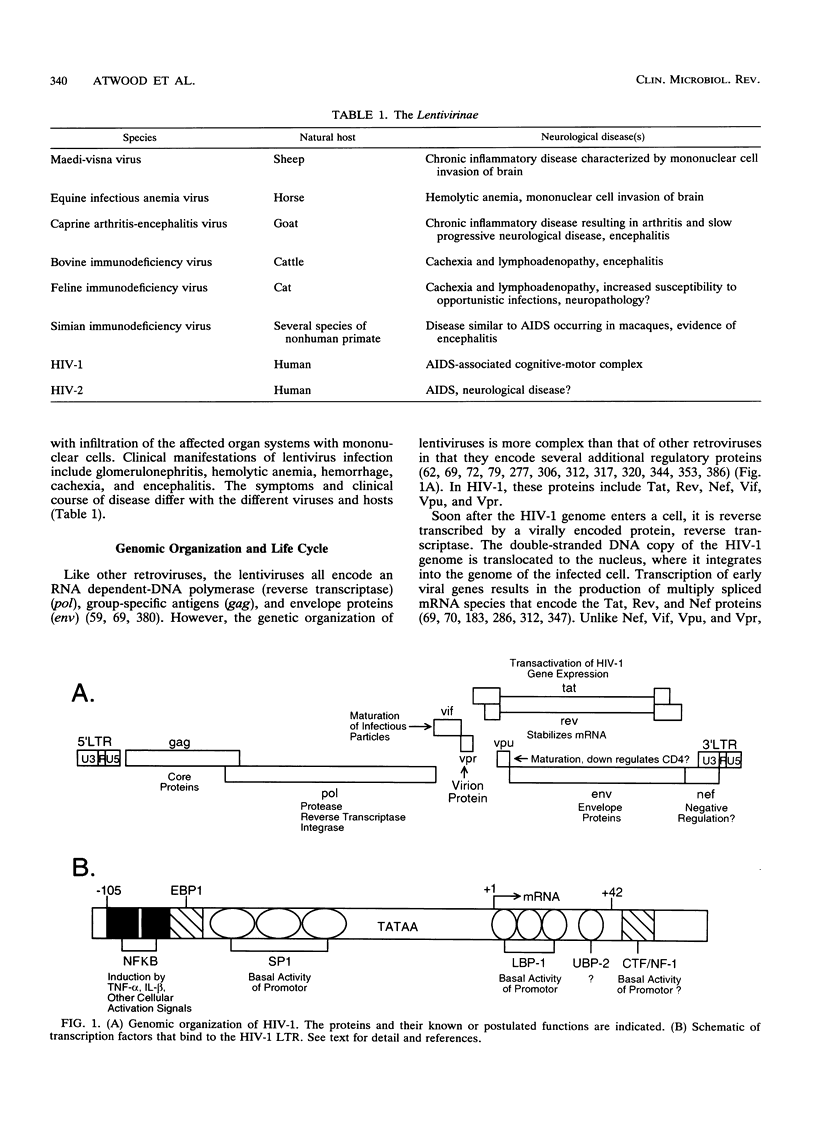
Abstract
Direct infection of the central nervous system by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1), the causative agent of AIDS, was not appreciated in the early years of the AIDS epidemic. Neurological complications associated with AIDS were largely attributed to opportunistic infections that arose as a result of the immunocompromised state of the patient and to depression. In 1985, several groups succeeded in isolating HIV-1 directly from brain tissue. Also that year, the viral genome was completely sequenced, and HIV-1 was found to belong to a neurotropic subfamily of retrovirus known as the Lentivirinae. These findings clearly indicated that direct HIV-1 infection of the central nervous system played a role in the development of AIDS-related neurological disease. This review summarizes the clinical manifestations of HIV-1 infection of the central nervous system and the related neuropathology, the tropism of HIV-1 for specific cell types both within and outside of the nervous system, the possible mechanisms by which HIV-1 damages the nervous system, and the current strategies for diagnosis and treatment of HIV-1-associated neuropathology.
Full text
PDF



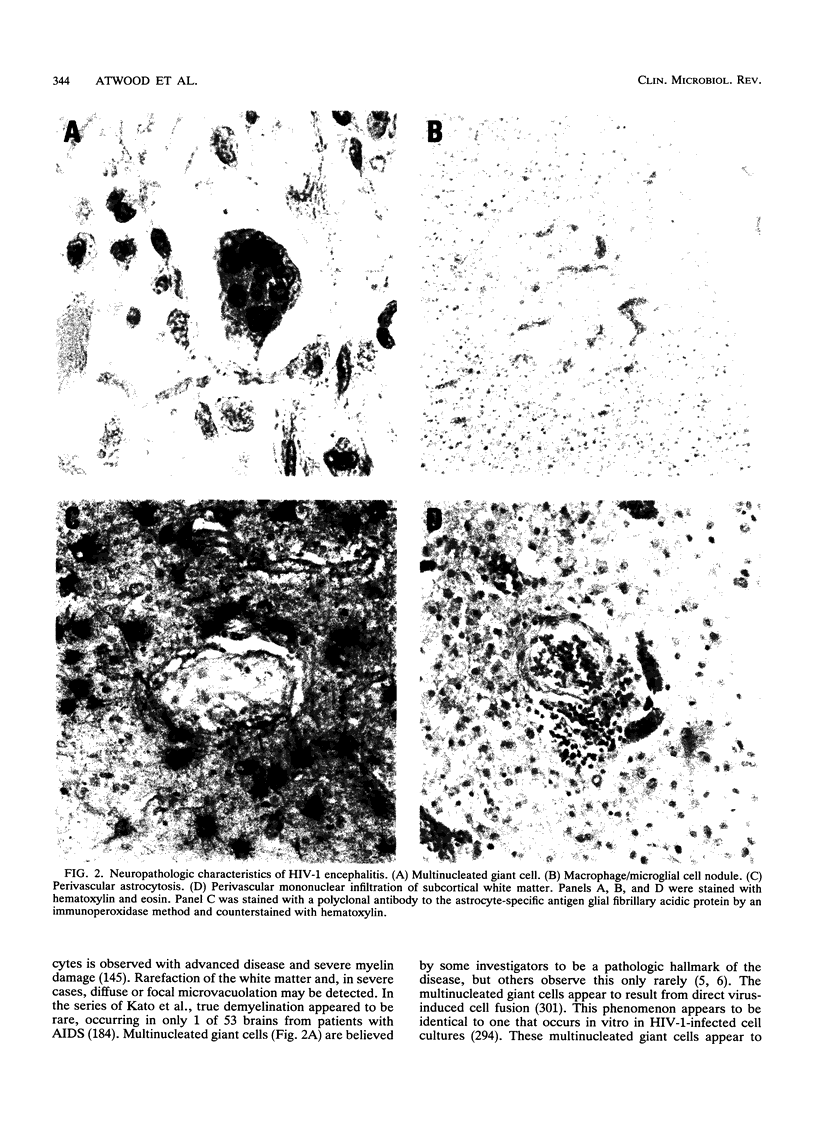



















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams E. J., Rogers M. F. Paediatric HIV infection. Baillieres Clin Haematol. 1991 Apr;4(2):333–359. doi: 10.1016/s0950-3536(05)80163-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adachi A., Gendelman H. E., Koenig S., Folks T., Willey R., Rabson A., Martin M. A. Production of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated retrovirus in human and nonhuman cells transfected with an infectious molecular clone. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):284–291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.284-291.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad N., Venkatesan S. Nef protein of HIV-1 is a transcriptional repressor of HIV-1 LTR. Science. 1988 Sep 16;241(4872):1481–1485. doi: 10.1126/science.3262235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anand R., Thayer R., Srinivasan A., Nayyar S., Gardner M., Luciw P., Dandekar S. Biological and molecular characterization of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1BR) from the brain of a patient with progressive dementia. Virology. 1989 Jan;168(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90406-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anders K. H., Guerra W. F., Tomiyasu U., Verity M. A., Vinters H. V. The neuropathology of AIDS. UCLA experience and review. Am J Pathol. 1986 Sep;124(3):537–558. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anders K., Steinsapir K. D., Iverson D. J., Glasgow B. J., Layfield L. J., Brown W. J., Cancilla P. A., Verity M. A., Vinters H. V. Neuropathologic findings in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Clin Neuropathol. 1986 Jan-Feb;5(1):1–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appleman M. E., Marshall D. W., Brey R. L., Houk R. W., Beatty D. C., Winn R. E., Melcher G. P., Wise M. G., Sumaya C. V., Boswell R. N. Cerebrospinal fluid abnormalities in patients without AIDS who are seropositive for the human immunodeficiency virus. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jul;158(1):193–199. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.1.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arendt G., Hefter H., Hoemberg V., Nelles H. W., Elsing C., Freund H. J. Early abnormalities of cognitive event-related potentials in HIV-infected patients without clinically evident CNS deficits. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol Suppl. 1990;41:370–380. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-444-81352-7.50044-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arthos J., Deen K. C., Chaikin M. A., Fornwald J. A., Sathe G., Sattentau Q. J., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., McDougal J. S., Pietropaolo C. Identification of the residues in human CD4 critical for the binding of HIV. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):469–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90922-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artigas J., Arastéh K., Averdunk R., Bachler B., Hornscheidt M., Grosse G., L'age M., Niedobitek F. Hyaline globules reacting positively with zidovudine antibody in brain and spinal cord of AIDS patients. Lancet. 1991 May 11;337(8750):1127–1128. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92790-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artigas J., Niedobitek F., Grosse G., Heise W., Gosztonyi G. Spongiform encephalopathy in AIDS dementia complex: report of five cases. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1989;2(4):374–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asjö B., Sharma U. K., Morfeldt-Månson L., Magnusson A., Barkhem T., Albert J., Olausson E., Von Gegerfelt A., Lind B., Biberfeld P. Naturally occurring HIV-1 isolates with differences in replicative capacity are distinguished by in situ hybridization of infected cells. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Oct;6(10):1177–1182. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.1177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachelerie F., Alcami J., Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Virelizier J. L. HIV enhancer activity perpetuated by NF-kappa B induction on infection of monocytes. Nature. 1991 Apr 25;350(6320):709–712. doi: 10.1038/350709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachelerie F., Alcami J., Hazan U., Israël N., Goud B., Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Virelizier J. L. Constitutive expression of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) nef protein in human astrocytes does not influence basal or induced HIV long terminal repeat activity. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3059–3062. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3059-3062.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagasra O., Hauptman S. P., Lischner H. W., Sachs M., Pomerantz R. J. Detection of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 provirus in mononuclear cells by in situ polymerase chain reaction. N Engl J Med. 1992 May 21;326(21):1385–1391. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199205213262103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagasra O., Pomerantz R. J. Human immunodeficiency virus type I provirus is demonstrated in peripheral blood monocytes in vivo: a study utilizing an in situ polymerase chain reaction. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1993 Jan;9(1):69–76. doi: 10.1089/aid.1993.9.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagasra O., Seshamma T., Pomerantz R. J. Polymerase chain reaction in situ: intracellular amplification and detection of HIV-1 proviral DNA and other specific genes. J Immunol Methods. 1993 Jan 14;158(1):131–145. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(93)90265-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barré-Sinoussi F., Chermann J. C., Rey F., Nugeyre M. T., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Dauguet C., Axler-Blin C., Vézinet-Brun F., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science. 1983 May 20;220(4599):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.6189183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartolomei F., Pellegrino P., Dhiver C., Quilichini R., Gastaut J. A., Gastaut J. L. Crises d'épilepsie au cours de l'infection par le VIH. 52 observations. Presse Med. 1991 Dec 7;20(42):2135–2138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaumanoir A., Burkhard P., Gauthier G., Le Floch-Rohr J., Ochsner F., Waldvogel F. EEG dans 19 cas de SIDA avec atteinte de l'encéphale. Neurophysiol Clin. 1988 Aug;18(4):313–322. doi: 10.1016/s0987-7053(88)80088-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckett A., Summergrad P., Manschreck T., Vitagliano H., Henderson M., Buttolph M. L., Jenike M. Symptomatic HIV infection of the CNS in a patient without clinical evidence of immune deficiency. Am J Psychiatry. 1987 Oct;144(10):1342–1344. doi: 10.1176/ajp.144.10.1342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belman A. L., Lantos G., Horoupian D., Novick B. E., Ultmann M. H., Dickson D. W., Rubinstein A. AIDS: calcification of the basal ganglia in infants and children. Neurology. 1986 Sep;36(9):1192–1199. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.9.1192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belman A. L., Ultmann M. H., Horoupian D., Novick B., Spiro A. J., Rubinstein A., Kurtzberg D., Cone-Wesson B. Neurological complications in infants and children with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1985 Nov;18(5):560–566. doi: 10.1002/ana.410180509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger J. R., Moskowitz L., Fischl M., Kelley R. E. Neurologic disease as the presenting manifestation of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. South Med J. 1987 Jun;80(6):683–686. doi: 10.1097/00007611-198706000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernton E. W., Bryant H. U., Decoster M. A., Orenstein J. M., Ribas J. L., Meltzer M. S., Gendelman H. E. No direct neuronotoxicity by HIV-1 virions or culture fluids from HIV-1-infected T cells or monocytes. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Apr;8(4):495–503. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat S., Spitalnik S. L., Gonzalez-Scarano F., Silberberg D. H. Galactosyl ceramide or a derivative is an essential component of the neural receptor for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein gp120. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7131–7134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenneman D. E., Westbrook G. L., Fitzgerald S. P., Ennist D. L., Elkins K. L., Ruff M. R., Pert C. B. Neuronal cell killing by the envelope protein of HIV and its prevention by vasoactive intestinal peptide. Nature. 1988 Oct 13;335(6191):639–642. doi: 10.1038/335639a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brew B. J., Bhalla R. B., Fleisher M., Paul M., Khan A., Schwartz M. K., Price R. W. Cerebrospinal fluid beta 2 microglobulin in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Neurology. 1989 Jun;39(6):830–834. doi: 10.1212/wnl.39.6.830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brew B. J., Bhalla R. B., Paul M., Sidtis J. J., Keilp J. J., Sadler A. E., Gallardo H., McArthur J. C., Schwartz M. K., Price R. W. Cerebrospinal fluid beta 2-microglobulin in patients with AIDS dementia complex: an expanded series including response to zidovudine treatment. AIDS. 1992 May;6(5):461–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brew B. J., Perdices M., Darveniza P., Edwards P., Whyte B., Burke W. J., Garrick R., O'Sullivan D., Penny R., Cooper D. A. The neurological features of early and 'latent' human immunodeficiency virus infection. Aust N Z J Med. 1989 Dec;19(6):700–705. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1989.tb00339.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton C. B., Miller J. R. Neurologic complications in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Neurol Clin. 1984 May;2(2):315–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunetti A., Berg G., Di Chiro G., Cohen R. M., Yarchoan R., Pizzo P. A., Broder S., Eddy J., Fulham M. J., Finn R. D. Reversal of brain metabolic abnormalities following treatment of AIDS dementia complex with 3'-azido-2',3'-dideoxythymidine (AZT, zidovudine): a PET-FDG study. J Nucl Med. 1989 May;30(5):581–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budka H., Costanzi G., Cristina S., Lechi A., Parravicini C., Trabattoni R., Vago L. Brain pathology induced by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). A histological, immunocytochemical, and electron microscopical study of 100 autopsy cases. Acta Neuropathol. 1987;75(2):185–198. doi: 10.1007/BF00687080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budka H., Wiley C. A., Kleihues P., Artigas J., Asbury A. K., Cho E. S., Cornblath D. R., Dal Canto M. C., DeGirolami U., Dickson D. HIV-associated disease of the nervous system: review of nomenclature and proposal for neuropathology-based terminology. Brain Pathol. 1991 Apr;1(3):143–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.1991.tb00653.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buffet R., Agut H., Chieze F., Katlama C., Bolgert F., Devillechabrolle A., Diquet B., Schuller E., Pierrot-Deseilligny C., Gentilini M. Virological markers in the cerebrospinal fluid from HIV-1-infected individuals. AIDS. 1991 Dec;5(12):1419–1424. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199112000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bursztyn E. M., Lee B. C., Bauman J. CT of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1984 Nov-Dec;5(6):711–714. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton S. W. The psychiatry of HIV infection. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 Jul 25;295(6592):228–229. doi: 10.1136/bmj.295.6592.228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese L. H., Proffitt M. R., Levin K. H., Yen-Lieberman B., Starkey C. Acute infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) associated with acute brachial neuritis and exanthematous rash. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Dec;107(6):849–851. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-6-849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. A. Aggressive psychosis in AIDS patient on high-dose steroids. Lancet. 1987 Sep 26;2(8561):750–751. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91119-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cann A. J., Zack J. A., Go A. S., Arrigo S. J., Koyanagi Y., Green P. L., Koyanagi Y., Pang S., Chen I. S. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 T-cell tropism is determined by events prior to provirus formation. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4735–4742. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4735-4742.