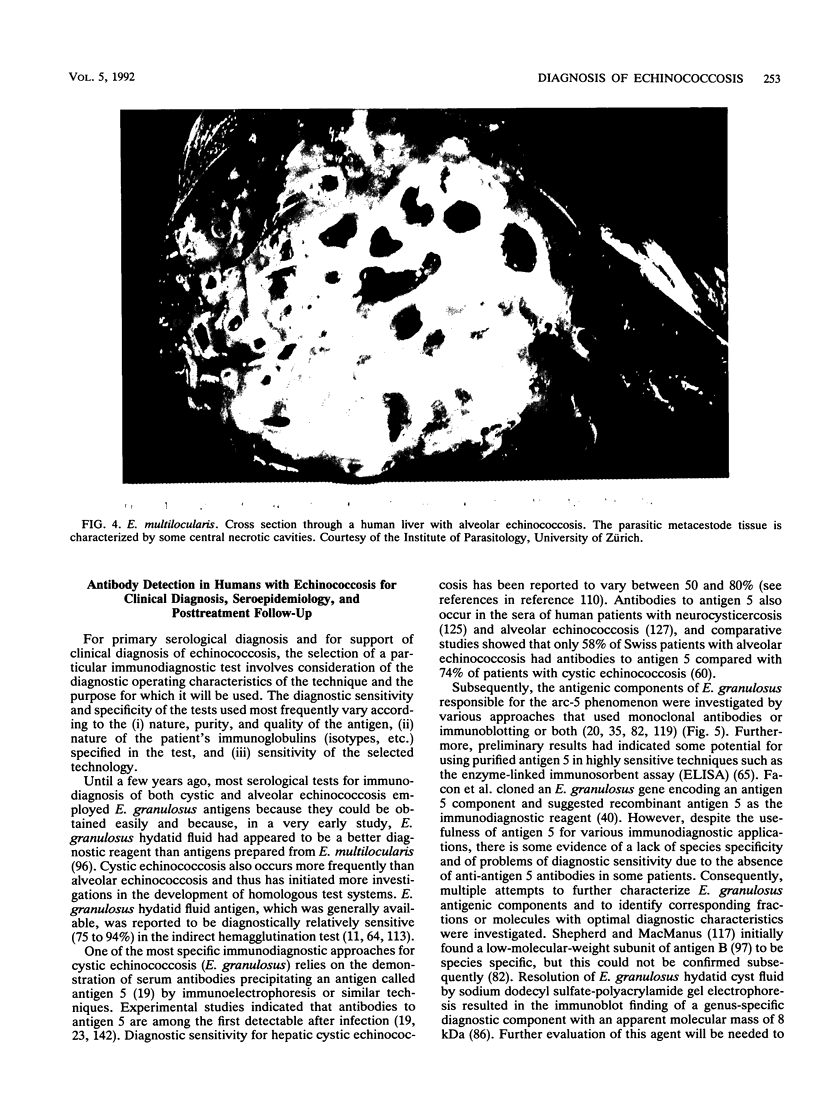








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Afferni C., Pini C., Misiti-Dorello P., Bernardini L., Conchedda M., Vicari G. Detection of specific IgE antibodies in sera from patients with hydatidosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Mar;55(3):587–592. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali-Khan Z., Rausch R. L. Demonstration of amyloid and immune complex deposits in renal and hepatic parenchyma of Alaskan alveolar hydatid disease patients. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1987 Aug;81(4):381–392. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1987.11812136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali-Khan Z., Siboo R. Pathogenesis and host response in subcutaneous alveolar hydatidosis. I. Histogenesis of alveolar cyst and a qualitative analysis of the inflammatory infiltrates. Z Parasitenkd. 1980;62(3):241–254. doi: 10.1007/BF00926565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkarmi T., Behbehani K. Echinococcus multilocularis: inhibition of murine neutrophil and macrophage chemotaxis. Exp Parasitol. 1989 Jul;69(1):16–22. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(89)90166-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ameglio F., Saba F., Bitti A., Aceti A., Tanigaki N., Sorrentino R., Dolei A., Tosi R. Antibody reactivity to HLA classes I and II in sera from patients with hydatidosis. J Infect Dis. 1987 Oct;156(4):673–676. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.4.673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammann R. W. Diagnose und Therapie der Echinokokkose. Schweiz Rundsch Med Prax. 1983 Dec 13;72(50):1568–1572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammann R., Tschudi K., von Ziegler M., Meister F., Cotting J., Eckert J., Witassek F., Freiburghaus A. Langzeitverlauf bei 60 Patienten mit alveolärer Echinokokkose unter Dauertherapie mit Mebendazol (1976-85). Klin Wochenschr. 1988 Nov 1;66(21):1060–1073. doi: 10.1007/BF01711918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Annen J. M., Köhler P., Eckert J. Cytotoxicity of Echinococcus granulosus cyst fluid in vitro. Z Parasitenkd. 1981;65(1):79–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00926556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auer H., Hermentin K., Aspöck H. Demonstration of a specific Echinococcus multilocularis antigen in the supernatant of in vitro maintained protoscolices. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1988 May;268(3):416–423. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(88)80026-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auer H., Picher O., Aspöck H. Combined application of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and indirect haemagglutination test (IHA) as a useful tool for the diagnosis and post-operative surveillance of human alveolar and cystic echinococcosis. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1988 Nov;270(1-2):313–325. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(88)80169-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron R. W., Tanner C. E. Echinococcus multilocularis in the mouse: the in vitro protoscolicidal activity of peritoneal macrophages. Int J Parasitol. 1977 Dec;7(6):489–495. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(77)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ismail R., Rouger P., Carme B., Gentilini M., Salmon C. Comparative automated assay of anti-P1 antibodies in acute hepatic distomiasis (fascioliasis) and in hydatidosis. Vox Sang. 1980;38(3):165–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1980.tb02345.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresson-Hadni S., Liance M., Meyer J. P., Houin R., Bresson J. L., Vuitton D. A. Cellular immunity in experimental Echinococcus multilocularis infection. II. Sequential and comparative phenotypic study of the periparasitic mononuclear cells in resistant and sensitive mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Nov;82(2):378–383. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05457.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresson-Hadni S., Vuitton D. A., Lenys D., Liance M., Racadot E., Miguet J. P. Cellular immune response in Echinococcus multilocularis infection in humans. I. Lymphocyte reactivity to Echinococcus antigens in patients with alveolar echinococcosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Oct;78(1):61–66. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Candolfi E., Kien T., Chaker E., Fourati M., Benyounes A. Intérêt de l'antigénémie et des anticorps IgG, IgM, IgA et IgE dans l'immunologie du kyste hydatique. Résultats de l'immuno-enzymologie. A propos de 87 cas. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1985;78(5 Pt 2):700–706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamekh M., Facon B., Dissous C., Haque A., Capron A. Use of a monoclonal antibody specific for a protein epitope of Echinococcus granulosus antigen 5 in a competitive antibody radioimmunoassay for diagnosis of hydatid disease. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Nov 6;134(1):129–137. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90121-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coltorti E. A. Standardization and evaluation of an enzyme immunoassay as a screening test for the seroepidemiology of human hydatidosis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 Sep;35(5):1000–1005. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.1000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coltorti E., Guarnera E., Larrieu E., Santillán G., Aquino A. Seroepidemiology of human hydatidosis: use of dried blood samples on filter paper. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1988;82(4):607–610. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(88)90527-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conder G. A., Andersen F. L., Schantz P. M. Immunodiagnostic tests for hydatidosis in sheep: an evaluation of double diffusion, immunoelectrophoresis, indirect hemagglutination, and intradermal tests. J Parasitol. 1980 Aug;66(4):577–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condie S. J., Crellin J. R., Andersen F. L., Schantz P. M. Participation in a community program to prevent hydatid disease. Public Health. 1981 Jan;95(1):28–35. doi: 10.1016/s0033-3506(81)80097-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig P. S., Macpherson C. N., Nelson G. S. The identification of eggs of Echinococcus by immunofluorescence using a specific anti-oncospheral monoclonal antibody. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 Jan;35(1):152–158. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig P. S., Nelson G. S. The detection of circulating antigen in human hydatid disease. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1984 Jun;78(3):219–227. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1984.11811805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig P. S., Zeyhle E., Romig T. Hydatid disease: research and control in Turkana. II. The role of immunological techniques for the diagnosis of hydatid disease. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1986;80(2):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(86)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crellin J. R., Andersen F. L., Schantz P. M., Condie S. J. Possible factors influencing distribution and prevalence of Echinococcus granulosus in Utah. Am J Epidemiol. 1982 Sep;116(3):463–474. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dar F. K., Buhidma M. A., Kidwai S. A. Hydatid false positive serological test results in malignancy. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Apr 21;288(6425):1197–1197. doi: 10.1136/bmj.288.6425.1197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deplazes P., Gottstein B. A monoclonal antibody against Echinococcus multilocularis Em2 antigen. Parasitology. 1991 Aug;103(Pt 1):41–49. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000059278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessaint J. P., Bout D., Wattre P., Capron A. Quantitative determination of specific IgE antibodies to Echinococcus granulosus and IgE levels in sera from patients with hydatid disease. Immunology. 1975 Nov;29(5):813–823. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Felice G., Pini C., Afferni C., Vicari G. Purification and partial characterization of the major antigen of Echinococcus granulosus (antigen 5) with monoclonal antibodies. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1986 Aug;20(2):133–142. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(86)90025-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon J. B., Jenkins P., Allan D. Immune recognition of Echinococcus granulosus. 1. Parasite-activated, primary transformation by normal murine lymph node cells. Parasite Immunol. 1982 Jan;4(1):33–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1982.tb00418.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert J., Ammann R. Information zum sogenannten "fuchsbandwurm". Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd. 1990;132(2):92–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis M. E., Sinner W., Asraf Ali M., Qadri S. M. Echinococcal disease and mycobacterial infection. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1991 Apr;85(2):243–251. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1991.11812552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facon B., Chamekh M., Dissous C., Capron A. Molecular cloning of an Echinococcus granulosus protein expressing an immunogenic epitope of antigen 5. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Apr;45(2):233–239. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90090-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frosch P. M., Frosch M., Pfister T., Schaad V., Bitter-Suermann D. Cloning and characterisation of an immunodominant major surface antigen of Echinococcus multilocularis. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Oct;48(2):121–130. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90108-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuya K., Nishizuka M., Honma H., Kumagai M., Sato N., Takahashi M., Uchino J. Prevalence of human alveolar echinococcosis in Hokkaido as evaluated by western blotting. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1990 Apr;43(2):43–49. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.43.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser R. B., Lightowlers M. W., Obendorf D. L., Jenkins D. J., Rickard M. D. Evaluation of a serological test system for the diagnosis of natural Echinococcus granulosus infection in dogs using E. granulosus protoscolex and oncosphere antigens. Aust Vet J. 1988 Dec;65(12):369–373. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1988.tb14274.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser R. B., Lightowlers M. W., Rickard M. D. A recombinant antigen with potential for serodiagnosis of Echinococcus granulosus infection in dogs. Int J Parasitol. 1990 Nov;20(7):943–950. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(90)90033-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemmell M. A., Lawson J. R., Roberts M. G. Population dynamics in echinococcosis and cysticercosis: biological parameters of Echinococcus granulosus in dogs and sheep. Parasitology. 1986 Jun;92(Pt 3):599–620. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000065483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillet M., Miguet J. P., Mantion G., Bresson-Hadni S., Becker M. C., Rouget C., Christophe J. L., Roullier M., Landecy G., Guerder L. Orthotopic liver transplantation in alveolar echinococcosis of the liver: analysis of a series of six patients. Transplant Proc. 1988 Feb;20(1 Suppl 1):573–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottstein B. An immunoassay for the detection of circulating antigens in human echinococcosis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1984 Nov;33(6):1185–1191. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1984.33.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottstein B., Deplazes P., Eckert J., Müller B., Schott E., Helle O., Boujon P., Wolff K., Wandeler A., Schwiete U. Serological (Em2-ELISA) and parasitological examinations of fox populations for Echinococcus multilocularis infections. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1991 May;38(3):161–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1991.tb00858.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottstein B., Eckert J., Fey H. Serological differentiation between Echinococcus granulosus and E. multilocularis infections in man. Z Parasitenkd. 1983;69(3):347–356. doi: 10.1007/BF00927876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottstein B., Eckert J., Woodtli W. Determination of parasite-specific immunoglobulins using the ELISA in patients with echinococcosis treated with mebendazole. Z Parasitenkd. 1984;70(3):385–389. doi: 10.1007/BF00927825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottstein B., Lengeler C., Bachmann P., Hagemann P., Kocher P., Brossard M., Witassek F., Eckert J. Sero-epidemiological survey for alveolar echinococcosis (by Em2-ELISA) of blood donors in an endemic area of Switzerland. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1987;81(6):960–964. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(87)90365-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottstein B., Mowatt M. R. Sequencing and characterization of an Echinococcus multilocularis DNA probe and its use in the polymerase chain reaction. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Feb;44(2):183–193. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90004-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottstein B., Müller N., Cryz S. J., Jr, Vogel M., Tanner I., Seebeck T. Humoral and cellular immune response in mice and dogs induced by a recombinant Echinococcus multilocularis antigen produced by a Salmonella typhimurium vaccine strain. Parasite Immunol. 1990 Mar;12(2):163–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1990.tb00945.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottstein B. Purification and characterization of a specific antigen from Echinococcus multilocularis. Parasite Immunol. 1985 May;7(3):201–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1985.tb00070.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottstein B., Schantz P. M., Todorov T., Saimot A. G., Jacquier P. An international study on the serological differential diagnosis of human cystic and alveolar echinococcosis. Bull World Health Organ. 