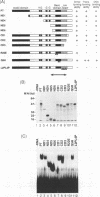
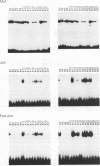
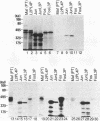
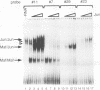
Abstract
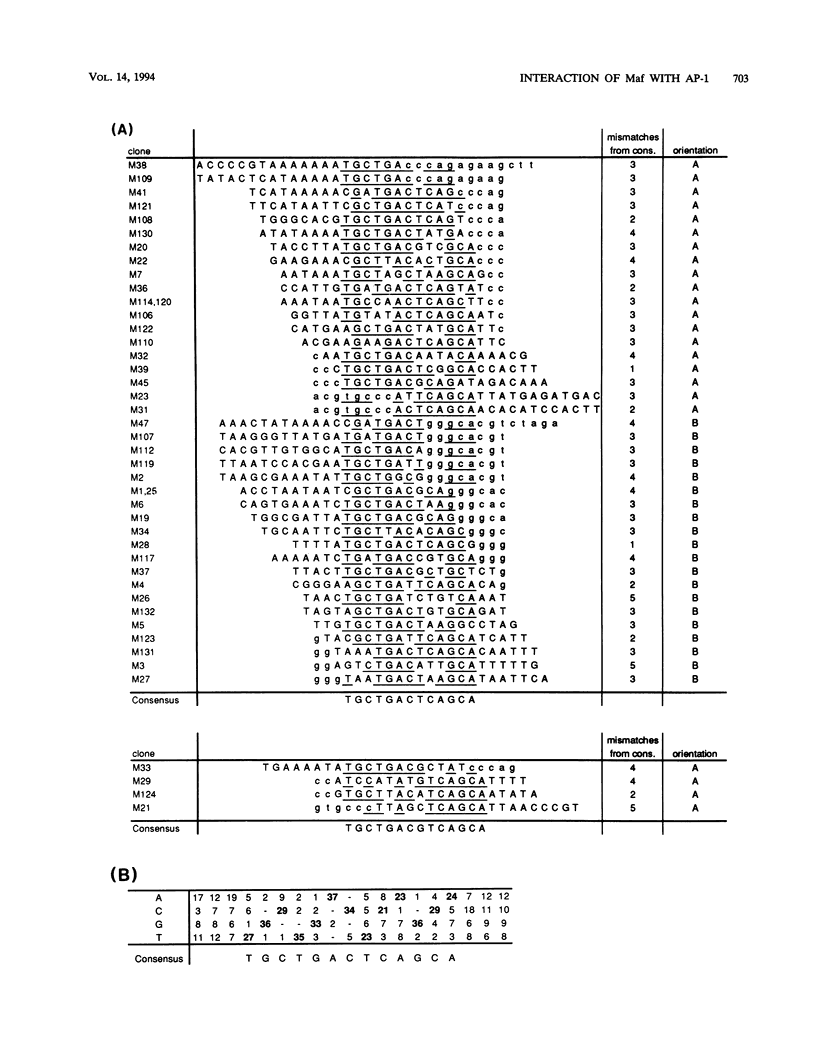
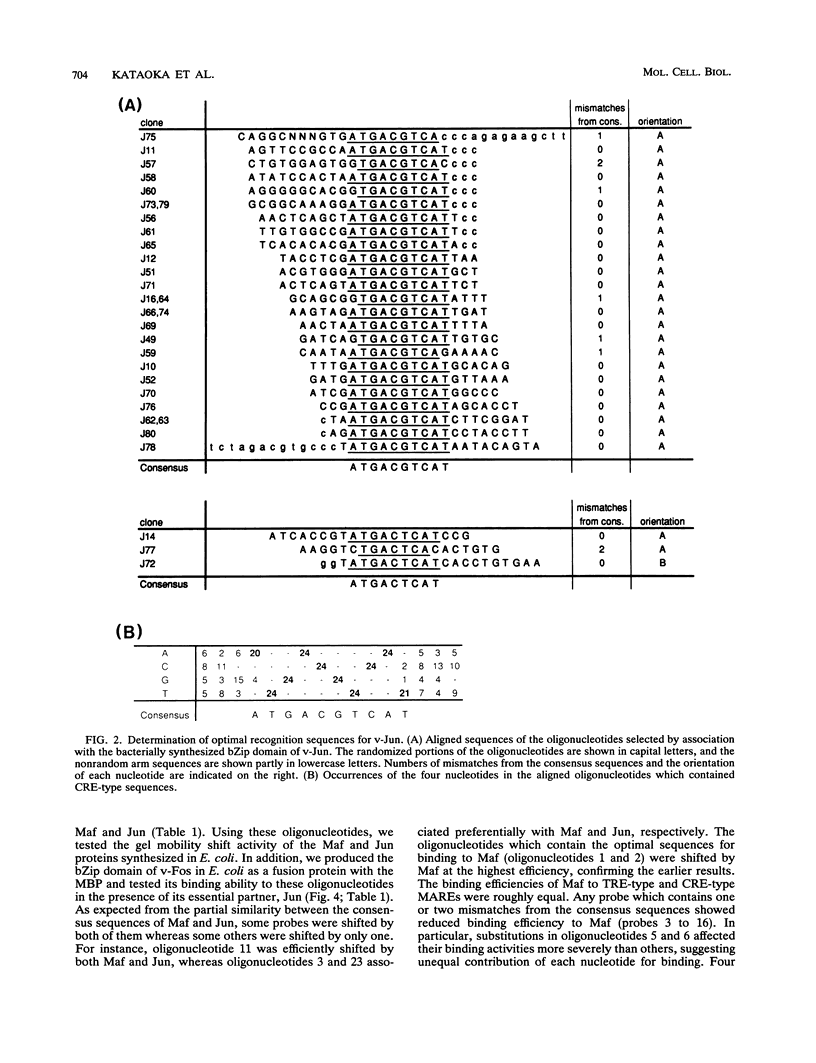
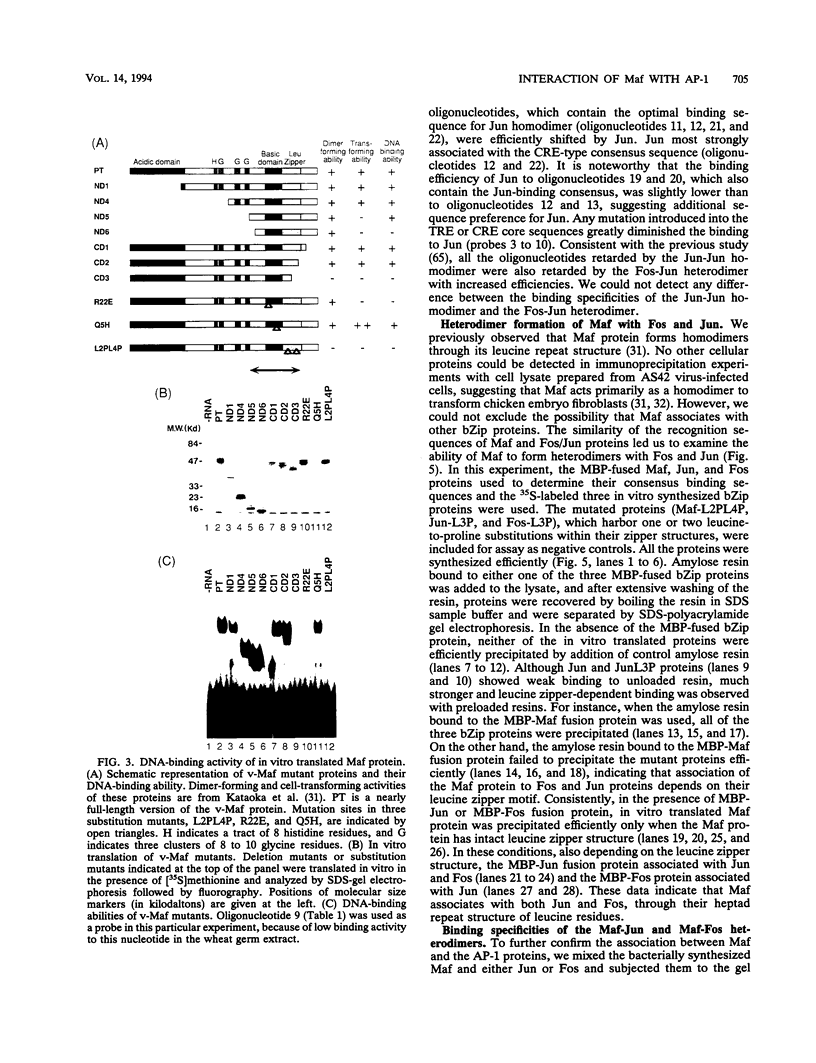
The v-maf oncogene, identified from AS42 avian retrovirus, encodes a nuclear bZip protein. To elucidate the molecular mechanism of cell transformation induced by this oncogene, we determined the specific binding sequences of its product. Maf protein recognized two types of relatively long palindromic consensus sequences, TGCTGACTCAGCA and TGCTGACGTCAGCA, at roughly equal efficiency. The middle parts of these Maf-binding sequences completely match with two binding sequences for AP-1 transcription factor, i.e., phorbol 12-O-tetradecanoate-13-acetate (TPA)-responsive element (TRE) and cyclic AMP responsive element, suggesting partial overlapping of the target genes for Maf and AP-1. Furthermore, Maf efficiently formed heterodimers with the components of AP-1, Fos and Jun, through their leucine zipper structures, and these heterodimers show binding specificities distinct from those for Maf-Maf and Jun-Jun homodimers. Thus, a multiple combination of the dimers should generate a greatly expanded repertoire of transcriptional regulatory potential. DNA data base search for the Maf-binding consensus sequences suggested that some of the TRE-like cis elements reported previously may actually be the targets for Maf family proteins or their heterodimers with other bZip proteins.
