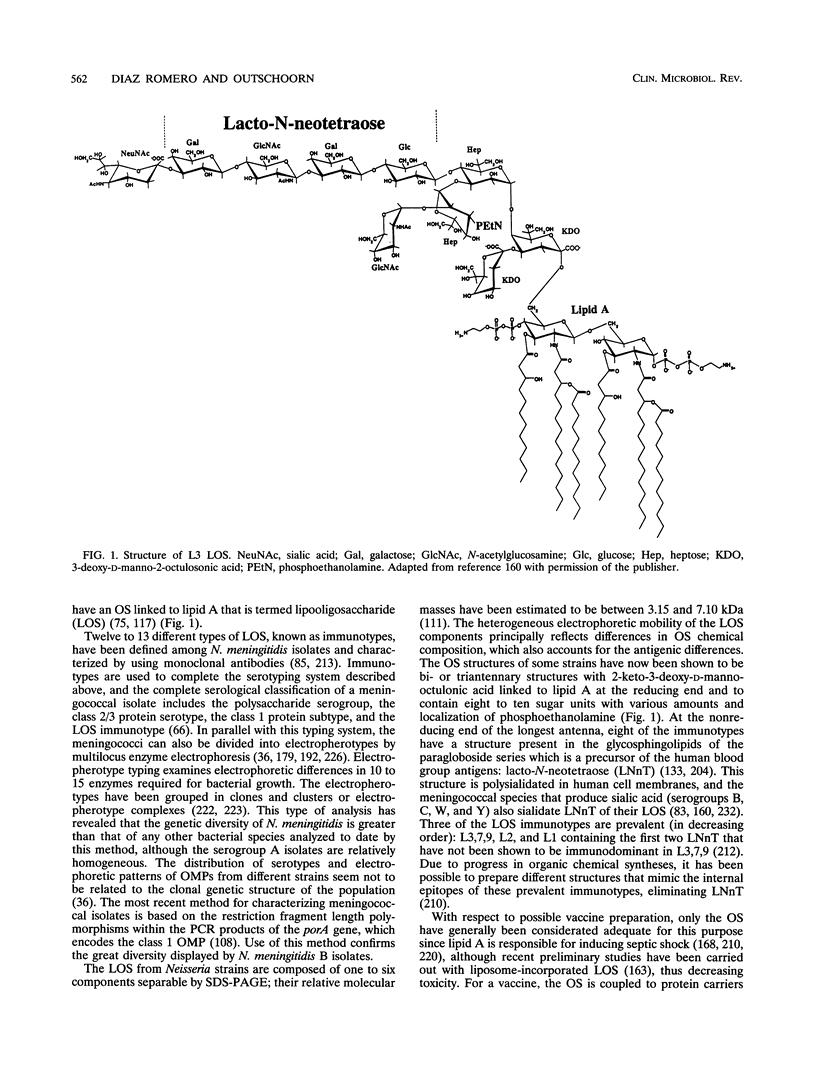
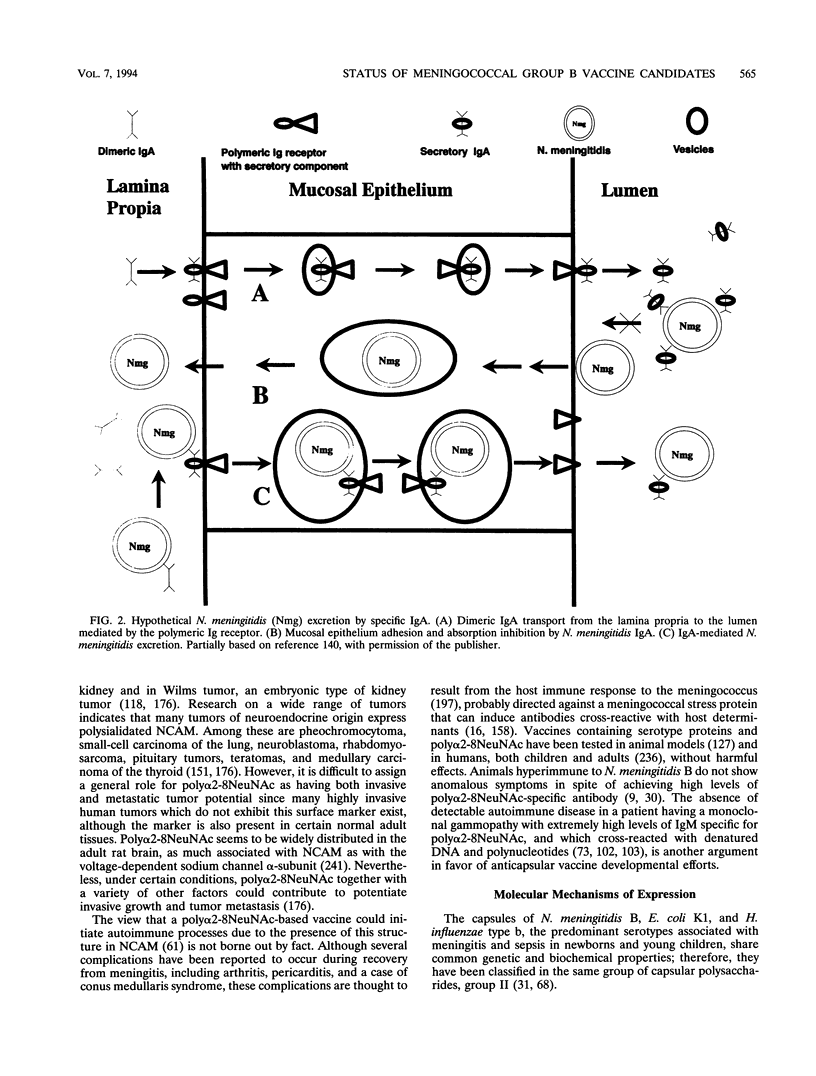
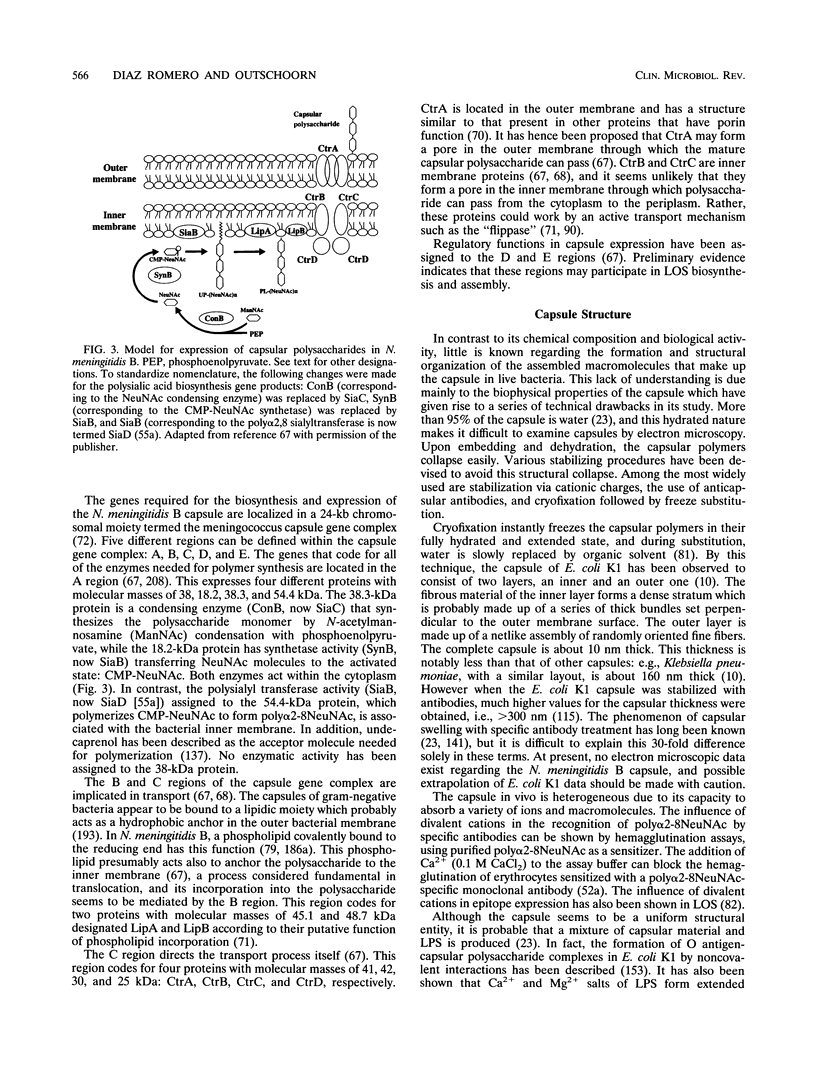
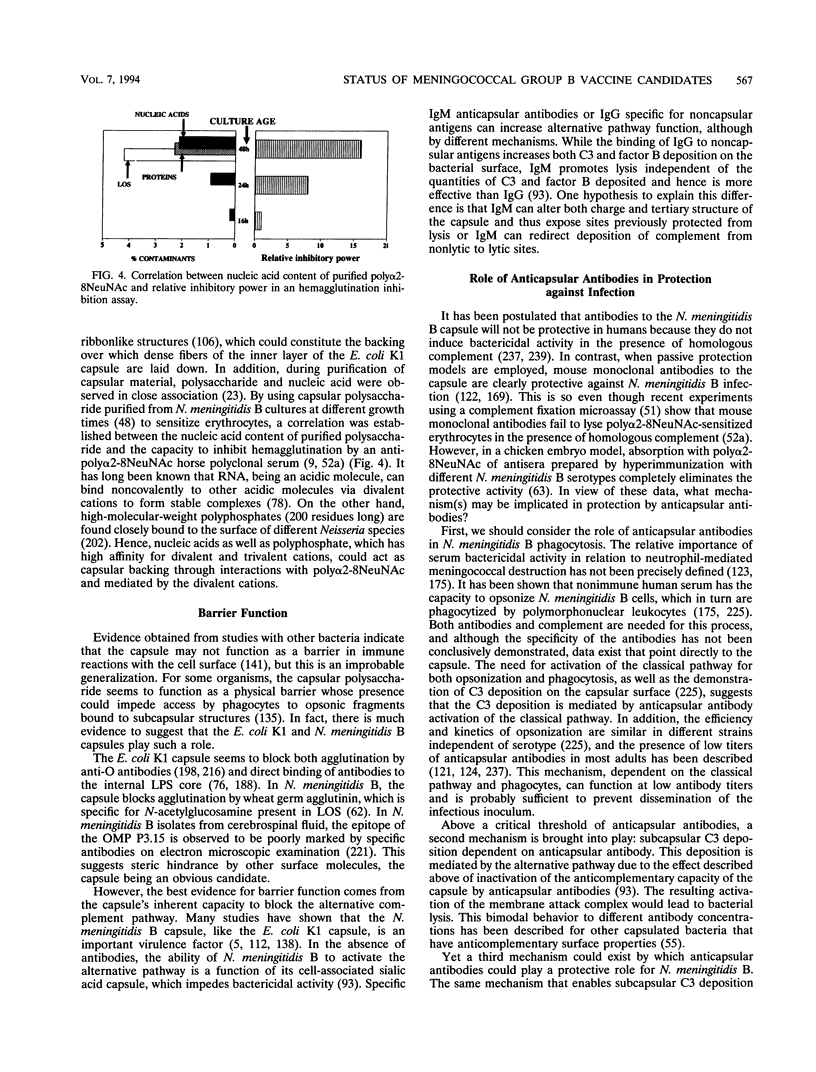
Abstract
Meningococcal meningitis is a severe, life-threatening infection for which no adequate vaccine exists. Current vaccines, based on the group-specific capsular polysaccharides, provide short-term protection in adults against serogroups A and C but are ineffective in infants and do not induce protection against group B strains, the predominant cause of infection in western countries, because the purified serogroup B polysaccharide fails to elicit human bactericidal antibodies. Because of the poor immunogenicity of group B capsular polysaccharide, different noncapsular antigens have been considered for inclusion in a vaccine against this serogroup: outer membrane proteins, lipooligosaccharides, iron-regulated proteins, Lip, pili, CtrA, and the immunoglobulin A proteases. Alternatively, attempts to increase the immunogenicity of the capsular polysaccharide have been made by using noncovalent complexes with outer membrane proteins, chemical modifications, and structural analogs. Here, we review the strategies employed for the development of a vaccine for Neisseria meningitidis serogroup B; the difficulties associated with the different approaches are discussed.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
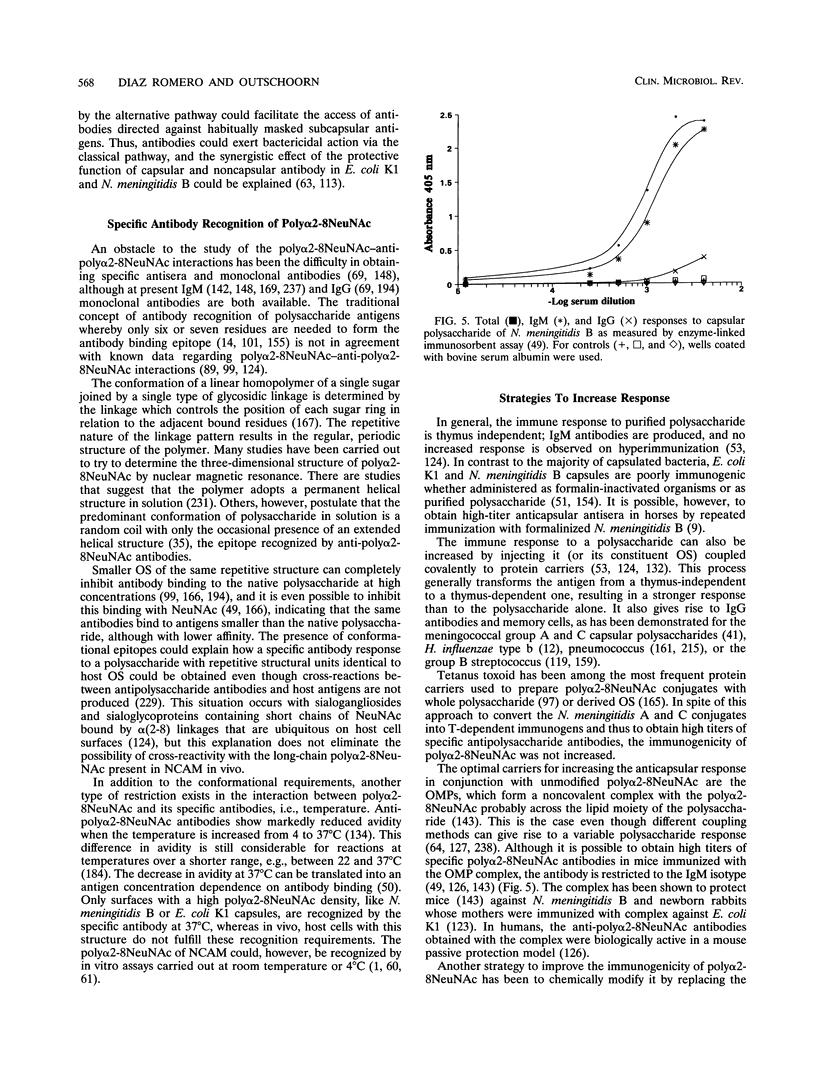
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acheson A., Sunshine J. L., Rutishauser U. NCAM polysialic acid can regulate both cell-cell and cell-substrate interactions. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(1):143–153. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Achtman M. Clonal properties of meningococci from epidemic meningitis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1991;85 (Suppl 1):24–31. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(91)90337-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Achtman M., Neibert M., Crowe B. A., Strittmatter W., Kusecek B., Weyse E., Walsh M. J., Slawig B., Morelli G., Moll A. Purification and characterization of eight class 5 outer membrane protein variants from a clone of Neisseria meningitidis serogroup A. J Exp Med. 1988 Aug 1;168(2):507–525. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.2.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed H., Gabius H. J. Purification and properties of a Ca2+-independent sialic acid-binding lectin from human placenta with preferential affinity to O-acetylsialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18673–18678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aho E. L. Molecular biology of class 5 outer membrane proteins of Neisseria meningitidis. Microb Pathog. 1989 Oct;7(4):249–253. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ala'Aldeen D. A., Powell N. B., Wall R. A., Borriello S. P. Localization of the meningococcal receptors for human transferrin. Infect Immun. 1993 Feb;61(2):751–759. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.2.751-759.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alcantara J., Yu R. H., Schryvers A. B. The region of human transferrin involved in binding to bacterial transferrin receptors is localized in the C-lobe. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jun;8(6):1135–1143. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01658.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen P. Z., Glode M., Schneerson R., Robbins J. B. Identification of immunoglobulin heavy-chain isotypes of specific antibodies of horse 46 group B meningococcal antiserum. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):324–329. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.324-329.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amako K., Meno Y., Takade A. Fine structures of the capsules of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli K1. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4960–4962. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4960-4962.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambrosino D. M., Bolon D., Collard H., Van Etten R., Kanchana M. V., Finberg R. W. Effect of Haemophilus influenzae polysaccharide outer membrane protein complex conjugate vaccine on macrophages. J Immunol. 1992 Dec 15;149(12):3978–3983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambrosino D. M., Sood S. K., Lee M. C., Chen D., Collard H. R., Bolon D. L., Johnson C., Daum R. S. IgG1, IgG2 and IgM responses to two Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccines in young infants. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1992 Oct;11(10):855–859. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199210000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreoni J., Käyhty H., Densen P. Vaccination and the role of capsular polysaccharide antibody in prevention of recurrent meningococcal disease in late complement component-deficient individuals. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jul;168(1):227–231. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.1.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arakatsu Y., Ashwell G., Kabat E. A. Immunochemical studies on dextrans. V. Specificity and cross-reactivity with dextrans of the antibodies formed in rabbits to isomaltonic and isomaltotrionic acids coupled to bovine serum albumin. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):858–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arakere G., Frasch C. E. Specificity of antibodies to O-acetyl-positive and O-acetyl-negative group C meningococcal polysaccharides in sera from vaccinees and carriers. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4349–4356. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4349-4356.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arakere G., Kessel M., Nguyen N., Frasch C. E. Characterization of a stress protein from group B Neisseria meningitidis. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jun;175(11):3664–3668. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.11.3664-3668.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arko R. J. Animal models for pathogenic Neisseria species. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Apr;2 (Suppl):S56–S59. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.suppl.s56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton F. E., Mancino L., Ryan A. J., Poolman J. T., Abdillahi H., Zollinger W. D. Serotypes and subtypes of Neisseria meningitidis serogroup B strains associated with meningococcal disease in Canada, 1977-1989. Can J Microbiol. 1991 Aug;37(8):613–617. doi: 10.1139/m91-104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton F. E., Ryan A., Diena B., Jennings H. J. A new serogroup (L) of Neisseria meningitidis. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):722–727. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.722-727.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton F. E., Ryan J. A., Michon F., Jennings H. J. Protective efficacy of mouse serum to the N-propionyl derivative of meningococcal group B polysaccharide. Microb Pathog. 1989 Jun;6(6):455–458. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90087-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee-Bhatnagar N., Frasch C. E. Expression of Neisseria meningitidis iron-regulated outer membrane proteins, including a 70-kilodalton transferrin receptor, and their potential for use as vaccines. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2875–2881. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2875-2881.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E., Thurow H. Polysaccharide capsule of Escherichia coli: microscope study of its size, structure, and sites of synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):911–936. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.911-936.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E. Visualization of the bacterial polysaccharide capsule. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;150:129–157. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74694-9_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee A. K., Moran E. E., Ray J. S., Zollinger W. D. Purification and characterization of H.8 antigen from group B Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):773–778. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.773-778.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee A. K., Moran E. E., Zollinger W. D. Antibodies to meningococcal H.8 (Lip) antigen fail to show bactericidal activity. Can J Microbiol. 