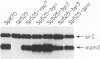
Abstract
We have shown that the expression of mam2, the gene encoding the Schizosaccharomyces pombe P-factor pheromone receptor, is dependent upon components of the pheromone signal transduction pathway, including Ras1, Gpa1, Byr1 and Byr2, each of which is required for both conjugation and sporulation. Studies of the expression of mam2 in mutant S. pombe cells confirm previous conclusions, based on the ability of cells to sporulate, that the Byr1 protein kinase acts downstream of the Byr2 protein kinase and that both act downstream of Ras1, the S. pombe RAS homolog, and Gpa1, the G alpha component that mediates the occupancy of the mam2 receptor. In addition, our present studies show that Ras1 and Gpa1 each act downstream from the other and hence act in concert. The Spk1 kinase, which is required for conjugation and sporulation and which is a structural and functional homolog of the vertebrate MAP kinases, is not required for mam2 expression.
Full text
PDF


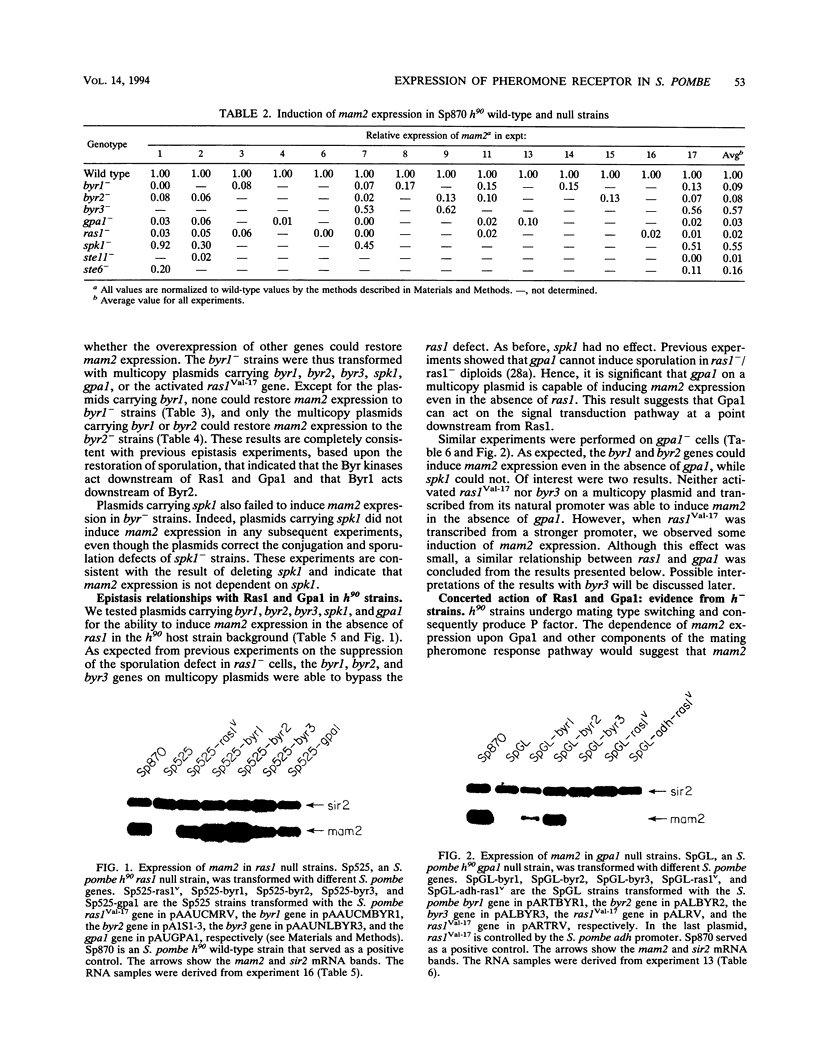
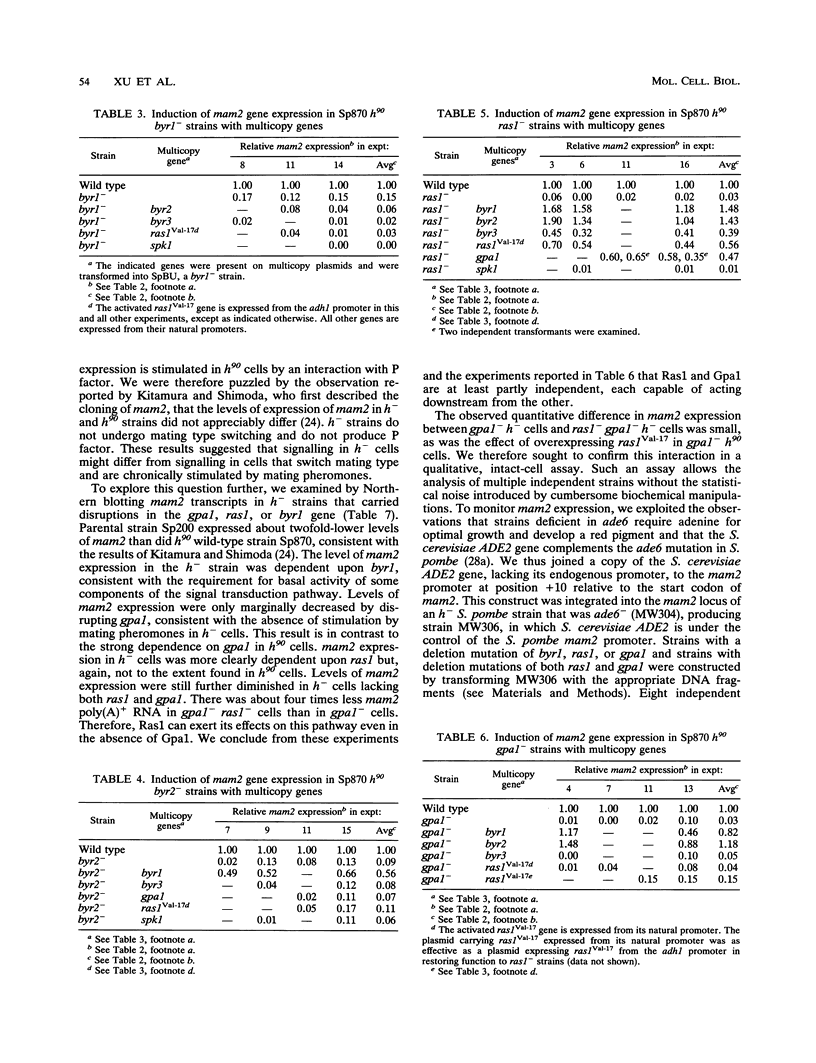

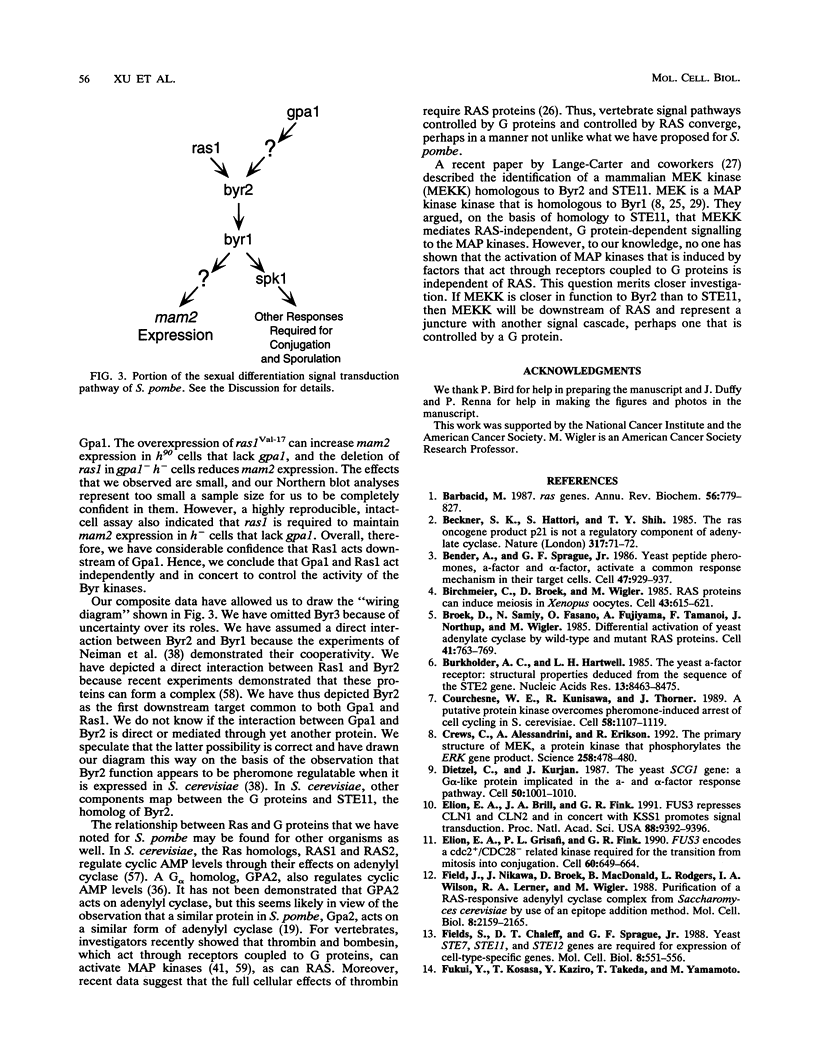


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbacid M. ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:779–827. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckner S. K., Hattori S., Shih T. Y. The ras oncogene product p21 is not a regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Nature. 1985 Sep 5;317(6032):71–72. doi: 10.1038/317071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender A., Sprague G. F., Jr Yeast peptide pheromones, a-factor and alpha-factor, activate a common response mechanism in their target cells. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):929–937. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90808-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchmeier C., Broek D., Wigler M. ras proteins can induce meiosis in Xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):615–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90233-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broek D., Samiy N., Fasano O., Fujiyama A., Tamanoi F., Northup J., Wigler M. Differential activation of yeast adenylate cyclase by wild-type and mutant RAS proteins. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):763–769. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkholder A. C., Hartwell L. H. The yeast alpha-factor receptor: structural properties deduced from the sequence of the STE2 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8463–8475. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courchesne W. E., Kunisawa R., Thorner J. A putative protein kinase overcomes pheromone-induced arrest of cell cycling in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1107–1119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90509-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews C. M., Alessandrini A., Erikson R. L. The primary structure of MEK, a protein kinase that phosphorylates the ERK gene product. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):478–480. doi: 10.1126/science.1411546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzel C., Kurjan J. The yeast SCG1 gene: a G alpha-like protein implicated in the a- and alpha-factor response pathway. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1001–1010. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90166-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion E. A., Brill J. A., Fink G. R. FUS3 represses CLN1 and CLN2 and in concert with KSS1 promotes signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9392–9396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion E. A., Grisafi P. L., Fink G. R. FUS3 encodes a cdc2+/CDC28-related kinase required for the transition from mitosis into conjugation. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):649–664. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90668-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field J., Nikawa J., Broek D., MacDonald B., Rodgers L., Wilson I. A., Lerner R. A., Wigler M. Purification of a RAS-responsive adenylyl cyclase complex from Saccharomyces cerevisiae by use of an epitope addition method. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2159–2165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Chaleff D. T., Sprague G. F., Jr Yeast STE7, STE11, and STE12 genes are required for expression of cell-type-specific genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):551–556. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen D. C., Sprague G. F., Jr Induction of the yeast alpha-specific STE3 gene by the peptide pheromone a-factor. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 5;178(4):835–852. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90314-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartig A., Holly J., Saari G., MacKay V. L. Multiple regulation of STE2, a mating-type-specific gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2106–2114. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes D. A., Fukui Y., Yamamoto M. Homologous activators of ras in fission and budding yeast. Nature. 1990 Mar 22;344(6264):355–357. doi: 10.1038/344355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isshiki T., Mochizuki N., Maeda T., Yamamoto M. Characterization of a fission yeast gene, gpa2, that encodes a G alpha subunit involved in the monitoring of nutrition. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2455–2462. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka T., Broek D., Wigler M. DNA sequence and characterization of the S. cerevisiae gene encoding adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):493–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90179-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka T., Powers S., McGill C., Fasano O., Strathern J., Broach J., Wigler M. Genetic analysis of yeast RAS1 and RAS2 genes. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):437–445. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90374-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M., Burke J., Smith M., Klar A., Beach D. Four mating-type genes control sexual differentiation in the fission yeast. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1537–1547. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02973.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura K., Shimoda C. The Schizosaccharomyces pombe mam2 gene encodes a putative pheromone receptor which has a significant homology with the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Ste2 protein. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3743–3751. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04943.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosako H., Gotoh Y., Matsuda S., Ishikawa M., Nishida E. Xenopus MAP kinase activator is a serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activated by threonine phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):2903–2908. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05359.