Abstract
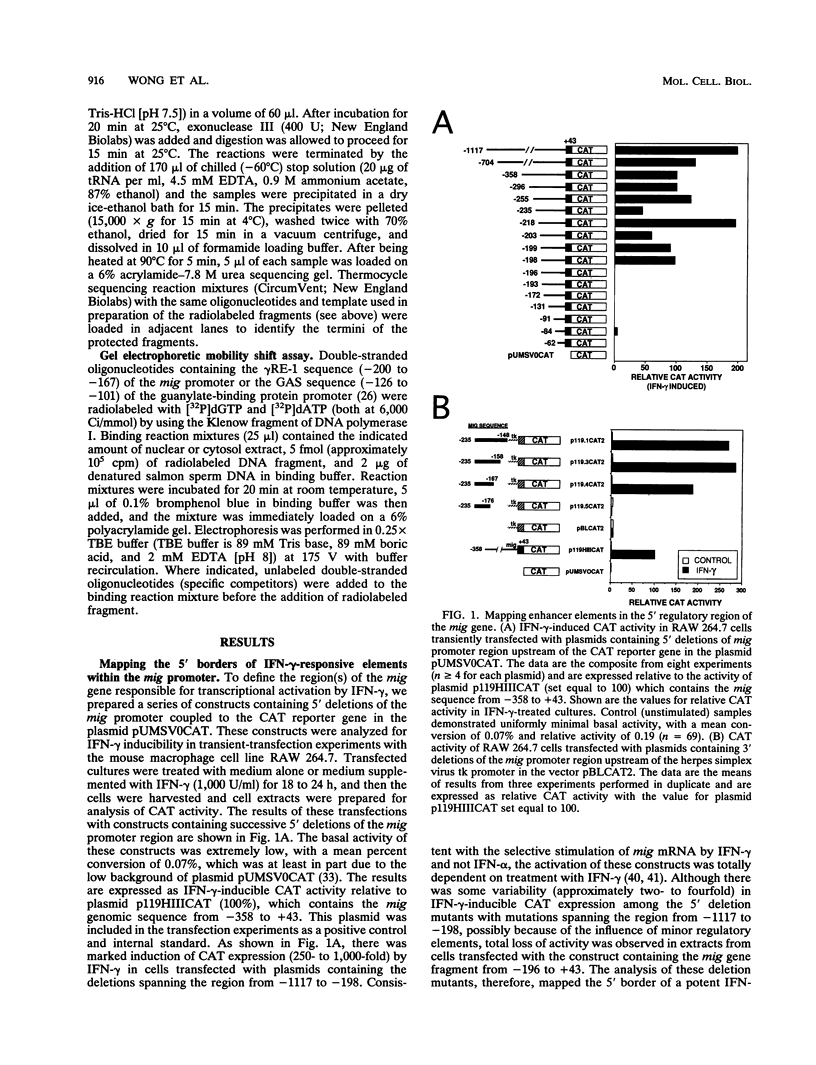
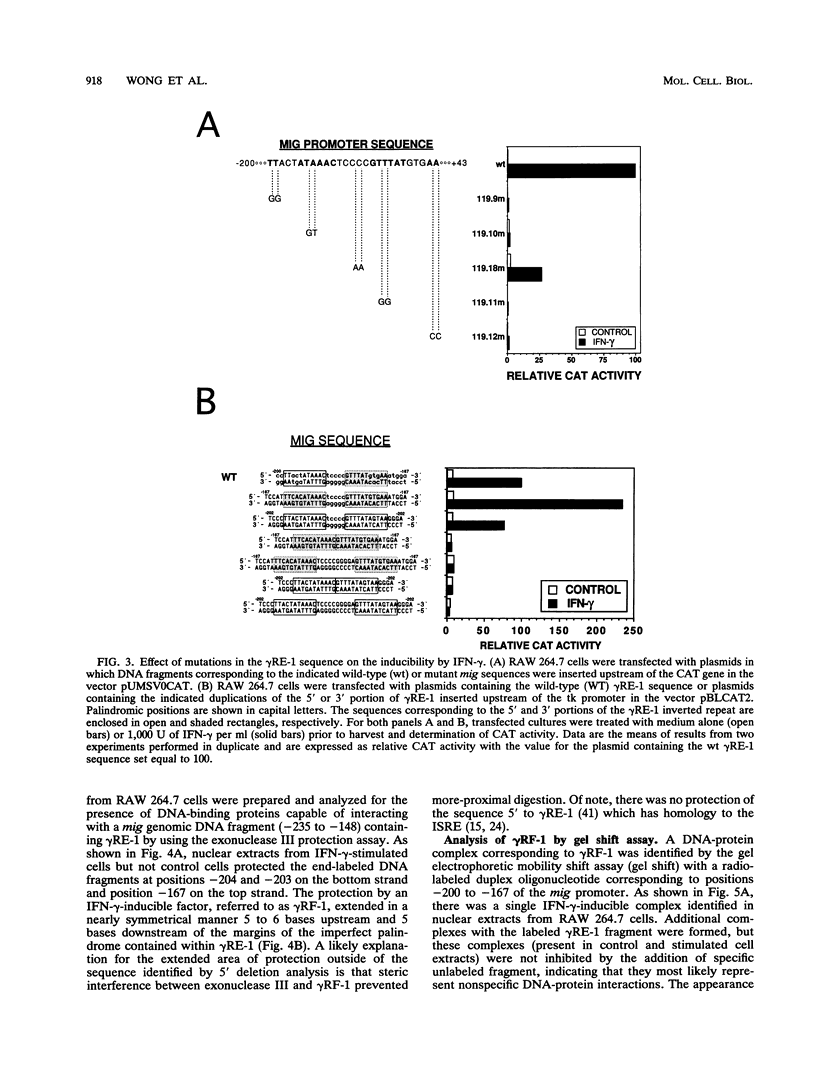
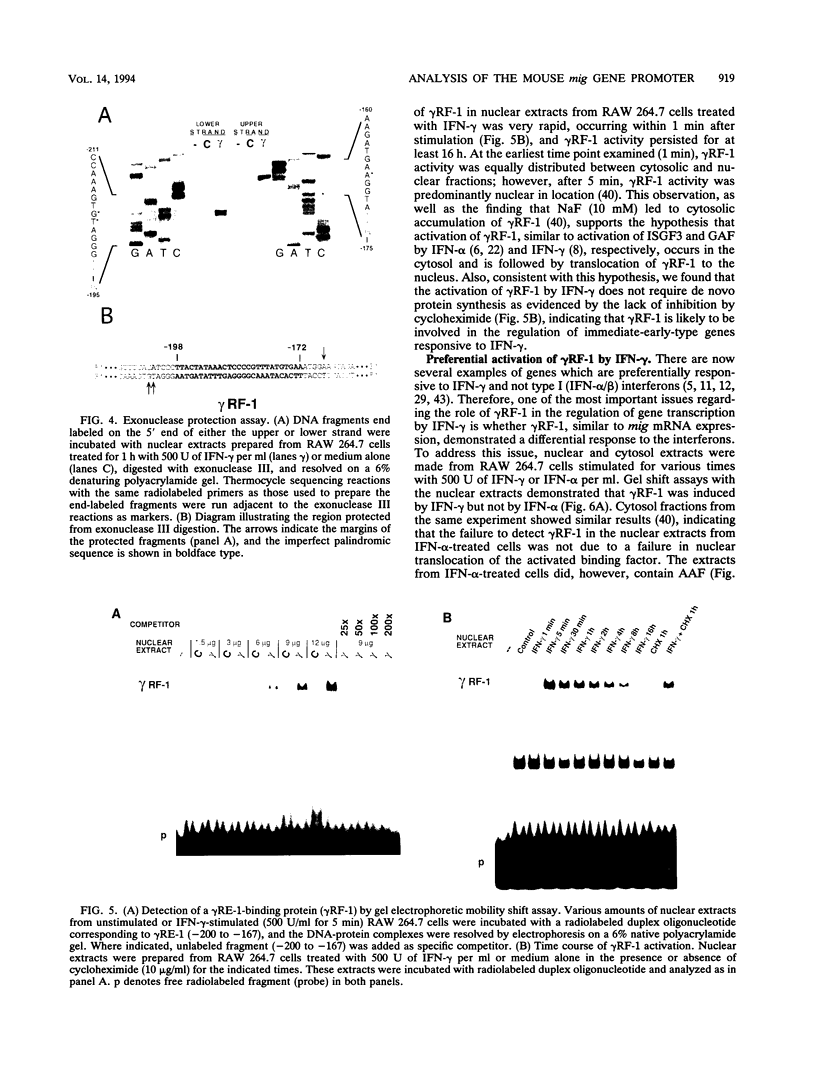
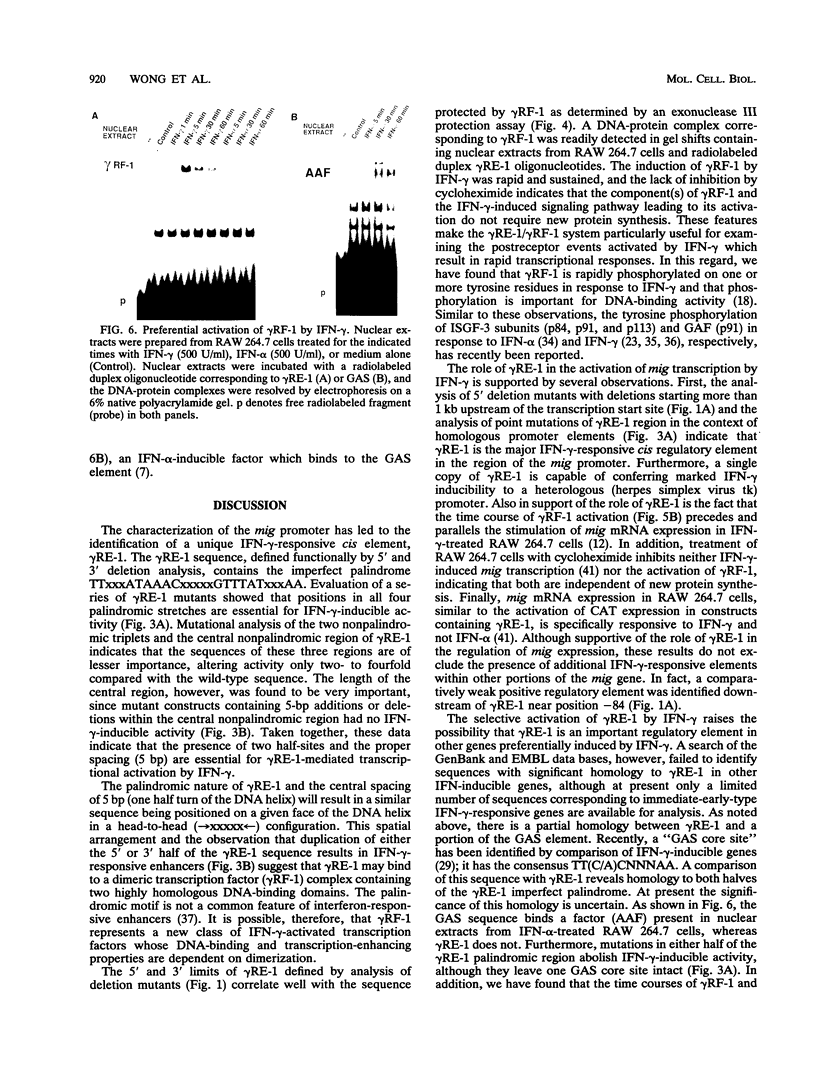
To define the molecular mechanisms involved in the action of gamma interferon (IFN-gamma), we have analyzed the transcriptional regulation of the mig (monokine induced by gamma interferon) gene, a member of the platelet factor 4-interleukin-8 cytokine family that is expressed in murine macrophages specifically in response to IFN-gamma. Analysis of mig/CAT chimeric constructs transiently transfected into the RAW 264.7 mouse monocytic cell line revealed a unique IFN-gamma-responsive element (gamma RE-1). The sequence of this cis regulatory element defined by deletion analysis contains an imperfect inverted repeat extending 27 bp. Examination of mig/CAT constructs with mutations in gamma RE-1 revealed that the palindromic positions in the element were essential for activity. Consistent with its function as an enhancer, a single copy of gamma RE-1 conferred IFN-gamma inducibility to a heterologous (herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase) promoter. Exonuclease III protection assays demonstrated symmetrical protection of a mig promoter fragment centered about the gamma RE-1 palindromic sequence. Using the gel electrophoretic mobility shift assay, we identified a factor (gamma RF-1) present in nuclear extracts prepared from IFN-gamma-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells which binds to gamma RE-1. The activation of gamma RF-1 occurred rapidly (within 1 min) in response to IFN-gamma and was independent of protein synthesis. Similar to the expression of mig mRNA, the formation of gamma RF-1 was selectively induced by IFN-gamma and not IFN-alpha. The regulation of gene expression through gamma RF-1 and gamma RE-1 may explain the preferential activation of a subset of interferon-inducible genes by IFN-gamma.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bandyopadhyay S. K., Kalvakolanu D. V., Sen G. C. Gene induction by interferons: functional complementation between trans-acting factors induced by alpha interferon and gamma interferon. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5055–5063. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basta P. V., Sherman P. A., Ting J. P. Identification of an interferon-gamma response region 5' of the human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen DR alpha chain gene which is active in human glioblastoma multiforme lines. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 15;138(4):1275–1280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins T., Korman A. J., Wake C. T., Boss J. M., Kappes D. J., Fiers W., Ault K. A., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Strominger J. L., Pober J. S. Immune interferon activates multiple class II major histocompatibility complex genes and the associated invariant chain gene in human endothelial cells and dermal fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4917–4921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonno R. J., Pang R. H. Induction of unique mRNAs by human interferons. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9234–9237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dai W., Gupta S. L. Regulation of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase gene expression in human fibroblasts by interferon-gamma. Upstream control region discriminates between interferon-gamma and interferon-alpha. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19871–19877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale T. C., Imam A. M., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Rapid activation by interferon alpha of a latent DNA-binding protein present in the cytoplasm of untreated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1203–1207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker T., Lew D. J., Darnell J. E., Jr Two distinct alpha-interferon-dependent signal transduction pathways may contribute to activation of transcription of the guanylate-binding protein gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5147–5153. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker T., Lew D. J., Mirkovitch J., Darnell J. E., Jr Cytoplasmic activation of GAF, an IFN-gamma-regulated DNA-binding factor. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):927–932. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08026.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedrick R. L., Jones P. P. Sequence elements required for activity of a murine major histocompatibility complex class II promoter bind common and cell-type-specific nuclear factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):593–604. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan X. D., Stark G. R., Bloom B. R. Molecular cloning of a gene selectively induced by gamma interferon from human macrophage cell line U937. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):1922–1928. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.1922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber J. M. A collection of mRNA species that are inducible in the RAW 264.7 mouse macrophage cell line by gamma interferon and other agents. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1535–1545. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber J. M. A macrophage mRNA selectively induced by gamma-interferon encodes a member of the platelet factor 4 family of cytokines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5238–5242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finn P. W., Kara C. J., Douhan J., 3rd, Van T. T., Folsom V., Glimcher L. H. Interferon gamma regulates binding of two nuclear protein complexes in a macrophage cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):914–918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Stark G. R. alpha-Interferon-induced transcription of HLA and metallothionein genes containing homologous upstream sequences. Nature. 1985 Apr 18;314(6012):637–639. doi: 10.1038/314637a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y., Kessler D. S., Veals S. A., Levy D. E., Darnell J. E., Jr ISGF3, the transcriptional activator induced by interferon alpha, consists of multiple interacting polypeptide chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8555–8559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., David M., Larner A. C., Finbloom D. S. In vitro activation of a transcription factor by gamma interferon requires a membrane-associated tyrosine kinase and is mimicked by vanadate. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):3984–3989. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.3984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ijzermans J. N., Marquet R. L. Interferon-gamma: a review. Immunobiology. 1989 Oct;179(4-5):456–473. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(89)80049-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley V. E., Fiers W., Strom T. B. Cloned human interferon-gamma, but not interferon-beta or -alpha, induces expression of HLA-DR determinants by fetal monocytes and myeloid leukemic cell lines. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):240–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler D. S., Veals S. A., Fu X. Y., Levy D. E. Interferon-alpha regulates nuclear translocation and DNA-binding affinity of ISGF3, a multimeric transcriptional activator. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1753–1765. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner A. C., David M., Feldman G. M., Igarashi K., Hackett R. H., Webb D. S., Sweitzer S. M., Petricoin E. F., 3rd, Finbloom D. S. Tyrosine phosphorylation of DNA binding proteins by multiple cytokines. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1730–1733. doi: 10.1126/science.8378773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Kessler D. S., Pine R., Reich N., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-induced nuclear factors that bind a shared promoter element correlate with positive and negative transcriptional control. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):383–393. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Lew D. J., Decker T., Kessler D. S., Darnell J. E., Jr Synergistic interaction between interferon-alpha and interferon-gamma through induced synthesis of one subunit of the transcription factor ISGF3. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1105–1111. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08216.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew D. J., Decker T., Strehlow I., Darnell J. E. Overlapping elements in the guanylate-binding protein gene promoter mediate transcriptional induction by alpha and gamma interferons. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):182–191. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N., Marks M. S., Driggers P. H., Ozato K. Interferon consensus sequence-binding protein, a member of the interferon regulatory factor family, suppresses interferon-induced gene transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):588–599. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse R. N., Feinman R., Ravetch J. V. Characterization of the promoter of the human gene encoding the high-affinity IgG receptor: transcriptional induction by gamma-interferon is mediated through common DNA response elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11305–11309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Langer J. A., Zoon K. C., Samuel C. E. Interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:727–777. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa F. M., Fellous M. Regulation of HLA-DR gene by IFN-gamma. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional control. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1660–1664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salier J. P., Kurachi K. A CAT expression vector with virtually no background: pUMSVOCAT. Biotechniques. 1989 Jan;7(1):30–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler C., Shuai K., Prezioso V. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of a latent cytoplasmic transcription factor. Science. 1992 Aug 7;257(5071):809–813. doi: 10.1126/science.1496401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuai K., Schindler C., Prezioso V. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Activation of transcription by IFN-gamma: tyrosine phosphorylation of a 91-kD DNA binding protein. Science. 1992 Dec 11;258(5089):1808–1812. doi: 10.1126/science.1281555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuai K., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M., Darnell J. E., Jr A single phosphotyrosine residue of Stat91 required for gene activation by interferon-gamma. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1744–1746. doi: 10.1126/science.7690989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims S. H., Cha Y., Romine M. F., Gao P. Q., Gottlieb K., Deisseroth A. B. A novel interferon-inducible domain: structural and functional analysis of the human interferon regulatory factor 1 gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):690–702. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil J., Epstein C. J., Epstein L. B., Sedmak J. J., Sabran J. L., Grossberg S. E. A unique set of polypeptides is induced by gamma interferon in addition to those induced in common with alpha and beta interferons. Nature. 1983 Feb 3;301(5899):437–439. doi: 10.1038/301437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright T. M., Farber J. M. 5' regulatory region of a novel cytokine gene mediates selective activation by interferon gamma. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):417–422. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
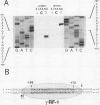
- Wu C. An exonuclease protection assay reveals heat-shock element and TATA box DNA-binding proteins in crude nuclear extracts. Nature. 1985 Sep 5;317(6032):84–87. doi: 10.1038/317084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynn T. A., Nicolet C. M., Paulnock D. M. Identification and characterization of a new gene family induced during macrophage activation. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 15;147(12):4384–4392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Z., Sugawara M., Ponath P. D., Wessendorf L., Banerji J., Li Y., Strominger J. L. Interferon gamma response region in the promoter of the human DPA gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9226–9230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]