Full text
PDF


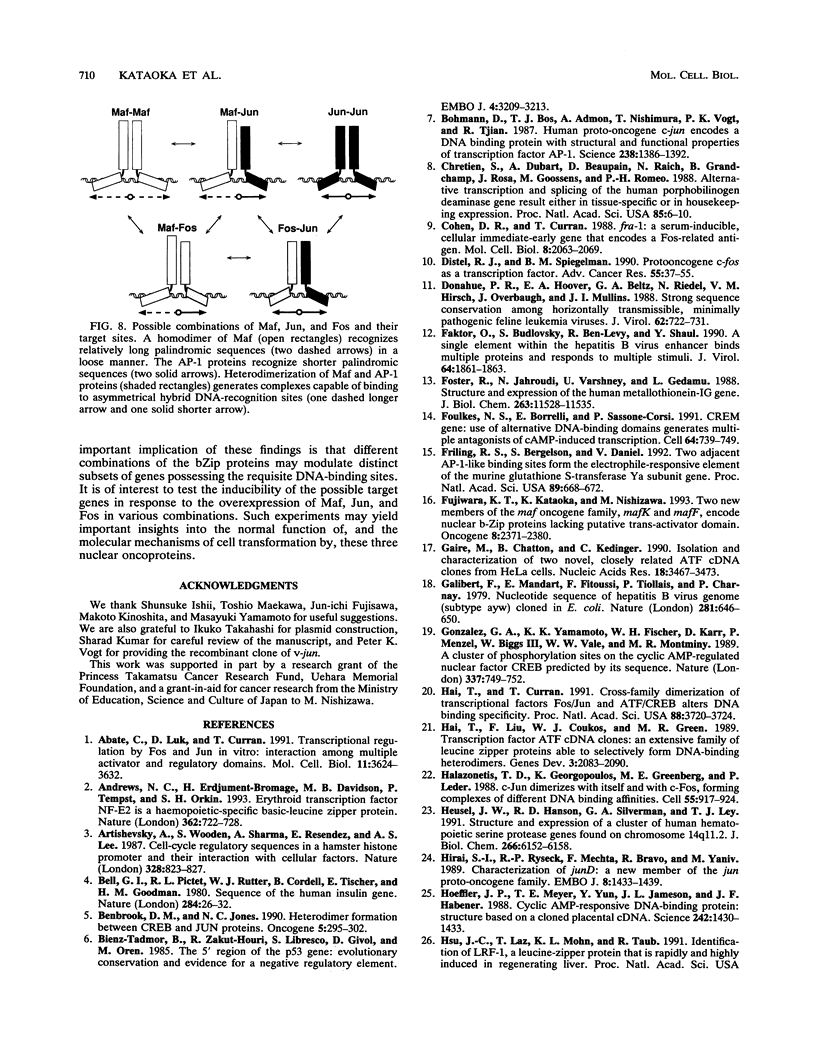


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abate C., Luk D., Curran T. Transcriptional regulation by Fos and Jun in vitro: interaction among multiple activator and regulatory domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3624–3632. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews N. C., Erdjument-Bromage H., Davidson M. B., Tempst P., Orkin S. H. Erythroid transcription factor NF-E2 is a haematopoietic-specific basic-leucine zipper protein. Nature. 1993 Apr 22;362(6422):722–728. doi: 10.1038/362722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artishevsky A., Wooden S., Sharma A., Resendez E., Jr, Lee A. S. Cell-cycle regulatory sequences in a hamster histone promoter and their interactions with cellular factors. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):823–827. doi: 10.1038/328823a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Pictet R. L., Rutter W. J., Cordell B., Tischer E., Goodman H. M. Sequence of the human insulin gene. Nature. 1980 Mar 6;284(5751):26–32. doi: 10.1038/284026a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benbrook D. M., Jones N. C. Heterodimer formation between CREB and JUN proteins. Oncogene. 1990 Mar;5(3):295–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz-Tadmor B., Zakut-Houri R., Libresco S., Givol D., Oren M. The 5' region of the p53 gene: evolutionary conservation and evidence for a negative regulatory element. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3209–3213. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04067.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Bos T. J., Admon A., Nishimura T., Vogt P. K., Tjian R. Human proto-oncogene c-jun encodes a DNA binding protein with structural and functional properties of transcription factor AP-1. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1386–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.2825349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chretien S., Dubart A., Beaupain D., Raich N., Grandchamp B., Rosa J., Goossens M., Romeo P. H. Alternative transcription and splicing of the human porphobilinogen deaminase gene result either in tissue-specific or in housekeeping expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):6–10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D. R., Curran T. fra-1: a serum-inducible, cellular immediate-early gene that encodes a fos-related antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2063–2069. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distel R. J., Spiegelman B. M. Protooncogene c-fos as a transcription factor. Adv Cancer Res. 1990;55:37–55. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60467-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue P. R., Hoover E. A., Beltz G. A., Riedel N., Hirsch V. M., Overbaugh J., Mullins J. I. Strong sequence conservation among horizontally transmissible, minimally pathogenic feline leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):722–731. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.722-731.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faktor O., Budlovsky S., Ben-Levy R., Shaul Y. A single element within the hepatitis B virus enhancer binds multiple proteins and responds to multiple stimuli. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1861–1863. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1861-1863.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster R., Jahroudi N., Varshney U., Gedamu L. Structure and expression of the human metallothionein-IG gene. Differential promoter activity of two linked metallothionein-I genes in response to heavy metals. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11528–11535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes N. S., Borrelli E., Sassone-Corsi P. CREM gene: use of alternative DNA-binding domains generates multiple antagonists of cAMP-induced transcription. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):739–749. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90503-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friling R. S., Bergelson S., Daniel V. Two adjacent AP-1-like binding sites form the electrophile-responsive element of the murine glutathione S-transferase Ya subunit gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):668–672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara K. T., Kataoka K., Nishizawa M. Two new members of the maf oncogene family, mafK and mafF, encode nuclear b-Zip proteins lacking putative trans-activator domain. Oncogene. 1993 Sep;8(9):2371–2380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaire M., Chatton B., Kedinger C. Isolation and characterization of two novel, closely related ATF cDNA clones from HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 25;18(12):3467–3473. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.12.3467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galibert F., Mandart E., Fitoussi F., Tiollais P., Charnay P. Nucleotide sequence of the hepatitis B virus genome (subtype ayw) cloned in E. coli. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):646–650. doi: 10.1038/281646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Yamamoto K. K., Fischer W. H., Karr D., Menzel P., Biggs W., 3rd, Vale W. W., Montminy M. R. A cluster of phosphorylation sites on the cyclic AMP-regulated nuclear factor CREB predicted by its sequence. Nature. 1989 Feb 23;337(6209):749–752. doi: 10.1038/337749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T. W., Liu F., Coukos W. J., Green M. R. Transcription factor ATF cDNA clones: an extensive family of leucine zipper proteins able to selectively form DNA-binding heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2083–2090. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T., Curran T. Cross-family dimerization of transcription factors Fos/Jun and ATF/CREB alters DNA binding specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3720–3724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halazonetis T. D., Georgopoulos K., Greenberg M. E., Leder P. c-Jun dimerizes with itself and with c-Fos, forming complexes of different DNA binding affinities. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):917–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90147-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heusel J. W., Hanson R. D., Silverman G. A., Ley T. J. Structure and expression of a cluster of human hematopoietic serine protease genes found on chromosome 14q11.2. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6152–6158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai S. I., Ryseck R. P., Mechta F., Bravo R., Yaniv M. Characterization of junD: a new member of the jun proto-oncogene family. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1433–1439. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03525.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeffler J. P., Meyer T. E., Yun Y., Jameson J. L., Habener J. F. Cyclic AMP-responsive DNA-binding protein: structure based on a cloned placental cDNA. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1430–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.2974179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huhtala P., Tuuttila A., Chow L. T., Lohi J., Keski-Oja J., Tryggvason K. Complete structure of the human gene for 92-kDa type IV collagenase. Divergent regulation of expression for the 92- and 72-kilodalton enzyme genes in HT-1080 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16485–16490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichinose A. Multiple members of the plasminogen-apolipoprotein(a) gene family associated with thrombosis. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 31;31(12):3113–3118. doi: 10.1021/bi00127a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivashkiv L. B., Liou H. C., Kara C. J., Lamph W. W., Verma I. M., Glimcher L. H. mXBP/CRE-BP2 and c-Jun form a complex which binds to the cyclic AMP, but not to the 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate, response element. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1609–1621. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaiswal A. K. Human NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase (NQO1) gene structure and induction by dioxin. Biochemistry. 1991 Nov 5;30(44):10647–10653. doi: 10.1021/bi00108a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka K., Nishizawa M., Kawai S. Structure-function analysis of the maf oncogene product, a member of the b-Zip protein family. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2133–2141. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2133-2141.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai S., Goto N., Kataoka K., Saegusa T., Shinno-Kohno H., Nishizawa M. Isolation of the avian transforming retrovirus, AS42, carrying the v-maf oncogene and initial characterization of its gene product. Virology. 1992 Jun;188(2):778–784. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90532-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Ziff E. The role of the leucine zipper in the fos-jun interaction. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):646–651. doi: 10.1038/336646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Jaiswal A. K. Regulation of human NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase gene. Role of AP1 binding site contained within human antioxidant response element. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):15097–15104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lok S., Breitman M. L., Chepelinsky A. B., Piatigorsky J., Gold R. J., Tsui L. C. Lens-specific promoter activity of a mouse gamma-crystallin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2221–2230. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lok S., Stevens W., Breitman M. L., Tsui L. C. Multiple regulatory elements of the murine gamma 2-crystallin promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3563–3582. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macgregor P. F., Abate C., Curran T. Direct cloning of leucine zipper proteins: Jun binds cooperatively to the CRE with CRE-BP1. Oncogene. 