1990 Feb;36(2):117–122. doi: 10.1139/m90-021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjune G., Høiby E. A., Grønnesby J. K., Arnesen O., Fredriksen J. H., Halstensen A., Holten E., Lindbak A. K., Nøkleby H., Rosenqvist E. Effect of outer membrane vesicle vaccine against group B meningococcal disease in Norway. Lancet. 1991 Nov 2;338(8775):1093–1096. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)91961-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell C. C., Jonsdottir K., Weir D. M., Hanson M. F., Cartwright K. A., Stewart J., Jones D., Mohammed I. Blood group, secretor status and susceptibility to bacterial meningitis. FEMS Microbiol Immunol. 1989 Jun;1(6-7):351–356. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1989.tb02420.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Eastby C. Studies on the gonococcal IgA1 protease II. Improved methods of enzyme purification and production of monoclonal antibodies to the enzyme. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Nov 22;144(2):215–221. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90088-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bortolussi R., Ferrier P. Protection against Escherichia coli K1 infection in newborn rats by antibody to K1 capsular polysaccharide antigen. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):111–117. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.111-117.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulnois G. J., Jann K. Bacterial polysaccharide capsule synthesis, export and evolution of structural diversity. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1819–1823. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00168.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P. Humoral immune response patterns of human mucosae: induction and relation to bacterial respiratory tract infections. J Infect Dis. 1992 Jun;165 (Suppl 1):S167–S176. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165-supplement_1-s167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks G. F., Lammel C. J., Blake M. S., Kusecek B., Achtman M. Antibodies against IgA1 protease are stimulated both by clinical disease and asymptomatic carriage of serogroup A Neisseria meningitidis. J Infect Dis. 1992 Dec;166(6):1316–1321. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.6.1316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bøvre K., Bryn K., Closs O., Hagen N., Frøholm L. O. Surface polysaccharide of Moraxella non-liquefaciens identical to Neisseria meningitidis group B capsular polysaccharide. A chemical and immunological investigation. NIPH Ann. 1983 Jun;6(1):65–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright K. A., Stuart J. M., Jones D. M., Noah N. D. The Stonehouse survey: nasopharyngeal carriage of meningococci and Neisseria lactamica. Epidemiol Infect. 1987 Dec;99(3):591–601. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800066449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caugant D. A., Mocca L. F., Frasch C. E., Frøholm L. O., Zollinger W. D., Selander R. K. Genetic structure of Neisseria meningitidis populations in relation to serogroup, serotype, and outer membrane protein pattern. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2781–2792. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2781-2792.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceesay S. J., Allen S. J., Menon A., Todd J. E., Cham K., Carlone G. M., Turner S. H., Gheesling L. L., DeWitt W., Plikaytis B. D. Decline in meningococcal antibody levels in African children 5 years after vaccination and the lack of an effect of booster immunization. J Infect Dis. 1993 May;167(5):1212–1216. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.5.1212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. Y., Genco C. A., Rock J. P., Morse S. A. Physiology and metabolism of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis: implications for pathogenesis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Apr;2 (Suppl):S35–S40. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.suppl.s35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christodoulides M., McGuinness B. T., Heckels J. E. Immunization with synthetic peptides containing epitopes of the class 1 outer-membrane protein of Neisseria meningitidis: production of bactericidal antibodies on immunization with a cyclic peptide. J Gen Microbiol. 1993 Aug;139(8):1729–1738. doi: 10.1099/00221287-139-8-1729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole M. F., Hale C. A. Cleavage of chimpanzee secretory immunoglobulin A by Haemophilus influenzae IgA1 protease. Microb Pathog. 1991 Jul;11(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(91)90092-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costantino P., Viti S., Podda A., Velmonte M. A., Nencioni L., Rappuoli R. Development and phase 1 clinical testing of a conjugate vaccine against meningococcus A and C. Vaccine. 1992;10(10):691–698. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(92)90091-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker M. D., Edwards K. M., Bradley R., Palmer P. Comparative trial in infants of four conjugate Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccines. J Pediatr. 1992 Feb;120(2 Pt 1):184–189. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)80424-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Densen P. Complement deficiencies and meningococcal disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Oct;86 (Suppl 1):57–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb06209.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Densen P. Interaction of complement with Neisseria meningitidis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Apr;2 (Suppl):S11–S17. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.suppl.s11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devi S. J., Robbins J. B., Schneerson R. Antibodies to poly[(2----8)-alpha-N-acetylneuraminic acid] and poly[(2----9)-alpha-N-acetylneuraminic acid] are elicited by immunization of mice with Escherichia coli K92 conjugates: potential vaccines for groups B and C meningococci and E. coli K1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7175–7179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devi S. J., Schneerson R., Egan W., Vann W. F., Robbins J. B., Shiloach J. Identity between polysaccharide antigens of Moraxella nonliquefaciens, group B Neisseria meningitidis, and Escherichia coli K1 (non-O acetylated). Infect Immun. 1991 Feb;59(2):732–736. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.2.732-736.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devoe I. W., Gilchrist J. E. Release of endotoxin in the form of cell wall blebs during in vitro growth of Neisseria meningitidis. J Exp Med. 1973 Nov 1;138(5):1156–1167. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.5.1156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz Romero J., Outschoorn I. Selective biotinylation of Neisseria meningitidis group B capsular polysaccharide and application in an improved ELISA for the detection of specific antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1993 Mar 15;160(1):35–47. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(93)90006-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick W. E., Jr, Beurret M. Glycoconjugates of bacterial carbohydrate antigens. A survey and consideration of design and preparation factors. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1989;10:48–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly J. J., Deck R. R., Liu M. A. Immunogenicity of a Haemophilus influenzae polysaccharide-Neisseria meningitidis outer membrane protein complex conjugate vaccine. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 1;145(9):3071–3079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards M. S., Nicholson-Weller A., Baker C. J., Kasper D. L. The role of specific antibody in alternative complement pathway-mediated opsonophagocytosis of type III, group B Streptococcus. J Exp Med. 1980 May 1;151(5):1275–1287. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.5.1275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feavers I. M., Heath A. B., Bygraves J. A., Maiden M. C. Role of horizontal genetic exchange in the antigenic variation of the class 1 outer membrane protein of Neisseria meningitidis. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(4):489–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01493.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández de Cossío M. E., Ohlin M., Llano M., Selander B., Cruz S., del Valle J., Borrebaeck C. A. Human monoclonal antibodies against an epitope on the class 5c outer membrane protein common to many pathogenic strains of Neisseria meningitidis. J Infect Dis. 1992 Dec;166(6):1322–1328. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.6.1322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferron L., Ferreiros C. M., Criado M. T., Pintor M. Immunogenicity and antigenic heterogeneity of a human transferrin-binding protein in Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):2887–2892. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.2887-2892.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa J. E., Densen P. Infectious diseases associated with complement deficiencies. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jul;4(3):359–395. doi: 10.1128/cmr.4.3.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finne J., Bitter-Suermann D., Goridis C., Finne U. An IgG monoclonal antibody to group B meningococci cross-reacts with developmentally regulated polysialic acid units of glycoproteins in neural and extraneural tissues. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4402–4407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finne J., Leinonen M., Mäkelä P. H. Antigenic similarities between brain components and bacteria causing meningitis. Implications for vaccine development and pathogenesis. Lancet. 1983 Aug 13;2(8346):355–357. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90340-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Parkes L., McNelis R. M., Gotschlich E. C. Protection against group B meningococcal disease. I. Comparison of group-specific and type-specific protection in the chick embryo model. J Exp Med. 1976 Aug 1;144(2):319–329. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Peppler M. S. Protection against group B Neisseria meningitidis disease: preparation of soluble protein and protein-polysaccharide immunogens. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):271–280. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.271-280.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E. Role of lipopolysaccharide in wheat germ agglutinin-mediated agglutination of Neisseria meningitidis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Oct;12(4):498–501. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.4.498-501.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Zahradnik J. M., Wang L. Y., Mocca L. F., Tsai C. M. Antibody response of adults to an aluminum hydroxide-adsorbed Neisseria meningitidis serotype 2b protein-group B polysaccharide vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):710–718. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Zollinger W. D., Poolman J. T. Serotype antigens of Neisseria meningitidis and a proposed scheme for designation of serotypes. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Jul-Aug;7(4):504–510. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.4.504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frosch M., Edwards U., Bousset K., Krausse B., Weisgerber C. Evidence for a common molecular origin of the capsule gene loci in gram-negative bacteria expressing group II capsular polysaccharides. Mol Microbiol. 1991 May;5(5):1251–1263. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frosch M., Görgen I., Boulnois G. J., Timmis K. N., Bitter-Suermann D. NZB mouse system for production of monoclonal antibodies to weak bacterial antigens: isolation of an IgG antibody to the polysaccharide capsules of Escherichia coli K1 and group B meningococci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frosch M., Müller A. Phospholipid substitution of capsular polysaccharides and mechanisms of capsule formation in Neisseria meningitidis. Mol Microbiol. 1993 May;8(3):483–493. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01592.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frosch M., Müller D., Bousset K., Müller A. Conserved outer membrane protein of Neisseria meningitidis involved in capsule expression. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):798–803. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.798-803.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frosch M., Weisgerber C., Meyer T. F. Molecular characterization and expression in Escherichia coli of the gene complex encoding the polysaccharide capsule of Neisseria meningitidis group B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1669–1673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawinowicz M. A., Merlini G., Birken S., Osserman E. F., Kabat E. A. Amino acid sequence of the FV region of a human monoclonal IgM (NOV) with specificity for the capsular polysaccharide of the group B meningococcus and of Escherichia coli K1, which cross-reacts with polynucleotides and with denatured DNA. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 1;147(3):915–920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebran S. J., Romano E. L., Pons H. A., Cariani L., Soyano A. N. A modified colorimetric method for the measurement of phagocytosis and antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity using 2,7-diaminofluorene. J Immunol Methods. 1992 Jul 6;151(1-2):255–260. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(92)90125-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson B. W., Melaugh W., Phillips N. J., Apicella M. A., Campagnari A. A., Griffiss J. M. Investigation of the structural heterogeneity of lipooligosaccharides from pathogenic Haemophilus and Neisseria species and of R-type lipopolysaccharides from Salmonella typhimurium by electrospray mass spectrometry. J Bacteriol. 1993 May;175(9):2702–2712. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.9.2702-2712.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigliotti F., Shenep J. L. Failure of monoclonal antibodies to core glycolipid to bind intact smooth strains of Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jun;151(6):1005–1011. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.6.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glode M. P., Lewin E. B., Sutton A., Le C. T., Gotschlich E. C., Robbins J. B. Comparative immunogenicity of vaccines prepared from capsular polysaccharides of group C Neisseria meningitidis O-acetyl-positive and O-acetyl-negative variants and Escherichia coli K92 in adult volunteers. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jan;139(1):52–59. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.1.52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman J. W., Roelants G. E., Byers V. S. RNA-antigen complexes: mechanism of formation and the testing of a postulated mode of action. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973 May 31;207:288–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb47491.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Fraser B. A., Nishimura O., Robbins J. B., Liu T. Y. Lipid on capsular polysaccharides of gram-negative bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):8915–8921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Liu T. Y., Artenstein M. S. Human immunity to the meningococcus. 3. Preparation and immunochemical properties of the group A, group B, and group C meningococcal polysaccharides. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1349–1365. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham L. L. Freeze-substitution studies of bacteria. Electron Microsc Rev. 1992;5(1):77–103. doi: 10.1016/0892-0354(92)90006-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregoriadis G., McCormack B., Wang Z., Lifely R. Polysialic acids: potential in drug delivery. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jan 11;315(3):271–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81177-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiss J. M., Schneider H., Mandrell R. E., Yamasaki R., Jarvis G. A., Kim J. J., Gibson B. W., Hamadeh R., Apicella M. A. Lipooligosaccharides: the principal glycolipids of the neisserial outer membrane. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10 (Suppl 2):S287–S295. doi: 10.1093/cid/10.supplement_2.s287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiss J. M., Yamasaki R., Estabrook M., Kim J. J. Meningococcal molecular mimicry and the search for an ideal vaccine. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1991;85 (Suppl 1):32–36. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(91)90338-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths E., Stevenson P., Ray A. Antigenic and molecular heterogeneity of the transferrin-binding protein of Neisseria meningitidis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 May;57(1-2):31–36. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90408-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu X. X., Tsai C. M. Preparation, characterization, and immunogenicity of meningococcal lipooligosaccharide-derived oligosaccharide-protein conjugates. Infect Immun. 1993 May;61(5):1873–1880. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.5.1873-1880.