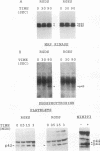
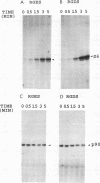
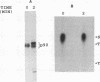
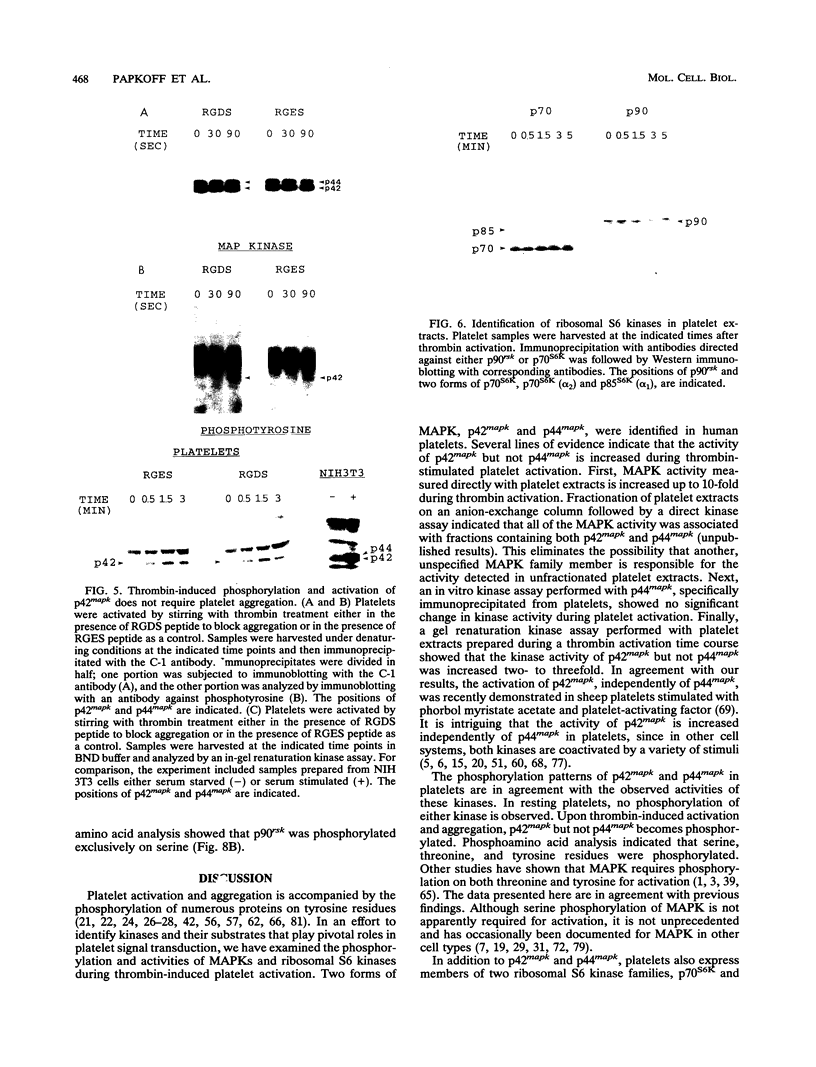
Abstract
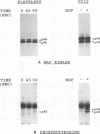
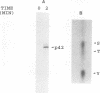
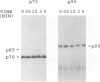
Human platelets provide an excellent model system for the study of phosphorylation events during signal transduction and cell adhesion. Platelets are terminally differentiated cells that exhibit rapid phosphorylation of many proteins upon agonist-induced activation and aggregation. We have sought to identify the kinases as well as the phosphorylated substrates that participate in thrombin-induced signal transduction and platelet aggregation. In this study, we have identified two forms of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), p42mapk and p44mapk, in platelets. The data demonstrate that p42mapk but not p44mapk becomes phosphorylated on serine, threonine, and tyrosine during platelet activation. Immune complex kinase assays, gel renaturation assays, and a direct assay for MAPK activity in platelet extracts all support the conclusion that p42mapk but not p44mapk shows increased kinase activity during platelet activation. The activation of p42mapk, independently of p44mapk, in platelets is unique since in other systems, both kinases are coactivated by a variety of stimuli. We also show that platelets express p90rsk, a ribosomal S6 kinase that has previously been characterized as a substrate for MAPK. p90rsk is phosphorylated on serine in resting platelets, and this phosphorylation is enhanced upon thrombin-induced platelet activation. Immune complex kinase assays demonstrate that the activity of p90rsk is markedly increased during platelet activation. Another ribosomal S6 protein kinase, p70S6K, is expressed by platelets but shows no change in kinase activity upon platelet activation with thrombin. Finally, we show that the increased phosphorylation and activity of both p42mapk and p90rsk does not require integrin-mediated platelet aggregation. Since platelets are nonproliferative cells, the signal transduction pathways that include p42mapk and p90rsk cannot lead to a mitogenic signal and instead may regulate cytoskeletal or secretory changes during platelet activation.
