Abstract
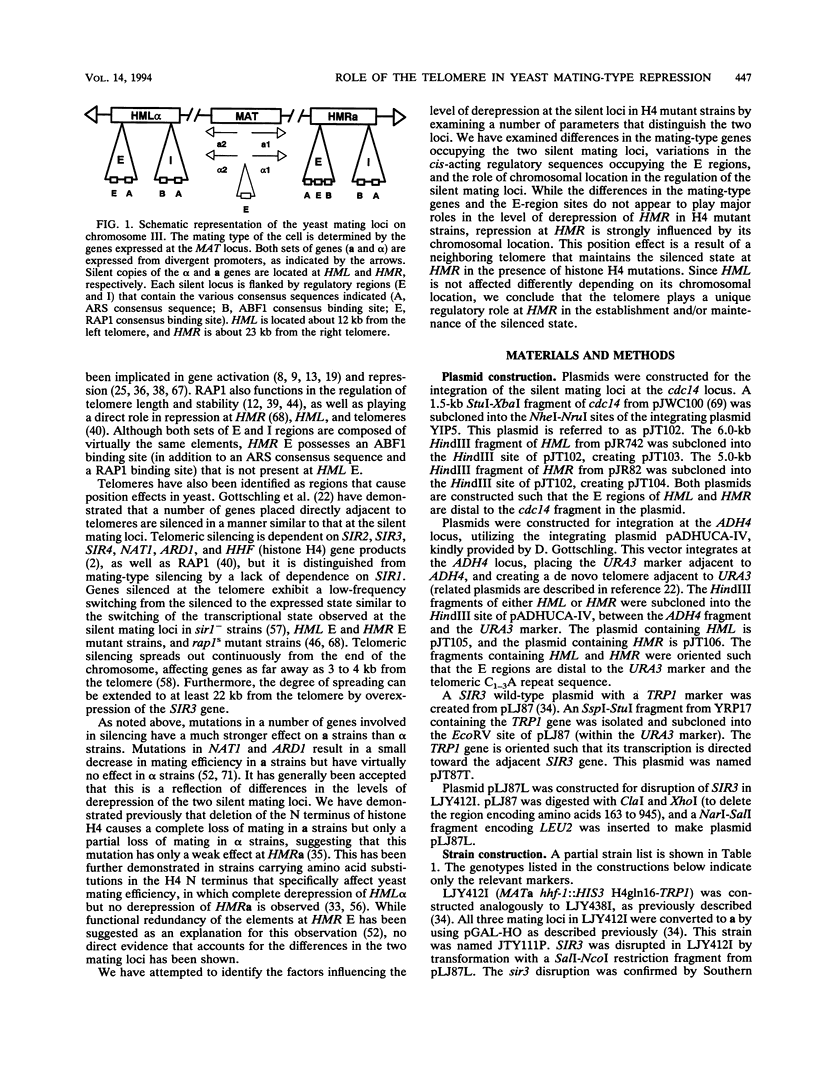
The yeast silent mating loci HML and HMR are located at opposite ends of chromosome III adjacent to the telomeres. Mutations in the N terminus of histone H4 have been previously found to derepress the yeast silent mating locus HML to a much greater extent than HMR. Although differences in the a and alpha mating-type regulatory genes and in the cis-acting silencer elements do not appear to strongly influence the level of derepression at HMR, we have found that the differential between the two silent cassettes is largely due to the position of the HMR cassette relative to the telomere on chromosome III. While HML is derepressed to roughly the same extent by mutations in histone H4 regardless of its chromosomal location, HMR is affected to different extends depending upon its chromosomal positioning. We have found that HMR is more severely derepressed by histone H4 mutations when positioned far from the telomere (cdc14 locus on chromosome VI) but is only minimally affected by the same mutations when integrated immediately adjacent to another telomere (ADH4 locus on chromosome VII). These data indicate that the degree of silencing at HMR is regulated in part by its neighboring telomere over a distance of at least 23 kb and that this form of regulation is unique for HMR and not present at HML. These data also indicate that histone H4 plays an important role in regulating the silenced state at both HML and HMR.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham J., Nasmyth K. A., Strathern J. N., Klar A. J., Hicks J. B. Regulation of mating-type information in yeast. Negative control requiring sequences both 5' and 3' to the regulated region. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 5;176(3):307–331. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90492-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aparicio O. M., Billington B. L., Gottschling D. E. Modifiers of position effect are shared between telomeric and silent mating-type loci in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1279–1287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90049-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astell C. R., Ahlstrom-Jonasson L., Smith M., Tatchell K., Nasmyth K. A., Hall B. D. The sequence of the DNAs coding for the mating-type loci of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90356-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand A. H., Breeden L., Abraham J., Sternglanz R., Nasmyth K. Characterization of a "silencer" in yeast: a DNA sequence with properties opposite to those of a transcriptional enhancer. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand A. H., Micklem G., Nasmyth K. A yeast silencer contains sequences that can promote autonomous plasmid replication and transcriptional activation. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):709–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90094-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer B. J., Fangman W. L. The localization of replication origins on ARS plasmids in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):463–471. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90642-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Kimmerly W. J., Rine J., Kornberg R. D. Two DNA-binding factors recognize specific sequences at silencers, upstream activating sequences, autonomously replicating sequences, and telomeres in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):210–225. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Lue N. F., Kornberg R. D. Connections between transcriptional activators, silencers, and telomeres as revealed by functional analysis of a yeast DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5086–5099. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers A., Tsang J. S., Stanway C., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. Transcriptional control of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae PGK gene by RAP1. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5516–5524. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charron M. J., Read E., Haut S. R., Michels C. A. Molecular evolution of the telomere-associated MAL loci of Saccharomyces. Genetics. 1989 Jun;122(2):307–316. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.2.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. A., Smith M. M., Le S. Y., Sternglanz R., Allfrey V. G. Nucleosome fractionation by mercury affinity chromatography. Contrasting distribution of transcriptionally active DNA sequences and acetylated histones in nucleosome fractions of wild-type yeast cells and cells expressing a histone H3 gene altered to encode a cysteine 110 residue. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6489–6498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad M. N., Wright J. H., Wolf A. J., Zakian V. A. RAP1 protein interacts with yeast telomeres in vivo: overproduction alters telomere structure and decreases chromosome stability. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):739–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90140-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Della Seta F., Ciafré S. A., Marck C., Santoro B., Presutti C., Sentenac A., Bozzoni I. The ABF1 factor is the transcriptional activator of the L2 ribosomal protein genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2437–2441. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffley J. F., Stillman B. Similarity between the transcriptional silencer binding proteins ABF1 and RAP1. Science. 1989 Nov 24;246(4933):1034–1038. doi: 10.1126/science.2511628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubey D. D., Davis L. R., Greenfeder S. A., Ong L. Y., Zhu J. G., Broach J. R., Newlon C. S., Huberman J. A. Evidence suggesting that the ARS elements associated with silencers of the yeast mating-type locus HML do not function as chromosomal DNA replication origins. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5346–5355. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eissenberg J. C. Position effect variegation in Drosophila: towards a genetics of chromatin assembly. Bioessays. 1989 Jul;11(1):14–17. doi: 10.1002/bies.950110105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman J. B., Hicks J. B., Broach J. R. Identification of sites required for repression of a silent mating type locus in yeast. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 5;178(4):815–834. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90313-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson B. M., Fangman W. L. A position effect on the time of replication origin activation in yeast. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):333–339. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90474-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giesman D., Best L., Tatchell K. The role of RAP1 in the regulation of the MAT alpha locus. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1069–1079. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman M. A. The chromatin domain as a unit of gene regulation. Bioessays. 1988 Aug-Sep;9(2-3):50–55. doi: 10.1002/bies.950090204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschling D. E., Aparicio O. M., Billington B. L., Zakian V. A. Position effect at S. cerevisiae telomeres: reversible repression of Pol II transcription. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):751–762. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90141-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschling D. E. Telomere-proximal DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is refractory to methyltransferase activity in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):4062–4065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.4062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goutte C., Johnson A. D. a1 protein alters the DNA binding specificity of alpha 2 repressor. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):875–882. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90429-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber J. E., Mascioli D. W., Rogers D. T. Illegal transposition of mating-type genes in yeast. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):519–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90638-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy C. F., Balderes D., Shore D. Dissection of a carboxy-terminal region of the yeast regulatory protein RAP1 with effects on both transcriptional activation and silencing. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1209–1217. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy C. F., Sussel L., Shore D. A RAP1-interacting protein involved in transcriptional silencing and telomere length regulation. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):801–814. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatton K. S., Dhar V., Brown E. H., Iqbal M. A., Stuart S., Didamo V. T., Schildkraut C. L. Replication program of active and inactive multigene families in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2149–2158. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Position-effect variegation after 60 years. Trends Genet. 1990 Dec;6(12):422–426. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90304-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann J. F., Laroche T., Brand A. H., Gasser S. M. RAP-1 factor is necessary for DNA loop formation in vitro at the silent mating type locus HML. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):725–737. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90788-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist G. P. Role of replication time in the control of tissue-specific gene expression. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Feb;40(2):151–173. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivy J. M., Klar A. J., Hicks J. B. Cloning and characterization of four SIR genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):688–702. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. M., Fisher-Adams G., Grunstein M. Identification of a non-basic domain in the histone H4 N-terminus required for repression of the yeast silent mating loci. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2201–2209. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05279.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. M., Kayne P. S., Kahn E. S., Grunstein M. Genetic evidence for an interaction between SIR3 and histone H4 in the repression of the silent mating loci in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6286–6290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayne P. S., Kim U. J., Han M., Mullen J. R., Yoshizaki F., Grunstein M. Extremely conserved histone H4 N terminus is dispensable for growth but essential for repressing the silent mating loci in yeast. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):27–39. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmerly W. J., Rine J. Replication and segregation of plasmids containing cis-acting regulatory sites of silent mating-type genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae are controlled by the SIR genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4225–4237. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmerly W., Buchman A., Kornberg R., Rine J. Roles of two DNA-binding factors in replication, segregation and transcriptional repression mediated by a yeast silencer. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2241–2253. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03064.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz S., Shore D. RAP1 protein activates and silences transcription of mating-type genes in yeast. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):616–628. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyrion G., Boakye K. A., Lustig A. J. C-terminal truncation of RAP1 results in the deregulation of telomere size, stability, and function in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):5159–5173. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.5159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyrion G., Liu K., Liu C., Lustig A. J. RAP1 and telomere structure regulate telomere position effects in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1146–1159. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurenson P., Rine J. Silencers, silencing, and heritable transcriptional states. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Dec;56(4):543–560. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.4.543-560.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S., Gross D. S. Conditional silencing: the HMRE mating-type silencer exerts a rapidly reversible position effect on the yeast HSP82 heat shock gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):727–738. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longtine M. S., Wilson N. M., Petracek M. E., Berman J. A yeast telomere binding activity binds to two related telomere sequence motifs and is indistinguishable from RAP1. Curr Genet. 1989 Oct;16(4):225–239. doi: 10.1007/BF00422108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustig A. J., Kurtz S., Shore D. Involvement of the silencer and UAS binding protein RAP1 in regulation of telomere length. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):549–553. doi: 10.1126/science.2237406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney D. J., Broach J. R. The HML mating-type cassette of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is regulated by two separate but functionally equivalent silencers. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4621–4630. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney D. J., Marquardt R., Shei G. J., Rose A. B., Broach J. R. Mutations in the HML E silencer of Saccharomyces cerevisiae yield metastable inheritance of transcriptional repression. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):605–615. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarroll R. M., Fangman W. L. Time of replication of yeast centromeres and telomeres. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):505–513. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90072-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNally F. J., Rine J. A synthetic silencer mediates SIR-dependent functions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5648–5659. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Megee P. C., Morgan B. A., Mittman B. A., Smith M. M. Genetic analysis of histone H4: essential role of lysines subject to reversible acetylation. Science. 1990 Feb 16;247(4944):841–845. doi: 10.1126/science.2106160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. M., Nasmyth K. A. Role of DNA replication in the repression of silent mating type loci in yeast. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):247–251. doi: 10.1038/312247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer R. K., Hawthorne D. C. Genetic Mapping in Saccharomyces IV. Mapping of Temperature-Sensitive Genes and Use of Disomic Strains in Localizing Genes. Genetics. 