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guttormsen H. K., Bjerknes R., Halstensen A., Naess A., Høiby E. A., Solberg C. O. Cross-reacting serum opsonins to meningococci after vaccination. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jun;167(6):1314–1319. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.6.1314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajishengallis G., Nikolova E., Russell M. W. Inhibition of Streptococcus mutans adherence to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite by human secretory immunoglobulin A (S-IgA) antibodies to cell surface protein antigen I/II: reversal by IgA1 protease cleavage. Infect Immun. 1992 Dec;60(12):5057–5064. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.12.5057-5064.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallenbeck P. C., Yu F., Troy F. A. Rapid separation of oligomers of polysialic acid by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1987 Feb 15;161(1):181–186. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90670-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halter R., Pohlner J., Meyer T. F. Mosaic-like organization of IgA protease genes in Neisseria gonorrhoeae generated by horizontal genetic exchange in vivo. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2737–2744. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08415.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Gottesman M. M. Is the multidrug transporter a flippase? Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Jan;17(1):18–21. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90419-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J. Unified nomenclature for pathogenic Neisseria species. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Apr;2 (Suppl):S64–S65. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.suppl.s64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubert B., Watier L., Garnerin P., Richardson S. Meningococcal disease and influenza-like syndrome: a new approach to an old question. J Infect Dis. 1992 Sep;166(3):542–545. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.3.542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hummell D. S., Mocca L. F., Frasch C. E., Winkelstein J. A., Jean-Baptiste H. J., Atilio Canas J., Leggiadro R. J. Meningitis caused by a nonencapsulated strain of Neisseria meningitidis in twin infants with a C6 deficiency. J Infect Dis. 1987 Apr;155(4):815–818. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.4.815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häyrinen J., Bitter-Suermann D., Finne J. Interaction of meningococcal group B monoclonal antibody and its Fab fragment with alpha 2-8-linked sialic acid polymers: requirement of a long oligosaccharide segment for binding. Mol Immunol. 1989 Jun;26(6):523–529. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(89)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis G. A., Vedros N. A. Sialic acid of group B Neisseria meningitidis regulates alternative complement pathway activation. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):174–180. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.174-180.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings H. J., Gamian A., Ashton F. E. N-propionylated group B meningococcal polysaccharide mimics a unique epitope on group B Neisseria meningitidis. J Exp Med. 1987 Apr 1;165(4):1207–1211. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.4.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings H. J., Gamian A., Michon F., Ashton F. E. Unique intermolecular bactericidal epitope involving the homosialopolysaccharide capsule on the cell surface of group B Neisseria meningitidis and Escherichia coli K1. J Immunol. 1989 May 15;142(10):3585–3591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings H. J., Lugowski C. Immunochemistry of groups A, B, and C meningococcal polysaccharide-tetanus toxoid conjugates. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1011–1018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings H. J., Roy R., Gamian A. Induction of meningococcal group B polysaccharide-specific IgG antibodies in mice by using an N-propionylated B polysaccharide-tetanus toxoid conjugate vaccine. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 1;137(5):1708–1713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings H. J., Roy R., Michon F. Determinant specificities of the groups B and C polysaccharides of Neisseria meningitidis. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2651–2657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings H. J. The capsular polysaccharide of group B Neisseria meningitidis as a vehicle for vaccine development. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1989;10:151–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabat E. A., Liao J., Osserman E. F., Gamian A., Michon F., Jennings H. J. The epitope associated with the binding of the capsular polysaccharide of the group B meningococcus and of Escherichia coli K1 to a human monoclonal macroglobulin, IgMNOV. J Exp Med. 1988 Aug 1;168(2):699–711. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.2.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabat E. A., Nickerson K. G., Liao J., Grossbard L., Osserman E. F., Glickman E., Chess L., Robbins J. B., Schneerson R., Yang Y. H. A human monoclonal macroglobulin with specificity for alpha(2----8)-linked poly-N-acetyl neuraminic acid, the capsular polysaccharide of group B meningococci and Escherichia coli K1, which crossreacts with polynucleotides and with denatured DNA. J Exp Med. 1986 Aug 1;164(2):642–654. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.2.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaetzel C. S., Robinson J. K., Chintalacharuvu K. R., Vaerman J. P., Lamm M. E. The polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (secretory component) mediates transport of immune complexes across epithelial cells: a local defense function for IgA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8796–8800. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper D. L., Winkelhake J. L., Zollinger W. D., Brandt B. L., Artenstein M. S. Immunochemical similarity between polysaccharide antigens of Escherichia coli 07: K1(L):NM and group B Neisseria meningitidis. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):262–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kertesz D. A., Byrne S. K., Chow A. W. Characterization of Neisseria meningitidis by polymerase chain reaction and restriction endonuclease digestion of the porA gene. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Oct;31(10):2594–2598. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.10.2594-2598.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M., Mestecky J., Russell M. W. Defense mechanisms involving Fc-dependent functions of immunoglobulin A and their subversion by bacterial immunoglobulin A proteases. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jun;52(2):296–303. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.2.296-303.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. J., Mandrell R. E., Griffiss J. M. Neisseria lactamica and Neisseria meningitidis share lipooligosaccharide epitopes but lack common capsular and class 1, 2, and 3 protein epitopes. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):602–608. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.602-608.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. J., Mandrell R. E., Hu Z., Westerink M. A., Poolman J. T., Griffiss J. M. Electromorphic characterization and description of conserved epitopes of the lipooligosaccharides of group A Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2631–2638. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2631-2638.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S., Itabashi H., Gemski P., Sadoff J., Warren R. L., Cross A. S. The K1 capsule is the critical determinant in the development of Escherichia coli meningitis in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1992 Sep;90(3):897–905. doi: 10.1172/JCI115965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S., Kang J. H., Cross A. S., Kaufman B., Zollinger W., Sadoff J. Functional activities of monoclonal antibodies to the O side chain of Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharides in vitro and in vivo. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):47–53. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld S. J., Plaut A. G. Secretory immunity and the bacterial IgA proteases. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 May-Jun;3(3):521–534. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.3.