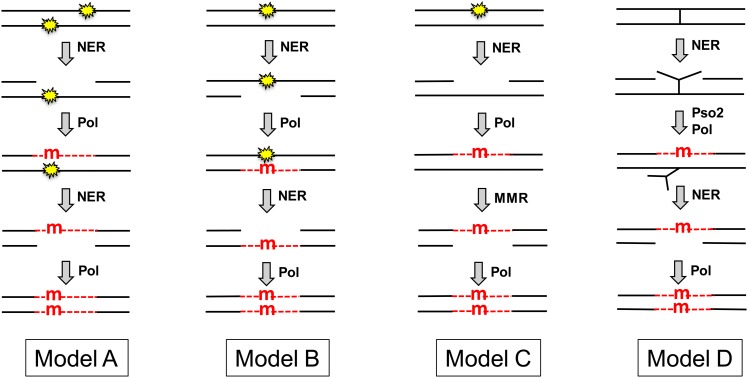
Figure 1.
Models for NER-associated mutagenesis. The NER machinery is recruited either by a UV-induced CPD or (6-4) photoproduct (yellow stars) or by an interstrand crosslink (|). NER excises an oligonucleotide either from the strand containing the lesion (models A, C, and D) or from the undamaged strand (model B). The resulting gap is filled by a DNA polymerase (Pol), which introduces a mutation (red “m”) opposite a lesion within the gap (models A, B, and D) or opposite an undamaged template (model C). Finally, the mutation is introduced into both DNA strands by a second round of NER (models A, B, and D) or by MMR (model C). The Pso2 protein is specifically required for the bypass of an interstrand crosslink. Newly synthesized DNA within NER or MMR-generated gaps is indicated by red dashed lines.