Abstract
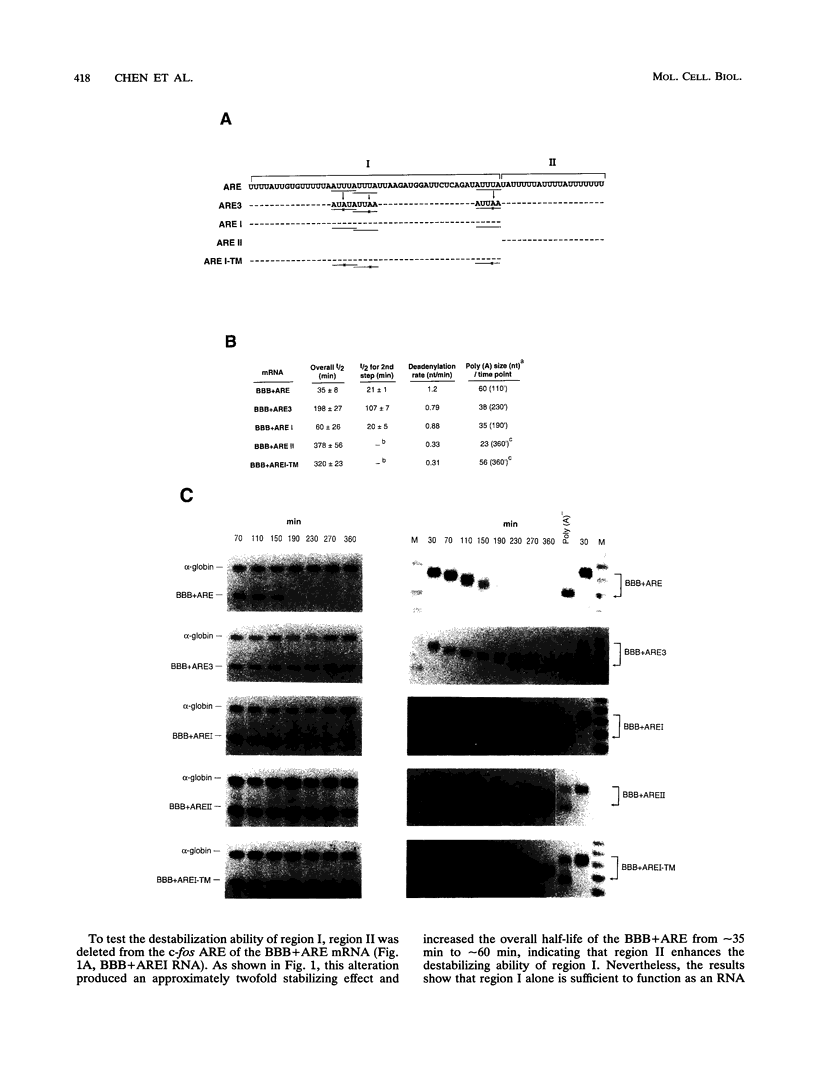
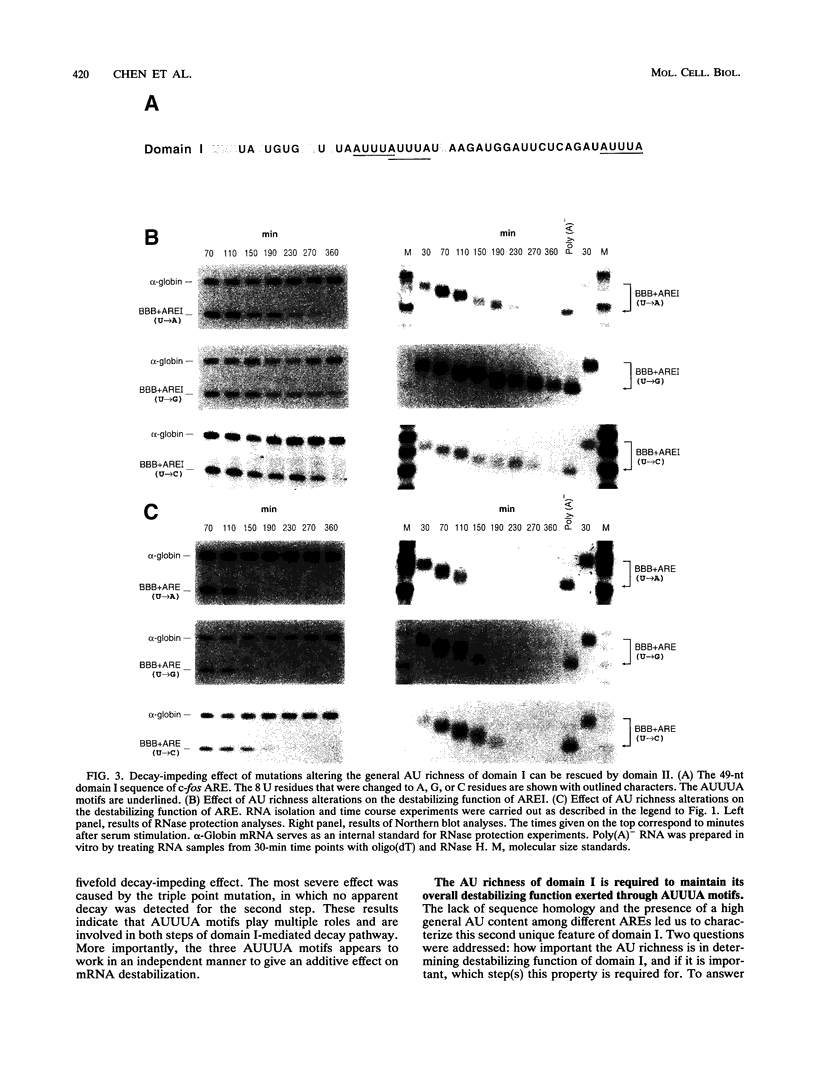
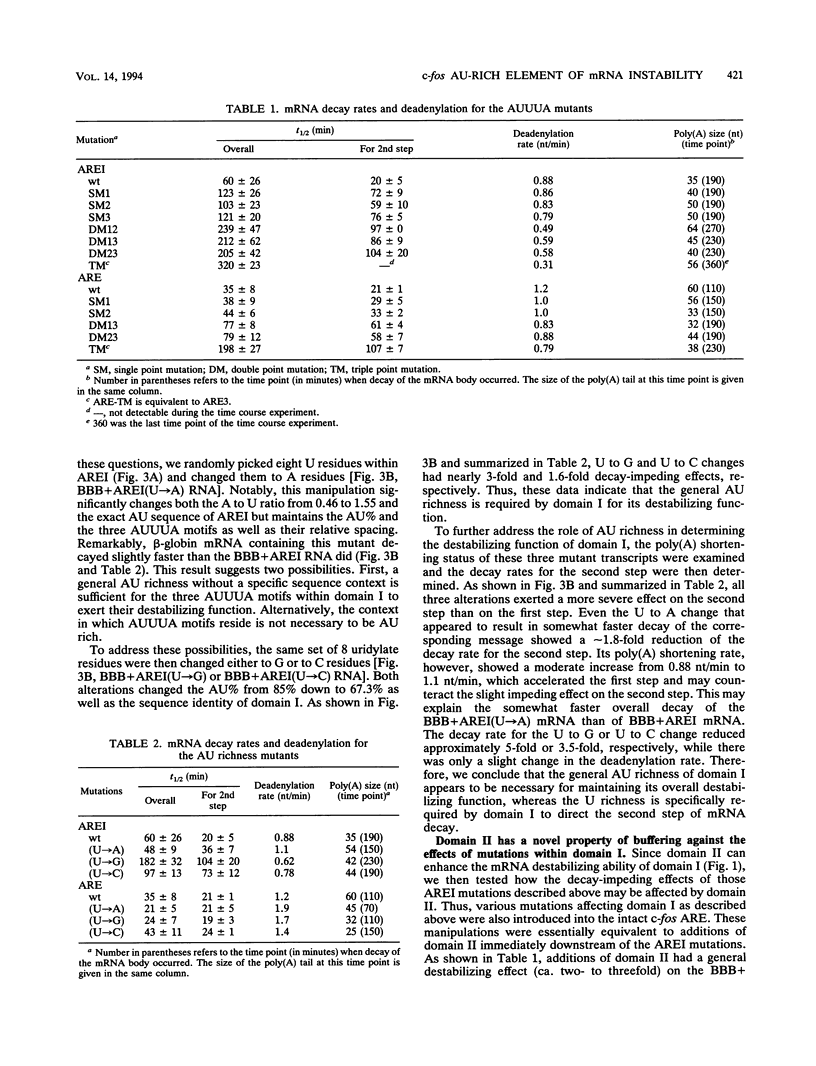
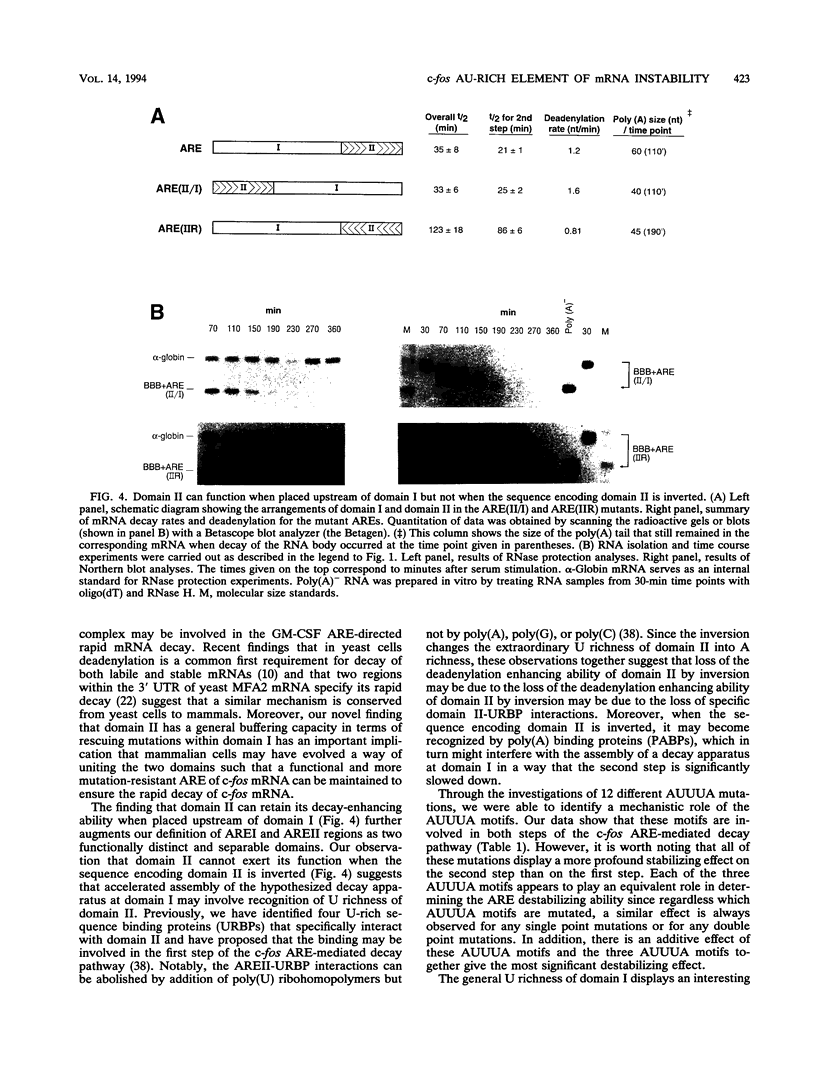
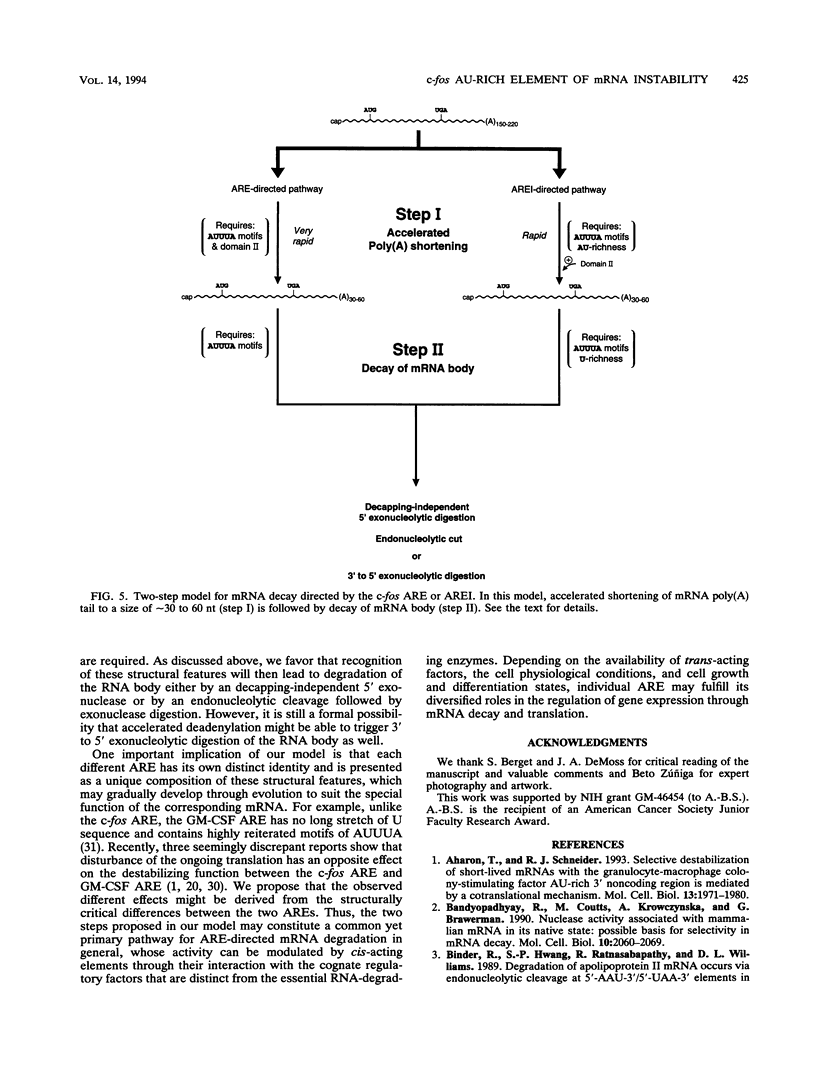
AU-rich elements (ARE) in the 3' untranslated region of many highly labile mRNAs for proto-oncogenes, lymphokines, and cytokines can act as an RNA-destabilizing element. The absence of a clear understanding of the key sequence and structural features of the ARE that are required for its destabilizing function has precluded the further elucidation of its mode of action and the basis of its specificity. Combining extensive mutagenesis of the c-fos ARE with in vivo analysis of mRNA stability, we were able to identify mutations that exhibited kinetic phenotypes consistent with the biphasic decay characteristic of a two-step mechanism: accelerated poly(A) shortening and subsequent decay of the transcribed portion of the mRNA. These mutations, which affected either an individual step or both steps, all changed the mRNA stability. Our experiments further revealed the existence of two structurally distinct and functionally interdependent domains that constitute the c-fos ARE. Domain I, which is located within the 5' 49-nucleotide segment of the ARE and contains the three AUUUA motifs, can function as an RNA destabilizer by itself. It forms the essential core unit necessary for the ARE-destabilizing function. Domain II is a 20-nucleotide U-rich sequence which is located within the 3' part of the c-fos ARE. Although it alone can not act as an RNA destabilizer, this domain serves two critical roles: (i) its presence enhances the destabilizing ability of domain I by accelerating the deadenylation step, and (ii) it has a novel capacity of buffering decay-impeding effects exerted by mutations introduced within domain I. A model is proposed to explain how these critical structural features may be involved in the c-fos ARE-directed mRNA decay pathway. These findings have important implications for furthering our understanding of the molecular basis of differential mRNA decay mediated by different AREs.