Abstract
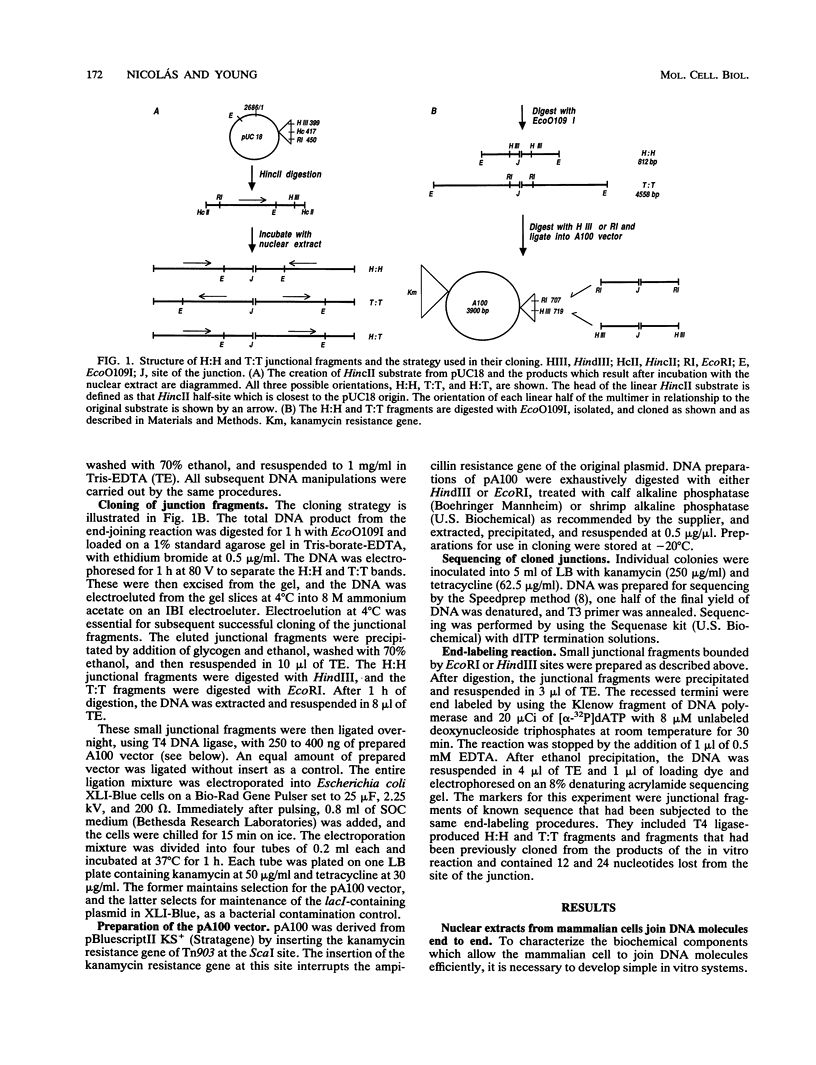
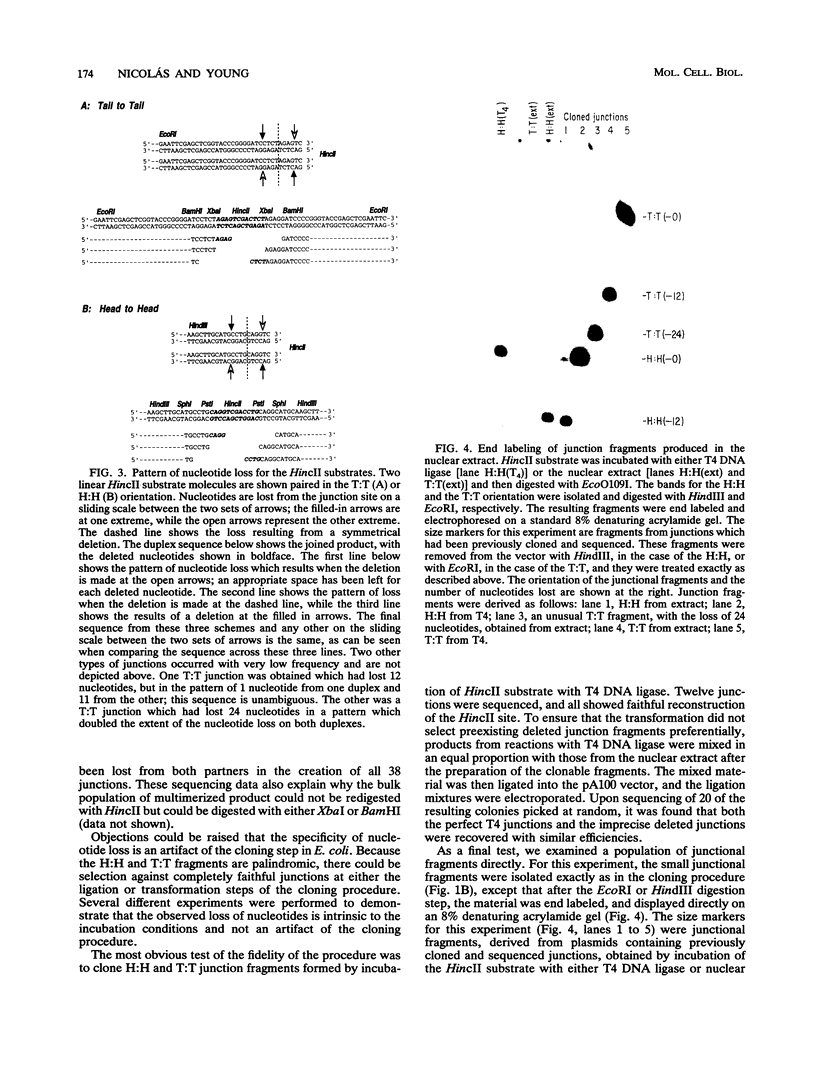
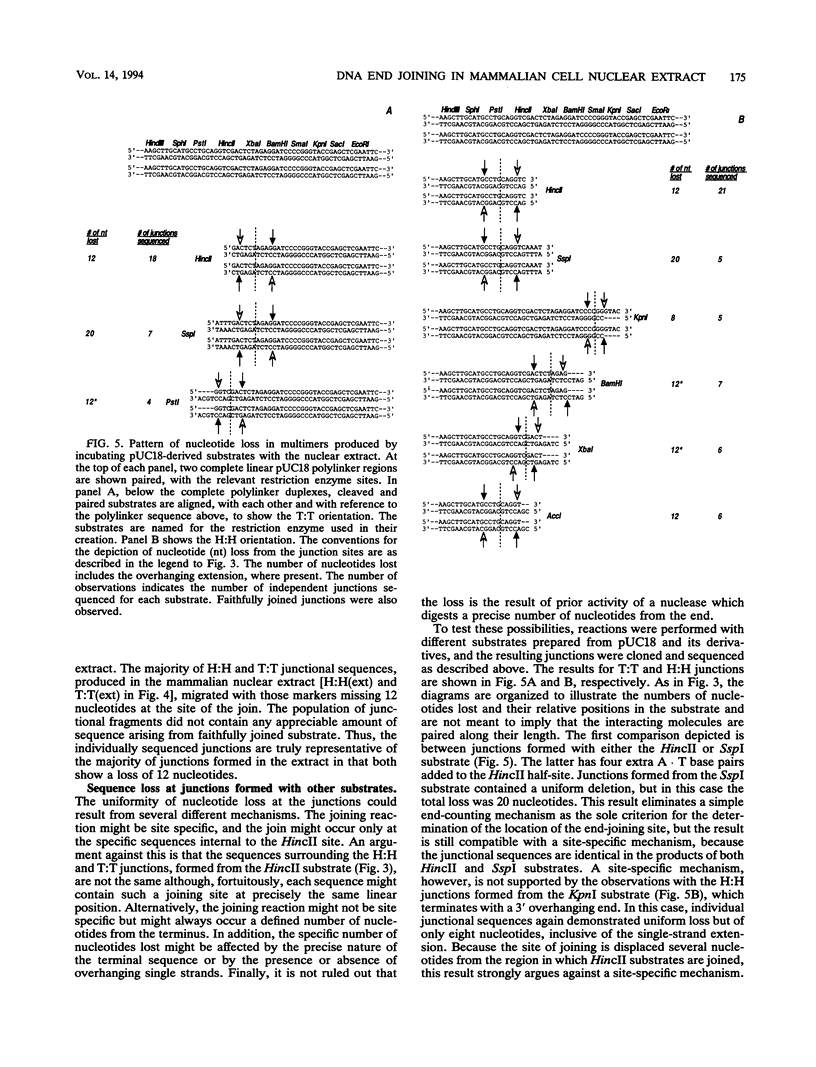
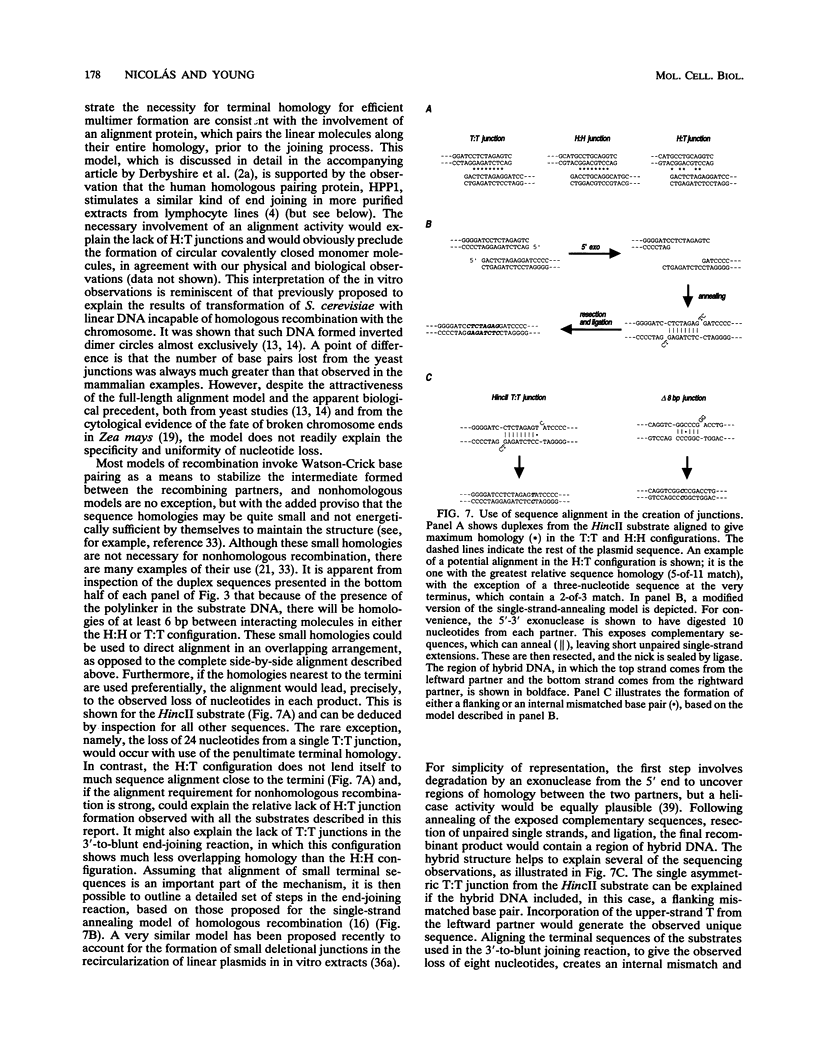
Mammalian cells have a marked capacity to repair double-strand breaks in DNA, but the molecular and biochemical mechanisms underlying this process are largely unknown. A previous report has described an activity from mammalian cell nuclei that is capable of multimerizing blunt-ended DNA substrates (R. Fishel, M.K. Derbyshire, S.P. Moore, and C.S.H. Young, Biochimie 73:257-267, 1991). In this report, we show that nuclear extracts from HeLa cells contain activities which preferentially join linear plasmid substrates in either a head-to-head or tail-to-tail configuration, that the joining reaction is covalent, and that the joining is accompanied by loss of sequence at the junction. Sequencing revealed that there was a loss of a uniform number of nucleotides from junctions formed from any one type of substrate. The loss was not determined by any simple site-specific mechanism, but the number of nucleotides lost was affected by the precise terminal sequence. There was no major effect on the efficiency or outcome of the joining reaction with substrates containing blunt ends or 3' or 5' protruding ends. Using a pair of plasmid molecules with distinguishable restriction enzyme sites, we also observed that blunt-ended DNA substrates could join with those containing protruding 3' ends. As with the junctions formed between molecules with identical ends, there was uniform loss of nucleotides. Taken together, the data are consistent with two models for the joining reaction in which molecules are aligned either throughout most of their length or by using small sequence homologies located toward their ends. Although either model can explain the preferential formation of head-to-head and tail-to-tail products, the latter predicts the precise lossof nucleotides observed. These activities are found in all cell lines examined so far and most likely represent an important repair activity of the mammalian cell.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett C. B., Lewis A. L., Baldwin K. K., Resnick M. A. Lethality induced by a single site-specific double-strand break in a dispensable yeast plasmid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5613–5617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biedermann K. A., Sun J. R., Giaccia A. J., Tosto L. M., Brown J. M. scid mutation in mice confers hypersensitivity to ionizing radiation and a deficiency in DNA double-strand break repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1394–1397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derbyshire M. K., Epstein L. H., Young C. S., Munz P. L., Fishel R. Nonhomologous recombination in human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):156–169. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairman M. P., Johnson A. P., Thacker J. Multiple components are involved in the efficient joining of double stranded DNA breaks in human cell extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 25;20(16):4145–4152. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.16.4145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishel R., Derbyshire M. K., Moore S. P., Young C. S. Biochemical studies of homologous and nonhomologous recombination in human cells. Biochimie. 1991 Feb-Mar;73(2-3):257–267. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90211-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folger K. R., Wong E. A., Wahl G., Capecchi M. R. Patterns of integration of DNA microinjected into cultured mammalian cells: evidence for homologous recombination between injected plasmid DNA molecules. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;2(11):1372–1387. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.11.1372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg E. C. Deoxyribonucleic acid repair in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Mar;52(1):70–102. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.1.70-102.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulop G. M., Phillips R. A. The scid mutation in mice causes a general defect in DNA repair. Nature. 1990 Oct 4;347(6292):479–482. doi: 10.1038/347479a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson E. A., Qin X. Q., Bump E. A., Schatz D. G., Oettinger M., Weaver D. T. A link between double-strand break-related repair and V(D)J recombination: the scid mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4061–4065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. N., Symington L. S. A 5'-3' exonuclease from Saccharomyces cerevisiae is required for in vitro recombination between linear DNA molecules with overlapping homology. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3125–3134. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeggo P. A. Studies on mammalian mutants defective in rejoining double-strand breaks in DNA. Mutat Res. 1990 Jul;239(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0165-1110(90)90028-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. W., Kolodner R. D. Strand exchange protein 1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. A novel multifunctional protein that contains DNA strand exchange and exonuclease activities. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):14046–14054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunes S., Botstein D., Fox M. S. Synapsis-mediated fusion of free DNA ends forms inverted dimer plasmids in yeast. Genetics. 1990 Jan;124(1):67–80. doi: 10.1093/genetics/124.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunes S., Botstein D., Fox M. S. Transformation of yeast with linearized plasmid DNA. Formation of inverted dimers and recombinant plasmid products. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 5;184(3):375–387. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90288-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman C. W., Carroll D. Homologous recombination catalyzed by a nuclear extract from Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10840–10844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. L., Sperle K., Sternberg N. Model for homologous recombination during transfer of DNA into mouse L cells: role for DNA ends in the recombination process. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1020–1034. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Barnes D. E. Mammalian DNA ligases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:251–281. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malone R. E., Esposito R. E. The RAD52 gene is required for homothallic interconversion of mating types and spontaneous mitotic recombination in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):503–507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClintock B. The Behavior in Successive Nuclear Divisions of a Chromosome Broken at Meiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1939 Aug;25(8):405–416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.25.8.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S. P., Fishel R. Purification and characterization of a protein from human cells which promotes homologous pairing of DNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11108–11117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munz P. L., Young C. S. The creation of adenovirus genomes with viable, stable, internal redundancies centered about the E2b region. Virology. 1987 May;158(1):52–60. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90237-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murnane J. P., Yezzi M. J., Young B. R. Recombination events during integration of transfected DNA into normal human cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 11;18(9):2733–2738. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.9.2733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalbantoglu J., Miles C., Meuth M. Insertion of unique and repetitive DNA fragments into the aprt locus of hamster cells. J Mol Biol. 1988 Apr 5;200(3):449–459. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90535-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North P., Ganesh A., Thacker J. The rejoining of double-strand breaks in DNA by human cell extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6205–6210. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandita T. K., Hittelman W. N. Initial chromosome damage but not DNA damage is greater in ataxia telangiectasia cells. Radiat Res. 1992 Apr;130(1):94–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandita T. K., Hittelman W. N. The contribution of DNA and chromosome repair deficiencies to the radiosensitivity of ataxia-telangiectasia. Radiat Res. 1992 Aug;131(2):214–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perucho M., Hanahan D., Wigler M. Genetic and physical linkage of exogenous sequences in transformed cells. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):309–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90178-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. L., Orth K., Calame K. L. Binding in vitro of multiple cellular proteins to immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4168–4178. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer P., Vielmetter W. Joining of nonhomologous DNA double strand breaks in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):907–924. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins D. M., Ripley S., Henderson A. S., Axel R. Transforming DNA integrates into the host chromosome. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):29–39. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90267-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. B., Porter T. N., Wilson J. H. Mechanisms of nonhomologous recombination in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2599–2607. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. B., Wilson J. H. Nonhomologous recombination in mammalian cells: role for short sequence homologies in the joining reaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4295–4304. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer L., Roy R., Humbert S., Moncollin V., Vermeulen W., Hoeijmakers J. H., Chambon P., Egly J. M. DNA repair helicase: a component of BTF2 (TFIIH) basic transcription factor. Science. 1993 Apr 2;260(5104):58–63. doi: 10.1126/science.8465201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Orr-Weaver T. L., Rothstein R. J., Stahl F. W. The double-strand-break repair model for recombination. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90331-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thacker J., Chalk J., Ganesh A., North P. A mechanism for deletion formation in DNA by human cell extracts: the involvement of short sequence repeats. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 11;20(23):6183–6188. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.23.6183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thacker J. The use of integrating DNA vectors to analyse the molecular defects in ionising radiation-sensitive mutants of mammalian cells including ataxia telangiectasia. Mutat Res. 1989 Mar-May;220(2-3):187–204. doi: 10.1016/0165-1110(89)90024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thode S., Schäfer A., Pfeiffer P., Vielmetter W. A novel pathway of DNA end-to-end joining. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90340-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troelstra C., van Gool A., de Wit J., Vermeulen W., Bootsma D., Hoeijmakers J. H. ERCC6, a member of a subfamily of putative helicases, is involved in Cockayne's syndrome and preferential repair of active genes. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):939–953. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90390-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake C. T., Vernaleone F., Wilson J. H. Topological requirements for homologous recombination among DNA molecules transfected into mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2080–2089. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiffenbach B., Haber J. E. Homothallic mating type switching generates lethal chromosome breaks in rad52 strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;1(6):522–534. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.6.522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. H., Berget P. B., Pipas J. M. Somatic cells efficiently join unrelated DNA segments end-to-end. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;2(10):1258–1269. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.10.1258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]