Full text
PDF




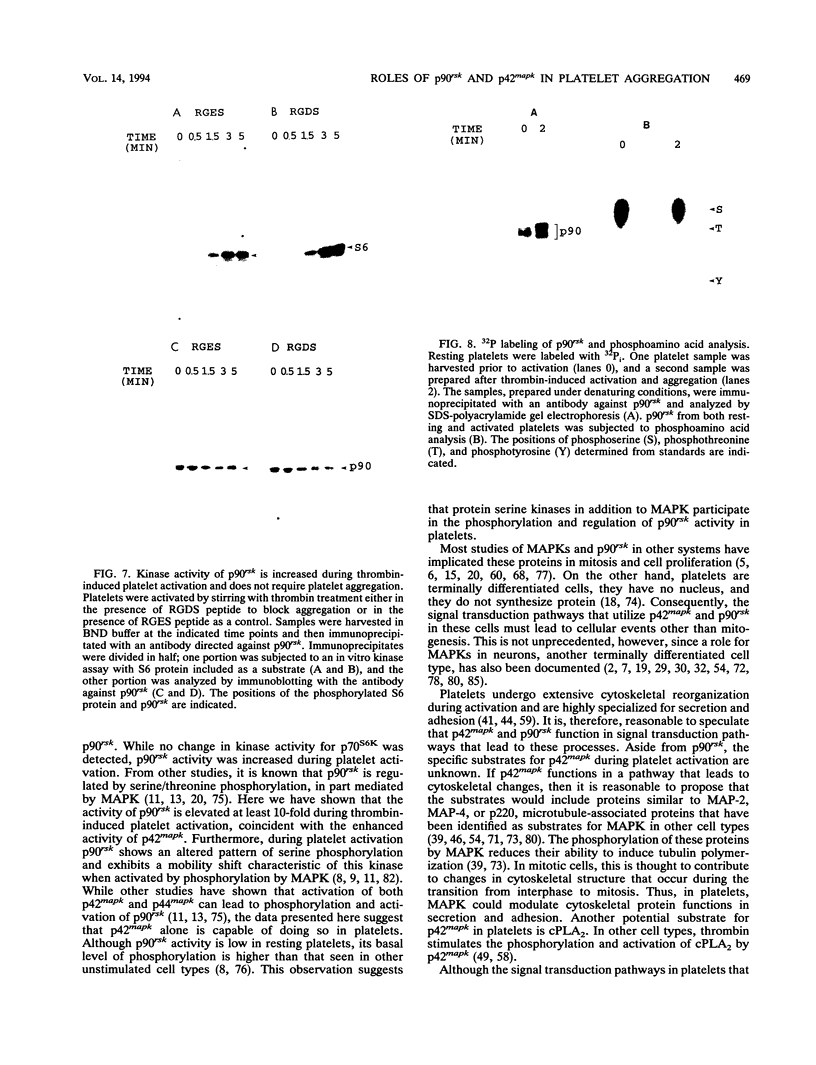



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson N. G., Maller J. L., Tonks N. K., Sturgill T. W. Requirement for integration of signals from two distinct phosphorylation pathways for activation of MAP kinase. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):651–653. doi: 10.1038/343651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bading H., Greenberg M. E. Stimulation of protein tyrosine phosphorylation by NMDA receptor activation. Science. 1991 Aug 23;253(5022):912–914. doi: 10.1126/science.1715095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballou L. M., Luther H., Thomas G. MAP2 kinase and 70K S6 kinase lie on distinct signalling pathways. Nature. 1991 Jan 24;349(6307):348–350. doi: 10.1038/349348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee P., Ahmad M. F., Grove J. R., Kozlosky C., Price D. J., Avruch J. Molecular structure of a major insulin/mitogen-activated 70-kDa S6 protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8550–8554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J. Growth-regulated signal transduction by the MAP kinases and RSKs. Cancer Cells. 1991 Nov;3(11):445–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J. Signal transduction via the MAP kinases: proceed at your own RSK. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):5889–5892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Nye S. H., Robbins D. J., Ip N. Y., Radziejewska E., Morgenbesser S. D., DePinho R. A., Panayotatos N., Cobb M. H., Yancopoulos G. D. ERKs: a family of protein-serine/threonine kinases that are activated and tyrosine phosphorylated in response to insulin and NGF. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):663–675. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90098-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. H., Blenis J. Identification of Xenopus S6 protein kinase homologs (pp90rsk) in somatic cells: phosphorylation and activation during initiation of cell proliferation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3204–3215. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. H., Chung J., Blenis J. Regulation of pp90rsk phosphorylation and S6 phosphotransferase activity in Swiss 3T3 cells by growth factor-, phorbol ester-, and cyclic AMP-mediated signal transduction. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1861–1867. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. H., Sarnecki C., Blenis J. Nuclear localization and regulation of erk- and rsk-encoded protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):915–927. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Chen R. H., Blenis J. Coordinate regulation of pp90rsk and a distinct protein-serine/threonine kinase activity that phosphorylates recombinant pp90rsk in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1868–1874. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Kuo C. J., Crabtree G. R., Blenis J. Rapamycin-FKBP specifically blocks growth-dependent activation of and signaling by the 70 kd S6 protein kinases. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1227–1236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90643-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Pelech S. L., Blenis J. Mitogen-activated Swiss mouse 3T3 RSK kinases I and II are related to pp44mpk from sea star oocytes and participate in the regulation of pp90rsk activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4981–4985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark E. A., Brugge J. S. Redistribution of activated pp60c-src to integrin-dependent cytoskeletal complexes in thrombin-stimulated platelets. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1863–1871. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb M. H., Boulton T. G., Robbins D. J. Extracellular signal-regulated kinases: ERKs in progress. Cell Regul. 1991 Dec;2(12):965–978. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.12.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Diverse mitogenic agents induce the phosphorylation of two related 42,000-dalton proteins on tyrosine in quiescent chick cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):30–37. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews C. M., Alessandrini A., Erikson R. L. The primary structure of MEK, a protein kinase that phosphorylates the ERK gene product. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):478–480. doi: 10.1126/science.1411546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely C. M., Oddie K. M., Litz J. S., Rossomando A. J., Kanner S. B., Sturgill T. W., Parsons S. J. A 42-kD tyrosine kinase substrate linked to chromaffin cell secretion exhibits an associated MAP kinase activity and is highly related to a 42-kD mitogen-stimulated protein in fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):731–742. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson R. L. Structure, expression, and regulation of protein kinases involved in the phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6007–6010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell J. E., Jr, Martin G. S. Platelet tyrosine-specific protein phosphorylation is regulated by thrombin. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3603–3610. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell J. E., Jr, Martin G. S. Tyrosine-specific protein phosphorylation is regulated by glycoprotein IIb-IIIa in platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2234–2238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell J. E., Jr, Wu M., Gerhart J. C., Martin G. S. Cell cycle tyrosine phosphorylation of p34cdc2 and a microtubule-associated protein kinase homolog in Xenopus oocytes and eggs. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1965–1971. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findik D., Presek P. Zn2+ enhances protein tyrosine kinase activity of human platelet membranes. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 1;235(1-2):51–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81232-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner T. K., Bennett J. S. The tetrapeptide analogue of the cell attachment site of fibronectin inhibits platelet aggregation and fibrinogen binding to activated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):11891–11894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden A., Brugge J. S., Shattil S. J. Role of platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb-IIIa in agonist-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of platelet proteins. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):3117–3127. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.3117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden A., Brugge J. S. Thrombin treatment induces rapid changes in tyrosine phosphorylation in platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):901–905. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden A., Nemeth S. P., Brugge J. S. Blood platelets express high levels of the pp60c-src-specific tyrosine kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):852–856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh Y., Nishida E., Matsuda S., Shiina N., Kosako H., Shiokawa K., Akiyama T., Ohta K., Sakai H. In vitro effects on microtubule dynamics of purified Xenopus M phase-activated MAP kinase. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):251–254. doi: 10.1038/349251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh Y., Nishida E., Yamashita T., Hoshi M., Kawakami M., Sakai H. Microtubule-associated-protein (MAP) kinase activated by nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor in PC12 cells. Identity with the mitogen-activated MAP kinase of fibroblastic cells. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 13;193(3):661–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19384.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S. K., Gallego C., Johnson G. L., Heasley L. E. MAP kinase is constitutively activated in gip2 and src transformed rat 1a fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):7987–7990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutkind J. S., Lacal P. M., Robbins K. C. Thrombin-dependent association of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase with p60c-src and p59fyn in human platelets. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3806–3809. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez N., Cohen P. Dissection of the protein kinase cascade by which nerve growth factor activates MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):170–173. doi: 10.1038/353170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez N., Tonks N. K., Morrison C., Harmar T., Cohen P. Evidence for communication between nerve growth factor and protein tyrosine phosphorylation. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 1;271(1-2):119–122. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80386-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haccard O., Jessus C., Cayla X., Goris J., Merlevede W., Ozon R. In vivo activation of a microtubule-associated protein kinase during meiotic maturation of the Xenopus oocyte. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Sep 24;192(3):633–642. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19270.