Abstract
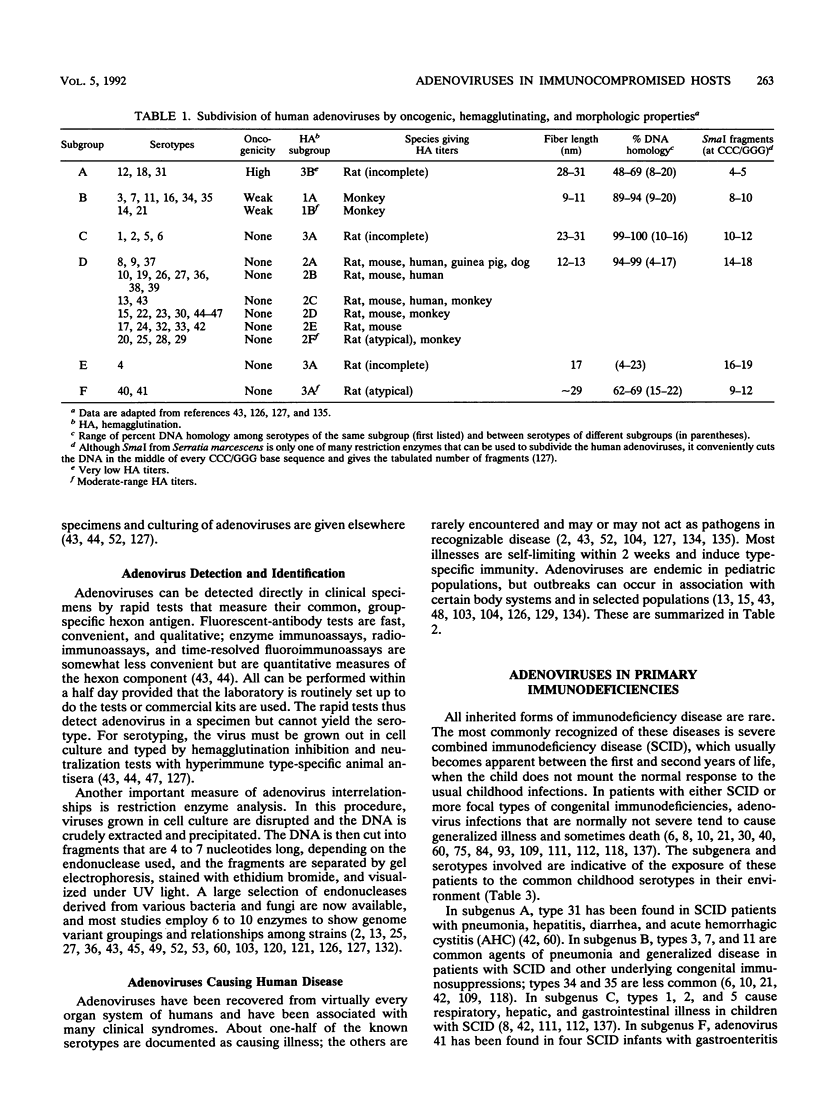
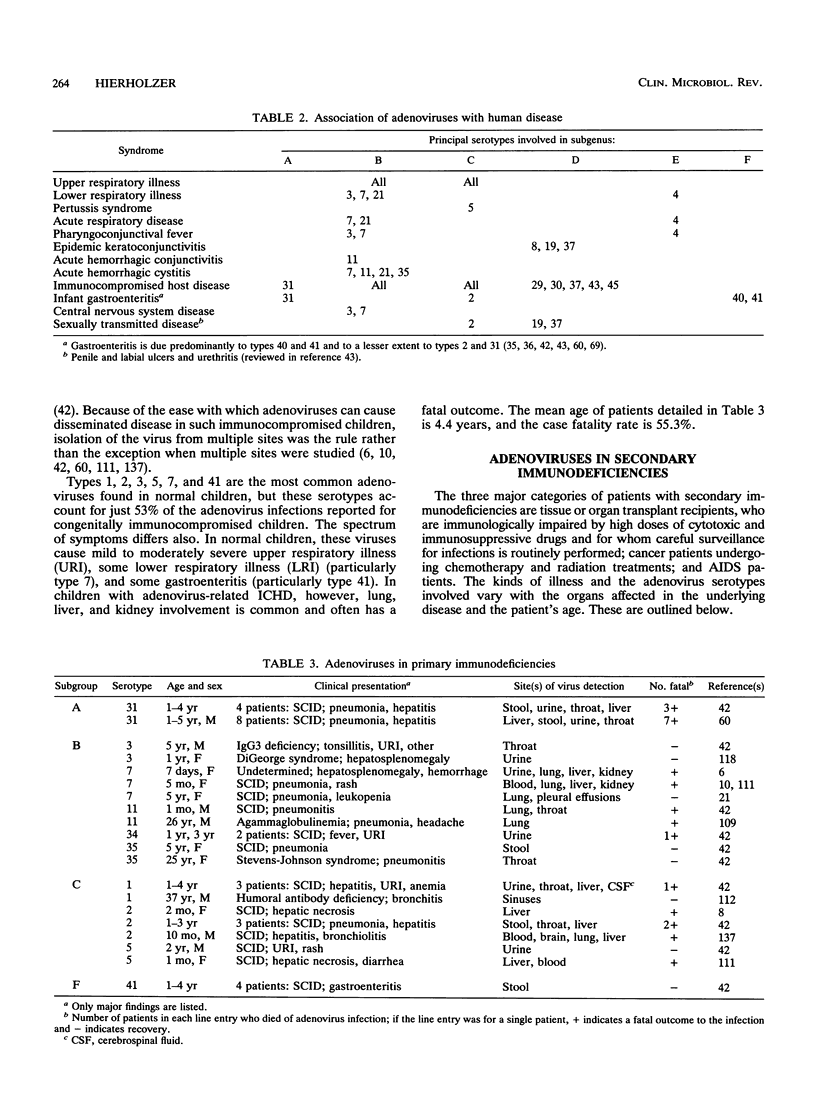
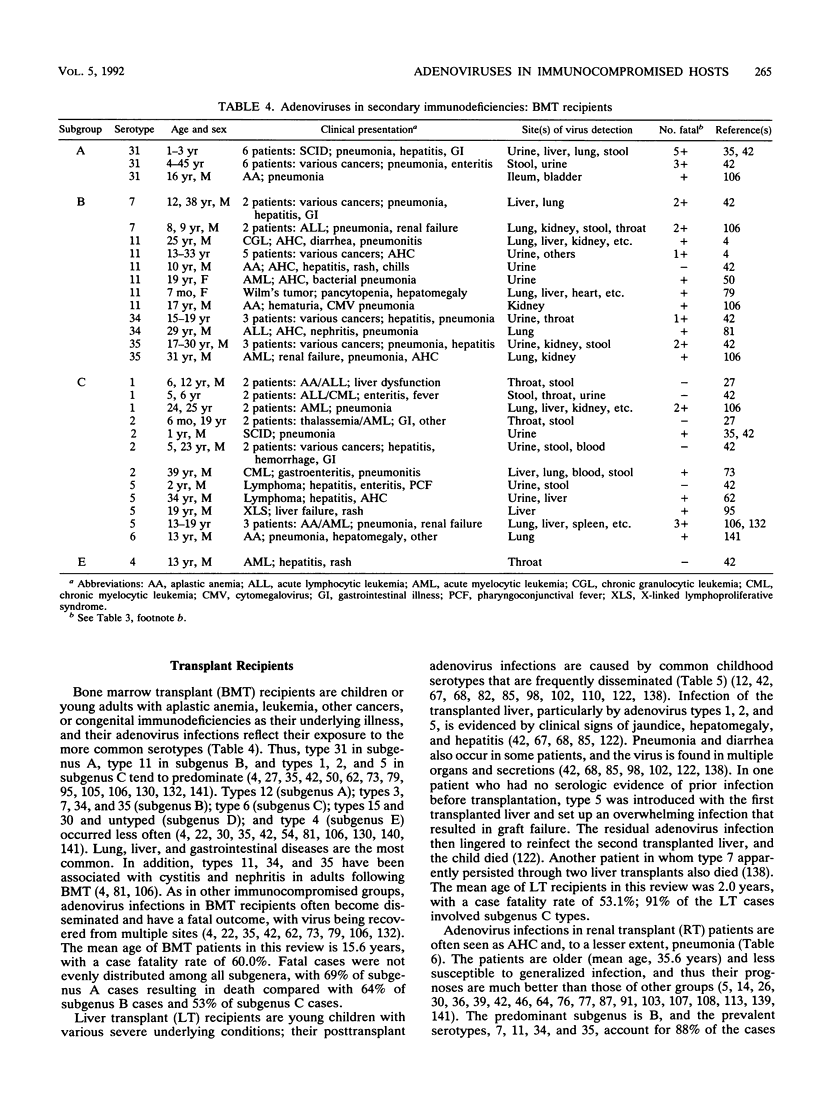
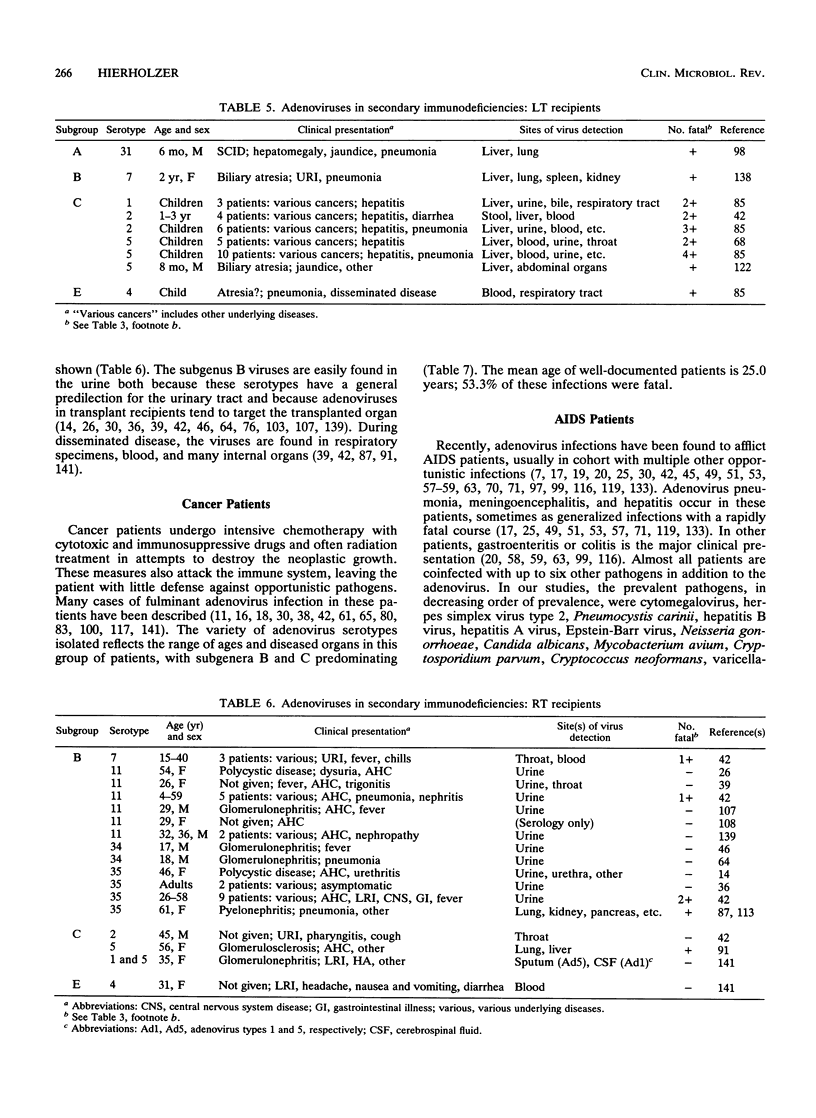
Adenoviruses are among the many pathogens and opportunistic agents that cause serious infection in the congenitally immunocompromised, in patients undergoing immunosuppressive treatment for organ and tissue transplants and for cancers, and in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients. Adenovirus infections in these patients tend to become disseminated and severe, and the serotypes involved are clustered according to the age of the patient and the nature of the immunosuppression. Over 300 adenovirus infections in immunocompromised patients, with an overall case fatality rate of 48%, are reviewed in this paper. Children with severe combined immunodeficiency syndrome and other primary immunodeficiencies are exposed to the serotypes of subgroups B and C that commonly infect young children, and thus their infections are due to types 1 to 7 and 31 of subgenus A. Children with bone marrow and liver transplants often have lung and liver adenovirus infections that are due to an expanded set of subgenus A, B, C, and E serotypes. Adults with kidney transplants have viruses of subgenus B, mostly types 11, 34, and 35, which cause cystitis. This review indicates that 11% of transplant recipients become infected with adenoviruses, with case fatality rates from 60% for bone marrow transplant patients to 18% for renal transplant patients. Patients with AIDS become infected with a diversity of serotypes of all subgenera because their adult age and life-style expose them to many adenoviruses, possibly resulting in antigenically intermediate strains that are not found elsewhere. Interestingly, isolates from the urine of AIDS patients are generally of subgenus B and comprise types 11, 21, 34, 35, and intermediate strains of these types, whereas isolates from stool are of subgenus D and comprise many rare, new, and intermediate strains that are untypeable for practical purposes. It has been estimated that adenoviruses cause active infection in 12% of AIDS patients and that 45% of these infections terminate in death within 2 months. In all immunocompromised patients, generalized illness involving the central nervous system, respiratory system, hepatitis, and gastroenteritis usually have a fulminant course and result in death. Treatments for adenovirus infections are of little proven value, although certain purine and pyrimidine analogs have shown beneficial effects in vitro and may be promising drugs.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams C. P., Jr, Cohen E. J., Albrecht J., Laibson P. R. Interferon treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitis. Am J Ophthalmol. 1984 Oct 15;98(4):429–432. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(84)90125-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian T., Wadell G., Hierholzer J. C., Wigand R. DNA restriction analysis of adenovirus prototypes 1 to 41. Arch Virol. 1986;91(3-4):277–290. doi: 10.1007/BF01314287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian T., Wigand R., Wadell G. Serological and biochemical characteristics of intermediate adenovirus strains of subgenus D. Arch Virol. 1987;97(3-4):347–357. doi: 10.1007/BF01314432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambinder R. F., Burns W., Forman M., Charache P., Arthur R., Beschorner W., Santos G., Saral R. Hemorrhagic cystitis associated with adenovirus infection in bone marrow transplantation. Arch Intern Med. 1986 Jul;146(7):1400–1401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. J., Jordan M. C. Viral pneumonia in recipients of solid organ transplants. Semin Respir Infect. 1990 Mar;5(1):38–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angella J. J., Connor J. D. Neonatal infection caused by adenovirus type 7. J Pediatr. 1968 Apr;72(4):474–478. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(68)80336-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong D. The acquired immune deficiency syndrome: viral infections and etiology. Prog Med Virol. 1984;30:1–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aterman K., Embil J., Easterbrook K. B., Haldane E. V., Crosby J. Liver necrosis, adenovirus type 2 and thymic dysplasia. Virchows Arch A Pathol Pathol Anat. 1973 Aug 9;360(2):155–171. doi: 10.1007/BF00543226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENYESH-MELNICK M., ROSENBERG H. S. THE ISOLATION OF ADENOVIRUS TYPE 7 FROM A FATAL CASE OF PNEUMONIA AND DISSEMINATED DISEASE. J Pediatr. 1964 Jan;64:83–87. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(64)80321-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baba M., Mori S., Shigeta S., De Clercq E. Selective inhibitory effect of (S)-9-(3-hydroxy-2-phosphonylmethoxypropyl)adenine and 2'-nor-cyclic GMP on adenovirus replication in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):337–339. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouabdallah K., Rigal-Huguet F., Alard C., Laurent G., Gayet-Mengelle C., Pris J., Delsol G. Hépatite fulminante à adénovirus type 5 au décours d'une maladie de Hodgkin. Ann Med Interne (Paris) 1990;141(1):81–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brummitt C. F., Cherrington J. M., Katzenstein D. A., Juni B. A., Van Drunen N., Edelman C., Rhame F. S., Jordan M. C. Nosocomial adenovirus infections: molecular epidemiology of an outbreak due to adenovirus 3a. J Infect Dis. 1988 Aug;158(2):423–432. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.2.423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan W., Bowman J. S., Jaffers G. Adenoviral acute hemorrhagic cystitis following renal transplantation. Am J Nephrol. 1990;10(4):350–351. doi: 10.1159/000168132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buehler J. W., Finton R. J., Goodman R. A., Choi K., Hierholzer J. C., Sikes R. K., Elsea W. R. Epidemic keratoconjunctivitis: report of an outbreak in an ophthalmology practice and recommendations for prevention. Infect Control. 1984 Aug;5(8):390–394. doi: 10.1017/s0195941700062238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael G. P., Jr, Zahradnik J. M., Moyer G. H., Porter D. D. Adenovirus hepatitis in an immunosuppressed adult patient. Am J Clin Pathol. 1979 Mar;71(3):352–355. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/71.3.352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chastel C., Plantin P., Chomel J. J., Legrand M. C., Demazure M., Guillet G., Aymard M. Infection respiratoire à adénovirus 37 chez un malade infecté par le VIH 1. Presse Med. 1990 Sep 15;19(29):1372–1372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou S. M., Roos R., Burrell R., Gutmann L., Harley J. B. Subacute focal adenovirus encephalitis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1973 Jan;32(1):34–50. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197301000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coldiron B. M., Freeman R. G., Beaudoing D. L. Isolation of adenovirus from a granuloma annulare-like lesion in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-related complex. Arch Dermatol. 1988 May;124(5):654–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham A. L., Grohman G. S., Harkness J., Law C., Marriott D., Tindall B., Cooper D. A. Gastrointestinal viral infections in homosexual men who were symptomatic and seropositive for human immunodeficiency virus. J Infect Dis. 1988 Aug;158(2):386–391. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.2.386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagan R., Schwartz R. H., Insel R. A., Menegus M. A. Severe diffuse adenovirus 7a pneumonia in a child with combined immunodeficiency: possible therapeutic effect of human immune serum globulin containing specific neutralizing antibody. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1984 May-Jun;3(3):246–251. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198405000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis D., Henslee P. J., Markesbery W. R. Fatal adenovirus meningoencephalitis in a bone marrow transplant patient. Ann Neurol. 1988 Apr;23(4):385–389. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E. New acquisitions in the chemotherapy of viral infections. Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 1990;52(1):69–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., Sakuma T., Baba M., Pauwels R., Balzarini J., Rosenberg I., Holý A. Antiviral activity of phosphonylmethoxyalkyl derivatives of purine and pyrimidines. Antiviral Res. 1987 Dec;8(5-6):261–272. doi: 10.1016/s0166-3542(87)80004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiala M., Payne J. E., Berne T. V., Poolsawat S., Schieble J., Guze L. B. Role of adenovirus type 11 in hemorrhagic cystitis secondary to immunosuppression. J Urol. 1974 Nov;112(5):595–597. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)59803-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fife K. H., Ashley R., Corey L. Isolation and characterization of six new genome types of human adenovirus types 1 and 2. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):20–23. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.20-23.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flomenberg P. R., Chen M., Horwitz M. S. Sequence and genetic organization of adenovirus type 35 early region 3. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4431–4437. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4431-4437.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flomenberg P. R., Chen M., Munk G., Horwitz M. S. Molecular epidemiology of adenovirus type 35 infections in immunocompromised hosts. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1127–1134. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freyler H., Sehorst W. Das Schicksal der Hornhautinfiltrate bei Keratoconjunctivitis epidemica. Eine Verlaufsstudie über 2 1/2 Jahre. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 1976 May 28;88(11):341–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freyler H., Sehorst W. Keratoconjunctivitis epidemica: Bericht über eine Klinikepidemie. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 1975 Jan;166(1):69–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher J. G., Khoobyarian N. Adenovirus susceptibility to interferon: sensitivity of types 2,7, and 12 to human interferon. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jan;130(1):137–142. doi: 10.3181/00379727-130-33506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleaves C. A., Smith T. F., Wold A. D., Wilson W. R. Detection of viral and chlamydial antigens in open-lung biopsy specimens. Am J Clin Pathol. 1985 Mar;83(3):371–374. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/83.3.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANSHAW J. B., WELLER T. H. Urinary excretion of cytomegaloviruses by children with generalized neoplastic disease. Correlation with clinical and histopathologic observations. J Pediatr. 1961 Mar;58:305–311. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(61)80259-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HECHT S. D., HANNA L., SERY T. W., JAWETZ E. TREATMENT OF EPIDEMIC KERATOCONJUNCTIVITIS WITH IDOXURIDINE (IDR). Arch Ophthalmol. 1965 Jan;73:49–64. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1965.00970030051012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond G. W., Mauthe G., Joshua J., Hannan C. K. Examination of uncommon clinical isolates of human adenoviruses by restriction endonuclease analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;21(4):611–616. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.4.611-616.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harnett G. B., Bucens M. R., Clay S. J., Saker B. M. Acute haemorrhagic cystitis caused by adenovirus type 11 in a recipient of a transplanted kidney. Med J Aust. 1982 Jun 26;1(13):565–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haworth J. C., Hoogstraten J., Taylor H. Thymic alymphoplasia. Arch Dis Child. 1967 Feb;42(221):40–54. doi: 10.1136/adc.42.221.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hierholzer J. C., Adrian T., Anderson L. J., Wigand R., Gold J. W. Analysis of antigenically intermediate strains of subgenus B and D adenoviruses from AIDS patients. Arch Virol. 1988;103(1-2):99–115. doi: 10.1007/BF01319812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hierholzer J. C., Atuk N. O., Gwaltney J. M., Jr New human adenovirus isolated from a renal transplant recipient: description and characterization of candiate adenovirus type 34. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Apr;1(4):366–376. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.4.366-376.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hierholzer J. C., Stone Y. O., Broderson J. R. Antigenic relationships among the 47 human adenoviruses determined in reference horse antisera. Arch Virol. 1991;121(1-4):179–197. doi: 10.1007/BF01316753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hierholzer J. C., Torrence A. E., Wright P. F. Generalized viral illness caused by an intermediate strain of adenovirus (21/H21 + 35). J Infect Dis. 1980 Mar;141(3):281–288. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.3.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hierholzer J. C., Wigand R., Anderson L. J., Adrian T., Gold J. W. Adenoviruses from patients with AIDS: a plethora of serotypes and a description of five new serotypes of subgenus D (types 43-47). J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):804–813. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraoka A., Ishikawa J., Kitayama H., Yamagami T., Teshima H., Nakamura H., Shibata H., Masaoka T., Ishigami S., Taguchi F. Hemorrhagic cystitis after bone marrow transplantation: importance of a thin sectioning technique on urinary sediments for diagnosis. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1991 Feb;7(2):107–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horoupian D. S., Pick P., Spigland I., Smith P., Portenoy R., Katzman R., Cho S. Acquired immune deficiency syndrome and multiple tract degeneration in a homosexual man. Ann Neurol. 