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kröncke K. D., Golecki J. R., Jann K. Further electron microscopic studies on the expression of Escherichia coli group II capsules. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3469–3472. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3469-3472.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulshin V. A., Zähringer U., Lindner B., Frasch C. E., Tsai C. M., Dmitriev B. A., Rietschel E. T. Structural characterization of the lipid A component of pathogenic Neisseria meningitidis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(6):1793–1800. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.6.1793-1800.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käyhty H., Poolman J., Abdillahi H., Sivonen A., Eskola J., Tarkka E., Peltola H. Sero- and subtypes of group B meningococci causing invasive infections in Finland in 1976-87. Scand J Infect Dis. 1989;21(5):527–535. doi: 10.3109/00365548909037881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn L. C., Kraehenbuhl J. P. Monoclonal antibodies recognizing the secreted and membrane domains of the IgA dimer receptor. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 30;409:751–759. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb26914.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagergard T., Shiloach J., Robbins J. B., Schneerson R. Synthesis and immunological properties of conjugates composed of group B streptococcus type III capsular polysaccharide covalently bound to tetanus toxoid. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):687–694. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.687-694.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B. C., Hill P. Identification of an outer-membrane haemoglobin-binding protein in Neisseria meningitidis. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Dec;138(12):2647–2656. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-12-2647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifely M. R., Esdaile J., Moreno C. Passive transfer of meningococcal group B polysaccharide antibodies to the offspring of pregnant rabbits and their protective role against infection with Escherichia coli K1. Vaccine. 1989 Feb;7(1):17–21. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(89)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifely M. R., Esdaile J. Specificity of the immune response to the group B polysaccharide of Neisseria meningitidis. Immunology. 1991 Nov;74(3):490–496. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifely M. R., Moreno C., Lindon J. C. An integrated molecular and immunological approach towards a meningococcal group B vaccine. Vaccine. 1987 Mar;5(1):11–26. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(87)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifely M. R., Nowicka U. T., Moreno C. Analysis of the chain length of oligomers and polymers of sialic acid isolated from Neisseria meningitidis group B and C and Escherichia coli K1 and K92. Carbohydr Res. 1986 Nov 15;156:123–135. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)90104-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifely M. R., Roberts S. C., Shepherd W. M., Esdaile J., Wang Z., Cleverly A., Aulaqi A. A., Moreno C. Immunogenicity in adult males of a Neisseria meningitidis group B vaccine composed of polysaccharide complexed with outer membrane proteins. Vaccine. 1991 Jan;9(1):60–66. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(91)90318-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifely M. R., Wang Z. Immune responses in mice to different noncovalent complexes of meningococcal B polysaccharide and outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3221–3227. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3221-3227.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu T. Y., Gotschlich E. C., Egan W., Robbins J. B. Sialic acid-containing polysaccharides of Neisseria meningitidis and Escherichia coli strain Bos-12: structure and immunology. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S71–S77. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomholt H., Poulsen K., Caugant D. A., Kilian M. Molecular polymorphism and epidemiology of Neisseria meningitidis immunoglobulin A1 proteases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2120–2124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowell G. H., Smith L. F., Griffiss J. M., Brandt B. L. IgA-dependent, monocyte-mediated, antibacterial activity. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):452–457. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackinnon F. G., Gorringe A. R., Funnell S. G., Robinson A. Intranasal infection of infant mice with Neisseria meningitidis. Microb Pathog. 1992 Jun;12(6):415–420. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(92)90004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrell R. E., Zollinger W. D. Measurement of antibodies to meningococcal group B polysaccharide: low avidity binding and equilibrium binding constants. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):2172–2178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marques M. B., Kasper D. L., Pangburn M. K., Wessels M. R. Prevention of C3 deposition by capsular polysaccharide is a virulence mechanism of type III group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1992 Oct;60(10):3986–3993. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.10.3986-3993.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P. V., Laviotola A., Ohayon H., Riou J. Y. Presence of a capsule in Neisseria lactamica, antigenically similar to the capsule of N. meningitidis. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 May-Jun;137A(3):279–285. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson L., Holbein B. E. Role of lipid intermediate(s) in the synthesis of serogroup B Neisseria meningitidis capsular polysaccharide. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):861–867. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.861-867.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazanec M. B., Kaetzel C. S., Lamm M. E., Fletcher D., Nedrud J. G. Intracellular neutralization of virus by immunoglobulin A antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6901–6905. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazanec M. B., Nedrud J. G., Kaetzel C. S., Lamm M. E. A three-tiered view of the role of IgA in mucosal defense. Immunol Today. 1993 Sep;14(9):430–435. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90245-G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meno Y., Amako K. Morphological evidence for penetration of anti-O antibody through the capsule of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1421–1428. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1421-1428.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno C., Hewitt J., Hastings K., Brown D. Immunological properties of monoclonal antibodies specific for meningococcal polysaccharides: the protective capacity of IgM antibodies specific for polysaccharide group B. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Aug;129(8):2451–2456. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-8-2451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno C., Lifely M. R., Esdaile J. Immunity and protection of mice against Neisseria meningitidis group B by vaccination, using polysaccharide complexed with outer membrane proteins: a comparison with purified B polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):527–533. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.527-533.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. A., Chen C. Y., LeFaou A., Mietzner T. A. A potential role for the major iron-regulated protein expressed by pathogenic Neisseria species. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10 (Suppl 2):S306–S310. doi: 10.1093/cid/10.supplement_2.s306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mostov K. E., Blobel G. Transcellular transport of polymeric immunoglobulin by secretory component: a model system for studying intracellular protein sorting. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 30;409:441–451. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb26888.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulks M. H., Plaut A. G., Feldman H. A., Frangione B. IgA proteases of two distinct specificities are released by Neisseria meningitidis. J Exp Med. 1980 Nov 1;152(5):1442–1447. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.5.1442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munkley A., Tinsley C. R., Virji M., Heckels J. E. Blocking of bactericidal killing of Neisseria meningitidis by antibodies directed against class 4 outer membrane protein. Microb Pathog. 1991 Dec;11(6):447–452. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(91)90041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä O., Péterfy F., Outschoorn I. G., Richter A. W., Seppälä I. Immunogenic properties of alpha (1----6) dextran, its protein conjugates, and conjugates of its breakdown products in mice. Scand J Immunol. 1984 Jun;19(6):541–550. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1984.tb00965.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nato F., Mazie J. C., Fournier J. M., Slizewicz B., Sagot N., Guibourdenche M., Postic D., Riou J. Y. Production of polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies against group A, B, and C capsular polysaccharides of Neisseria meningitidis and preparation of latex reagents. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jul;29(7):1447–1452. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.7.1447-1452.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen N. Y., Suzuki A., Boykins R. A., Liu T. Y. The amino acid sequence of Limulus C-reactive protein. Evidence of polymorphism. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10456–10465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen H. E., Koch C., Magnussen P., Lind I. Complement deficiencies in selected groups of patients with meningococcal disease. Scand J Infect Dis. 1989;21(4):389–396. doi: 10.3109/00365548909167442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson O. Carbohydrate antigens in human lung carcinomas. APMIS Suppl. 1992;27:149–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orren A., Warren R. E., Potter P. C., Jones A. M., Lachmann P. J., Poolman J. T. Antibodies to meningococcal class 1 outer membrane proteins in South African complement-deficient and complement-sufficient subjects. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4510–4516. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4510-4516.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov F., Orskov I. Complex formation between Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide O antigen and capsular K antigen as detected by immunoelectrophoresis. APMIS. 1991 Jul;99(7):615–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov F., Orskov I., Sutton A., Schneerson R., Lin W., Egan W., Hoff G. E., Robbins J. B. Form variation in Escherichia coli K1: determined by O-acetylation of the capsular polysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1979 Mar 1;149(3):669–685. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.3.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Outschoorn I. M., Ashwell G., Gruezo F., Kabat E. A. Immunochemical studies on dextrans. 8. Specificity and cross-reactivity with dextrans of the antibodies formed in rabbits to isomaltohexaonic acid coupled to bovine serum albumin. J Immunol. 1974 Sep;113(3):896–903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbeek B. P., Veringa E. M. Role of antibodies and antibiotics in aerobic gram-negative septicemia: possible synergism between antimicrobial treatment and immunotherapy. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Jul-Aug;13(4):751–760. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.4.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padeh S., Jaffe C. L., Passwell J. H. Activation of human monocytes via their sIgA receptors. Immunology. 1991 Feb;72(2):188–193. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pannekoek Y., Schuurman I. G., Dankert J., van Putten J. P. Immunogenicity of the meningococcal stress protein MSP63 during natural infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Sep;93(3):377–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb08188.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paoletti L. C., Wessels M. R., Michon F., DiFabio J., Jennings H. J., Kasper D. L. Group B Streptococcus type II polysaccharide-tetanus toxoid conjugate vaccine. Infect Immun. 1992 Oct;60(10):4009–4014. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.10.4009-4014.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavliak V., Brisson J. R., Michon F., Uhrín D., Jennings H. J. Structure of the sialylated L3 lipopolysaccharide of Neisseria meningitidis. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 5;268(19):14146–14152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeters C. C., Tenbergen-Meekes A. M., Poolman J. T., Zegers B. J., Rijkers G. T. Immunogenicity of a Streptococcus pneumoniae type 4 polysaccharide--protein conjugate vaccine is decreased by admixture of high doses of free saccharide. Vaccine. 1992;10(12):833–840. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(92)90046-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelkonen S., Häyrinen J., Finne J. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of the capsular polysaccharides of Escherichia coli K1 and other bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2646–2653. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2646-2653.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrov A. B., Semenov B. F., Vartanyan Y. P., Zakirov M. M., Torchilin V. P., Trubetskoy V. S., Koshkina N. V., L'Vov V. L., Verner I. K., Lopyrev I. V. Toxicity and immunogenicity of Neisseria meningitidis lipopolysaccharide incorporated into liposomes. Infect Immun. 1992 Sep;60(9):3897–3903. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.9.3897-3903.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson A., Kuipers B., Pelzer M., Verhagen E., Tiesjema R. H., Tommassen J., Poolman J. T. Monoclonal antibodies against the 70-kilodalton iron-regulated protein of Neisseria meningitidis are bactericidal and strain specific. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):3036–3041. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.3036-3041.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raetz C. R. Bacterial endotoxins: extraordinary lipids that activate eucaryotic signal transduction. J Bacteriol. 1993 Sep;175(18):5745–5753. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.18.5745-5753.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raza M. W., Ogilvie M. M., Blackwell C. C., Stewart J., Elton R. A., Weir D. M. Effect of respiratory syncytial virus infection on binding of Neisseria meningitidis and Haemophilus influenzae type b to a human epithelial cell line (HEp-2). Epidemiol Infect. 1993 Apr;110(2):339–347. doi: 10.1017/s095026880006828x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinholdt J., Kilian M. Lack of cleavage of immunoglobulin A (IgA) from rhesus monkeys by bacterial IgA1 proteases. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):2219–2221. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.2219-2221.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenqvist E., Høiby E. A., Bjune G., Bryn K., Closs O., Feiring B., Klem A., Nøkleby H., Frølm L. O. Human antibody responses after vaccination with the Norwegian group B meningococcal outer membrane vesicle vaccine: results from ELISA studies. NIPH Ann. 1991 Dec;14(2):169–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenqvist E., Høiby E. A., Wedege E., Kusecek B., Achtman M. The 5C protein of Neisseria meningitidis is highly immunogenic in humans and induces bactericidal antibodies. J Infect Dis. 1993 May;167(5):1065–1073. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.5.1065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross S. C., Rosenthal P. J., Berberich H. M., Densen P. Killing of Neisseria meningitidis by human neutrophils: implications for normal and complement-deficient individuals. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1266–1275. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutishauser U., Acheson A., Hall A. K., Mann D. M., Sunshine J. The neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) as a regulator of cell-cell interactions. Science. 1988 Apr 1;240(4848):53–57. doi: 10.1126/science.3281256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacchi C. T., Pessoa L. L., Ramos S. R., Milagres L. G., Camargo M. C., Hidalgo N. T., Melles C. E., Caugant D. A., Frasch C. E. Ongoing group B Neisseria meningitidis epidemic in São Paulo, Brazil, due to increased prevalence of a single clone of the ET-5 complex. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jul;30(7):1734–1738. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.7.1734-1738.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffell J. L., Walsh F. S., Doherty P. Direct activation of second messenger pathways mimics cell adhesion molecule-dependent neurite outgrowth. J Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;118(3):663–670. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.3.