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aharon T., Schneider R. J. Selective destabilization of short-lived mRNAs with the granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor AU-rich 3' noncoding region is mediated by a cotranslational mechanism. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1971–1980. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandyopadhyay R., Coutts M., Krowczynska A., Brawerman G. Nuclease activity associated with mammalian mRNA in its native state: possible basis for selectivity in mRNA decay. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2060–2069. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. mRNA decay: finding the right targets. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):9–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90166-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer G., Ross J. Poly(A) shortening and degradation of the 3' A+U-rich sequences of human c-myc mRNA in a cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1697–1708. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. D., Harland R. M. Endonucleolytic cleavage of a maternal homeo box mRNA in Xenopus oocytes. Genes Dev. 1990 Nov;4(11):1925–1935. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.11.1925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caput D., Beutler B., Hartog K., Thayer R., Brown-Shimer S., Cerami A. Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Yen T. J. Multiple determinants of eukaryotic mRNA stability. New Biol. 1989 Nov;1(2):121–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutts M., Brawerman G. A 5' exoribonuclease from cytoplasmic extracts of mouse sarcoma 180 ascites cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Apr 29;1173(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(93)90242-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker C. J., Parker R. A turnover pathway for both stable and unstable mRNAs in yeast: evidence for a requirement for deadenylation. Genes Dev. 1993 Aug;7(8):1632–1643. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.8.1632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Rech J., Vie A., Piechaczyk M., Bonnieu A., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Regulation of c-fos gene expression in hamster fibroblasts: initiation and elongation of transcription and mRNA degradation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5657–5667. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallie D. R. The cap and poly(A) tail function synergistically to regulate mRNA translational efficiency. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):2108–2116. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.2108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu C. L., Stevens A. Yeast cells lacking 5'-->3' exoribonuclease 1 contain mRNA species that are poly(A) deficient and partially lack the 5' cap structure. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;13(8):4826–4835. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.4826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huarte J., Stutz A., O'Connell M. L., Gubler P., Belin D., Darrow A. L., Strickland S., Vassalli J. D. Transient translational silencing by reversible mRNA deadenylation. Cell. 1992 Jun 12;69(6):1021–1030. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90620-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. J., Standart N. Do the poly(A) tail and 3' untranslated region control mRNA translation? Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):15–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90235-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. R., Cole M. D. Rapid cytoplasmic turnover of c-myc mRNA: requirement of the 3' untranslated sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4513–4521. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeller D. M., Horowitz J. A., Casey J. L., Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. Translation and the stability of mRNAs encoding the transferrin receptor and c-fos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7778–7782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird-Offringa I. A., de Wit C. L., Elfferich P., van der Eb A. J. Poly(A) tail shortening is the translation-dependent step in c-myc mRNA degradation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6132–6140. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muhlrad D., Parker R. Mutations affecting stability and deadenylation of the yeast MFA2 transcript. Genes Dev. 1992 Nov;6(11):2100–2111. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.11.2100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munroe D., Jacobson A. Tales of poly(A): a review. Gene. 1990 Jul 16;91(2):151–158. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90082-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltz S. W., Brewer G., Bernstein P., Hart P. A., Ross J. Regulation of mRNA turnover in eukaryotic cells. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1991;1(2):99–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahmsdorf H. J., Schönthal A., Angel P., Litfin M., Rüther U., Herrlich P. Posttranscriptional regulation of c-fos mRNA expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1643–1659. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B., Davis R. W. The poly(A) binding protein is required for poly(A) shortening and 60S ribosomal subunit-dependent translation initiation. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):857–867. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90938-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B. Messenger RNA degradation in eukaryotes. Cell. 1993 Aug 13;74(3):413–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80043-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. The role of poly(A) in the translation and stability of mRNA. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;2(6):1092–1098. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(90)90161-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savant-Bhonsale S., Cleveland D. W. Evidence for instability of mRNAs containing AUUUA motifs mediated through translation-dependent assembly of a > 20S degradation complex. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1927–1939. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyu A. B., Belasco J. G., Greenberg M. E. Two distinct destabilizing elements in the c-fos message trigger deadenylation as a first step in rapid mRNA decay. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):221–231. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyu A. B., Greenberg M. E., Belasco J. G. The c-fos transcript is targeted for rapid decay by two distinct mRNA degradation pathways. Genes Dev. 1989 Jan;3(1):60–72. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckle M. Y., Hanafusa H. Processing of 9E3 mRNA and regulation of its stability in normal and Rous sarcoma virus-transformed cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4738–4745. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartwout S. G., Kinniburgh A. J. c-myc RNA degradation in growing and differentiating cells: possible alternate pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):288–295. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittemore L. A., Maniatis T. Postinduction turnoff of beta-interferon gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1329–1337. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T., Treisman R. Removal of poly(A) and consequent degradation of c-fos mRNA facilitated by 3' AU-rich sequences. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):396–399. doi: 10.1038/336396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- You Y., Chen C. Y., Shyu A. B. U-rich sequence-binding proteins (URBPs) interacting with a 20-nucleotide U-rich sequence in the 3' untranslated region of c-fos mRNA may be involved in the first step of c-fos mRNA degradation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):2931–2940. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.2931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]