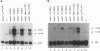Abstract
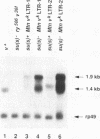
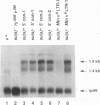
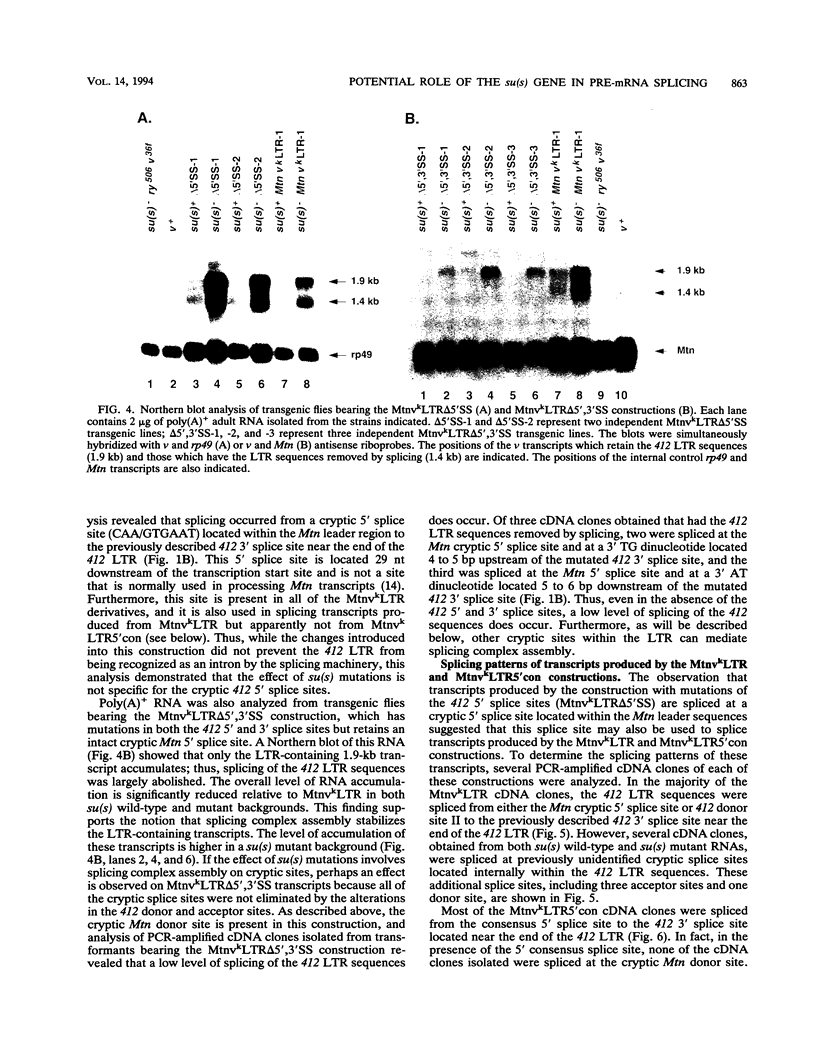
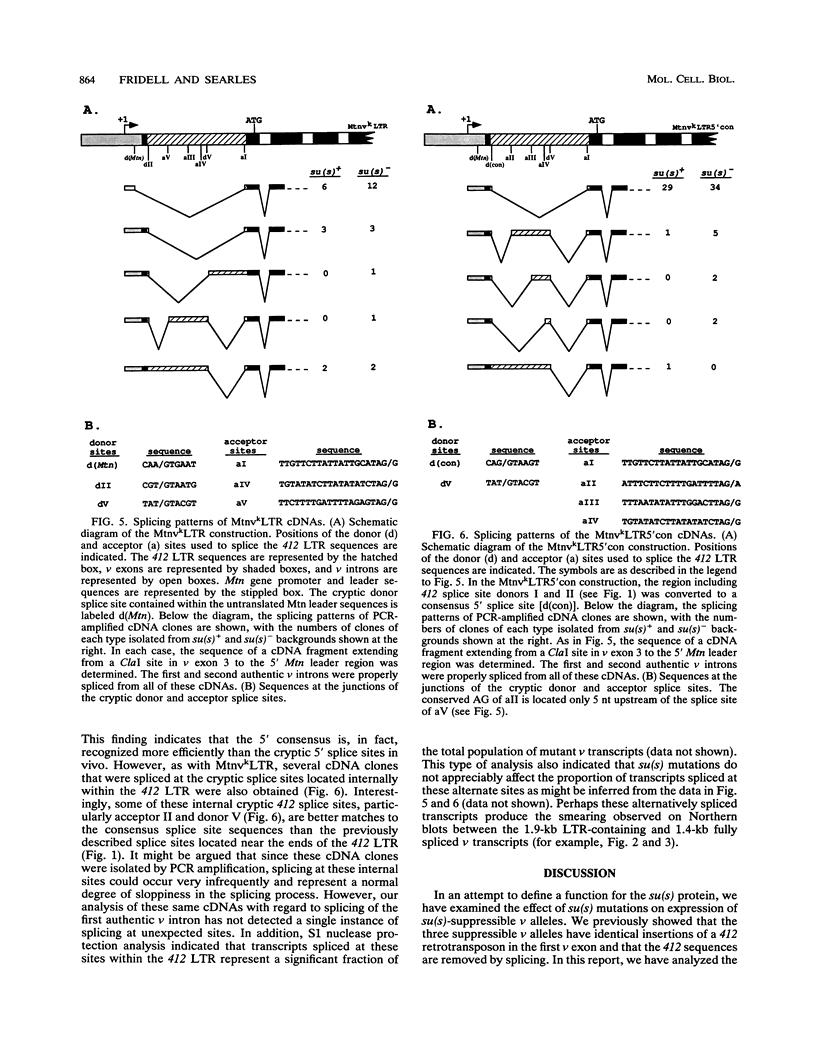
Recessive mutations of the Drosophila melanogaster suppressor of sable [su(s)] gene result in elevated accumulation of RNA from vermilion (v) mutant alleles that have an insertion of the 7.5-kb retrotransposon 412 in the first exon of the v gene. During transcription of such a v mutant gene, the 412 sequences are incorporated into the primary transcripts and are subsequently removed by splicing at cryptic sites within 412 sequences. In a su(s)+ background, the level of these unusually spliced transcripts is exceedingly low, and su(s) mutations increase their accumulation. We previously proposed that v RNA levels are elevated in su(s) mutants because of increased recognition of the cryptic splice sites, and the aim of this study was to test this hypothesis. We generated a v mutant derivative with a smaller 412 insertion, introduced alterations into the 412-associated splice sites, and examined the effect of su(s) mutations on expression of these derivatives after germ line transformation. To increase overall expression levels, the v promoter was replaced with the stronger Metallothionein (Mtn) gene promoter. We found that transformants bearing a v derivative with 480 bp of 412 sequences accumulate both transcripts, with 412 sequences spliced out and transcripts that retain 412 sequences. Mutations of su(s) increase the levels of both transcript classes without affecting the relative amounts of the two forms. Strikingly, replacement of the cryptic 5' splice sites with a 5' consensus produces the same effect as, and eliminates the response to, a su(s) mutation. In addition, we demonstrated that mutations of su(s) lead to increased accumulation of v transcripts even when the previously identified cryptic 412 5' and 3' splice sites were destroyed and that other cryptic splice sites reside within Mtn and 412 sequences. These results indicate that the v mutant transcripts are stabilized by assembly of the 412 sequences into splicing complexes and support the hypothesis that splicing complexes more readily assemble on cryptic splice sites in su(s) mutants.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bingham P. M., Levis R., Rubin G. M. Cloning of DNA sequences from the white locus of D. melanogaster by a novel and general method. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):693–704. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90176-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridell R. A., Pret A. M., Searles L. L. A retrotransposon 412 insertion within an exon of the Drosophila melanogaster vermilion gene is spliced from the precursor RNA. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):559–566. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridell Y. W., Searles L. L. In vivo transcriptional analysis of the TATA-less promoter of the Drosophila melanogaster vermilion gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4571–4577. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge H., Zuo P., Manley J. L. Primary structure of the human splicing factor ASF reveals similarities with Drosophila regulators. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):373–382. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90626-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geyer P. K., Chien A. J., Corces V. G., Green M. M. Mutations in the su(s) gene affect RNA processing in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7116–7120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Biochemical mechanisms of constitutive and regulated pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:559–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreitman M., Landweber L. F. A strategy for producing single-stranded DNA in the polymerase chain reaction. A direct method for genomic sequencing. Gene Anal Tech. 1989 Jul-Aug;6(4):84–88. doi: 10.1016/0735-0651(89)90021-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroni G., Otto E., Lastowski-Perry D. Molecular and cytogenetic characterization of a metallothionein gene of Drosophila. Genetics. 1986 Mar;112(3):493–504. doi: 10.1093/genetics/112.3.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeda A., Krainer A. R. Regulation of alternative pre-mRNA splicing by hnRNP A1 and splicing factor SF2. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):365–375. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90477-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mismer D., Rubin G. M. Analysis of the promoter of the ninaE opsin gene in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1987 Aug;116(4):565–578. doi: 10.1093/genetics/116.4.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell P. O., Rosbash M. Sequence, structure, and codon preference of the Drosophila ribosomal protein 49 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5495–5513. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'hare K., Levis R., Rubin G. M. Transcription of the white locus in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6917–6921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pret A. M., Searles L. L. Splicing of retrotransposon insertions from transcripts of the Drosophila melanogaster vermilion gene in a revertant. Genetics. 1991 Dec;129(4):1137–1145. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.4.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purugganan M., Wessler S. The splicing of transposable elements and its role in intron evolution. Genetica. 1992;86(1-3):295–303. doi: 10.1007/BF00133728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutledge B. J., Mortin M. A., Schwarz E., Thierry-Mieg D., Meselson M. Genetic interactions of modifier genes and modifiable alleles in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1988 Jun;119(2):391–397. doi: 10.1093/genetics/119.2.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searles L. L., Ruth R. S., Pret A. M., Fridell R. A., Ali A. J. Structure and transcription of the Drosophila melanogaster vermilion gene and several mutant alleles. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1423–1431. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searles L. L., Voelker R. A. Molecular characterization of the Drosophila vermilion locus and its suppressible alleles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):404–408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro M. B., Senapathy P. RNA splice junctions of different classes of eukaryotes: sequence statistics and functional implications in gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7155–7174. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA transferred or dotted nitrocellulose paper. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:255–266. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voelker R. A., Gibson W., Graves J. P., Sterling J. F., Eisenberg M. T. The Drosophila suppressor of sable gene encodes a polypeptide with regions similar to those of RNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):894–905. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voelker R. A., Graves J., Gibson W., Eisenberg M. Mobile element insertions causing mutations in the Drosophila suppressor of sable locus occur in DNase I hypersensitive subregions of 5'-transcribed nontranslated sequences. Genetics. 1990 Dec;126(4):1071–1082. doi: 10.1093/genetics/126.4.1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]