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander B., Sideras P., Möller E. Expression of B220 antigen on an interleukin 4- and interleukin 5-producing T-cell line. Scand J Immunol. 1988 Jul;28(1):63–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb02415.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarff L. D., McCracken G. H., Schiffer M. S., Glode M. P., Robbins J. B., Orskov I., Orskov F. Epidemiology of Escherichia coli K1 in healthy and diseased newborns. Lancet. 1975 May 17;1(7916):1099–1104. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92496-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saukkonen K., Leinonen M., Abdillahi H., Poolman J. T. Comparative evaluation of potential components for group B meningococcal vaccine by passive protection in the infant rat and in vitro bactericidal assay. Vaccine. 1989 Aug;7(4):325–328. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(89)90194-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaad U. B. Arthritis in disease due to Neisseria meningitidis. Rev Infect Dis. 1980 Nov-Dec;2(6):880–888. doi: 10.1093/clinids/2.6.880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior B. W., Loomes L. M., Kerr M. A. The production and activity in vivo of Proteus mirabilis IgA protease in infections of the urinary tract. J Med Microbiol. 1991 Oct;35(4):203–207. doi: 10.1099/00222615-35-4-203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierra G. V., Campa H. C., Varcacel N. M., Garcia I. L., Izquierdo P. L., Sotolongo P. F., Casanueva G. V., Rico C. O., Rodriguez C. R., Terry M. H. Vaccine against group B Neisseria meningitidis: protection trial and mass vaccination results in Cuba. NIPH Ann. 1991 Dec;14(2):195–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöholm A. G. Inherited complement deficiency states: implications for immunity and immunological disease. APMIS. 1990 Oct;98(10):861–874. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1990.tb05008.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skevakis L., Frasch C. E., Zahradnik J. M., Dolin R. Class-specific human bactericidal antibodies to capsular and noncapsular surface antigens of Neisseria meningitidis. J Infect Dis. 1984 Mar;149(3):387–396. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.3.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. M., Smith N. H., O'Rourke M., Spratt B. G. How clonal are bacteria? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4384–4388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stearns D. J., Kurosawa S., Sims P. J., Esmon N. L., Esmon C. T. The interaction of a Ca2+-dependent monoclonal antibody with the protein C activation peptide region. Evidence for obligatory Ca2+ binding to both antigen and antibody. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):826–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens D. S., Spellman P. A., Swartley J. S. Effect of the (alpha 2-->8)-linked polysialic acid capsule on adherence of Neisseria meningitidis to human mucosal cells. J Infect Dis. 1993 Feb;167(2):475–479. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.2.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens D. S., Whitney A. M., Schoolnik G. K., Zollinger W. D. Common epitopes of pilin of Neisseria meningitidis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Aug;158(2):332–342. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.2.332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steven N. M., Nathwani D. Facial palsy, meningococcal meningitis, and reactivation of herpes simplex virus. Clin Infect Dis. 1993 Jan;16(1):181–181. doi: 10.1093/clinids/16.1.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens P., Chu C. L., Young L. S. K-1 antigen content and the presence of an additional sialic acid-containing antigen among bacteremic K-1 Escherichia coli: correlation with susceptibility to opsonophagocytosis. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):1055–1061. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.1055-1061.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson P., Williams P., Griffiths E. Common antigenic domains in transferrin-binding protein 2 of Neisseria meningitidis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2391–2396. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2391-2396.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen U. B., Blom J. Capsular polysaccharide is linked to the outer surface of type 6A pneumococcal cell walls. APMIS. 1992 Oct;100(10):891–893. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1992.tb04015.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarkka E., Sarvas M. Cloning of an outer membrane protein of Neisseria meningitidis in Escherichia coli. Microb Pathog. 1987 Dec;3(6):445–453. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinsley C. R., Manjula B. N., Gotschlich E. C. Purification and characterization of polyphosphate kinase from Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1993 Sep;61(9):3703–3710. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.9.3703-3710.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinsley C. R., Virji M., Heckels J. E. Antibodies recognizing a variety of different structural motifs on meningococcal Lip antigen fail to demonstrate bactericidal activity. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Nov;138(11):2321–2328. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-11-2321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Civin C. I. Eight lipooligosaccharides of Neisseria meningitidis react with a monoclonal antibody which binds lacto-N-neotetraose (Gal beta 1-4GlcNAc beta 1-3Gal beta 1-4Glc). Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3604–3609. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3604-3609.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzanakaki G., Blackwell C. C., Kremastinou J., Weir D. M., Mentis A., Fallon R. J. Serogroups, serotypes and subtypes of Neisseria meningitidis isolated from patients and carriers in Greece. J Med Microbiol. 1993 Jan;38(1):19–22. doi: 10.1099/00222615-38-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Ley P., Poolman J. T. Construction of a multivalent meningococcal vaccine strain based on the class 1 outer membrane protein. Infect Immun. 1992 Aug;60(8):3156–3161. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.8.3156-3161.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vella P. P., Staub J. M., Armstrong J., Dolan K. T., Rusk C. M., Szymanski S., Greer W. E., Marburg S., Kniskern P. J., Schofield T. L. Immunogenicity of a new Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine (meningococcal protein conjugate) (PedvaxHIB). Pediatrics. 1990 Apr;85(4 Pt 2):668–675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheul A. F., Boons G. J., Van der Marel G. A., Van Boom J. H., Jennings H. J., Snippe H., Verhoef J., Hoogerhout P., Poolman J. T. Minimal oligosaccharide structures required for induction of immune responses against meningococcal immunotype L1, L2, and L3,7,9 lipopolysaccharides determined by using synthetic oligosaccharide-protein conjugates. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3566–3573. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3566-3573.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheul A. F., Braat A. K., Leenhouts J. M., Hoogerhout P., Poolman J. T., Snippe H., Verhoef J. Preparation, characterization, and immunogenicity of meningococcal immunotype L2 and L3,7,9 phosphoethanolamine group-containing oligosaccharide-protein conjugates. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):843–851. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.843-851.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheul A. F., Poolman J. T., Snippe H., Verhoef J. The influence of the adjuvant Quil A on the epitope specificity of meningococcal lipopolysaccharide anti-carbohydrate antibodies. Mol Immunol. 1991 Nov;28(11):1193–1200. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(91)90005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheul A. F., Snippe H., Poolman J. T. Meningococcal lipopolysaccharides: virulence factor and potential vaccine component. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Mar;57(1):34–49. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.1.34-49.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheul A. F., Van Gaans J. A., Wiertz E. J., Snippe H., Verhoef J., Poolman J. T. Meningococcal lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-derived oligosaccharide-protein conjugates evoke outer membrane protein- but not LPS-specific bactericidal antibodies in mice: influence of adjuvants. Infect Immun. 1993 Jan;61(1):187–196. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.1.187-196.