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Y. Z., Friedman-Kien A. E., Huang Y. X., Li X. L., Mirabile M., Moudgil T., Zucker-Franklin D., Ho D. D. CD4-independent, productive human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection of hepatoma cell lines in vitro. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2553–2559. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2553-2559.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carne C. A., Tedder R. S., Smith A., Sutherland S., Elkington S. G., Daly H. M., Preston F. E., Craske J. Acute encephalopathy coincident with seroconversion for anti-HTLV-III. Lancet. 1985 Nov 30;2(8466):1206–1208. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90740-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalmers A. C., Aprill B. S., Shephard H. Cerebrospinal fluid and human immunodeficiency virus. Findings in healthy, asymptomatic, seropositive men. Arch Intern Med. 1990 Jul;150(7):1538–1540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng-Mayer C. Biological and molecular features of HIV-1 related to tissue tropism. AIDS. 1990;4 (Suppl 1):S49–S56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng-Mayer C., Iannello P., Shaw K., Luciw P. A., Levy J. A. Differential effects of nef on HIV replication: implications for viral pathogenesis in the host. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1629–1632. doi: 10.1126/science.2531920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng-Mayer C., Levy J. A. Distinct biological and serological properties of human immunodeficiency viruses from the brain. Ann Neurol. 1988;23 (Suppl):S58–S61. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng-Mayer C., Seto D., Levy J. A. Altered host range of HIV-1 after passage through various human cell types. Virology. 1991 Mar;181(1):288–294. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90494-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng-Mayer C., Weiss C., Seto D., Levy J. A. Isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 from the brain may constitute a special group of the AIDS virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8575–8579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chermann J. C. HIV-associated diseases: acute and regressive encephalopathy in a seropositive man. Res Virol. 1990 Mar-Apr;141(2):137–141. doi: 10.1016/0923-2516(90)90015-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodi F., Fuerstenberg S., Gidlund M., Asjö B., Fenyö E. M. Infection of brain-derived cells with the human immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1244–1247. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1244-1247.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodi F., Valentin A., Keys B., Schwartz S., Asjö B., Gartner S., Popovic M., Albert J., Sundqvist V. A., Fenyö E. M. Biological characterization of paired human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates from blood and cerebrospinal fluid. Virology. 1989 Nov;173(1):178–187. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90233-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciardi A., Sinclair E., Scaravilli F., Harcourt-Webster N. J., Lucas S. The involvement of the cerebral cortex in human immunodeficiency virus encephalopathy: a morphological and immunohistochemical study. Acta Neuropathol. 1990;81(1):51–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00662637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapham P. R., Weber J. N., Whitby D., McIntosh K., Dalgleish A. G., Maddon P. J., Deen K. C., Sweet R. W., Weiss R. A. Soluble CD4 blocks the infectivity of diverse strains of HIV and SIV for T cells and monocytes but not for brain and muscle cells. Nature. 1989 Jan 26;337(6205):368–370. doi: 10.1038/337368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements G. J., Price-Jones M. J., Stephens P. E., Sutton C., Schulz T. F., Clapham P. R., McKeating J. A., McClure M. O., Thomson S., Marsh M. The V3 loops of the HIV-1 and HIV-2 surface glycoproteins contain proteolytic cleavage sites: a possible function in viral fusion? AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Jan;7(1):3–16. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coceani F., Bishai I., Dinarello C. A., Fitzpatrick F. A. Prostaglandin E2 and thromboxane B2 in cerebrospinal fluid of afebrile and febrile cat. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jun;244(6):R785–R793. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1983.244.6.R785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen E. A., Dehni G., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. Human immunodeficiency virus vpr product is a virion-associated regulatory protein. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3097–3099. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3097-3099.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen E. A., Terwilliger E. F., Jalinoos Y., Proulx J., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. Identification of HIV-1 vpr product and function. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(1):11–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen E. A., Terwilliger E. F., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. Identification of a protein encoded by the vpu gene of HIV-1. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):532–534. doi: 10.1038/334532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collman R., Godfrey B., Cutilli J., Rhodes A., Hassan N. F., Sweet R., Douglas S. D., Friedman H., Nathanson N., Gonzalez-Scarano F. Macrophage-tropic strains of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 utilize the CD4 receptor. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4468–4476. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4468-4476.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. A., Gold J., Maclean P., Donovan B., Finlayson R., Barnes T. G., Michelmore H. M., Brooke P., Penny R. Acute AIDS retrovirus infection. Definition of a clinical illness associated with seroconversion. Lancet. 1985 Mar 9;1(8428):537–540. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91205-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corboy J. R., Buzy J. M., Zink M. C., Clements J. E. Expression directed from HIV long terminal repeats in the central nervous system of transgenic mice. Science. 1992 Dec 11;258(5089):1804–1808. doi: 10.1126/science.1465618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordonnier A., Montagnier L., Emerman M. Single amino-acid changes in HIV envelope affect viral tropism and receptor binding. Nature. 1989 Aug 17;340(6234):571–574. doi: 10.1038/340571a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Garrett E. D. A comparison of regulatory features in primate lentiviruses. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Mar;8(3):387–393. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Greene W. C. Regulatory pathways governing HIV-1 replication. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):423–426. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90420-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Malim M. H. The HIV-1 Rev protein: prototype of a novel class of eukaryotic post-transcriptional regulators. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Sep;16(9):346–350. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90141-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Mechanism of action of regulatory proteins encoded by complex retroviruses. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Sep;56(3):375–394. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.3.375-394.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Regulation of HIV-1 gene expression. FASEB J. 1991 Jul;5(10):2361–2368. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.10.1712325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Regulation of human immunodeficiency virus replication. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991;45:219–250. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. The HIV-1 Tat protein: an RNA sequence-specific processivity factor? Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):655–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90129-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Trans-activation of human immunodeficiency virus occurs via a bimodal mechanism. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):973–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90696-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings M. A., Cummings K. L., Rapaport M. H., Atkinson J. H., Grant I. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome presenting as schizophrenia. West J Med. 1987 May;146(5):615–618. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currie J., Benson E., Ramsden B., Perdices M., Cooper D. Eye movement abnormalities as a predictor of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome dementia complex. Arch Neurol. 1988 Sep;45(9):949–953. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1988.00520330027006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Agostino D. M., Felber B. K., Harrison J. E., Pavlakis G. N. The Rev protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 promotes polysomal association and translation of gag/pol and vpu/env mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1375–1386. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgleish A. G., Beverley P. C., Clapham P. R., Crawford D. H., Greaves M. F., Weiss R. A. The CD4 (T4) antigen is an essential component of the receptor for the AIDS retrovirus. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):763–767. doi: 10.1038/312763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. E., Hjelle B. L., Miller V. E., Palmer D. L., Llewellyn A. L., Merlin T. L., Young S. A., Mills R. G., Wachsman W., Wiley C. A. Early viral brain invasion in iatrogenic human immunodeficiency virus infection. Neurology. 1992 Sep;42(9):1736–1739. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.9.1736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S. L., Halsted C. C., Levy N., Ellis W. Acquired immune deficiency syndrome presenting as progressive infantile encephalopathy. J Pediatr. 1987 Jun;110(6):884–888. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80402-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day J. J., Grant I., Atkinson J. H., Brysk L. T., McCutchan J. A., Hesselink J. R., Heaton R. K., Weinrich J. D., Spector S. A., Richman D. D. Incidence of AIDS dementia in a two-year follow-up of AIDS and ARC patients on an initial phase II AZT placebo-controlled study: San Diego cohort. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1992 Winter;4(1):15–20. doi: 10.1176/jnp.4.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton A. I., Sodroski J. G., Rosen C. A., Goh W. C., Haseltine W. A. The trans-activator gene of the human T cell lymphotropic virus type III is required for replication. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):941–947. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denning D. W., Anderson J., Rudge P., Smith H. Acute myelopathy associated with primary infection with human immunodeficiency virus. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 Jan 17;294(6565):143–144. doi: 10.1136/bmj.294.6565.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derix M. M., de Gans J., Stam J., Portegies P. Mental changes in patients with AIDS. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 1990;92(3):215–222. doi: 10.1016/0303-8467(90)90023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derse D., Dorn P. L., Levy L., Stephens R. M., Rice N. R., Casey J. W. Characterization of equine infectious anemia virus long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):743–747. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.743-747.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewhurst S., Bresser J., Stevenson M., Sakai K., Evinger-Hodges M. J., Volsky D. J. Susceptibility of human glial cells to infection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). FEBS Lett. 1987 Mar 9;213(1):138–143. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81479-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer E. B., Kaiser P. K., Offermann J. T., Lipton S. A. HIV-1 coat protein neurotoxicity prevented by calcium channel antagonists. Science. 1990 Apr 20;248(4953):364–367. doi: 10.1126/science.2326646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunbar N., Perdices M., Grunseit A., Cooper D. A. Changes in neuropsychological performance of AIDS-related complex patients who progress to AIDS. AIDS. 1992 Jul;6(7):691–700. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199207000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop O., Bruun J. N., Myrvang B., Fagerhol M. K. Calprotectin in cerebrospinal fluid of the HIV infected: a diagnostic marker of opportunistic central nervous system infection? Scand J Infect Dis. 1991;23(6):687–689. doi: 10.3109/00365549109024294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durum S. K., Schmidt J. A., Oppenheim J. J. Interleukin 1: an immunological perspective. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:263–287. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.001403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein H., Knight R. T. Severe parkinsonism in two AIDS patients taking prochlorperazine. Lancet. 1987 Aug 8;2(8554):341–342. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90937-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan V. G., Crawford J. R., Brettle R. P., Goodwin G. M. The Edinburgh cohort of HIV-positive drug users: current intellectual function is impaired, but not due to early AIDS dementia complex. AIDS. 1990 Jul;4(7):651–656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ell P. J., Costa D. C., Harrison M. Imaging cerebral damage in HIV infection. Lancet. 1987 Sep 5;2(8558):569–570. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92955-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elovaara I., Iivanainen M., Poutiainen E., Valle S. L., Weber T., Suni J., Lähdevirta J. CSF and serum beta-2-microglobulin in HIV infection related to neurological dysfunction. Acta Neurol Scand. 