1973 May;74(1):33–54. doi: 10.1093/genetics/74.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullen J. R., Kayne P. S., Moerschell R. P., Tsunasawa S., Gribskov M., Colavito-Shepanski M., Grunstein M., Sherman F., Sternglanz R. Identification and characterization of genes and mutants for an N-terminal acetyltransferase from yeast. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2067–2075. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03615.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. A., Tatchell K., Hall B. D., Astell C., Smith M. A position effect in the control of transcription at yeast mating type loci. Nature. 1981 Jan 22;289(5795):244–250. doi: 10.1038/289244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. A. The regulation of yeast mating-type chromatin structure by SIR: an action at a distance affecting both transcription and transposition. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):567–578. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90253-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver S. G., van der Aart Q. J., Agostoni-Carbone M. L., Aigle M., Alberghina L., Alexandraki D., Antoine G., Anwar R., Ballesta J. P., Benit P. The complete DNA sequence of yeast chromosome III. Nature. 1992 May 7;357(6373):38–46. doi: 10.1038/357038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park E. C., Szostak J. W. Point mutations in the yeast histone H4 gene prevent silencing of the silent mating type locus HML. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4932–4934. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pillus L., Rine J. Epigenetic inheritance of transcriptional states in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):637–647. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renauld H., Aparicio O. M., Zierath P. D., Billington B. L., Chhablani S. K., Gottschling D. E. Silent domains are assembled continuously from the telomere and are defined by promoter distance and strength, and by SIR3 dosage. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1133–1145. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds A. E., McCarroll R. M., Newlon C. S., Fangman W. L. Time of replication of ARS elements along yeast chromosome III. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4488–4494. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rine J., Herskowitz I. Four genes responsible for a position effect on expression from HML and HMR in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1987 May;116(1):9–22. doi: 10.1093/genetics/116.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivier D. H., Rine J. An origin of DNA replication and a transcription silencer require a common element. Science. 1992 May 1;256(5057):659–663. doi: 10.1126/science.1585179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S., Davis R. W. Replacement of chromosome segments with altered DNA sequences constructed in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4951–4955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Nasmyth K. Purification and cloning of a DNA binding protein from yeast that binds to both silencer and activator elements. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siliciano P. G., Tatchell K. Transcription and regulatory signals at the mating type locus in yeast. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):969–978. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90431-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh J., Klar A. J. Active genes in budding yeast display enhanced in vivo accessibility to foreign DNA methylases: a novel in vivo probe for chromatin structure of yeast. Genes Dev. 1992 Feb;6(2):186–196. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.2.186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussel L., Shore D. Separation of transcriptional activation and silencing functions of the RAP1-encoded repressor/activator protein 1: isolation of viable mutants affecting both silencing and telomere length. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7749–7753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussel L., Vannier D., Shore D. Epigenetic switching of transcriptional states: cis- and trans-acting factors affecting establishment of silencing at the HMR locus in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):3919–3928. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.3919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan J., Xu H., Grunstein M. CDC14 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cloning, sequence analysis, and transcription during the cell cycle. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):11274–11280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteway M., Freedman R., Van Arsdell S., Szostak J. W., Thorner J. The yeast ARD1 gene product is required for repression of cryptic mating-type information at the HML locus. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3713–3722. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