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harfenist E. J., Packham M. A., Mustard J. F. Effects of the cell adhesion peptide, Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser, on responses of washed platelets from humans, rabbits, and rats. Blood. 1988 Jan;71(1):132–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverstick D. M., Cowan J. F., Yamada K. M., Santoro S. A. Inhibition of platelet adhesion to fibronectin, fibrinogen, and von Willebrand factor substrates by a synthetic tetrapeptide derived from the cell-binding domain of fibronectin. Blood. 1985 Oct;66(4):946–952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horak I. D., Corcoran M. L., Thompson P. A., Wahl L. M., Bolen J. B. Expression of p60fyn in human platelets. Oncogene. 1990 Apr;5(4):597–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi M., Ohta K., Gotoh Y., Mori A., Murofushi H., Sakai H., Nishida E. Mitogen-activated-protein-kinase-catalyzed phosphorylation of microtubule-associated proteins, microtubule-associated protein 2 and microtubule-associated protein 4, induces an alteration in their function. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jan 15;203(1-2):43–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb19825.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. M., Bolen J. B., Barnwell J. W., Shattil S. J., Brugge J. S. Membrane glycoprotein IV (CD36) is physically associated with the Fyn, Lyn, and Yes protein-tyrosine kinases in human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7844–7848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. The complexity of platelet adhesion to extracellular matrices. Thromb Haemost. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):40–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara N., Nagao K., Kobayashi B. Tyrosine phosphorylation of platelet protein induced by phorbol ester. Thromb Haemost. 1985 Oct 30;54(3):579–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P. Determination of phosphoamino acid composition by acid hydrolysis of protein blotted to Immobilon. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:21–27. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01005-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieffer N., Phillips D. R. Platelet membrane glycoproteins: functions in cellular interactions. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:329–357. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.001553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll M. H., Schafer A. I. Biochemical mechanisms of platelet activation. Blood. 1989 Sep;74(4):1181–1195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landreth G. E., Smith D. S., McCabe C., Gittinger C. Characterization of a nerve growth factor-stimulated protein kinase in PC12 cells which phosphorylates microtubule-associated protein 2 and pp250. J Neurochem. 1990 Aug;55(2):514–523. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04165.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane H. A., Morley S. J., Dorée M., Kozma S. C., Thomas G. Identification and early activation of a Xenopus laevis p70s6k following progesterone-induced meiotic maturation. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1743–1749. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05226.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange-Carter C. A., Pleiman C. M., Gardner A. M., Blumer K. J., Johnson G. L. A divergence in the MAP kinase regulatory network defined by MEK kinase and Raf. Science. 1993 Apr 16;260(5106):315–319. doi: 10.1126/science.8385802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. L., Wartmann M., Lin A. Y., Knopf J. L., Seth A., Davis R. J. cPLA2 is phosphorylated and activated by MAP kinase. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90666-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipfert L., Haimovich B., Schaller M. D., Cobb B. S., Parsons J. T., Brugge J. S. Integrin-dependent phosphorylation and activation of the protein tyrosine kinase pp125FAK in platelets. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(4):905–912. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.4.905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maller J. L. Xenopus oocytes and the biochemistry of cell division. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 3;29(13):3157–3166. doi: 10.1021/bi00465a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meloche S., Pagès G., Pouysségur J. Functional expression and growth factor activation of an epitope-tagged p44 mitogen-activated protein kinase, p44mapk. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jan;3(1):63–71. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell C. A., Jefferson A. B., Bejeck B. E., Brugge J. S., Deuel T. F., Majerus P. W. Thrombin-stimulated immunoprecipitation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase from human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9396–9400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyasaka T., Chao M. V., Sherline P., Saltiel A. R. Nerve growth factor stimulates a protein kinase in PC-12 cells that phosphorylates microtubule-associated protein-2. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4730–4735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K. D., Martinez R., Weber M. J. Tyrosine phosphorylation of specific proteins after mitogen stimulation of chicken embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;3(3):380–390. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.3.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Takeuchi F., Tomizawa T., Takasaki N., Kondo H., Yamamura H. Two separate tyrosine protein kinases in human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1985 May 6;184(1):56–59. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80652-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Yamamura H. Thrombin and collagen induce rapid phosphorylation of a common set of cellular proteins on tyrosine in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7089–7091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemenoff R. A., Winitz S., Qian N. X., Van Putten V., Johnson G. L., Heasley L. E. Phosphorylation and activation of a high molecular weight form of phospholipase A2 by p42 microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase and protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):1960–1964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nievelstein P. F., de Groot P. G. Interaction of blood platelets with the vessel wall. Haemostasis. 1988;18(4-6):342–359. doi: 10.1159/000215816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Sanghera J. S., Daya-Makin M. Protein kinase cascades in meiotic and mitotic cell cycle control. Biochem Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;68(12):1297–1330. doi: 10.1139/o90-194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Sanghera J. S. MAP kinases: charting the regulatory pathways. Science. 1992 Sep 4;257(5075):1355–1356. doi: 10.1126/science.1382311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E., Marguerie G. A., Ginsberg M. H. The effect of Arg-Gly-Asp-containing peptides on fibrinogen and von Willebrand factor binding to platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8057–8061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posada J., Cooper J. A. Requirements for phosphorylation of MAP kinase during meiosis in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1992 Jan 10;255(5041):212–215. doi: 10.1126/science.1313186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray L. B., Sturgill T. W. Insulin-stimulated microtubule-associated protein kinase is phosphorylated on tyrosine and threonine in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3753–3757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rendu F., Lebret M., Danielian S., Fagard R., Levy-Toledano S., Fischer S. High pp60c-src level in human platelet dense bodies. Blood. 1989 May 1;73(6):1545–1551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins D. J., Cobb M. H. Extracellular signal-regulated kinases 2 autophosphorylates on a subset of peptides phosphorylated in intact cells in response to insulin and nerve growth factor: analysis by peptide mapping. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Mar;3(3):299–308. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.3.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts T. M. Cell biology. A signal chain of events. Nature. 1992 Dec 10;360(6404):534–535. doi: 10.1038/360534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samiei M., Sanghera J. S., Pelech S. L. Activation of myelin basic protein and S6 peptide kinases in phorbol ester- and PAF-treated sheep platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Apr 16;1176(3):287–298. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(93)90057-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanghera J. S., Paddon H. B., Bader S. A., Pelech S. L. Purification and characterization of a maturation-activated myelin basic protein kinase from sea star oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):52–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato C., Nishizawa K., Nakayama T., Ohtsuka K., Nakamura H., Kobayashi T., Inagaki M. Rapid phosphorylation of MAP-2-related cytoplasmic and nuclear Mr 300,000 protein by serine kinases after growth stimulation in quiescent cells. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Mar;175(1):136–147. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90261-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schanen-King C., Nel A., Williams L. K., Landreth G. Nerve growth factor stimulates the tyrosine phosphorylation of MAP2 kinase in PC12 cells. Neuron. 