1989 Feb;79(2):81–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1989.tb03717.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elovaara I., Iivanainen M., Valle S. L., Suni J., Tervo T., Lähdevirta J. CSF protein and cellular profiles in various stages of HIV infection related to neurological manifestations. J Neurol Sci. 1987 May;78(3):331–342. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(87)90046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elovaara I., Poutiainen E., Raininko R., Valanne L., Virta A., Valle S. L., Lähdevirta J., Iivanainen M. Mild brain atrophy in early HIV infection: the lack of association with cognitive deficits and HIV-specific intrathecal immune response. J Neurol Sci. 1990 Nov;99(2-3):121–136. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(90)90149-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elovaara I., Saar P., Valle S. L., Hokkanen L., Iivanainen M., Lähdevirta J. EEG in early HIV-1 infection is characterized by anterior dysrhythmicity of low maximal amplitude. Clin Electroencephalogr. 1991 Jul;22(3):131–140. doi: 10.1177/155005949102200303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. G., Gendelman H. E. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection of the nervous system: pathogenetic mechanisms. Ann Neurol. 1993 May;33(5):429–436. doi: 10.1002/ana.410330502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. G., Goudsmit J., Paul D. A., Morrison S. H., Connor E. M., Oleske J. M., Holland B. Expression of human immunodeficiency virus in cerebrospinal fluid of children with progressive encephalopathy. Ann Neurol. 1987 Apr;21(4):397–401. doi: 10.1002/ana.410210413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. G., Sharer L. R., Cho E. S., Myenhofer M., Navia B., Price R. W. HTLV-III/LAV-like retrovirus particles in the brains of patients with AIDS encephalopathy. AIDS Res. 1984;1(6):447–454. doi: 10.1089/aid.1.1983.1.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. G., Sharer L. R., Joshi V. V., Fojas M. M., Koenigsberger M. R., Oleske J. M. Progressive encephalopathy in children with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1985 May;17(5):488–496. doi: 10.1002/ana.410170512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. G., Sharer L. R., Oleske J. M., Connor E. M., Goudsmit J., Bagdon L., Robert-Guroff M., Koenigsberger M. R. Neurologic manifestations of human immunodeficiency virus infection in children. Pediatrics. 1986 Oct;78(4):678–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esiri M. M., Morris C. S., Millard P. R. Fate of oligodendrocytes in HIV-1 infection. AIDS. 1991 Sep;5(9):1081–1088. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199109000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everall I. P., Luthert P. J., Lantos P. L. Neuronal loss in the frontal cortex in HIV infection. Lancet. 1991 May 11;337(8750):1119–1121. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92786-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulstich M. E. Acquired immune deficiency syndrome: an overview of central nervous system complications and neuropsychological sequelae. Int J Neurosci. 1986 Nov;30(4):249–254. doi: 10.3109/00207458608985675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felber B. K., Drysdale C. M., Pavlakis G. N. Feedback regulation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 expression by the Rev protein. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3734–3741. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3734-3741.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenyö E. M., Morfeldt-Månson L., Chiodi F., Lind B., von Gegerfelt A., Albert J., Olausson E., Asjö B. Distinct replicative and cytopathic characteristics of human immunodeficiency virus isolates. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4414–4419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4414-4419.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiala M., Mosca J. D., Barry P., Luciw P. A., Vinters H. V. Multi-step pathogenesis of AIDS--role of cytomegalovirus. Res Immunol. 1991 Feb;142(2):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0923-2494(91)90016-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- First isolation of HTLV-III. Nature. 1986 May 8;321(6066):119–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folks T., Powell D. M., Lightfoote M. M., Benn S., Martin M. A., Fauci A. S. Induction of HTLV-III/LAV from a nonvirus-producing T-cell line: implications for latency. Science. 1986 Feb 7;231(4738):600–602. doi: 10.1126/science.3003906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. D., Pabo C. O. Cellular uptake of the tat protein from human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1189–1193. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90263-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I., Feldon S. E. Eye movements in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Arch Neurol. 1989 Aug;46(8):841–841. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1989.00520440021008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita K., Silver J., Peden K. Changes in both gp120 and gp41 can account for increased growth potential and expanded host range of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4445–4451. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4445-4451.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabuzda D. H., Ho D. D., de la Monte S. M., Hirsch M. S., Rota T. R., Sobel R. A. Immunohistochemical identification of HTLV-III antigen in brains of patients with AIDS. Ann Neurol. 1986 Sep;20(3):289–295. doi: 10.1002/ana.410200304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabuzda D. H., Levy S. R., Chiappa K. H. Electroencephalography in AIDS and AIDS-related complex. Clin Electroencephalogr. 1988 Jan;19(1):1–6. doi: 10.1177/155005948801900103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajdusek D. C., Amyx H. L., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Asher D. M., Rodgers-Johnson P., Epstein L. G., Sarin P. S., Gallo R. C., Maluish A., Arthur L. O. Infection of chimpanzees by human T-lymphotropic retroviruses in brain and other tissues from AIDS patients. Lancet. 1985 Jan 5;1(8419):55–56. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
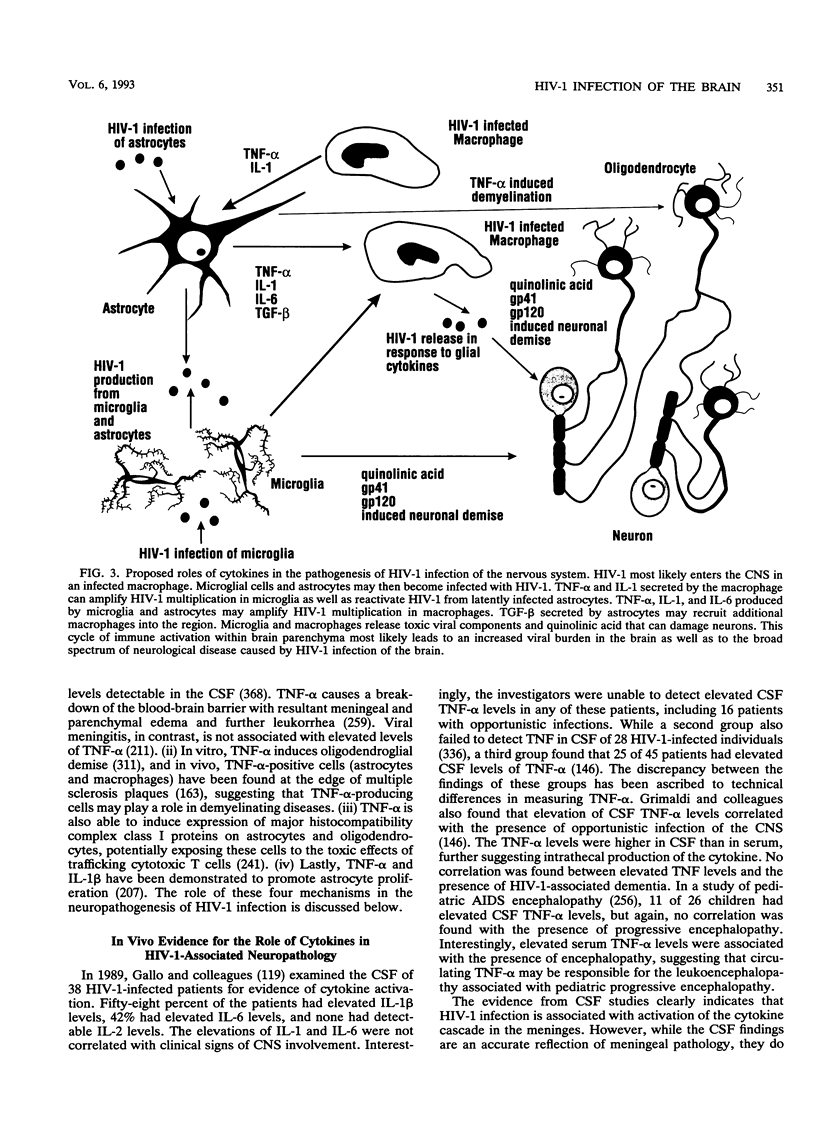
- Gallo P., Frei K., Rordorf C., Lazdins J., Tavolato B., Fontana A. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection of the central nervous system: an evaluation of cytokines in cerebrospinal fluid. J Neuroimmunol. 1989 Jul;23(2):109–116. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(89)90029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo P., Piccinno M. G., Krzalic L., Tavolato B. Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha) and neurological diseases. Failure in detecting TNF alpha in the cerebrospinal fluid from patients with multiple sclerosis, AIDS dementia complex, and brain tumours. J Neuroimmunol. 1989 Jun;23(1):41–44. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(89)90071-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C., Salahuddin S. Z., Popovic M., Shearer G. M., Kaplan M., Haynes B. F., Palker T. J., Redfield R., Oleske J., Safai B. Frequent detection and isolation of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and at risk for AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):500–503. doi: 10.1126/science.6200936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. V., Miller A. D. Serine phosphorylation-independent downregulation of cell-surface CD4 by nef. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):508–511. doi: 10.1038/350508a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett E. D., Tiley L. S., Cullen B. R. Rev activates expression of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 vif and vpr gene products. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1653–1657. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1653-1657.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garry R. F., Kort J. J., Koch-Nolte F., Koch G. Similarities of viral proteins to toxins that interact with monovalent cation channels. AIDS. 1991 Nov;5(11):1381–1384. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199111000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner S., Markovits P., Markovitz D. M., Betts R. F., Popovic M. Virus isolation from and identification of HTLV-III/LAV-producing cells in brain tissue from a patient with AIDS. JAMA. 1986 Nov 7;256(17):2365–2371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner S., Markovits P., Markovitz D. M., Kaplan M. H., Gallo R. C., Popovic M. The role of mononuclear phagocytes in HTLV-III/LAV infection. Science. 1986 Jul 11;233(4760):215–219. doi: 10.1126/science.3014648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner S., Ohashi K., Popovic M. Virus-host cell interactions in human immunodeficiency virus infections. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1991;300:45–55. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5976-0_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner S., Popovic M. Macrophage tropism of HIV-1. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Aug;6(8):1017–1021. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.1017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gendelman H. E., Narayan O., Kennedy-Stoskopf S., Clements J. E., Pezeshkpour G. H. Slow virus-macrophage interactions. Characterization of a transformed cell line of sheep alveolar macrophages that express a marker for susceptibility to ovine-caprine lentivirus infections. Lab Invest. 1984 Nov;51(5):547–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gendelman H. E., Narayan O., Molineaux S., Clements J. E., Ghotbi Z. Slow, persistent replication of lentiviruses: role of tissue macrophages and macrophage precursors in bone marrow. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7086–7090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gendelman H. E., Orenstein J. M., Martin M. A., Ferrua C., Mitra R., Phipps T., Wahl L. A., Lane H. C., Fauci A. S., Burke D. S. Efficient isolation and propagation of human immunodeficiency virus on recombinant colony-stimulating factor 1-treated monocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1428–1441. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genis P., Jett M., Bernton E. W., Boyle T., Gelbard H. A., Dzenko K., Keane R. W., Resnick L., Mizrachi Y., Volsky D. J. Cytokines and arachidonic metabolites produced during human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected macrophage-astroglia interactions: implications for the neuropathogenesis of HIV disease. J Exp Med. 1992 Dec 1;176(6):1703–1718. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.6.1703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giangaspero F., Scanabissi E., Baldacci M. C., Betts C. M. Massive neuronal destruction in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) encephalitis. A clinico-pathological study of a pediatric case. Acta Neuropathol. 1989;78(6):662–665. doi: 10.1007/BF00691293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs A., Andrewes D. G., Szmukler G., Mulhall B., Bowden S. C. Early HIV-related neuropsychological impairment: relationship to stage of viral infection. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 1990 Oct;12(5):766–780. doi: 10.1080/01688639008401018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulian D., Vaca K., Noonan C. A. Secretion of neurotoxins by mononuclear phagocytes infected with HIV-1. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1593–1596. doi: 10.1126/science.2148832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulian D., Young D. G., Woodward J., Brown D. C., Lachman L. B. Interleukin-1 is an astroglial growth factor in the developing brain. J Neurosci. 1988 Feb;8(2):709–714. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-02-00709.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goethe K. E., Mitchell J. E., Marshall D. W., Brey R. L., Cahill W. T., Leger G. D., Hoy L. J., Boswell R. N. Neuropsychological and neurological function of human immunodeficiency virus seropositive asymptomatic individuals. Arch Neurol. 1989 Feb;46(2):129–133. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1989.00520380029008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda M. A., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C., Clements J. E., Narayan O., Gilden R. V. Sequence homology and morphologic similarity of HTLV-III and visna virus, a pathogenic lentivirus. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):173–177. doi: 10.1126/science.2981428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goswami K. K., Kaye S., Miller R., McAllister R., Tedder R. Intrathecal IgG synthesis and specificity of oligoclonal IgG in patients infected with HIV-1 do not correlate with CNS disease. J Med Virol. 1991 Feb;33(2):106–113. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890330208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudsmit J., Lange J. M., Krone W. J., Teunissen M. B., Epstein L. G., Danner S. A., van den Berg H., Breederveld C., Smit L., Bakker M. Pathogenesis of HIV and its implications for serodiagnosis and monitoring of antiviral therapy. J Virol Methods. 1987 Aug;17(1-2):19–34. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(87)90065-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudsmit J., de Wolf F., Paul D. A., Epstein L. G., Lange J. M., Krone W. J., Speelman H., Wolters E. C., Van der Noordaa J., Oleske J. M. Expression of human immunodeficiency virus antigen (HIV-Ag) in serum and cerebrospinal fluid during acute and chronic infection. Lancet. 1986 Jul 26;2(8500):177–180. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92485-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray F., Gherardi R., Scaravilli F. The neuropathology of the acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). A review. Brain. 1988 Apr;111(Pt 2):245–266. doi: 10.1093/brain/111.2.