1986;64(1):101–105. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottstein B., Schantz P. M., Wilson J. F. Serological screening for Echinococcus multilocularis infections with ELISA. Lancet. 1985 May 11;1(8437):1097–1098. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92394-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottstein B., Tschudi K., Eckert J., Ammann R. Em2-ELISA for the follow-up of alveolar echinococcosis after complete surgical resection of liver lesions. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1989 May-Jun;83(3):389–393. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(89)90512-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottstein B., Witassek F., Eckert J. Neues zur Echinokokkose. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1986 Jun 14;116(24):810–817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerberg B., Musoke A. J., Williams J. F. Activation of complement by hydatid cyst fluid of Echinococcus granulosus. J Parasitol. 1977 Apr;63(2):327–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings L., McManus D. P. The isolation, by differential antibody screening, of Echinococcus multilocularis antigen gene clones with potential for immunodiagnosis. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Mar 1;33(2):171–182. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90031-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess U., Eckert J., Fröhlich A. Vergleich serologischer Methoden für die Diagnose der zystischen und alveolären Echinokokkose des Menschen. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1974 Jun 15;104(24):853–859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hira P. R., Bahr G. M., Shweiki H. M., Behbehani K. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using an arc 5 antigen for the diagnosis of cystic hydatid disease. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1990 Apr;84(2):157–162. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1990.11812449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacona A., Pini C., Vicari G. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in the serodiagnosis of hydatid disease. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1980 Jan;29(1):95–102. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1980.29.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins D. J., Gasser R. B., Zeyhle E., Romig T., Macpherson C. N. Assessment of a serological test for the detection of Echinococcus granulosus infection in dogs in Kenya. Acta Trop. 1990 May;47(4):245–248. doi: 10.1016/0001-706x(90)90016-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins D. J., Rickard M. D. Specific antibody responses to Taenia hydatigena, Taenia pisiformis and Echinococcus granulosus infection in dogs. Aust Vet J. 1985 Mar;62(3):72–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1985.tb14142.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins D. J., Rickard M. D. Specificity of scolex and oncosphere antigens for the serological diagnosis of taeniid cestode infections in dogs. Aust Vet J. 1986 Feb;63(2):40–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1986.tb02918.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai Y., Koshino I., Kawanishi N., Sakamoto H., Sasaki E., Kumagai M. Alveolar echinococcosis of the liver; studies on 60 operated cases. Ann Surg. 1980 Feb;191(2):145–152. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198002000-00003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassis A. I., Tanner C. E. Echinococcus multilocularis: complement's role in vivo in hydatid disease. Exp Parasitol. 1977 Dec;43(2):390–395. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(77)90045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knobloch J., Biedermann H., Mannweiler E. Serum antibodies in patients with alveolar echinococcosis before and after therapy. Trop Med Parasitol. 1985 Sep;36(3):155–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knobloch J., Lederer I., Mannweiler E. Species-specific immunodiagnosis of human echinococcosis with crude antigens. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;3(6):554–555. doi: 10.1007/BF02013618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIBY P. D., OLSEN O. W. THE CESTODE ECHINOCOCCUS MULTILOCULARIS IN FOXES IN NORTH DAKOTA. Science. 1964 Sep 4;145(3636):1066–1066. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3636.1066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer J. C., Rose D. B., Keystone J. S., Taylor B. R., Langer B. Diagnosis and management of hydatid disease of the liver. A 15-year North American experience. Ann Surg. 1984 Apr;199(4):412–417. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198404000-00007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier A. P., Trujillo D. E., Schantz P. M., Wilson J. F., Gottstein B., McMahon B. J. Comparison of serologic tests for the diagnosis and follow-up of alveolar hydatid disease. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 Nov;37(3):609–615. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.37.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liance M., Bresson-Hadni S., Meyer J. P., Houin R., Vuitton D. A. Cellular immunity in experimental Echinococcus multilocularis infection. I. Sequential and comparative study of specific in vivo delayed-type hypersensitivity against E. multilocularis antigens in resistant and sensitive mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Nov;82(2):373–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05456.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightowlers M. W. Cestode infections in animals: immunological diagnosis and vaccination. Rev Sci Tech. 1990 Jun;9(2):463–487. doi: 10.20506/rst.9.2.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightowlers M. W. Immunology and molecular biology of Echinococcus infections. Int J Parasitol. 1990 Jul;20(4):471–478. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(90)90194-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightowlers M. W., Liu D. Y., Haralambous A., Rickard M. D. Subunit composition and specificity of the major cyst fluid antigens of Echinococcus granulosus. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Dec;37(2):171–182. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90149-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd S. Progress in immunization against parasitic helminths. Parasitology. 1981 Aug;83(Pt 1):225–242. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000050186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lymbery A. J., Thompson R. C. Genetic differences between cysts of Echinococcus granulosus from the same host. Int J Parasitol. 1989 Dec;19(8):961–964. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(89)90129-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacPherson C. N., Romig T., Zeyhle E., Rees P. H., Were J. B. Portable ultrasound scanner versus serology in screening for hydatid cysts in a nomadic population. Lancet. 1987 Aug 1;2(8553):259–261. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90839-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddison S. E., Slemenda S. B., Schantz P. M., Fried J. A., Wilson M., Tsang V. C. A specific diagnostic antigen of Echinococcus granulosus with an apparent molecular weight of 8 kDA. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1989 Apr;40(4):377–383. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1989.40.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matossian R. M., Kane G. J., Chantler S. M., Batty I., Sarhadian H. The specific immunoglobulin in hydatid disease. Immunology. 1972 Mar;22(3):423–430. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus D. P. Characterisation of taeniid cestodes by DNA analysis. Rev Sci Tech. 1990 Jun;9(2):489–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miguet J. P., Bresson-Hadni S. Alveolar echinococcosis of the liver. J Hepatol. 1989 May;8(3):373–379. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(89)90037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikhael M. A., Ciric I. S., Tarkington J. A. MR imaging in spinal echinococcosis. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1985 Mar-Apr;9(2):398–400. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198503000-00038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mlika N., Larouzé B., Gaudebout C., Braham B., Allegue M., Dazza M. C., Dridi M., Gharbi S., Gaumer B., Bchir A. Echotomographic and serologic screening for hydatidosis in a Tunisian village. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 Jul;35(4):815–817. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movsesijan M., Sokolić A., Mladenović Z. Studies on the immunological potentiality of irradiated Echinococcus granulosus forms: immunization experiments in dogs. Br Vet J. 1968 Oct;124(10):425–432. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)39151-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller N., Gottstein B., Vogel M., Flury K., Seebeck T. Application of a recombinant Echinococcus multilocularis antigen in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for immunodiagnosis of human alveolar echinococcosis. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Sep;36(2):151–159. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90187-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller N., Vogel M., Gottstein B., Scholle A., Seebeck T. Plasmid vector for overproduction and export of recombinant protein in Escherichia coli: efficient one-step purification of a recombinant antigen from Echinococcus multilocularis (Cestoda). Gene. 1989 Feb 20;75(2):329–334. