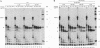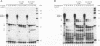Abstract
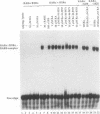
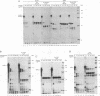
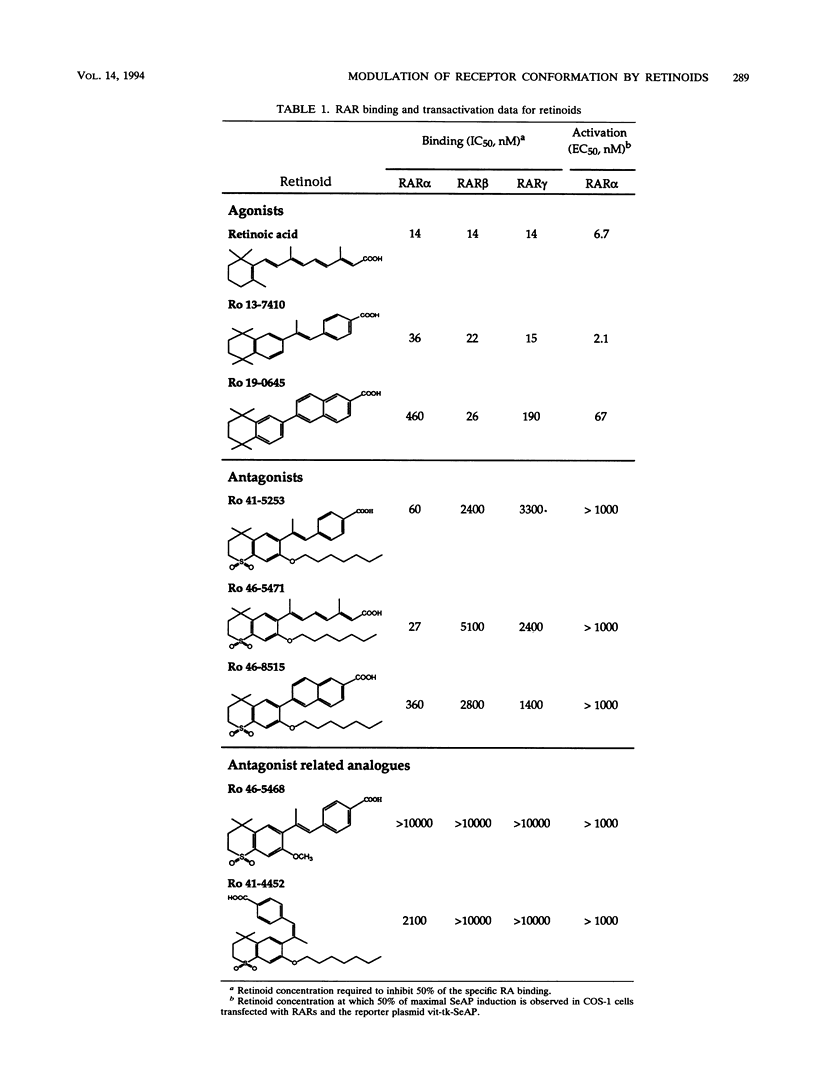
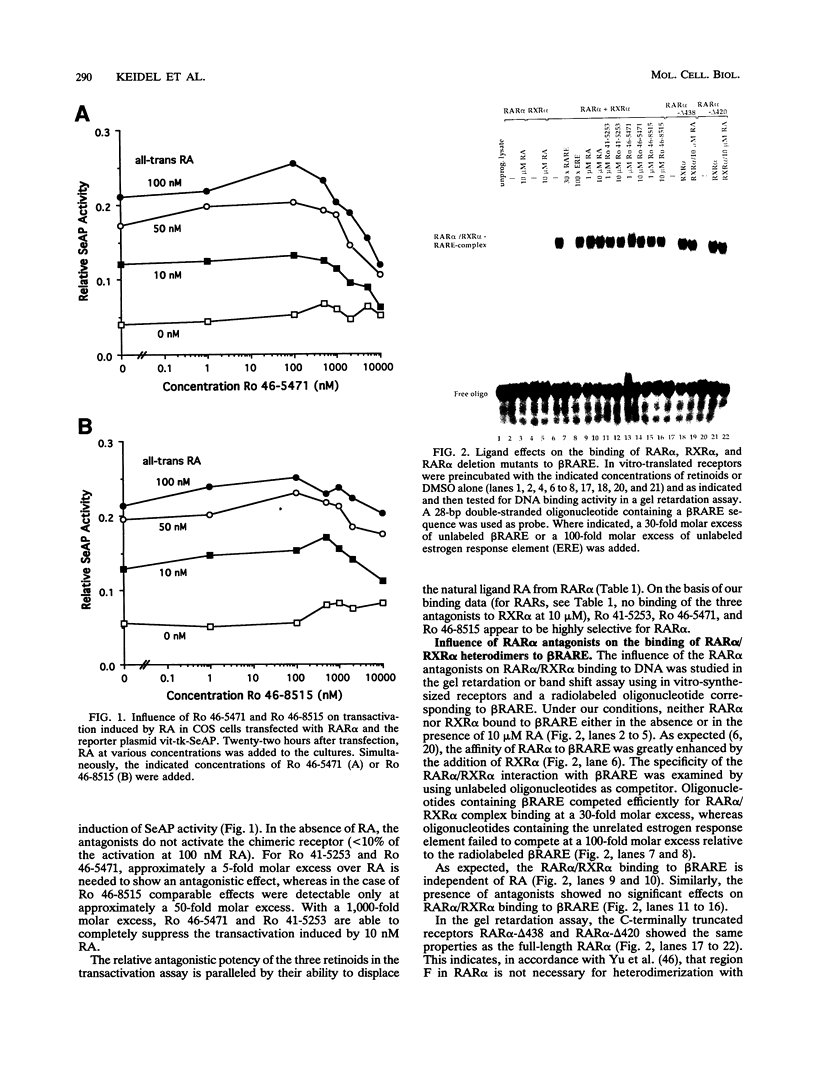
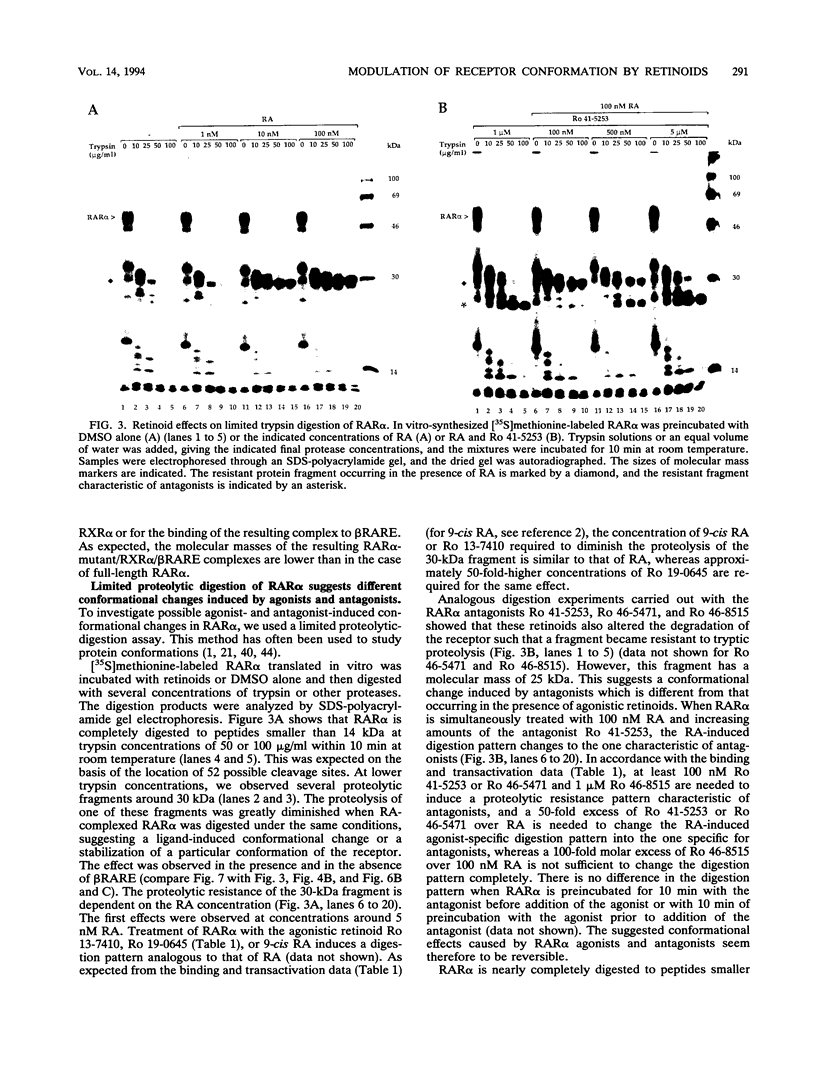
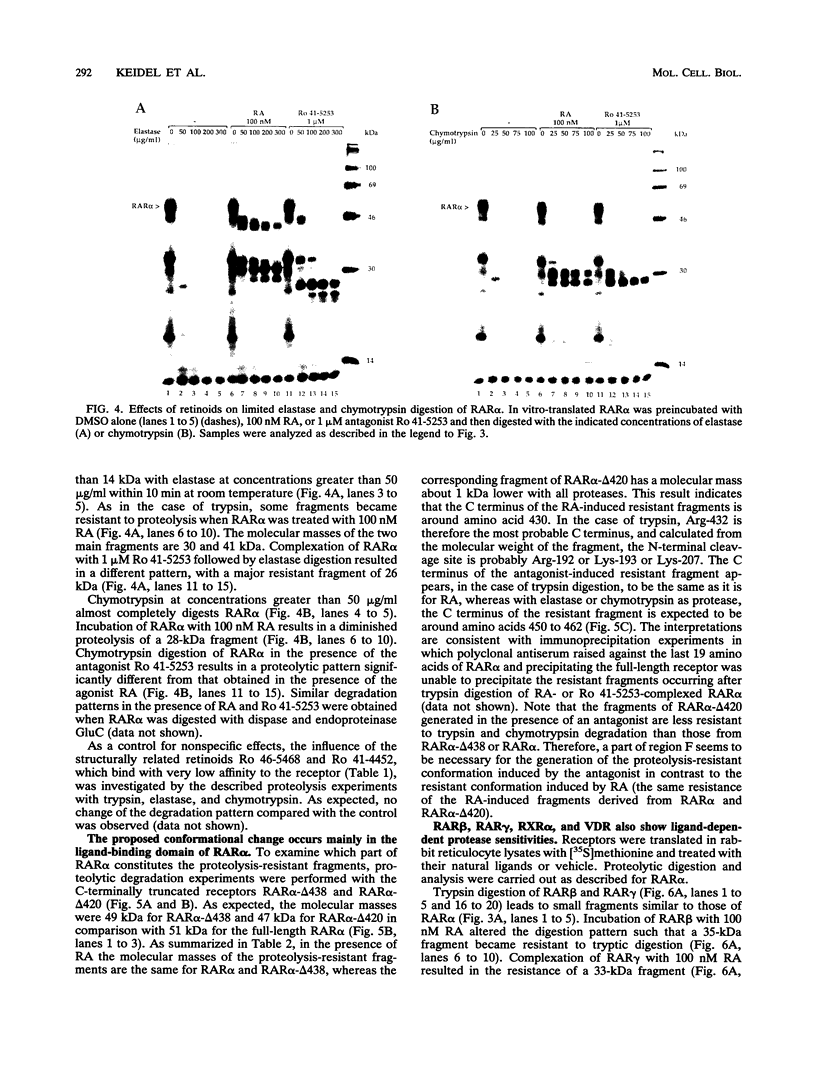
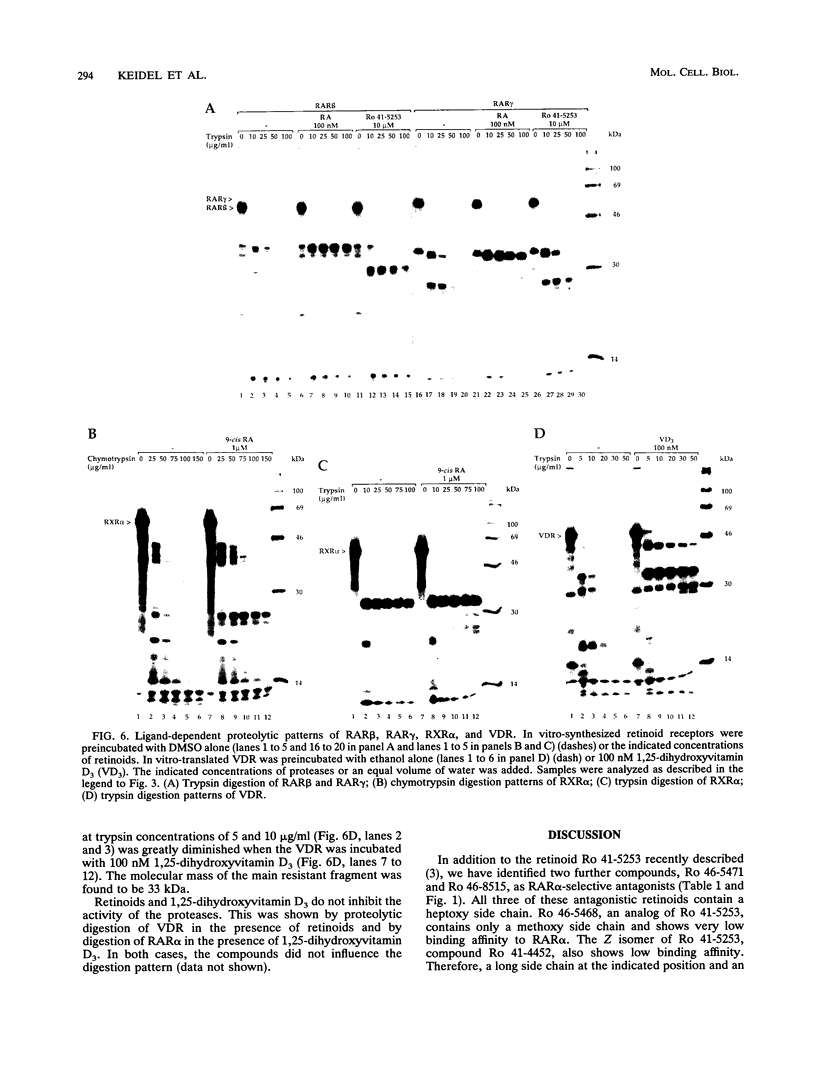
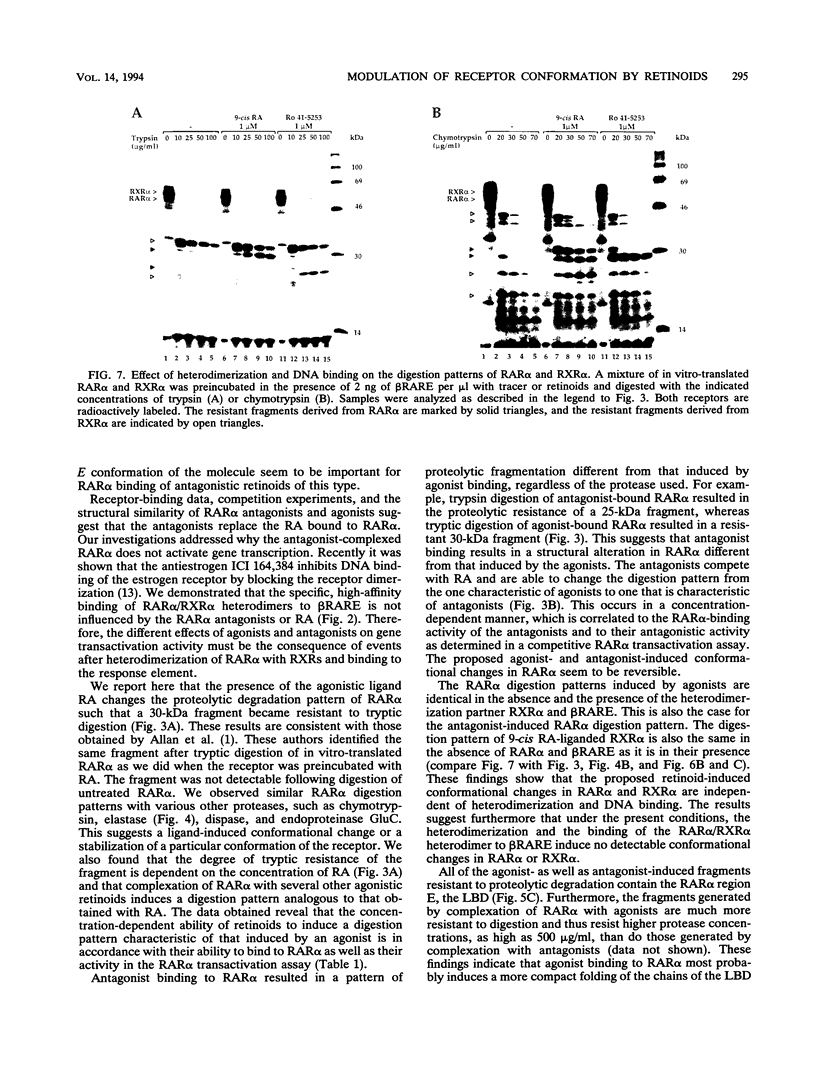
The pleiotropic effects of retinoic acid on cell differentiation and proliferation are mediated by two subfamilies of nuclear receptors, the retinoic acid receptors (RARs) and the retinoid X receptors (RXRs). Recently the synthetic retinoid Ro 41-5253 was identified as a selective RAR alpha antagonist. As demonstrated by gel retardation assays, Ro 41-5253 and two related new RAR alpha antagonists do not influence RAR alpha/RXR alpha heterodimerization and DNA binding. In a limited trypsin digestion assay, complexation of RAR alpha with retinoic acid or several other agonistic retinoids altered the degradation of the receptor such that a 30-kDa proteolytic fragment became resistant to proteolysis. This suggests a ligand-induced conformational change, which may be necessary for the interaction of the DNA-bound RAR alpha/RXR alpha heterodimer with other transcription factors. Our results demonstrate that antagonists compete with agonists for binding to RAR alpha and may induce a different structural alteration, suggested by the tryptic resistance of a shorter 25-kDa protein fragment in the digestion assay. This RAR alpha conformation seems to allow RAR alpha/RXR alpha binding to DNA but not the subsequent transactivation of target genes. Protease mapping with C-terminally truncated receptors revealed that the proposed conformational changes mainly occur in the DE regions of RAR alpha. Complexation of RAR beta, RAR gamma, and RXR alpha, as well as the vitamin D3 receptor, with their natural ligands resulted in a similar resistance of fragments to proteolytic digestion. This could mean that ligand-induced conformational changes are a general feature in the hormonal activation of vitamin D3 and retinoid receptors.