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray F., Haug H., Chimelli L., Geny C., Gaston A., Scaravilli F., Budka H. Prominent cortical atrophy with neuronal loss as correlate of human immunodeficiency virus encephalopathy. Acta Neuropathol. 1991;82(3):229–233. doi: 10.1007/BF00294450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi L. M., Martino G. V., Franciotta D. M., Brustia R., Castagna A., Pristerà R., Lazzarin A. Elevated alpha-tumor necrosis factor levels in spinal fluid from HIV-1-infected patients with central nervous system involvement. Ann Neurol. 1991 Jan;29(1):21–25. doi: 10.1002/ana.410290106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groenink M., Fouchier R. A., de Goede R. E., de Wolf F., Gruters R. A., Cuypers H. T., Huisman H. G., Tersmette M. Phenotypic heterogeneity in a panel of infectious molecular human immunodeficiency virus type 1 clones derived from a single individual. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1968–1975. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1968-1975.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullotta F., Kuchelmeister K., Masini T., Ghidoni P., Cappricci E. Zur Morphologie der HIV-Enzephalopathie. Zentralbl Allg Pathol. 1989;135(1):5–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase A. T., Stowring L., Harris J. D., Traynor B., Ventura P., Peluso R., Brahic M. Visna DNA synthesis and the tempo of infection in vitro. Virology. 1982 Jun;119(2):399–410. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90099-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haggerty S., Stevenson M. Predominance of distinct viral genotypes in brain and lymph node compartments of HIV-1-infected individuals. Viral Immunol. 1991 Summer;4(2):123–131. doi: 10.1089/vim.1991.4.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammes S. R., Dixon E. P., Malim M. H., Cullen B. R., Greene W. C. Nef protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1: evidence against its role as a transcriptional inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9549–9553. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harouse J. M., Bhat S., Spitalnik S. L., Laughlin M., Stefano K., Silberberg D. H., Gonzalez-Scarano F. Inhibition of entry of HIV-1 in neural cell lines by antibodies against galactosyl ceramide. Science. 1991 Jul 19;253(5017):320–323. doi: 10.1126/science.1857969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harouse J. M., Laughlin M. A., Pletcher C., Friedman H. M., Gonzalez-Scarano F. Entry of human immunodeficiency virus-1 into glial cells proceeds via an alternate, efficient pathway. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Jun;49(6):605–609. doi: 10.1002/jlb.49.6.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrich D., Garcia J., Wu F., Mitsuyasu R., Gonazalez J., Gaynor R. Role of SP1-binding domains in in vivo transcriptional regulation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2585–2591. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2585-2591.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauber J., Perkins A., Heimer E. P., Cullen B. R. Trans-activation of human immunodeficiency virus gene expression is mediated by nuclear events. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6364–6368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helbert M., Robinson D., Peddle B., Forster S., Kocsis A., Jeffries D., Pinching A. J. Acute meningo-encephalitis on dose reduction of zidovudine. Lancet. 1988 Jun 4;1(8597):1249–1252. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyes M. P., Brew B. J., Saito K., Quearry B. J., Price R. W., Lee K., Bhalla R. B., Der M., Markey S. P. Inter-relationships between quinolinic acid, neuroactive kynurenines, neopterin and beta 2-microglobulin in cerebrospinal fluid and serum of HIV-1-infected patients. J Neuroimmunol. 1992 Sep;40(1):71–80. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(92)90214-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyes M. P., Brew B., Martin A., Markey S. P., Price R. W., Bhalla R. B., Salazar A. Cerebrospinal fluid quinolinic acid concentrations are increased in acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1991;294:687–690. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5952-4_94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickey W. F., Kimura H. Perivascular microglial cells of the CNS are bone marrow-derived and present antigen in vivo. Science. 1988 Jan 15;239(4837):290–292. doi: 10.1126/science.3276004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Rota T. R., Schooley R. T., Kaplan J. C., Allan J. D., Groopman J. E., Resnick L., Felsenstein D., Andrews C. A., Hirsch M. S. Isolation of HTLV-III from cerebrospinal fluid and neural tissues of patients with neurologic syndromes related to the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 12;313(24):1493–1497. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512123132401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Sarngadharan M. G., Resnick L., Dimarzoveronese F., Rota T. R., Hirsch M. S. Primary human T-lymphotropic virus type III infection. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Dec;103(6 ):880–883. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-6-880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofman F. M., Hinton D. R., Johnson K., Merrill J. E. Tumor necrosis factor identified in multiple sclerosis brain. J Exp Med. 1989 Aug 1;170(2):607–612. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.2.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander H., Golden J., Mendelson T., Cortland D. Extrapyramidal symptoms in AIDS patients given low-dose metoclopramide or chlorpromazine. Lancet. 1985 Nov 23;2(8465):1186–1186. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92706-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander H., Stringari S. Human immunodeficiency virus-associated meningitis. Clinical course and correlations. Am J Med. 1987 Nov;83(5):813–816. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90635-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollweg M., Riedel R. R., Goebel F. D., Schick U., Naber D. Remarkable improvement of neuropsychiatric symptoms in HIV-infected patients after AZT therapy. Klin Wochenschr. 1991 Jun 18;69(9):409–412. doi: 10.1007/BF01647415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman B. L., Garada B., Johnson K. A., Mendelson J., Hallgring E., Teoh S. K., Worth J., Navia B. A comparison of brain perfusion SPECT in cocaine abuse and AIDS dementia complex. J Nucl Med. 1992 Jul;33(7):1312–1315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtzman D. M., Kaku D. A., So Y. T. New-onset seizures associated with human immunodeficiency virus infection: causation and clinical features in 100 cases. Am J Med. 1989 Aug;87(2):173–177. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(89)80693-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoxie J. A., Haggarty B. S., Rackowski J. L., Pillsbury N., Levy J. A. Persistent noncytopathic infection of normal human T lymphocytes with AIDS-associated retrovirus. Science. 1985 Sep 27;229(4720):1400–1402. doi: 10.1126/science.2994222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hriso E., Kuhn T., Masdeu J. C., Grundman M. Extrapyramidal symptoms due to dopamine-blocking agents in patients with AIDS encephalopathy. Am J Psychiatry. 1991 Nov;148(11):1558–1561. doi: 10.1176/ajp.148.11.1558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes P. J., McLean K. A., Lane R. J. Cranial polyneuropathy and brainstem disorder at the time of seroconversion in HIV infection. Int J STD AIDS. 1992 Jan-Feb;3(1):60–61. doi: 10.1177/095646249200300117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang S. S., Boyle T. J., Lyerly H. K., Cullen B. R. Identification of the envelope V3 loop as the primary determinant of cell tropism in HIV-1. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):71–74. doi: 10.1126/science.1905842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itil T. M., Ferracuti S., Freedman A. M., Sherer C., Mehta P., Itil K. Z. Computer-analyzed EEG (CEEG) and dynamic brain mapping in AIDS and HIV related syndrome: a pilot study. Clin Electroencephalogr. 1990 Jul;21(3):140–144. doi: 10.1177/155005949002100309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanoff L. A., Dubay J. W., Morris J. F., Roberts S. J., Gutshall L., Sternberg E. J., Hunter E., Matthews T. J., Petteway S. R., Jr V3 loop region of the HIV-1 gp120 envelope protein is essential for virus infectivity. Virology. 1992 Apr;187(2):423–432. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90444-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobsen J., Gyldensted C., Brun B., Bruhn P., Helweg-Larsen S., Arlien-Søborg P. Cerebral ventricular enlargement relates to neuropsychological measures in unselected AIDS patients. Acta Neurol Scand. 1989 Jan;79(1):59–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1989.tb03710.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen R. S., Cornblath D. R., Epstein L. G., McArthur J., Price R. W. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection and the nervous system: report from the American Academy of Neurology AIDS Task Force. Neurology. 1989 Jan;39(1):119–122. doi: 10.1212/wnl.39.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen R. S., Nwanyanwu O. C., Selik R. M., Stehr-Green J. K. Epidemiology of human immunodeficiency virus encephalopathy in the United States. Neurology. 1992 Aug;42(8):1472–1476. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.8.1472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen R. S., Saykin A. J., Cannon L., Campbell J., Pinsky P. F., Hessol N. A., O'Malley P. M., Lifson A. R., Doll L. S., Rutherford G. W. Neurological and neuropsychological manifestations of HIV-1 infection: association with AIDS-related complex but not asymptomatic HIV-1 infection. Ann Neurol. 1989 Nov;26(5):592–600. doi: 10.1002/ana.410260503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen R. S., Saykin A. J., Kaplan J. E., Spira T. J., Pinsky P. F., Sprehn G. C., Hoffman J. C., Mayer W. B., Jr, Schonberger L. B. Neurological complications of human immunodeficiency virus infection in patients with lymphadenopathy syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1988 Jan;23(1):49–55. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C. C., Fuchs B. A. Time dependent uptake of (-)125I-iodocyanopindolol but not (-)125I-iodopindolol by murine splenic lymphocytes. J Recept Res. 1991;11(6):959–964. doi: 10.3109/10799899109064690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan C. A., Watkins B. A., Kufta C., Dubois-Dalcq M. Infection of brain microglial cells by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 is CD4 dependent. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):736–742. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.736-742.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamine J., Chinnadurai G. Synergistic activation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 promoter by the viral Tat protein and cellular transcription factor Sp1. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3932–3936. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3932-3936.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J. Control of human immunodeficiency virus replication by the tat, rev, nef and protease genes. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991 Aug;3(4):526–536. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(91)90016-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato T., Hirano A., Llena J. F., Dembitzer H. M. Neuropathology of acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) in 53 autopsy cases with particular emphasis on microglial nodules and multinucleated giant cells. Acta Neuropathol. 1987;73(3):287–294. doi: 10.1007/BF00686624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz R. L., Alappattu C., Glass J. P., Bruner J. M. Cerebrospinal fluid manifestations of the neurologic complications of human immunodeficiency virus infection. Acta Cytol. 1989 Mar-Apr;33(2):233–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami K., Scheidereit C., Roeder R. G. Identification and purification of a human immunoglobulin-enhancer-binding protein (NF-kappa B) that activates transcription from a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 promoter in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4700–4704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kermani E. J., Borod J. C., Brown P. H., Tunnell G. New psychopathologic findings in AIDS: case report. J Clin Psychiatry. 1985 Jun;46(6):240–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kermani E., Drob S., Alpert M. Organic brain syndrome in three cases of acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Compr Psychiatry. 1984 May-Jun;25(3):294–297. doi: 10.1016/0010-440x(84)90061-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kestler H. W., 3rd, Ringler D. J., Mori K., Panicali D. L., Sehgal P. K., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C. Importance of the nef gene for maintenance of high virus loads and for development of AIDS. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):651–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90097-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketzler S., Weis S., Haug H., Budka H. Loss of neurons in the frontal cortex in AIDS brains. Acta Neuropathol. 1990;80(1):92–94. doi: 10.1007/BF00294228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keys B., Albert J., Kövamees J., Chiodi F. Brain-derived cells can be infected with HIV isolates derived from both blood and brain. Virology. 1991 Aug;183(2):834–839. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)91021-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S., Ikeuchi K., Byrn R., Groopman J., Baltimore D. Lack of a negative influence on viral growth by the nef gene of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9544–9548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S., Ikeuchi K., Groopman J., Baltimore D. Factors affecting cellular tropism of human immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5600–5604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5600-5604.