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMorte V. J., Kennedy E. D., Collins L. R., Goldstein D., Harootunian A. T., Brown J. H., Feramisco J. R. A requirement for Ras protein function in thrombin-stimulated mitogenesis in astrocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 15;268(26):19411–19415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange-Carter C. A., Pleiman C. M., Gardner A. M., Blumer K. J., Johnson G. L. A divergence in the MAP kinase regulatory network defined by MEK kinase and Raf. Science. 1993 Apr 16;260(5106):315–319. doi: 10.1126/science.8385802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leevers S. J., Marshall C. J. Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase, ERK2, by p21ras oncoprotein. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):569–574. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05088.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda S., Kosako H., Takenaka K., Moriyama K., Sakai H., Akiyama T., Gotoh Y., Nishida E. Xenopus MAP kinase activator: identification and function as a key intermediate in the phosphorylation cascade. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):973–982. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05136.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod M., Beach D. Homology between the ran1+ gene of fission yeast and protein kinases. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3665–3671. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04697.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima I., Nakafuku M., Nakayama N., Brenner C., Miyajima A., Kaibuchi K., Arai K., Kaziro Y., Matsumoto K. GPA1, a haploid-specific essential gene, encodes a yeast homolog of mammalian G protein which may be involved in mating factor signal transduction. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1011–1019. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90167-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadin-Davis S. A., Nasim A. A gene which encodes a predicted protein kinase can restore some functions of the ras gene in fission yeast. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):985–993. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02905.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadin-Davis S. A., Nasim A., Beach D. Involvement of ras in sexual differentiation but not in growth control in fission yeast. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2963–2971. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04593.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadin-Davis S. A., Nasim A. Schizosaccharomyces pombe ras1 and byr1 are functionally related genes of the ste family that affect starvation-induced transcription of mating-type genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):549–560. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakafuku M., Obara T., Kaibuchi K., Miyajima I., Miyajima A., Itoh H., Nakamura S., Arai K., Matsumoto K., Kaziro Y. Isolation of a second yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene (GPA2) coding for guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein: studies on its structure and possible functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1374–1378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama N., Kaziro Y., Arai K., Matsumoto K. Role of STE genes in the mating factor signaling pathway mediated by GPA1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3777–3783. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neiman A. M., Stevenson B. J., Xu H. P., Sprague G. F., Jr, Herskowitz I., Wigler M., Marcus S. Functional homology of protein kinases required for sexual differentiation in Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Saccharomyces cerevisiae suggests a conserved signal transduction module in eukaryotic organisms. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Jan;4(1):107–120. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen O., Davey J., Egel R. The ras1 function of Schizosaccharomyces pombe mediates pheromone-induced transcription. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1391–1395. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05184.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obara T., Nakafuku M., Yamamoto M., Kaziro Y. Isolation and characterization of a gene encoding a G-protein alpha subunit from Schizosaccharomyces pombe: involvement in mating and sporulation pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5877–5881. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang L., Decker S. J., Saltiel A. R. Bombesin and epidermal growth factor stimulate the mitogen-activated protein kinase through different pathways in Swiss 3T3 cells. Biochem J. 1993 Jan 1;289(Pt 1):283–287. doi: 10.1042/bj2890283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponticelli A. S., Smith G. R. Chromosomal context dependence of a eukaryotic recombinational hot spot. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):227–231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROMAN H. Studies of gene mutation in Saccharomyces. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1956;21:175–185. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1956.021.01.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes N., Connell L., Errede B. STE11 is a protein kinase required for cell-type-specific transcription and signal transduction in yeast. Genes Dev. 1990 Nov;4(11):1862–1874. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.11.1862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins D. J., Cheng M., Zhen E., Vanderbilt C. A., Feig L. A., Cobb M. H. Evidence for a Ras-dependent extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK) cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6924–6928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya E. K., Polverino A. J., Chang E., Wigler M., Ruderman J. V. Oncogenic ras triggers the activation of 42-kDa mitogen-activated protein kinase in extracts of quiescent Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9831–9835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stotz A., Linder P. The ADE2 gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: sequence and new vectors. Gene. 1990 Oct 30;95(1):91–98. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90418-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto A., Iino Y., Maeda T., Watanabe Y., Yamamoto M. Schizosaccharomyces pombe ste11+ encodes a transcription factor with an HMG motif that is a critical regulator of sexual development. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):1990–1999. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.1990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Davey J., Imai Y., Yamamoto M. Schizosaccharomyces pombe map3+ encodes the putative M-factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):80–88. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatchell K., Chaleff D. T., DeFeo-Jones D., Scolnick E. M. Requirement of either of a pair of ras-related genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for spore viability. Nature. 1984 Jun 7;309(5968):523–527. doi: 10.1038/309523a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas S. M., DeMarco M., D'Arcangelo G., Halegoua S., Brugge J. S. Ras is essential for nerve growth factor- and phorbol ester-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of MAP kinases. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1031–1040. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90075-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Shimanuki M., Yanagida M. Fission yeast genes that confer resistance to staurosporine encode an AP-1-like transcription factor and a protein kinase related to the mammalian ERK1/MAP2 and budding yeast FUS3 and KSS1 kinases. Genes Dev. 1991 Jan;5(1):60–73. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Uno I., Ishikawa T., Powers S., Kataoka T., Broek D., Cameron S., Broach J., Matsumoto K., Wigler M. In yeast, RAS proteins are controlling elements of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):27–36. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90305-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Aelst L., Barr M., Marcus S., Polverino A., Wigler M. Complex formation between RAS and RAF and other protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6213–6217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vouret-Craviari V., Van Obberghen-Schilling E., Scimeca J. C., Van Obberghen E., Pouysségur J. Differential activation of p44mapk (ERK1) by alpha-thrombin and thrombin-receptor peptide agonist. Biochem J. 1993 Jan 1;289(Pt 1):209–214. doi: 10.1042/bj2890209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Boguski M., Riggs M., Rodgers L., Wigler M. sar1, a gene from Schizosaccharomyces pombe encoding a protein that regulates ras1. Cell Regul. 1991 Jun;2(6):453–465. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.6.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Xu H. P., Riggs M., Rodgers L., Wigler M. byr2, a Schizosaccharomyces pombe gene encoding a protein kinase capable of partial suppression of the ras1 mutant phenotype. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3554–3563. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteway M., Hougan L., Dignard D., Thomas D. Y., Bell L., Saari G. C., Grant F. J., O'Hara P., MacKay V. L. The STE4 and STE18 genes of yeast encode potential beta and gamma subunits of the mating factor receptor-coupled G protein. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):467–477. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90249-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood K. W., Sarnecki C., Roberts T. M., Blenis J. ras mediates nerve growth factor receptor modulation of three signal-transducing protein kinases: MAP kinase, Raf-1, and RSK. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1041–1050. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90076-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu H. P., Rajavashisth T., Grewal N., Jung V., Riggs M., Rodgers L., Wigler M. A gene encoding a protein with seven zinc finger domains acts on the sexual differentiation pathways of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jul;3(7):721–734. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.7.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu H. P., Riggs M., Rodgers L., Wigler M. A gene from S. pombe with homology to E. coli RNAse III blocks conjugation and sporulation when overexpressed in wild type cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5304–5304. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu H. P., Wang Y., Riggs M., Rodgers L., Wigler M. Biological activity of the mammalian RAP genes in yeast. Cell Regul. 1990 Sep;1(10):763–769. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.10.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]