1984 May;15(5):502–505. doi: 10.1002/ana.410150518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. S., Valderrama G., Hatcher V., Korn R., deJong P., Spigland I. Characterization of adenovirus isolates from AIDS patients. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1984;437:161–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1984.tb37132.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell C. L., Miller M. J., Martin W. J. Comparison of rates of virus isolation from leukocyte populations separated from blood by conventional and Ficoll-Paque/Macrodex methods. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):533–537. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.533-537.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janner D., Petru A. M., Belchis D., Azimi P. H. Fatal adenovirus infection in a child with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1990 Jun;9(6):434–436. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199006000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janoff E. N., Orenstein J. M., Manischewitz J. F., Smith P. D. Adenovirus colitis in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1991 Apr;100(4):976–979. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90272-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janoff E. N., Smith P. D. Perspectives on gastrointestinal infections in AIDS. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1988 Sep;17(3):451–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson M. E., Brown M., Hierholzer J. C., Thörner A., Ushijima H., Wadell G. Genome analysis of adenovirus type 31 strains from immunocompromised and immunocompetent patients. J Infect Dis. 1991 Feb;163(2):293–299. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.2.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson M. E., Wirgart B. Z., Grillner L., Björk O. Severe gastroenteritis in an immunocompromised child caused by adenovirus type 5. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1990 Jun;9(6):449–450. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199006000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. R., Yin J. A., Morris D. J., Desai M., Cinkotai K. I., McKeogh M. M. Fulminant hepatic necrosis caused by adenovirus type 5 following bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1990 May;5(5):345–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaljot K. T., Ling J. P., Gold J. W., Laughon B. E., Bartlett J. G., Kotler D. P., Oshiro L. S., Greenberg H. B. Prevalence of acute enteric viral pathogens in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patients with diarrhea. Gastroenterology. 1989 Oct;97(4):1031–1032. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)91516-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller E. W., Rubin R. H., Black P. H., Hirsch M. S., Hierholzer J. C. Isolation of adenovirus type 34 from a renal transplant recipient with interstitial pneumonia. Transplantation. 1977 Feb;23(2):188–191. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197702000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelsey D. S. Adenovirus meningoencephalitis. Pediatrics. 1978 Feb;61(2):291–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitajewski J., Schneider R. J., Safer B., Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E., Thimmappaya B., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA antagonizes the antiviral action of interferon by preventing activation of the interferon-induced eIF-2 alpha kinase. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):195–200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90383-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer S., Garcia J., Pearson L., Soultanakis E., Dasgupta A., Gaynor R. Multiple transcriptional regulatory domains in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat are involved in basal and E1A/E1B-induced promoter activity. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4616–4625. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4616-4625.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koneru B., Atchison R., Jaffe R., Cassavilla A., Van Thiel D. H., Starzl T. E. Serological studies of adenoviral hepatitis following pediatric liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1990 Aug;22(4):1547–1548. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koneru B., Jaffe R., Esquivel C. O., Kunz R., Todo S., Iwatsuki S., Starzl T. E. Adenoviral infections in pediatric liver transplant recipients. JAMA. 1987 Jul 24;258(4):489–492. doi: 10.1001/jama.1987.03400040087027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krajden M., Brown M., Petrasek A., Middleton P. J. Clinical features of adenovirus enteritis: a review of 127 cases. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1990 Sep;9(9):636–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krilov L. R., Kaplan M. H., Frogel M., Rubin L. G. Fatal adenovirus disease and human immunodeficiency virus infection. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1990 Oct;9(10):753–753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krilov L. R., Rubin L. G., Frogel M., Gloster E., Ni K., Kaplan M., Lipson S. M. Disseminated adenovirus infection with hepatic necrosis in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection and other immunodeficiency states. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Mar-Apr;12(2):303–307. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.2.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laibson P. R., Dhiri S., Oconer J., Ortolan G. Corneal infiltrates in epidemic keratoconjunctivitis. Response to double-blind corticosteroid therapy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1970 Jul;84(1):36–40. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1970.00990040038010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landry M. L., Fong C. K., Neddermann K., Solomon L., Hsiung G. D. Disseminated adenovirus infection in an immunocompromised host. Pitfalls in diagnosis. Am J Med. 1987 Sep;83(3):555–559. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90770-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laspia M. F., Rice A. P., Mathews M. B. HIV-1 Tat protein increases transcriptional initiation and stabilizes elongation. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90290-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau Y. L., Levinsky R. J., Morgan G., Strobel S. Dual meningoencephalitis with echovirus type 11 and adenovirus in combined (common variable) immunodeficiency. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1988 Dec;7(12):873–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecatsas G., Prozesky O. W., van Wyk J. Letter: Adenovirus type II associated with haemorrhagic cystitis after renal transplantation. S Afr Med J. 1974 Sep 21;48(46):1932–1932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecatsas G., van Wyk J. A. DNA viruses in urine after renal transplantation. S Afr Med J. 1978 May 20;53(20):787–788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennette D. A., Eiferman R. A. Inhibition of adenovirus replication in vitro by trifluridine. Arch Ophthalmol. 1978 Sep;96(9):1662–1663. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1978.03910060288022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J., Wodell R. A., August C. S., Bayever E. Adenovirus-related hemophagocytic syndrome after bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1990 Nov;6(5):349–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungman P., Ehrnst A., Björkstrand B., Hellström E., Ingelman-Sundberg H., Juliusson G., Lönnqvist B. Lethal disseminated adenovirus type 1 infection in a patient with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Scand J Infect Dis. 1990;22(5):601–605. doi: 10.3109/00365549009027103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungman P., Gleaves C. A., Meyers J. D. Respiratory virus infection in immunocompromised patients. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1989 Jan;4(1):35–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCALLISTER R. M., LANDING B. H., GOODHEART C. R. ISOLATION OF AGENOVIRUSES FROM NEOPLASTIC AND NON-NEOPLASTIC TISSUES OF CHILDREN. Lab Invest. 1964 Aug;13:894–901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markin R. S., Langnas A. N., Donovan J. P., Zetterman R. K., Stratta R. J. Opportunistic viral hepatitis in liver transplant recipients. Transplant Proc. 1991 Feb;23(1 Pt 2):1520–1521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain K., Gehrz R., Grierson H., Purtilo D., Filipovich A. Virus-associated histiocytic proliferations in children. Frequent association with Epstein-Barr virus and congenital or acquired immunodeficiencies. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1988 Fall;10(3):196–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaels M. G., Green M., Wald E. R., Starzl T. E. Adenovirus infection in pediatric liver transplant recipients. J Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;165(1):170–174. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.1.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R. L., Stalder H., Oxman M. N., Levin M. J., Moore M., Leith J. D., Gantz N. M., Hierholzer J. C., Hierholzer J. C. Fatal disseminated adenovirus infection in a renal transplant recipient. Am J Med. 1975 Oct;59(4):591–598. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90267-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G. J., Rice S. A., Knipe D. M., Baltimore D. Alternative mechanisms for activation of human immunodeficiency virus enhancer in T cells. Science. 1988 Mar 11;239(4845):1299–1302. doi: 10.1126/science.2830675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noppen M., Vanmaele L., Schandevyl W. Severe adenovirus pneumonia in an adult civilian. Eur J Respir Dis. 1986 Sep;69(3):188–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E. The structural and functional diversity of Adenovirus capsid components. J Gen Virol. 1969 Sep;5(2):221–236. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-5-2-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris S. H., Butler T. C., Glass N., Tran R. Fatal hepatic necrosis caused by disseminated type 5 adenovirus infection in a renal transplant recipient. Am J Nephrol. 1989;9(2):101–105. doi: 10.1159/000167945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odio C., McCracken G. H., Jr, Nelson J. D. Disseminated adenovirus infection: a case report and review of the literature. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1984 Jan-Feb;3(1):46–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohbu M., Sasaki K., Okudaira M., Iidaka K., Aoyama Y. Adenovirus hepatitis in a patient with severe combined immunodeficiency. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1987 Apr;37(4):655–664. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1987.tb00400.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavan-Langston D., Dohlman C. H. A double blind clinical study of adenine arabinoside therapy of viral keratoconjunctivitis. Am J Ophthalmol. 1972 Jul;74(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(72)91130-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purtilo D. T., White R., Filipovich A., Kersey J., Zelkowitz L. Fulminant liver failure induced by adenovirus after bone marrow transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jun 27;312(26):1707–1708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly S., Dhillon B. J., Nkanza K. M., D'Souza A. M., Taylor N., Hobbs S. J., Freke A., Roome A. P. Adenovirus type 8 keratoconjunctivitis--an outbreak and its treatment with topical human fibroblast interferon. J Hyg (Lond) 1986 Jun;96(3):557–575. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400066365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldo C. R., Jr, Kingsley L. A., Lyter D. W., Bodner A. J., Weiss S. H., Saxinger W. C. Excretion of cytomegalovirus in semen associated with HTLV-III seropositivity in asymptomatic homosexual men. J Med Virol. 1986 Sep;20(1):17–22. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890200104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez F. H., Jr, Liuzza G. E., Gohd R. H. Disseminated adenovirus serotype 31 infection in an immunocompromised host. Am J Clin Pathol. 1984 Nov;82(5):615–618. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/82.5.615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos R., Chou S. M., Rogers N. G., Basnight M., Gajdusek D. C. Isolation of an adenovirus 32 strain from human brain in a case of subacute encephalitis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Feb;139(2):636–640. doi: 10.3181/00379727-139-36204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salt A., Sutehall G., Sargaison M., Woodward C., Barnes N. D., Calne R. Y., Wreghitt T. G. Viral and toxoplasma gondii infections in children after liver transplantation. J Clin Pathol. 1990 Jan;43(1):63–67. doi: 10.1136/jcp.43.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirm J., Manson W. L., Schröder F. P., Tegzess A. M., van der Avoort H. G., de Jong J. C. Een adenovirusepidemie onder niertransplantatiepatiënten. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 1991 Jul 20;135(29):1310–1314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz H., Wigand R., Heinrich W. Worldwide epidemiology of human adenovirus infections. Am J Epidemiol. 1983 Apr;117(4):455–466. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanley J. D., Jordan M. C. Viral pneumonia in the immunocompromised patient. Semin Respir Infect. 1986 Sep;1(3):193–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields A. F., Hackman R. C., Fife K. H., Corey L., Meyers J. D. Adenovirus infections in patients undergoing bone-marrow transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1985 Feb 28;312(9):529–533. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198502283120901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shindo K., Kitayama T., Ura T., Matsuya F., Kusaba Y., Kanetake H., Saito Y. Acute hemorrhagic cystitis caused by adenovirus type 11 after renal transplantation. Urol Int. 1986;41(2):152–155. doi: 10.1159/000281186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiramizu T., Satoh T., Jinushi K., Oka N., Inokuchi K. Renal allograft dysfunction with acute hemorrhagic cystitis caused by adenovirus in a recipient of a transplanted kidney. Tokai J Exp Clin Med. 1986 Nov;11(5):371–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegal F. P., Dikman S. H., Arayata R. B., Bottone E. J. Fatal disseminated adenovirus 11 pneumonia in an agammaglobulinemic patient. Am J Med. 1981 Dec;71(6):1062–1067. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90343-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokal E. M., Veyckemans F., de Ville de Goyet J., Moulin D., Van Hoorebeeck N., Alberti D., Buts J. P., Rahier J., Van Obbergh L., Clapuyt P. Liver transplantation in children less than 1 year of age. J Pediatr. 1990 Aug;117(2 Pt 1):205–210. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)80531-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- South M. A., Dolen J., Beach D. K., Mirkovic R. R. Fatal adenovirus hepatic necrosis in severe combined immune deficiency. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1982 Nov-Dec;1(6):416–419. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198211000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector S. L., English G. M., McIntosh K., Farr R. S. Adenovirus in the sinuses of an asthmatic patient with apparent selective antibody deficiencies. Am J Med. 1973 Aug;55(2):227–231. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90173-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalder H., Hierholzer J. C., Oxman M. N. New human adenovirus (candidate adenovirus type 35) causing fatal disseminated infection in a renal transplant recipient. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Sep;6(3):257–265. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.3.257-265.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan C. J., Jordan M. C. Diagnosis of viral pneumonia. Semin Respir Infect. 1988 Jun;3(2):148–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takafuji E. T., Gaydos J. C., Allen R. G., Top F. H., Jr Simultaneous administration of live, enteric-coated adenovirus types 4, 7 and 21 vaccines: safety and immunogenicity. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jul;140(1):48–53. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.1.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobinai K., Shimoyama M. [Recent advances in clinical research on T-cell lymphoma]. Rinsho Ketsueki. 1990 May;31(5):564–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuvia J., Weisselberg B., Shif I., Keren G. Aplastic anaemia complicating adenovirus infection in DiGeorge syndrome. Eur J Pediatr. 1988 Aug;147(6):643–644. doi: 10.1007/BF00442482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valainis G. T., Carlisle J. T., Daroca P. J., Gohd R. S., Enelow T. J. Respiratory failure complicated by adenovirus serotype 29 in a patient with AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1989 Aug;160(2):349–351. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.2.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valderrama-Leon G., Flomenberg P., Horwitz M. S. Restriction endonuclease mapping of adenovirus 35, a type isolated from immunocompromised hosts. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):647–650. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.647-650.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varki N. M., Bhuta S., Drake T., Porter D. D. Adenovirus hepatitis in two successive liver transplants in a child. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1990 Jan;114(1):106–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varsano I., Schonfeld T. M., Matoth Y., Shohat B., Englander T., Rotter V., Trainin N. Severe disseminated adenovirus infection successfully treated with a thymic humoral factor, THF. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1977 May;66(3):329–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1977.tb07902.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesh L. K., Arens M. Q., Subramanian T., Chinnadurai G. Selective induction of toxicity to human cells expressing human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat by a conditionally cytotoxic adenovirus vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8746–8750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ventura A. M., Arens M. Q., Srinivasan A., Chinnadurai G. Silencing of human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat expression by an adenovirus E1a mutant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1310–1314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadell G. Molecular epidemiology of human adenoviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1984;110:191–220. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-46494-2_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring GO E. d., Laibson P. R., Satz J. E., Joseph N. H. Use of vidarabine in epidemic keratoconjunctivitis due to adenovirus types 3, 7, 8, and 19. Am J Ophthalmol. 1976 Nov;82(5):781–785. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(76)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren D., Nelson K. E., Farrar J. A., Hurwitz E., Hierholzer J., Ford E., Anderson L. J. A large outbreak of epidemic keratoconjunctivitis: problems in controlling nosocomial spread. J Infect Dis. 1989 Dec;160(6):938–943. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.6.938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman R., August C. S., Plotkin S. A. Viral infections in pediatric bone marrow transplant patients. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1988 Feb;7(2):109–115. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198802000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassileva P. I., Galabov A. S. Uber die Behandlung der epidemischen Keratokonjunktivitis mit ABOB Klinische und Laboruntersuchungen. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 1975 Jan;166(1):77–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb D. H., Shields A. F., Fife K. H. Genomic variation of adenovirus type 5 isolates recovered from bone marrow transplant recipients. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):305–308. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.305-308.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West T. E., Papasian C. J., Park B. H., Parker S. W. Adenovirus type 2 encephalitis and concurrent Epstein-Barr virus infection in an adult man. Arch Neurol. 1985 Aug;42(8):815–817. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1985.04210090083023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigand R., Bartha A., Dreizin R. S., Esche H., Ginsberg H. S., Green M., Hierholzer J. C., Kalter S. S., McFerran J. B., Pettersson U. Adenoviridae: second report. Intervirology. 1982;18(4):169–176. doi: 10.1159/000149322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigand R., Sehn N., Hierholzer J. C., de Jong J. C., Adrian T. Immunological and biochemical characterization of human adenoviruses from subgenus B. I. Antigenic relationships. Arch Virol. 1985;84(1-2):63–78. doi: 10.1007/BF01310554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigger H. J., Blanc W. A. Fatal hepatic and bronchial necrosis in adenovirus infection with thymic alymphoplasia. N Engl J Med. 1966 Oct 20;275(16):870–874. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196610202751603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wreghitt T. G., Gray J. J., Ward K. N., Salt A., Taylor D. L., Alp N. J., Tyms A. S. Disseminated adenovirus infection after liver transplantation and its possible treatment with ganciclovir. J Infect. 1989 Jul;19(1):88–89. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(89)95214-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagisawa T., Takahashi K., Yamaguchi Y., Teraoka S., Horita S., Toma H., Agishi T., Ota K. Adenovirus induced nephropathy in kidney transplant recipients. Transplant Proc. 1989 Feb;21(1 Pt 2):2097–2099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Bishop C. A., Townsend T. R., Bolyard E. A., Bartlett J., Santos G. W., Saral R. Infectious gastroenteritis in bone-marrow-transplant recipients. N Engl J Med. 1982 Apr 29;306(17):1010–1012. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198204293061701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahradnik J. M., Spencer M. J., Porter D. D. Adenovirus infection in the immunocompromised patient. Am J Med. 1980 May;68(5):725–732. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90262-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong P. J., Valderrama G., Spigland I., Horwitz M. S. Adenovirus isolates from urine of patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Lancet. 1983 Jun 11;1(8337):1293–1296. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92411-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Avoort H. G., Wermenbol A. G., Zomerdijk T. P., Kleijne J. A., van Asten J. A., Jensma P., Osterhaus A. D., Kidd A. H., de Jong J. C. Characterization of fastidious adenovirus types 40 and 41 by DNA restriction enzyme analysis and by neutralizing monoclonal antibodies. Virus Res. 1989 Feb;12(2):139–157. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(89)90060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