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan G. F., Leng X., Tsai S. Y., Weigel N. L., Edwards D. P., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Hormone and antihormone induce distinct conformational changes which are central to steroid receptor activation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19513–19520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allenby G., Bocquel M. T., Saunders M., Kazmer S., Speck J., Rosenberger M., Lovey A., Kastner P., Grippo J. F., Chambon P. Retinoic acid receptors and retinoid X receptors: interactions with endogenous retinoic acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):30–34. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apfel C., Bauer F., Crettaz M., Forni L., Kamber M., Kaufmann F., LeMotte P., Pirson W., Klaus M. A retinoic acid receptor alpha antagonist selectively counteracts retinoic acid effects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7129–7133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benbrook D., Lernhardt E., Pfahl M. A new retinoic acid receptor identified from a hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):669–672. doi: 10.1038/333669a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugge T. H., Pohl J., Lonnoy O., Stunnenberg H. G. RXR alpha, a promiscuous partner of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptors. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1409–1418. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05186.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlberg C., Bendik I., Wyss A., Meier E., Sturzenbecker L. J., Grippo J. F., Hunziker W. Two nuclear signalling pathways for vitamin D. Nature. 1993 Feb 18;361(6413):657–660. doi: 10.1038/361657a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollé P., Ruberte E., Leroy P., Morriss-Kay G., Chambon P. Retinoic acid receptors and cellular retinoid binding proteins. I. A systematic study of their differential pattern of transcription during mouse organogenesis. Development. 1990 Dec;110(4):1133–1151. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.4.1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichele G. Retinoids and vertebrate limb pattern formation. Trends Genet. 1989 Aug;5(8):246–251. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90096-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawell S. E., White R., Hoare S., Sydenham M., Page M., Parker M. G. Inhibition of estrogen receptor-DNA binding by the "pure" antiestrogen ICI 164,384 appears to be mediated by impaired receptor dimerization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6883–6887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguere V., Ong E. S., Segui P., Evans R. M. Identification of a receptor for the morphogen retinoic acid. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):624–629. doi: 10.1038/330624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronemeyer H. Transcription activation by estrogen and progesterone receptors. Annu Rev Genet. 1991;25:89–123. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.25.120191.000513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyman R. A., Mangelsdorf D. J., Dyck J. A., Stein R. B., Eichele G., Evans R. M., Thaller C. 9-cis retinoic acid is a high affinity ligand for the retinoid X receptor. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90479-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastner P., Krust A., Mendelsohn C., Garnier J. M., Zelent A., Leroy P., Staub A., Chambon P. Murine isoforms of retinoic acid receptor gamma with specific patterns of expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2700–2704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keidel S., Rupp E., Szardenings M. Recombinant human retinoic acid receptor alpha. Binding of DNA and synthetic retinoids to the protein expressed in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Mar 15;204(3):1141–1148. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16739.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller H., Dreyer C., Medin J., Mahfoudi A., Ozato K., Wahli W. Fatty acids and retinoids control lipid metabolism through activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-retinoid X receptor heterodimers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2160–2164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer S. A., Umesono K., Mangelsdorf D. J., Evans R. M. Retinoid X receptor interacts with nuclear receptors in retinoic acid, thyroid hormone and vitamin D3 signalling. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):446–449. doi: 10.1038/355446a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouns W. C., Hadvary P., Haering P., Steiner B. Conformational modulation of purified glycoprotein (GP) IIb-IIIa allows proteolytic generation of active fragments from either active or inactive GPIIb-IIIa. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18844–18851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krust A., Kastner P., Petkovich M., Zelent A., Chambon P. A third human retinoic acid receptor, hRAR-gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5310–5314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leid M., Kastner P., Lyons R., Nakshatri H., Saunders M., Zacharewski T., Chen J. Y., Staub A., Garnier J. M., Mader S. Purification, cloning, and RXR identity of the HeLa cell factor with which RAR or TR heterodimerizes to bind target sequences efficiently. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):377–395. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90478-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy P., Krust A., Zelent A., Mendelsohn C., Garnier J. M., Kastner P., Dierich A., Chambon P. Multiple isoforms of the mouse retinoic acid receptor alpha are generated by alternative splicing and differential induction by retinoic acid. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):59–69. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07921.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin A. A., Sturzenbecker L. J., Kazmer S., Bosakowski T., Huselton C., Allenby G., Speck J., Kratzeisen C., Rosenberger M., Lovey A. 9-cis retinoic acid stereoisomer binds and activates the nuclear receptor RXR alpha. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):359–361. doi: 10.1038/355359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan R., Clifford J. L. Nuclear receptors for retinoids: mediators of retinoid effects on normal and malignant cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 1991;45(4-5):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0753-3322(91)90102-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan R. Effects of vitamin A and its analogs (retinoids) on normal and neoplastic cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Mar 12;605(1):33–91. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(80)90021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Borgmeyer U., Heyman R. A., Zhou J. Y., Ong E. S., Oro A. E., Kakizuka A., Evans R. M. Characterization of three RXR genes that mediate the action of 9-cis retinoic acid. Genes Dev. 1992 Mar;6(3):329–344. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.3.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Ong E. S., Dyck J. A., Evans R. M. Nuclear receptor that identifies a novel retinoic acid response pathway. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):224–229. doi: 10.1038/345224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Umesono K., Kliewer S. A., Borgmeyer U., Ong E. S., Evans R. M. A direct repeat in the cellular retinol-binding protein type II gene confers differential regulation by RXR and RAR. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):555–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks M. S., Hallenbeck P. L., Nagata T., Segars J. H., Appella E., Nikodem V. M., Ozato K. H-2RIIBP (RXR beta) heterodimerization provides a mechanism for combinatorial diversity in the regulation of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone responsive genes. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1419–1435. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05187.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagpal S., Friant S., Nakshatri H., Chambon P. RARs and RXRs: evidence for two autonomous transactivation functions (AF-1 and AF-2) and heterodimerization in vivo. EMBO J. 1993 Jun;12(6):2349–2360. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05889.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagpal S., Saunders M., Kastner P., Durand B., Nakshatri H., Chambon P. Promoter context- and response element-dependent specificity of the transcriptional activation and modulating functions of retinoic acid receptors. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):1007–1019. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90250-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petkovich M., Brand N. J., Krust A., Chambon P. A human retinoic acid receptor which belongs to the family of nuclear receptors. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):444–450. doi: 10.1038/330444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruberte E., Dolle P., Chambon P., Morriss-Kay G. Retinoic acid receptors and cellular retinoid binding proteins. II. Their differential pattern of transcription during early morphogenesis in mouse embryos. Development. 