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90279-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman L., Kagan I. G., Allain D. S. Preparation and evaluation of antigens for use in the serologic diagnosis of human hydatid disease. II. Isolation and characterization from extracts of cysts of Echinococcus multilocularis of serologically reactive elements found in hydatid fluid of Echinococcus granulosus. J Immunol. 1966 May;96(5):822–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oriol R., Williams J. F., Pérez Esandi M. V., Oriol C. Purification of lipoprotein antigens of Echinococcus granulosus from sheep hydatid fluid. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1971 Jul;20(4):569–574. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1971.20.569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinon J. M., Poirriez J., Lepan H., Geers R., Penna R., Fernandez D. Value of isotypic characterization of antibodies to Echinococcus granulosus by enzyme-linked immuno-filtration assay. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jun;6(3):291–295. doi: 10.1007/BF02017615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAUSCH R., SCHILLER E. L. Studies on the helminth fauna of Alaska. XXIV. Echinococcus sibiricensis n. sp., from St. Lawrence Island. J Parasitol. 1954 Dec;40(6):659–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rausch R. L., Wilson J. F., Schantz P. M., McMahon B. J. Spontaneous death of Echinococcus multilocularis: cases diagnosed serologically (by Em2 ELISA) and clinical significance. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 May;36(3):576–585. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.36.576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley E. M., Dixon J. B. Experimental Echinococcus granulosus infection in mice: immunocytochemical analysis of lymphocyte populations in local lymphoid infections during early infection. Parasitology. 1987 Jun;94(Pt 3):523–532. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000055864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rishi A. K., McManus D. P. Genomic cloning of human Echinococcus granulosus DNA: isolation of recombinant plasmids and their use as genetic markers in strain characterization. Parasitology. 1987 Apr;94(Pt 2):369–383. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000054020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schantz P. M., Wilson J. F., Wahlquist S. P., Boss L. P., Rausch R. L. Serologic tests for diagnosis and post-treatment evaluation of patients with alveolar hydatid disease (Echinococcus multilocularis). Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1983 Nov;32(6):1381–1386. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1983.32.1381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schantz P. M., von Reyn C. F., Welty T., Schultz M. G. Echinococcosis in Arizona and New Mexico. Survey of hospital records, 1969-1974. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1976 Mar;25(2):312–317. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1976.25.312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholle A., Vreemann J., Blank V., Nold A., Boos W., Manson M. D. Sequence of the mglB gene from Escherichia coli K12: comparison of wild-type and mutant galactose chemoreceptors. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jun;208(1-2):247–253. doi: 10.1007/BF00330450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd J. C., McManus D. P. Specific and cross-reactive antigens of Echinococcus granulosus hydatid cyst fluid. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Sep;25(2):143–154. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh B. P., Dhar D. N. Indirect fluorescent antibody test for the detection of antibodies to Echinococcus granulosus in experimentally infected pups. Vet Parasitol. 1988 May;28(3):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0304-4017(88)90106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siracusano A., Ioppolo S., Notargiacomo S., Ortona E., Riganó R., Teggi A., De Rosa F., Vicari G. Detection of antibodies against Echinococcus granulosus major antigens and their subunits by immunoblotting. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1991 Mar-Apr;85(2):239–243. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(91)90039-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siracusano A., Teggi A., Quintieri F., Notargiacomo S., De Rosa F., Vicari G. Cellular immune responses of hydatid patients to Echinococcus granulosus antigens. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Jun;72(3):400–405. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. C., Eckert J. Observations on Echinococcus multilocularis in the definitive host. Z Parasitenkd. 1983;69(3):335–345. doi: 10.1007/BF00927875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varela-Díaz V. M., Coltorti E. A., D'Alessandro A. Immunoelectrophoresis tests showing Echinococcus granulosus arc 5 in human cases of Echinococcus vogeli and cysticercosis-multiple myeloma. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1978 May;27(3):554–557. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1978.27.554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varela-Díaz V. M., Coltorti E. A., de Zavaleta O., Pérez-Caviglia H., Zabert E. I., Guarnera E. A. Immunodiagnosis of human hydatid disease: applications and contributions to a control program in Argentina. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1983 Sep;32(5):1079–1087. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1983.32.1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varela-Díaz V. M., Eckert J., Rausch R. L., Coltorti E. A., Hess U. Detection of the Echinococcus granulosus diagnostic arc 5 in sera from patients with surgically-confirmed E. multilocularis infection. Z Parasitenkd. 1977 Sep 21;53(2):183–188. doi: 10.1007/BF00380463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel M., Gottstein B., Müller N., Seebeck T. Production of a recombinant antigen of Echinococcus multilocularis with high immunodiagnostic sensitivity and specificity. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Nov;31(2):117–125. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90162-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel M., Müller N., Gottstein B., Flury K., Eckert J., Seebeck T. Echinococcus multilocularis: characterization of a DNA probe. Acta Trop. 1990 Dec;48(2):109–116. doi: 10.1016/0001-706x(90)90050-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuitton D. A., Bresson-Hadni S., Laroche L., Kaiserlian D., Guerret-Stocker S., Bresson J. L., Gillet M. Cellular immune response in Echinococcus multilocularis infection in humans. II. Natural killer cell activity and cell subpopulations in the blood and in the periparasitic granuloma of patients with alveolar echinococcosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Oct;78(1):67–74. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuitton D. A., Bresson-Hadni S., Lenys D., Flausse F., Liance M., Wattre P., Miguet J. P., Capron A. IgE-dependent humoral immune response in Echinococcus multilocularis infection: circulating and basophil-bound specific IgE against Echinococcus antigens in patients with alveolar echinococcosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Feb;71(2):247–252. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuitton D. A., Lasségue A., Miguet J. P., Hervé P., Barale T., Seillés E., Capron A. Humoral and cellular immunity in patients with hepatic alveolar echinococcosis. A 2 year follow-up with and without flubendazole treatment. Parasite Immunol. 1984 Jul;6(4):329–340. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1984.tb00805.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wangoo A., Ganguly N. K., Mahajan R. C. Lymphocyte subpopulations & blast transformation studies in experimental hydatidosis. Indian J Med Res. 1987 Feb;85:149–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wangoo A., Ganguly N. K., Mahajan R. C. Specific T cell cytotoxicity in experimental Echinococcus granulosus infected mice. Indian J Med Res. 1987 Nov;86:588–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wattal C., Mohan C., Agarwal S. C. Evaluation of specific immunoglobulin E by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in hydatid disease. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1988;87(1):98–100. doi: 10.1159/000234656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. F., Pérez Esandi M. V. Reaginic antibodies in dogs infected with Echinococcus granulosus. Immunology. 1971 Apr;20(4):451–455. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. F., Rausch R. L. Alveolar hydatid disease. A review of clinical features of 33 indigenous cases of Echinococcus multilocularis infection in Alaskan Eskimos. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1980 Nov;29(6):1340–1355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yap K. W., Thompson R. C., Pawlowski I. D. The development of nonradioactive total genomic probes for strain and egg differentiation in taeniid cestodes. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988 Nov;39(5):472–477. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1988.39.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yong W. K., Heath D. D. 'Arc 5' antibodies in sera of sheep infected with Echinococcus granulosus, Taenia hydatigena and Taenia ovis. Parasite Immunol. 1979 Spring;1(1):27–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1979.tb00693.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Yaman F. M., Knobloch J. Isolation and partial characterization of species-specific and cross-reactive antigens of Echinococcus granulosus cyst fluid. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Nov;37(1):101–107. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90106-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]