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatzmann D., Barré-Sinoussi F., Nugeyre M. T., Danquet C., Vilmer E., Griscelli C., Brun-Veziret F., Rouzioux C., Gluckman J. C., Chermann J. C. Selective tropism of lymphadenopathy associated virus (LAV) for helper-inducer T lymphocytes. Science. 1984 Jul 6;225(4657):59–63. doi: 10.1126/science.6328660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatzmann D., Champagne E., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Guetard D., Hercend T., Gluckman J. C., Montagnier L. T-lymphocyte T4 molecule behaves as the receptor for human retrovirus LAV. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):767–768. doi: 10.1038/312767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klecker R. W., Jr, Collins J. M., Yarchoan R., Thomas R., Jenkins J. F., Broder S., Myers C. E. Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid pharmacokinetics of 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine: a novel pyrimidine analog with potential application for the treatment of patients with AIDS and related diseases. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1987 Apr;41(4):407–412. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1987.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleihues P., Lang W., Burger P. C., Budka H., Vogt M., Maurer R., Lüthy R., Siegenthaler W. Progressive diffuse leukoencephalopathy in patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Acta Neuropathol. 1985;68(4):333–339. doi: 10.1007/BF00690837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleihues P., Leib S. L., Strittmatter C., Wiestler O. D., Lang W. HIV encephalopathy: incidence, definition and pathogenesis. Results of a Swiss collaborative study. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1991 Mar;41(3):197–205. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1991.tb01647.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotman M. E., Kim S., Buchbinder A., DeRossi A., Baltimore D., Wong-Staal F. Kinetics of expression of multiply spliced RNA in early human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection of lymphocytes and monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):5011–5015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.5011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig S., Gendelman H. E., Orenstein J. M., Dal Canto M. C., Pezeshkpour G. H., Yungbluth M., Janotta F., Aksamit A., Martin M. A., Fauci A. S. Detection of AIDS virus in macrophages in brain tissue from AIDS patients with encephalopathy. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1089–1093. doi: 10.1126/science.3016903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohleisen B., Neumann M., Herrmann R., Brack-Werner R., Krohn K. J., Ovod V., Ranki A., Erfle V. Cellular localization of Nef expressed in persistently HIV-1-infected low-producer astrocytes. AIDS. 1992 Dec;6(12):1427–1436. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199212000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyanagi Y., Miles S., Mitsuyasu R. T., Merrill J. E., Vinters H. V., Chen I. S. Dual infection of the central nervous system by AIDS viruses with distinct cellular tropisms. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):819–822. doi: 10.1126/science.3646751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer E. L., Sanger J. J. Brain imaging in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome dementia complex. Semin Nucl Med. 1990 Oct;20(4):353–363. doi: 10.1016/s0001-2998(05)80239-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krown S. E., Niedzwiecki D., Bhalla R. B., Flomenberg N., Bundow D., Chapman D. Relationship and prognostic value of endogenous interferon-alpha, beta 2-microglobulin, and neopterin serum levels in patients with Kaposi sarcoma and AIDS. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1991;4(9):871–880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunsch C., Hartle H. T., Wigdahl B. Infection of human fetal dorsal root ganglion glial cells with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 involves an entry mechanism independent of the CD4 T4A epitope. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5054–5061. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5054-5061.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kure K., Llena J. F., Lyman W. D., Soeiro R., Weidenheim K. M., Hirano A., Dickson D. W. Human immunodeficiency virus-1 infection of the nervous system: an autopsy study of 268 adult, pediatric, and fetal brains. Hum Pathol. 1991 Jul;22(7):700–710. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(91)90293-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachman L. B., Brown D. C., Dinarello C. A. Growth-promoting effect of recombinant interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor for a human astrocytoma cell line. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):2913–2916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky L. A., Nakamura G., Smith D. H., Fennie C., Shimasaki C., Patzer E., Berman P., Gregory T., Capon D. J. Delineation of a region of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 glycoprotein critical for interaction with the CD4 receptor. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90524-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latham P. S., Lewis A. M., Varesio L., Pavlakis G. N., Felber B. K., Ruscetti F. W., Young H. A. Expression of human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat in the human promonocyte cell line U937: effect of endotoxin and cytokines. Cell Immunol. 1990 Sep;129(2):513–518. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90225-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. R., Ho D. D., Gurney M. E. Functional interaction and partial homology between human immunodeficiency virus and neuroleukin. Science. 1987 Aug 28;237(4818):1047–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.3039662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leist T. P., Frei K., Kam-Hansen S., Zinkernagel R. M., Fontana A. Tumor necrosis factor alpha in cerebrospinal fluid during bacterial, but not viral, meningitis. Evaluation in murine model infections and in patients. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1743–1748. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard J. M., Abramczuk J. W., Pezen D. S., Rutledge R., Belcher J. H., Hakim F., Shearer G., Lamperth L., Travis W., Fredrickson T. Development of disease and virus recovery in transgenic mice containing HIV proviral DNA. Science. 1988 Dec 23;242(4886):1665–1670. doi: 10.1126/science.3201255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin H. S., Williams D. H., Borucki M. J., Hillman G. R., Williams J. B., Guinto F. C., Jr, Amparo E. G., Crow W. N., Pollard R. B. Magnetic resonance imaging and neuropsychological findings in human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(8):757–762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Hoffman A. D., Kramer S. M., Landis J. A., Shimabukuro J. M., Oshiro L. S. Isolation of lymphocytopathic retroviruses from San Francisco patients with AIDS. Science. 1984 Aug 24;225(4664):840–842. doi: 10.1126/science.6206563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Shimabukuro J., Hollander H., Mills J., Kaminsky L. Isolation of AIDS-associated retroviruses from cerebrospinal fluid and brain of patients with neurological symptoms. Lancet. 1985 Sep 14;2(8455):586–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R. M., Bredesen D. E. Central nervous system dysfunction in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1988;1(1):41–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X. L., Moudgil T., Vinters H. V., Ho D. D. CD4-independent, productive infection of a neuronal cell line by human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1383–1387. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1383-1387.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindholm D., Heumann R., Meyer M., Thoenen H. Interleukin-1 regulates synthesis of nerve growth factor in non-neuronal cells of rat sciatic nerve. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):658–659. doi: 10.1038/330658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton S. A. Memantine prevents HIV coat protein-induced neuronal injury in vitro. Neurology. 1992 Jul;42(7):1403–1405. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.7.1403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton S. A., Sucher N. J., Kaiser P. K., Dreyer E. B. Synergistic effects of HIV coat protein and NMDA receptor-mediated neurotoxicity. Neuron. 1991 Jul;7(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90079-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Z. Q., Wood C., Levy J. A., Cheng-Mayer C. The viral envelope gene is involved in macrophage tropism of a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 strain isolated from brain tissue. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6148–6153. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6148-6153.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunn S., Skydsbjerg M., Schulsinger H., Parnas J., Pedersen C., Mathiesen L. A preliminary report on the neuropsychologic sequelae of human immunodeficiency virus. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1991 Feb;48(2):139–142. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1991.01810260047007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabrouk K., Van Rietschoten J., Vives E., Darbon H., Rochat H., Sabatier J. M. Lethal neurotoxicity in mice of the basic domains of HIV and SIV Rev proteins. Study of these regions by circular dichroism. FEBS Lett. 1991 Sep 2;289(1):13–17. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80898-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa T., Sakura H., Sudo T., Ishii S. Putative metal finger structure of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 enhancer binding protein HIV-EP1. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14591–14593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maj M. Organic mental disorders in HIV-1 infection. AIDS. 1990 Sep;4(9):831–840. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199009000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Major E. O., Amemiya K., Tornatore C. S., Houff S. A., Berger J. R. Pathogenesis and molecular biology of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, the JC virus-induced demyelinating disease of the human brain. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1992 Jan;5(1):49–73. doi: 10.1128/cmr.5.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Böhnlein S., Fenrick R., Le S. Y., Maizel J. V., Cullen B. R. Functional comparison of the Rev trans-activators encoded by different primate immunodeficiency virus species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8222–8226. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Böhnlein S., Hauber J., Cullen B. R. Functional dissection of the HIV-1 Rev trans-activator--derivation of a trans-dominant repressor of Rev function. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90416-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Cullen B. R. HIV-1 structural gene expression requires the binding of multiple Rev monomers to the viral RRE: implications for HIV-1 latency. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):241–248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90158-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Hauber J., Fenrick R., Cullen B. R. Immunodeficiency virus rev trans-activator modulates the expression of the viral regulatory genes. Nature. 1988 Sep 8;335(6186):181–183. doi: 10.1038/335181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. L., Gartner S., Le Sane F., Buchow H., Popovic M. HIV-1 transmission and function of virus-infected monocytes/macrophages. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 15;144(6):2152–2158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. L., Gartner S., LeSane F., Blattner W. A., Popovic M. Cell surface antigens and function of monocytes and a monocyte-like cell line before and after infection with HIV. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1990 Feb;54(2):174–183. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(90)90079-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall D. W., Brey R. L., Butzin C. A. Lack of cerebrospinal fluid myelin basic protein in HIV-infected asymptomatic individuals with intrathecal synthesis of IgG. Neurology. 1989 Aug;39(8):1127–1129. doi: 10.1212/wnl.39.8.1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall D. W., Brey R. L., Butzin C. A., Lucey D. R., Abbadessa S. M., Boswell R. N. CSF changes in a longitudinal study of 124 neurologically normal HIV-1-infected U.S. Air Force personnel. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1991;4(8):777–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall D. W., Brey R. L., Cahill W. T., Houk R. W., Zajac R. A., Boswell R. N. Spectrum of cerebrospinal fluid findings in various stages of human immunodeficiency virus infection. Arch Neurol. 1988 Sep;45(9):954–958. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1988.00520330032007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masdeu J. C., Yudd A., Van Heertum R. L., Grundman M., Hriso E., O'Connell R. A., Luck D., Camli U., King L. N. Single-photon emission computed tomography in human immunodeficiency virus encephalopathy: a preliminary report. J Nucl Med. 1991 Aug;32(8):1471–1475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masliah E., Achim C. L., Ge N., DeTeresa R., Terry R. D., Wiley C. A. Spectrum of human immunodeficiency virus-associated neocortical damage. Ann Neurol. 1992 Sep;32(3):321–329. doi: 10.1002/ana.410320304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masliah E., Ge N., Morey M., DeTeresa R., Terry R. D., Wiley C. A. Cortical dendritic pathology in human immunodeficiency virus encephalitis. Lab Invest. 1992 Mar;66(3):285–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastroianni C. M., Liuzzi G. M., Jirillo E., Vullo V., Delia S., Riccio P. Cerebrospinal fluid markers for the monitoring of AIDS dementia complex severity: usefulness of anti-myelin basic protein antibody detection. AIDS. 1991 Apr;5(4):464–465. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199104000-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauerhoff T., Pujol-Borrell R., Mirakian R., Bottazzo G. F. Differential expression and regulation of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) products in neural and glial cells of the human fetal brain. J Neuroimmunol. 1988 Jul;18(4):271–289. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(88)90049-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McArthur J. C., Nance-Sproson T. E., Griffin D. E., Hoover D., Selnes O. A., Miller E. N., Margolick J. B., Cohen B. A., Farzadegan H., Saah A. The diagnostic utility of elevation in cerebrospinal fluid beta 2-microglobulin in HIV-1 dementia. Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study. Neurology. 1992 Sep;42(9):1707–1712. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.9.1707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McArthur J. C. Neurologic manifestations of AIDS. Medicine (Baltimore) 1987 Nov;66(6):407–437. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198711000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal J. S., Kennedy M. S., Sligh J. M., Cort S. P., Mawle A., Nicholson J. K. Binding of HTLV-III/LAV to T4+ T cells by a complex of the 110K viral protein and the T4 molecule. Science. 1986 Jan 24;231(4736):382–385. doi: 10.1126/science.3001934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal J. S., Mawle A., Cort S. P., Nicholson J. K., Cross G. D., Scheppler-Campbell J. A., Hicks D., Sligh J. Cellular tropism of the human retrovirus HTLV-III/LAV. I. Role of T cell activation and expression of the T4 antigen. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3151–3162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal J. S., Nicholson J. K., Cross G. D., Cort S. P., Kennedy M. S., Mawle A. C. Binding of the human retrovirus HTLV-III/LAV/ARV/HIV to the CD4 (T4) molecule: conformation dependence, epitope mapping, antibody inhibition, and potential for idiotypic mimicry. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2937–2944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer M. S., Skillman D. R., Gomatos P. J., Kalter D. C., Gendelman H. E. Role of mononuclear phagocytes in the pathogenesis of human immunodeficiency virus infection. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:169–194. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.001125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon D. K., Ainsworth J. G., Cox I. J., Coker R. C., Sargentoni J., Coutts G. A., Baudouin C. J., Kocsis A. E., Harris J. R. Proton MR spectroscopy of the brain in AIDS dementia complex. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1992 Jul-Aug;16(4):538–542. doi: 10.1097/00004728-199207000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill J. E., Chen I. S. HIV-1, macrophages, glial cells, and cytokines in AIDS nervous system disease. FASEB J. 1991 Jul;5(10):2391–2397. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.10.2065887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill J. E., Koyanagi Y., Zack J., Thomas L., Martin F., Chen I. S. Induction of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha in brain cultures by human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2217–2225. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2217-2225.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill P. T., Paige G. D., Abrams R. A., Jacoby R. G., Clifford D. B. Ocular motor abnormalities in human immunodeficiency virus infection. Ann Neurol. 1991 Aug;30(2):130–138. doi: 10.1002/ana.410300203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzer W. S. Movement disorders with AIDS encephalopathy: case report. Neurology. 1987 Aug;37(8):1438–1438. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.8.1438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaels J., Price R. W., Rosenblum M. K. Microglia in the giant cell encephalitis of acquired immune deficiency syndrome: proliferation, infection and fusion. Acta Neuropathol. 1988;76(4):373–379. doi: 10.1007/BF00686974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. N., Selnes O. A., McArthur J. C., Satz P., Becker J. T., Cohen B. A., Sheridan K., Machado A. M., Van Gorp W. G., Visscher B. Neuropsychological performance in HIV-1-infected homosexual men: The Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study (MACS) Neurology. 1990 Feb;40(2):197–203. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.2.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz M., Rapaport R., Oleske J. M., Connor E. M., Koenigsberger M. R., Denny T., Epstein L. G. Elevated serum levels of tumor necrosis factor are associated with progressive encephalopathy in children with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Dis Child. 1989 Jul;143(7):771–774. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1989.02150190021012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirra S. S., Anand R., Spira T. J. HTLV-III/LAV infection of the central nervous system in a 57-year-old man with progressive dementia of unknown cause. N Engl J Med. 1986 May 1;314(18):1191–1192. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198605013141815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moeller J. R., Strother S. C., Sidtis J. J., Rottenberg D. A. Scaled subprofile model: a statistical approach to the analysis of functional patterns in positron emission tomographic data. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1987 Oct;7(5):649–658. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1987.118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa M. M., Lebel M. H., Ramilo O., Olsen K. D., Reisch J. S., Beutler B., McCracken G. H., Jr Correlation of interleukin-1 beta and cachectin concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid and outcome from bacterial meningitis. J Pediatr. 1989 Aug;115(2):208–213. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(89)80067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Baltimore D. An inducible transcription factor activates expression of human immunodeficiency virus in T cells. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):711–713. doi: 10.1038/326711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan O., Kennedy-Stoskopf S., Zink M. C. Lentivirus-host interactions: lessons from visna and caprine arthritis-encephalitis viruses. Ann Neurol. 1988;23 (Suppl):S95–100. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan O., Zink M. C., Huso D., Sheffer D., Crane S., Kennedy-Stoskopf S., Jolly P. E., Clements J. E. Lentiviruses of animals are biological models of the human immunodeficiency viruses. Microb Pathog. 1988 Sep;5(3):149–157. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan O., Zink M. C. Role of macrophages in lentivirus infections. Adv Vet Sci Comp Med. 1988;32:129–148. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-039232-2.50009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navia B. A., Cho E. S., Petito C. K., Price R. W. The AIDS dementia complex: II. Neuropathology. Ann Neurol. 1986 Jun;19(6):525–535. doi: 10.1002/ana.410190603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navia B. A., Jordan B. D., Price R. W. The AIDS dementia complex: I. Clinical features. Ann Neurol. 1986 Jun;19(6):517–524. doi: 10.1002/ana.410190602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navia B. A., Price R. W. The acquired immunodeficiency syndrome dementia complex as the presenting or sole manifestation of human immunodeficiency virus infection. Arch Neurol. 1987 Jan;44(1):65–69. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1987.00520130051017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen N., Rimmer S., Katz B. Slowed saccades in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 1989 Apr 15;107(4):356–360. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(89)90658-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederman T. M., Garcia J. V., Hastings W. R., Luria S., Ratner L. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef protein inhibits NF-kappa B induction in human T cells. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):6213–6219. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.6213-6219.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S. L., Petito C. K., Urmacher C. D., Posner J. B. Subacute encephalitis in acquired immune deficiency syndrome: a postmortem study. Am J Clin Pathol. 1984 Dec;82(6):678–682. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/82.6.678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman S. E., Chediak A. D., Freeman C., Kiel M., Mendez A., Duncan R., Simoneau J., Nolan B. Sleep disturbances in men with asymptomatic human immunodeficiency (HIV) infection. Sleep. 1992 Apr;15(2):150–155. doi: 10.1093/sleep/15.2.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman S. E., Resnick L., Cohn M. A., Duara R., Herbst J., Berger J. R. Sleep disturbances in HIV-seropositive patients. JAMA. 1988 Aug 19;260(7):922–922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurnberg H. G., Prudic J., Fiori M., Freedman E. P. Psychopathology complicating acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Am J Psychiatry. 1984 Jan;141(1):95–96. doi: 10.1176/ajp.141.1.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuwer M. R., Miller E. N., Visscher B. R., Niedermeyer E., Packwood J. W., Carlson L. G., Satz P., Jankel W., McArthur J. C. Asymptomatic HIV infection does not cause EEG abnormalities: results from the Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study (MACS) Neurology. 1992 Jun;42(6):1214–1219. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.6.1214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien W. A., Koyanagi Y., Namazie A., Zhao J. Q., Diagne A., Idler K., Zack J. A., Chen I. S. HIV-1 tropism for mononuclear phagocytes can be determined by regions of gp120 outside the CD4-binding domain. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):69–73. doi: 10.1038/348069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa K., Shibata R., Kiyomasu T., Higuchi I., Kishida Y., Ishimoto A., Adachi A. Mutational analysis of the human immunodeficiency virus vpr open reading frame. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):4110–4114. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.4110-4114.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ollo C., Johnson R., Jr, Grafman J. Signs of cognitive change in HIV disease: an event-related brain potential study. Neurology. 1991 Feb;41(2 ):209–215. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.2_part_1.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen W. L., Longo F. M., Mills C. M., Norman D. White matter disease in AIDS: findings at MR imaging. Radiology. 1988 Nov;169(2):445–448. doi: 10.1148/radiology.169.2.3174991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano M. A., Cahn P. E., Garau M. L., Mangone C. A., Figini H. A., Yorio A. A., Dellepiane M. C., Amores M. G., Perez H. M., Casiró A. D. Brain-stem auditory evoked potentials in human immunodeficiency virus-seropositive patients with and without acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Arch Neurol. 1992 Feb;49(2):166–169. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1992.00530260068022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parisi A., Di Perri G., Strosselli M., Nappi G., Minoli L., Rondanelli E. G. Usefulness of computerized electroencephalography in diagnosing, staging and monitoring AIDS-dementia complex. AIDS. 1989 Apr;3(4):209–213. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198904000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parisi A., Strosselli M., Di Perri G., Cairoli S., Minoli L., Bono G., Moglia A., Nappi G. Electroencephalography in the early diagnosis of HIV-related subacute encephalitis: analysis of 185 patients. Clin Electroencephalogr. 1989 Jan;20(1):1–5. doi: 10.1177/155005948902000105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parisi A., Strosselli M., Pan A., Maserati R., Minoli L. HIV-related encephalitis presenting as convulsant disease. Clin Electroencephalogr. 1991 Jan;22(1):1–4. doi: 10.1177/155005949102200104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrott C., Seidner T., Duh E., Leonard J., Theodore T. S., Buckler-White A., Martin M. A., Rabson A. B. Variable role of the long terminal repeat Sp1-binding sites in human immunodeficiency virus replication in T lymphocytes. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1414–1419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1414-1419.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton P., Poly H., Gonnaud P. M., Tardy J. C., Fontana J., Kindbeiter K., Tête R., Madjar J. J. Acute meningoradiculitis concomitant with seroconversion to human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Res Virol. 1990 Jul-Aug;141(4):427–433. doi: 10.1016/0923-2516(90)90043-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlakis G. N., Felber B. K. Regulation of expression of human immunodeficiency virus. New Biol. 1990 Jan;2(1):20–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry S., Belsky-Barr D., Barr W. B., Jacobsberg L. Neuropsychological function in physically asymptomatic, HIV-seropositive men. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1989 Summer;1(3):296–302. doi: 10.1176/jnp.1.3.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peudenier S., Hery C., Montagnier L., Tardieu M. Human microglial cells: characterization in cerebral tissue and in primary culture, and study of their susceptibility to HIV-1 infection. Ann Neurol. 1991 Feb;29(2):152–161. doi: 10.1002/ana.410290207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzo P. A., Eddy J., Falloon J., Balis F. M., Murphy R. F., Moss H., Wolters P., Brouwers P., Jarosinski P., Rubin M. Effect of continuous intravenous infusion of zidovudine (AZT) in children with symptomatic HIV infection. N Engl J Med. 1988 Oct 6;319(14):889–896. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198810063191401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Gartner S. Isolation of HIV-1 from monocytes but not T lymphocytes. Lancet. 1987 Oct 17;2(8564):916–916. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91403-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Mellert W., Erfle V., Gartner S. Role of mononuclear phagocytes and accessory cells in human immunodeficiency virus type I infection of the brain. Ann Neurol. 1988;23 (Suppl):S74–S77. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Sarngadharan M. G., Read E., Gallo R. C. Detection, isolation, and continuous production of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and pre-AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):497–500. doi: 10.1126/science.6200935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portegies P., Epstein L. G., Hung S. T., de Gans J., Goudsmit J. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 antigen in cerebrospinal fluid. Correlation with clinical neurologic status. Arch Neurol. 1989 Mar;46(3):261–264. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1989.00520390027010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portegies P., de Gans J., Lange J. M., Derix M. M., Speelman H., Bakker M., Danner S. A., Goudsmit J. Declining incidence of AIDS dementia complex after introduction of zidovudine treatment. BMJ. 1989 Sep 30;299(6703):819–821. doi: 10.1136/bmj.299.6703.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post M. J., Berger J. R., Quencer R. M. Asymptomatic and neurologically symptomatic HIV-seropositive individuals: prospective evaluation with cranial MR imaging. Radiology. 1991 Jan;178(1):131–139. doi: 10.1148/radiology.178.1.1984291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post M. J., Levin B. E., Berger J. R., Duncan R., Quencer R. M., Calabro G. Sequential cranial MR findings of asymptomatic and neurologically symptomatic HIV+ subjects. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1992 Jan-Feb;13(1):359–370. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. W., Brew B. J. The AIDS dementia complex. J Infect Dis. 1988 Nov;158(5):1079–1083. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.5.1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. W., Brew B., Sidtis J., Rosenblum M., Scheck A. C., Cleary P. The brain in AIDS: central nervous system HIV-1 infection and AIDS dementia complex. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):586–592. doi: 10.1126/science.3277272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price W. A., Forejt J. Neuropsychiatric aspects of AIDS: a case report. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 1986 Jan;8(1):7–10. doi: 10.1016/0163-8343(86)90057-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragni M. V., Urbach A. H., Taylor S., Claassen D., Gupta P., Lewis J. H., Ho D. D., Shaw G. M. Isolation of human immunodeficiency virus and detection of HIV DNA sequences in the brain of an ELISA antibody-negative child with acquired immune deficiency syndrome and progressive encephalopathy. J Pediatr. 1987 Jun;110(6):892–894. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80404-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner L., Haseltine W., Patarca R., Livak K. J., Starcich B., Josephs S. F., Doran E. R., Rafalski J. A., Whitehorn E. A., Baumeister K. Complete nucleotide sequence of the AIDS virus, HTLV-III. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):277–284. doi: 10.1038/313277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinvang I., Frøland S. S., Skripeland V. Prevalence of neuropsychological deficit in HIV infection. Incipient signs of AIDS dementia complex in patients with AIDS. Acta Neurol Scand. 1991 May;83(5):289–293. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1991.tb04703.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick L., Berger J. R., Shapshak P., Tourtellotte W. W. Early penetration of the blood-brain-barrier by HIV. Neurology. 1988 Jan;38(1):9–14. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes R. H. Histopathology of the central nervous system in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Hum Pathol. 1987 Jun;18(6):636–643. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(87)80365-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins D. S., Shirazi Y., Drysdale B. E., Lieberman A., Shin H. S., Shin M. L. Production of cytotoxic factor for oligodendrocytes by stimulated astrocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 15;139(8):2593–2597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert-Guroff M., Popovic M., Gartner S., Markham P., Gallo R. C., Reitz M. S. Structure and expression of tat-, rev-, and nef-specific transcripts of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in infected lymphocytes and macrophages. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3391–3398. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3391-3398.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson K. R., Hall C. D. Human immunodeficiency virus-related cognitive impairment and the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome dementia complex. Semin Neurol. 1992 Mar;12(1):18–27. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1041153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblum M. K. Infection of the central nervous system by the human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Morphology and relation to syndromes of progressive encephalopathy and myelopathy in patients with AIDS. Pathol Annu. 1990;25(Pt 1):117–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenhall U., Håkansson C., Löwhagen G. B., Hanner P., Jonsson-Ehk B. Otoneurological abnormalities in asymptomatic HIV-seropositive patients. Acta Neurol Scand. 1989 Feb;79(2):140–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1989.tb03726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg D. A., Moeller J. R., Strother S. C., Sidtis J. J., Navia B. A., Dhawan V., Ginos J. Z., Price R. W. The metabolic pathology of the AIDS dementia complex. Ann Neurol. 1987 Dec;22(6):700–706. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow K., Olsen K., Stiegler G., Payne S. L., Montelaro R. C., Issel C. J. Lentivirus genomic organization: the complete nucleotide sequence of the env gene region of equine infectious anemia virus. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):309–321. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90195-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rytik P. G., Eremin V. F., Kvacheva Z. B., Poleschuk N. N., Popov S. A., Schröder H. C., Bachmann M., Weiler B. E., Müller W. E. Susceptibility of primary human glial fibrillary acidic protein-positive brain cells to human immunodeficiency virus infection in vitro: anti-HIV activity of memantine. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Jan;7(1):89–95. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabatier J. M., Vives E., Mabrouk K., Benjouad A., Rochat H., Duval A., Hue B., Bahraoui E. Evidence for neurotoxic activity of tat from human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):961–967. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.961-967.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Pescador R., Power M. D., Barr P. J., Steimer K. S., Stempien M. M., Brown-Shimer S. L., Gee W. W., Renard A., Randolph A., Levy J. A. Nucleotide sequence and expression of an AIDS-associated retrovirus (ARV-2). Science. 1985 Feb 1;227(4686):484–492. doi: 10.1126/science.2578227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satz P., Morgenstern H., Miller E. N., Selnes O. A., McArthur J. C., Cohen B. A., Wesch J., Becker J. T., Jacobson L., D'Elia L. F. Low education as a possible risk factor for cognitive abnormalities in HIV-1: findings from the multicenter AIDS Cohort Study (MACS). J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1993 May;6(5):503–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saulsbury F. T., Bringelsen K. A., Normansell D. E. Effects of prednisone on human immunodeficiency virus infection. South Med J. 1991 Apr;84(4):431–435. doi: 10.1097/00007611-199104000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpini E., Sacilotto G., Lazzarin A., Geremia L., Doronzo R., Scarlato G. Acute ataxia coincident with seroconversion for anti-HIV. J Neurol. 1991 Sep;238(6):356–357. doi: 10.1007/BF00315340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schielke E., Tatsch K., Pfister H. W., Trenkwalder C., Leinsinger G., Kirsch C. M., Matuschke A., Einhäupl K. M. Reduced cerebral blood flow in early stages of human immunodeficiency virus infection. Arch Neurol. 1990 Dec;47(12):1342–1345. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1990.00530120088015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt F. A., Bigley J. W., McKinnis R., Logue P. E., Evans R. W., Drucker J. L. Neuropsychological outcome of zidovudine (AZT) treatment of patients with AIDS and AIDS-related complex. N Engl J Med. 1988 Dec 15;319(24):1573–1578. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198812153192404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S., Felber B. K., Benko D. M., Fenyö E. M., Pavlakis G. N. Cloning and functional analysis of multiply spliced mRNA species of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2519–2529. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2519-2529.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S., Felber B. K., Fenyö E. M., Pavlakis G. N. Env and Vpu proteins of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 are produced from multiple bicistronic mRNAs. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5448–5456. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5448-5456.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S., Felber B. K., Pavlakis G. N. Distinct RNA sequences in the gag region of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 decrease RNA stability and inhibit expression in the absence of Rev protein. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):150–159. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.150-159.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S., Felber B. K., Pavlakis G. N. Expression of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 vif and vpr mRNAs is Rev-dependent and regulated by splicing. Virology. 1991 Aug;183(2):677–686. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90996-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S., Felber B. K., Pavlakis G. N. Mechanism of translation of monocistronic and multicistronic human immunodeficiency virus type 1 mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):207–219. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwenk J., Cruz-Sanchez F., Gosztonyi G., Cervos-Navarro J. Spongiform encephalopathy in a patient with acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Acta Neuropathol. 1987;74(4):389–392. doi: 10.1007/BF00687217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott G. B., Hutto C., Makuch R. W., Mastrucci M. T., O'Connor T., Mitchell C. D., Trapido E. J., Parks W. P. Survival in children with perinatally acquired human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. N Engl J Med. 1989 Dec 28;321(26):1791–1796. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198912283212604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharer L. R., Epstein L. G., Cho E. S., Joshi V. V., Meyenhofer M. F., Rankin L. F., Petito C. K. Pathologic features of AIDS encephalopathy in children: evidence for LAV/HTLV-III infection of brain. Hum Pathol. 1986 Mar;17(3):271–284. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(83)80220-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharer L. R. Pathology of HIV-1 infection of the central nervous system. A review. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1992 Jan;51(1):3–11. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199201000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpless N. E., O'Brien W. A., Verdin E., Kufta C. V., Chen I. S., Dubois-Dalcq M. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 tropism for brain microglial cells is determined by a region of the env glycoprotein that also controls macrophage tropism. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2588–2593. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2588-2593.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaskan E. G., Thompson R. M., Price R. W. Undetectable tumor necrosis factor-alpha in spinal fluid from HIV-1-infected patients. Ann Neurol. 1992 Jun;31(6):687–689. doi: 10.1002/ana.410310623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G. M., Harper M. E., Hahn B. H., Epstein L. G., Gajdusek D. C., Price R. W., Navia B. A., Petito C. K., O'Hara C. J., Groopman J. E. HTLV-III infection in brains of children and adults with AIDS encephalopathy. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):177–182. doi: 10.1126/science.2981429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinforiani E., Mauri M., Bono G., Muratori S., Alessi E., Minoli L. Cognitive abnormalities and disease progression in a selected population of asymptomatic HIV-positive subjects. AIDS. 1991 Sep;5(9):1117–1120. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199109000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skoraszewski M. J., Ball J. D., Mikulka P. Neuropsychological functioning of HIV-infected males. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 1991 Mar;13(2):278–290. doi: 10.1080/01688639108401043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skowronski J. Expression of a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat/simian virus 40 early region fusion gene in transgenic mice. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):754–762. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.754-762.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider W. D., Simpson D. M., Nielsen S., Gold J. W., Metroka C. E., Posner J. B. Neurological complications of acquired immune deficiency syndrome: analysis of 50 patients. Ann Neurol. 