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheul A. F., Versteeg A. A., De Reuver M. J., Jansze M., Snippe H. Modulation of the immune response to pneumococcal type 14 capsular polysaccharide-protein conjugates by the adjuvant Quil A depends on the properties of the conjugates. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1078–1083. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1078-1083.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen C., Cross A., Byrne W. R., Zollinger W. Quantitative relationship between capsular content and killing of K1-encapsulated Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2723–2730. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2723-2730.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virji M., Alexandrescu C., Ferguson D. J., Saunders J. R., Moxon E. R. Variations in the expression of pili: the effect on adherence of Neisseria meningitidis to human epithelial and endothelial cells. Mol Microbiol. 1992 May;6(10):1271–1279. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00848.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virji M., Kayhty H., Ferguson D. J., Alexandrescu C., Heckels J. E., Moxon E. R. The role of pili in the interactions of pathogenic Neisseria with cultured human endothelial cells. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Aug;5(8):1831–1841. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00807.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virji M., Makepeace K., Ferguson D. J., Achtman M., Sarkari J., Moxon E. R. Expression of the Opc protein correlates with invasion of epithelial and endothelial cells by Neisseria meningitidis. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Oct;6(19):2785–2795. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01458.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Aasen A. O. Different role of cytokine mediators in septic shock related to meningococcal disease and surgery/polytrauma. Immunol Rev. 1992 Jun;127:221–230. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1992.tb01416.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall R. A., Davies H. A., Borriello S. P. Epitopes of serogroup B Neisseria meningitidis analysed in vitro and directly from cerebrospinal fluid. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Nov;53(1-2):129–135. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90379-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. F., Caugant D. A., Li X., Hu X., Poolman J. T., Crowe B. A., Achtman M. Clonal and antigenic analysis of serogroup A Neisseria meningitidis with particular reference to epidemiological features of epidemic meningitis in the People's Republic of China. Infect Immun. 1992 Dec;60(12):5267–5282. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.12.5267-5282.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. F., Caugant D. A., Morelli G., Koumaré B., Achtman M. Antigenic and epidemiologic properties of the ET-37 complex of Neisseria meningitidis. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jun;167(6):1320–1329. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.6.1320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. Y., Frasch C. E. Development of a Neisseria meningitidis group B serotype 2b protein vaccine and evaluation in a mouse model. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):408–414. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.408-414.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward K. N., Fleer A., Verhoef J., Jones D. M. Opsonisation and phagocytosis of group B meningococci by polymorphonuclear leucocytes: comparison of sulphonamide sensitive and resistant strains. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Apr;40(4):361–367. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.4.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedege E., Caugant D. A., Frøholm L. O., Zollinger W. D. Characterization of serogroup A and B strains of Neisseria meningitidis with serotype 4 and 21 monoclonal antibodies and by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jul;29(7):1486–1492. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.7.1486-1492.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedege E., Dalseg R., Caugant D. A., Poolman J. T., Frøholm L. O. Expression of an inaccessible P1.7 subtype epitope on meningococcal class 1 proteins. J Med Microbiol. 1993 Jan;38(1):23–28. doi: 10.1099/00222615-38-1-23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weihe P., Mathiassen B., Rasmussen J. M., Petersen T., Isager H. An epidemic outbreak of group B meningococcal disease on the Faroe Islands. Scand J Infect Dis. 1988;20(3):291–296. doi: 10.3109/00365548809032454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessels M. R., Kasper D. L. Antibody recognition of the type 14 pneumococcal capsule. Evidence for a conformational epitope in a neutral polysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):2121–2131. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.2121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki R., Bacon B. Three-dimensional structural analysis of the group B polysaccharide of Neisseria meningitidis 6275 by two-dimensional NMR: the polysaccharide is suggested to exist in helical conformations in solution. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 22;30(3):851–857. doi: 10.1021/bi00217a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki R., Griffiss J. M., Quinn K. P., Mandrell R. E. Neuraminic acid is alpha 2-->3 linked in the lipooligosaccharide of Neisseria meningitidis serogroup B strain 6275. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(14):4565–4568. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.14.4565-4568.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang P., Yin X., Rutishauser U. Intercellular space is affected by the polysialic acid content of NCAM. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(6):1487–1496. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.6.1487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapata G. A., Vann W. F., Rubinstein Y., Frasch C. E. Identification of variable region differences in Neisseria meningitidis class 3 protein sequences among five group B serotypes. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Dec;6(23):3493–3499. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01784.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Boslego J. E., Frasch C. E., Froholm L. O. Safety of vaccines containing meningococcal group B polysaccharide. Lancet. 1984 Jul 21;2(8395):166–166. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Boslego J., Moran E., Garcia J., Cruz C., Ruiz S., Brandt B., Martinez M., Arthur J., Underwood P. Meningococcal serogroup B vaccine protection trial and follow-up studies in Chile. The Chilean National Committee for Meningococcal Disease. NIPH Ann. 1991 Dec;14(2):211–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Mandrell R. E., Griffiss J. M., Altieri P., Berman S. Complex of meningococcal group B polysaccharide and type 2 outer membrane protein immunogenic in man. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):836–848. doi: 10.1172/JCI109383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Mandrell R. E. Importance of complement source in bactericidal activity of human antibody and murine monoclonal antibody to meningococcal group B polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):257–264. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.257-264.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Moran E. Meningococcal vaccines--present and future. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1991;85 (Suppl 1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(91)90339-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorgani A. A., Stewart J., Blackwell C. C., Elton R. A., Weir D. M. Secretor status and humoral immune responses to Neisseria lactamica and Neisseria meningitidis. Epidemiol Infect. 1992 Dec;109(3):445–452. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800050433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Moraes J. C., Perkins B. A., Camargo M. C., Hidalgo N. T., Barbosa H. A., Sacchi C. T., Landgraf I. M., Gattas V. L., Vasconcelos H. de G., Gral I. M. Protective efficacy of a serogroup B meningococcal vaccine in Sao Paulo, Brazil. Lancet. 1992 Oct 31;340(8827):1074–1078. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)93086-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Ley P., Heckels J. E., Virji M., Hoogerhout P., Poolman J. T. Topology of outer membrane porins in pathogenic Neisseria spp. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):2963–2971. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.2963-2971.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