1990 Apr;5(4):451–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa T., Imamoto F., Merlino G. T., Pastan I., Ishii S. Cooperative function of two separate enhancers of the human epidermal growth factor receptor proto-oncogene. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5488–5494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa T., Sakura H., Kanei-Ishii C., Sudo T., Yoshimura T., Fujisawa J., Yoshida M., Ishii S. Leucine zipper structure of the protein CRE-BP1 binding to the cyclic AMP response element in brain. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2023–2028. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03610.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki Y., Bos T. J., Davis C., Starbuck M., Vogt P. K. Avian sarcoma virus 17 carries the jun oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2848–2852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui M., Tokuhara M., Konuma Y., Nomura N., Ishizaki R. Isolation of human fos-related genes and their expression during monocyte-macrophage differentiation. Oncogene. 1990 Mar;5(3):249–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meeker T. C., Loeb J., Ayres M., Sellers W. The human Pim-1 gene is selectively transcribed in different hemato-lymphoid cell lines in spite of a G + C-rich housekeeping promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1680–1688. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignotte V., Eleouet J. F., Raich N., Romeo P. H. Cis- and trans-acting elements involved in the regulation of the erythroid promoter of the human porphobilinogen deaminase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6548–6552. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignotte V., Wall L., deBoer E., Grosveld F., Romeo P. H. Two tissue-specific factors bind the erythroid promoter of the human porphobilinogen deaminase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):37–54. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon A. M., Ley T. J. Conservation of the primary structure, organization, and function of the human and mouse beta-globin locus-activating regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7693–7697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R., Dixon M., Smith R., Peters G., Dickson C. Complete nucleotide sequence of a milk-transmitted mouse mammary tumor virus: two frameshift suppression events are required for translation of gag and pol. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):480–490. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.480-490.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naeve G. S., Sharma A., Lee A. S. Identification of a 10-base pair protein binding site in the promoter of the hamster H3.2 gene required for the S phase dependent increase in transcription and its interaction with a Jun-like nuclear factor. Cell Growth Differ. 1992 Dec;3(12):919–928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Nathans D. The basic region of Fos mediates specific DNA binding. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3833–3841. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08561.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Ryder K., Nathans D. DNA binding activities of three murine Jun proteins: stimulation by Fos. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):907–915. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90146-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans J., Hogness D. S. Isolation and nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding human rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4851–4855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishina H., Sato H., Suzuki T., Sato M., Iba H. Isolation and characterization of fra-2, an additional member of the fos gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3619–3623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizawa M., Goto N., Kawai S. An avian transforming retrovirus isolated from a nephroblastoma that carries the fos gene as the oncogene. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3733–3740. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3733-3740.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizawa M., Kataoka K., Goto N., Fujiwara K. T., Kawai S. v-maf, a viral oncogene that encodes a "leucine zipper" motif. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7711–7715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura N., Zu Y. L., Maekawa T., Tabata S., Akiyama T., Ishii S. Isolation and characterization of a novel member of the gene family encoding the cAMP response element-binding protein CRE-BP1. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):4259–4266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda A., Sakai M., Muramatsu M. The structure of the rat glutathione S-transferase P gene and related pseudogenes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3858–3863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins A. S., Fishel R., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. Evi-1, a murine zinc finger proto-oncogene, encodes a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2665–2674. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Cohen D. R., Curran T., Bos T. J., Vogt P. K., Bohmann D., Tjian R., Franza B. R., Jr Fos-associated protein p39 is the product of the jun proto-oncogene. Science. 1988 May 20;240(4855):1010–1016. doi: 10.1126/science.3130660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray A., Tatter S. B., May L. T., Sehgal P. B. Activation of the human "beta 2-interferon/hepatocyte-stimulating factor/interleukin 6" promoter by cytokines, viruses, and second messenger agonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6701–6705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risse G., Jooss K., Neuberg M., Brüller H. J., Müller R. Asymmetrical recognition of the palindromic AP1 binding site (TRE) by Fos protein complexes. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3825–3832. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08560.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Lanahan A., Perez-Albuerne E., Nathans D. jun-D: a third member of the jun gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1500–1503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Lau L. F., Nathans D. A gene activated by growth factors is related to the oncogene v-jun. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1487–1491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryseck R. P., Bravo R. c-JUN, JUN B, and JUN D differ in their binding affinities to AP-1 and CRE consensus sequences: effect of FOS proteins. Oncogene. 1991 Apr;6(4):533–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai M., Okuda A., Muramatsu M. Multiple regulatory elements and phorbol 12-O-tetradecanoate 13-acetate responsiveness of the rat placental glutathione transferase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9456–9460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Ransone L. J., Lamph W. W., Verma I. M. Direct interaction between fos and jun nuclear oncoproteins: role of the 'leucine zipper' domain. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):692–695. doi: 10.1038/336692a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Seiki M. Regulatory mechanism of 92 kDa type IV collagenase gene expression which is associated with invasiveness of tumor cells. Oncogene. 1993 Feb;8(2):395–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selten G., Cuypers H. T., Boelens W., Robanus-Maandag E., Verbeek J., Domen J., van Beveren C., Berns A. The primary structure of the putative oncogene pim-1 shows extensive homology with protein kinases. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):603–611. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90886-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma A., Bos T. J., Pekkala-Flagan A., Vogt P. K., Lee A. S. Interaction of cellular factors related to the Jun oncoprotein with the promoter of a replication-dependent hamster histone H3.2 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):491–495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaul Y., Ben-Levy R. Multiple nuclear proteins in liver cells are bound to hepatitis B virus enhancer element and its upstream sequences. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):1913–1920. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02451.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibahara S., Morimoto Y., Furutani Y., Notake M., Takahashi H., Shimizu S., Horikawa S., Numa S. Isolation and sequence analysis of the human corticotropin-releasing factor precursor gene. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):775–779. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01499.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeal T., Angel P., Meek J., Karin M. Different requirements for formation of Jun: Jun and Jun: Fos complexes. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2091–2100. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaroop A., Xu J. Z., Pawar H., Jackson A., Skolnick C., Agarwal N. A conserved retina-specific gene encodes a basic motif/leucine zipper domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):266–270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., Sigler P. B., McKnight S. L. Scissors-grip model for DNA recognition by a family of leucine zipper proteins. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):911–916. doi: 10.1126/science.2683088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt P. K., Bos T. J. jun: oncogene and transcription factor. Adv Cancer Res. 1990;55:1–35. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60466-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerial M., Toschi L., Ryseck R. P., Schuermann M., Müller R., Bravo R. The product of a novel growth factor activated gene, fos B, interacts with JUN proteins enhancing their DNA binding activity. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):805–813. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03441.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]