1991 Jan;111(1):45–60. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruberte E., Friederich V., Chambon P., Morriss-Kay G. Retinoic acid receptors and cellular retinoid binding proteins. III. Their differential transcript distribution during mouse nervous system development. Development. 1993 May;118(1):267–282. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.1.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Matthias P., Müller M. M., Schaffner W. Identification of a novel lymphoid specific octamer binding protein (OTF-2B) by proteolytic clipping bandshift assay (PCBA). EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4221–4229. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03319.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schräder M., Wyss A., Sturzenbecker L. J., Grippo J. F., LeMotte P., Carlberg C. RXR-dependent and RXR-independent transactivation by retinoic acid receptors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Mar 11;21(5):1231–1237. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.5.1231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons S. S., Jr, Sistare F. D., Chakraborti P. K. Steroid binding activity is retained in a 16-kDa fragment of the steroid binding domain of rat glucocorticoid receptors. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14493–14497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. A., Parkinson D. R., Cheson B. D., Friedman M. A. Retinoids in cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol. 1992 May;10(5):839–864. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1992.10.5.839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sucov H. M., Murakami K. K., Evans R. M. Characterization of an autoregulated response element in the mouse retinoic acid receptor type beta gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5392–5396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan S., Richmond T. J. DNA binding-induced conformational change of the yeast transcriptional activator PRTF. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):367–377. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90373-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vivanco Ruiz M. M., Bugge T. H., Hirschmann P., Stunnenberg H. G. Functional characterization of a natural retinoic acid responsive element. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3829–3838. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04952.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. C., Delsert C., Andersen B., Holloway J. M., Devary O. V., När A. M., Kim S. Y., Boutin J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. RXR beta: a coregulator that enhances binding of retinoic acid, thyroid hormone, and vitamin D receptors to their cognate response elements. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1251–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90301-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelent A., Krust A., Petkovich M., Kastner P., Chambon P. Cloning of murine alpha and beta retinoic acid receptors and a novel receptor gamma predominantly expressed in skin. Nature. 1989 Jun 29;339(6227):714–717. doi: 10.1038/339714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelent A., Mendelsohn C., Kastner P., Krust A., Garnier J. M., Ruffenach F., Leroy P., Chambon P. Differentially expressed isoforms of the mouse retinoic acid receptor beta generated by usage of two promoters and alternative splicing. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):71–81. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07922.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Hoffmann B., Tran P. B., Graupner G., Pfahl M. Retinoid X receptor is an auxiliary protein for thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):441–446. doi: 10.1038/355441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Lehmann J., Hoffmann B., Dawson M. I., Cameron J., Graupner G., Hermann T., Tran P., Pfahl M. Homodimer formation of retinoid X receptor induced by 9-cis retinoic acid. Nature. 1992 Aug 13;358(6387):587–591. doi: 10.1038/358587a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Thé H., Marchio A., Tiollais P., Dejean A. A novel steroid thyroid hormone receptor-related gene inappropriately expressed in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):667–670. doi: 10.1038/330667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]