1991 Jun;6(6):915–922. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90232-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiina N., Moriguchi T., Ohta K., Gotoh Y., Nishida E. Regulation of a major microtubule-associated protein by MPF and MAP kinase. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):3977–3984. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05491.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W. Molecular mechanisms of platelet activation. Physiol Rev. 1989 Jan;69(1):58–178. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgill T. W., Ray L. B., Erikson E., Maller J. L. Insulin-stimulated MAP-2 kinase phosphorylates and activates ribosomal protein S6 kinase II. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):715–718. doi: 10.1038/334715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet L. J., Alcorta D. A., Erikson R. L. Two distinct enzymes contribute to biphasic S6 phosphorylation in serum-stimulated chicken embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2787–2792. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. MAP kinase by any other name smells just as sweet. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):3–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90199-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas S. M., DeMarco M., D'Arcangelo G., Halegoua S., Brugge J. S. Ras is essential for nerve growth factor- and phorbol ester-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of MAP kinases. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1031–1040. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90075-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobe K., Kadowaki T., Tamemoto H., Ueki K., Hara K., Koshio O., Momomura K., Gotoh Y., Nishida E., Akanuma Y. Insulin and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate activation of two immunologically distinct myelin basic protein/microtubule-associated protein 2 (MBP/MAP2) kinases via de novo phosphorylation of threonine and tyrosine residues. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24793–24803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao H., Aletta J. M., Greene L. A. Nerve growth factor and fibroblast growth factor selectively activate a protein kinase that phosphorylates high molecular weight microtubule-associated proteins. Detection, partial purification, and characterization in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15471–15480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuy F. P., Henry J., Rosenfeld C., Kahn A. High tyrosine kinase activity in normal nonproliferating cells. 1983 Sep 29-Oct 5Nature. 305(5933):435–438. doi: 10.1038/305435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshney G. C., Henry J., Kahn A., Phan-Dinh-Tuy F. Tyrosine kinases in normal human blood cells. Platelet but not erythrocyte band 3 tyrosine kinase is p60c-src. FEBS Lett. 1986 Sep 1;205(1):97–103. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80873-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vik T. A., Sweet L. J., Erikson R. L. Coinfection of insect cells with recombinant baculovirus expressing pp60v-src results in the activation of a serine-specific protein kinase pp90rsk. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2685–2689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu T. K., Hung D. T., Wheaton V. I., Coughlin S. R. Molecular cloning of a functional thrombin receptor reveals a novel proteolytic mechanism of receptor activation. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1057–1068. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90261-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S., Reynolds A. B., Papkoff J. Platelet activation leads to increased c-src kinase activity and association of c-src with an 85-kDa tyrosine phosphoprotein. Oncogene. 1992 Dec;7(12):2407–2415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood K. W., Sarnecki C., Roberts T. M., Blenis J. ras mediates nerve growth factor receptor modulation of three signal-transducing protein kinases: MAP kinase, Raf-1, and RSK. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1041–1050. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90076-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Y. H., Krueger J. G., Sudol M. Expression of cellular-yes protein in mammalian tissues. Oncogene. 1990 Nov;5(11):1629–1635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot P. G., Sixma J. J. Platelet adhesion. Br J Haematol. 1990 Jul;75(3):308–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb04341.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]