1983 Oct;14(4):403–418. doi: 10.1002/ana.410140404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Goh W. C., Rosen C., Dayton A., Terwilliger E., Haseltine W. A second post-transcriptional trans-activator gene required for HTLV-III replication. Nature. 1986 May 22;321(6068):412–417. doi: 10.1038/321412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonigo P., Alizon M., Staskus K., Klatzmann D., Cole S., Danos O., Retzel E., Tiollais P., Haase A., Wain-Hobson S. Nucleotide sequence of the visna lentivirus: relationship to the AIDS virus. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):369–382. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80132-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava K. K., Fernandez-Larsson R., Zinkus D. M., Robinson H. L. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 NL4-3 replication in four T-cell lines: rate and efficiency of entry, a major determinant of permissiveness. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3900–3902. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3900-3902.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffy K., Wong-Staal F. Genetic regulation of human immunodeficiency virus. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jun;55(2):193–205. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.2.193-205.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern Y., Marder K., Bell K., Chen J., Dooneief G., Goldstein S., Mindry D., Richards M., Sano M., Williams J. Multidisciplinary baseline assessment of homosexual men with and without human immunodeficiency virus infection. III. Neurologic and neuropsychological findings. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1991 Feb;48(2):131–138. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1991.01810260039006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiehm E. R., Bryson Y. J., Frenkel L. M., Szelc C. M., Gillespie S., Williams M. E., Watkins J. M. Prednisone improves human immunodeficiency virus encephalopathy in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1992 Jan;11(1):49–50. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199201000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoler M. H., Eskin T. A., Benn S., Angerer R. C., Angerer L. M. Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type III infection of the central nervous system. A preliminary in situ analysis. JAMA. 1986 Nov 7;256(17):2360–2364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W., Perkins M. N. Quinolinic acid: a potent endogenous excitant at amino acid receptors in CNS. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 10;72(4):411–412. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strebel K., Klimkait T., Maldarelli F., Martin M. A. Molecular and biochemical analyses of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 vpu protein. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3784–3791. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3784-3791.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strebel K., Klimkait T., Martin M. A. A novel gene of HIV-1, vpu, and its 16-kilodalton product. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1221–1223. doi: 10.1126/science.3261888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundar S. K., Cierpial M. A., Kamaraju L. S., Long S., Hsieh S., Lorenz C., Aaron M., Ritchie J. C., Weiss J. M. Human immunodeficiency virus glycoprotein (gp120) infused into rat brain induces interleukin 1 to elevate pituitary-adrenal activity and decrease peripheral cellular immune responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11246–11250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundar S. K., Cierpial M. A., Kilts C., Ritchie J. C., Weiss J. M. Brain IL-1-induced immunosuppression occurs through activation of both pituitary-adrenal axis and sympathetic nervous system by corticotropin-releasing factor. J Neurosci. 1990 Nov;10(11):3701–3706. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-11-03701.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swingler S., Easton A., Morris A. Cytokine augmentation of HIV-1 LTR-driven gene expression in neural cells. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Apr;8(4):487–493. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sönnerborg A., Säf J., Alexius B., Strannegård O., Wahlund L. O., Wetterberg L. Quantitative detection of brain aberrations in human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected individuals by magnetic resonance imaging. J Infect Dis. 1990 Dec;162(6):1245–1251. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.6.1245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THORMAR H. The growth cycle of visna virus in monolayer cultures of sheep cells. Virology. 1963 Mar;19:273–278. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90064-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenhula W. N., Xu S. Z., Madigan M. C., Heller K., Freeman W. R., Sadun A. A. Morphometric comparisons of optic nerve axon loss in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 1992 Jan 15;113(1):14–20. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)75746-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. S., Toone B. K., el Komy A., Harwin B., Farthing C. P. HTLV-III and psychiatric disturbance. Lancet. 1985 Aug 17;2(8451):395–396. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92542-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinuper P., de Carolis P., Galeotti M., Baldrati A., Gritti F. M., Sacquegna T. Electroencephalogram and HIV infection: a prospective study in 100 patients. Clin Electroencephalogr. 1990 Jul;21(3):145–150. doi: 10.1177/155005949002100310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornatore C., Nath A., Amemiya K., Major E. O. Persistent human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection in human fetal glial cells reactivated by T-cell factor(s) or by the cytokines tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1 beta. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6094–6100. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6094-6100.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tross S., Price R. W., Navia B., Thaler H. T., Gold J., Hirsch D. A., Sidtis J. J. Neuropsychological characterization of the AIDS dementia complex: a preliminary report. AIDS. 1988 Apr;2(2):81–88. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198804000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyor W. R., Glass J. D., Griffin J. W., Becker P. S., McArthur J. C., Bezman L., Griffin D. E. Cytokine expression in the brain during the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1992 Apr;31(4):349–360. doi: 10.1002/ana.410310402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Gorp W. G., Miller E. N., Satz P., Visscher B. Neuropsychological performance in HIV-1 immunocompromised patients: a preliminary report. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 1989 Oct;11(5):763–773. doi: 10.1080/01688638908400930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitković L., Wood G. P., Major E. O., Fauci A. S. Human astrocytes stimulate HIV-1 expression in a chronically infected promonocyte clone via interleukin-6. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Sep;7(9):723–727. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlach J., Pitha P. M. Activation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 provirus in T-cells and macrophages is associated with induction of inducer-specific NF-kappa B binding proteins. Virology. 1992 Mar;187(1):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90295-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel J., Hinrichs S. H., Reynolds R. K., Luciw P. A., Jay G. The HIV tat gene induces dermal lesions resembling Kaposi's sarcoma in transgenic mice. Nature. 1988 Oct 13;335(6191):606–611. doi: 10.1038/335606a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Halstensen A., Shalaby R., Brandtzaeg P., Kierulf P., Espevik T. Local production of tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 1, and interleukin 6 in meningococcal meningitis. Relation to the inflammatory response. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):1859–1867. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.1859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M., Allen J. B., McCartney-Francis N., Morganti-Kossmann M. C., Kossmann T., Ellingsworth L., Mai U. E., Mergenhagen S. E., Orenstein J. M. Macrophage- and astrocyte-derived transforming growth factor beta as a mediator of central nervous system dysfunction in acquired immune deficiency syndrome. J Exp Med. 1991 Apr 1;173(4):981–991. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.4.981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins B. A., Dorn H. H., Kelly W. B., Armstrong R. C., Potts B. J., Michaels F., Kufta C. V., Dubois-Dalcq M. Specific tropism of HIV-1 for microglial cells in primary human brain cultures. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):549–553. doi: 10.1126/science.2200125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J., Clapham P., McKeating J., Stratton M., Robey E., Weiss R. Infection of brain cells by diverse human immunodeficiency virus isolates: role of CD4 as receptor. J Gen Virol. 1989 Oct;70(Pt 10):2653–2660. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-10-2653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J. M., Sundar S. K., Cierpial M. A., Ritchie J. C. Effects of interleukin-1 infused into brain are antagonized by alpha-MSH in a dose-dependent manner. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jan 3;192(1):177–179. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90087-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner T., Ferroni S., Saermark T., Brack-Werner R., Banati R. B., Mager R., Steinaa L., Kreutzberg G. W., Erfle V. HIV-1 Nef protein exhibits structural and functional similarity to scorpion peptides interacting with K+ channels. AIDS. 1991 Nov;5(11):1301–1308. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199111000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigdahl B., Guyton R. A., Sarin P. S. Human immunodeficiency virus infection of the developing human nervous system. Virology. 1987 Aug;159(2):440–445. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90483-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley C. A., Masliah E., Morey M., Lemere C., DeTeresa R., Grafe M., Hansen L., Terry R. Neocortical damage during HIV infection. Ann Neurol. 1991 Jun;29(6):651–657. doi: 10.1002/ana.410290613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley C. A., Schrier R. D., Nelson J. A., Lampert P. W., Oldstone M. B. Cellular localization of human immunodeficiency virus infection within the brains of acquired immune deficiency syndrome patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7089–7093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willey R. L., Maldarelli F., Martin M. A., Strebel K. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vpu protein induces rapid degradation of CD4. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7193–7200. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7193-7200.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. M., Sachdev P. S., Perkins R. J., Rodriguez P. Zidovudine-related mania. Med J Aust. 1989 Mar 20;150(6):339–341. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1989.tb136499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu F. K., Garcia J. A., Harrich D., Gaynor R. B. Purification of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 enhancer and TAR binding proteins EBP-1 and UBP-1. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2117–2130. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03051.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yahi N., Baghdiguian S., Moreau H., Fantini J. Galactosyl ceramide (or a closely related molecule) is the receptor for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 on human colon epithelial HT29 cells. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4848–4854. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4848-4854.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasu K., Onoe H., Soma G., Oshima H., Mizuno D. Secretion of tumor necrosis factor during fetal and neonatal development of the mouse: ontogenic inflammation. J Biol Response Mod. 1989 Dec;8(6):644–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaniv A., Dahlberg J. E., Tronick S. R., Chiu I. M., Aaronson S. A. Molecular cloning of integrated caprine arthritis-encephalitis virus. Virology. 1985 Sep;145(2):340–345. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90169-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao X. J., Göttlinger H., Haseltine W. A., Cohen E. A. Envelope glycoprotein and CD4 independence of vpu-facilitated human immunodeficiency virus type 1 capsid export. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):5119–5126. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.5119-5126.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- York-Higgins D., Cheng-Mayer C., Bauer D., Levy J. A., Dina D. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 cellular host range, replication, and cytopathicity are linked to the envelope region of the viral genome. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):4016–4020. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.4016-4020.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeman A., Donaghy M. Acute infection with human immunodeficiency virus presenting with neurogenic urinary retention. Genitourin Med. 1991 Aug;67(4):345–347. doi: 10.1136/sti.67.4.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Ronde A., Klaver B., Keulen W., Smit L., Goudsmit J. Natural HIV-1 NEF accelerates virus replication in primary human lymphocytes. Virology. 1992 May;188(1):391–395. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90772-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Monte S. M., Ho D. D., Schooley R. T., Hirsch M. S., Richardson E. P., Jr Subacute encephalomyelitis of AIDS and its relation to HTLV-III infection. Neurology. 1987 Apr;37(4):562–569. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.4.562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]