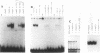Abstract
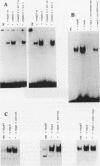
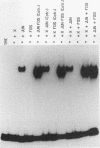
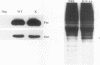
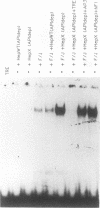
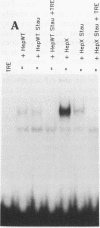
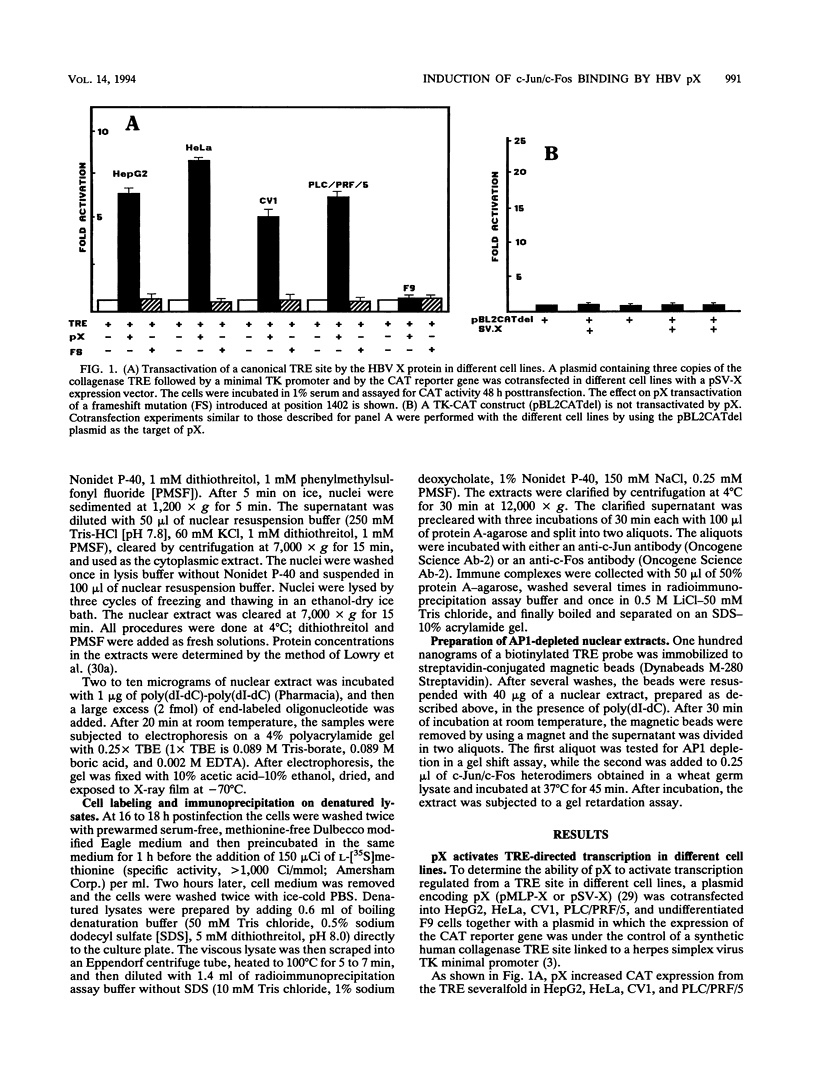
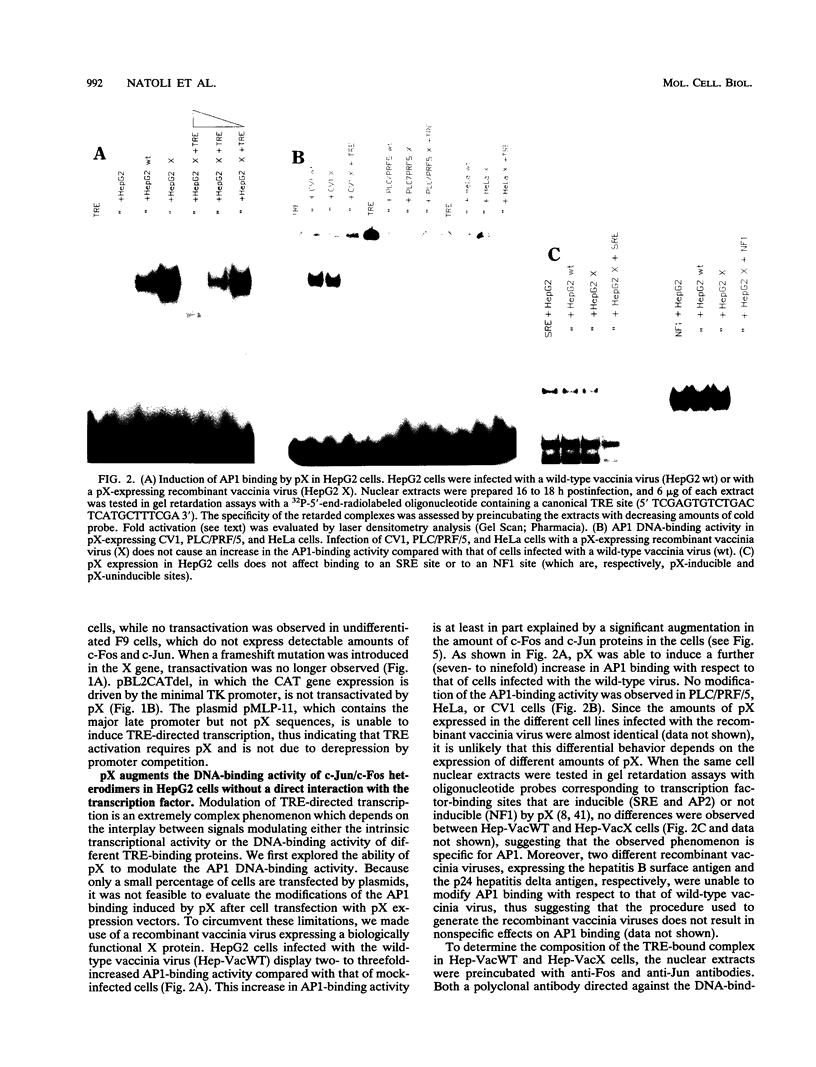
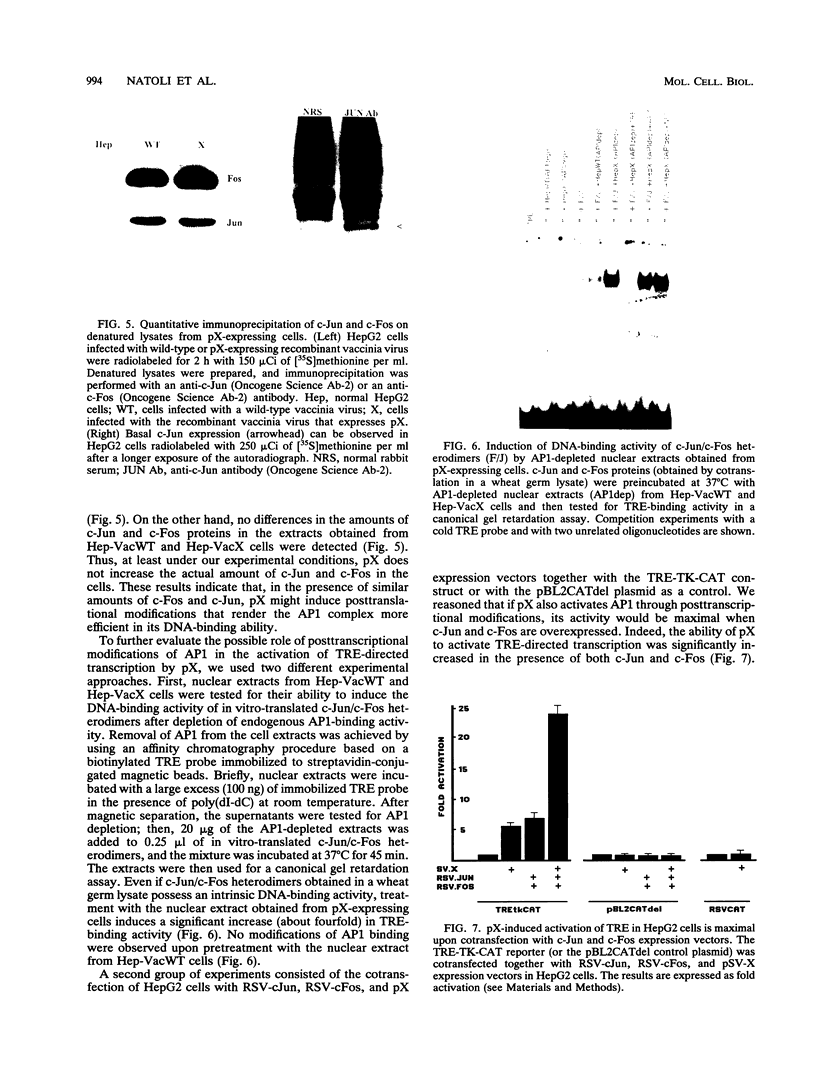
The hepatitis B virus (HBV) X protein (pX) is capable of activating transcription regulated by viral and cellular promoters containing binding sites for different transcription factors, including AP1. In this study we have analyzed the mechanisms of AP1 induction by pX. The hepatitis B virus transactivator was able to activate TRE (12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate response element)-directed transcription in different cell lines, including HepG2, HeLa, CV1, and PLC/PRF/5 cells. pX-induced AP1 activation in HepG2 cells was associated with an increase in the DNA-binding activity of c-Jun/c-Fos heterodimers, which was not dependent either on an increase in the overall amount of c-Fos and c-Jun proteins in the cells or on formation of dimers between pX and the two proteins, thus suggesting the involvement of posttranslational modifications of the transcription factor. The observation that the overexpression of c-Jun and c-Fos in the cells results in a strong augmentation of the effect of pX on TRE-directed transcription is additional evidence indicating the involvement of posttranscriptional modifications of c-Jun/c-Fos heterodimers. The increased AP1 binding observed in the presence of pX was unaffected by the protein kinase C inhibitors calphostin C and sphingosine and by the protein kinase A inhibitor HA1004, while it was almost completely blocked by staurosporine, a potent and nonspecific protein kinase inhibitor, suggesting that protein kinase C- and A-independent phosphorylation events might play a role in the phenomenon. The ability of pX also to increase TRE-directed transcription in cell lines in which AP1-binding activity is not increased (i.e., HeLa, CV1, and PLC/PRF/5 cells) suggests that pX can activate canonical TRE sites by different mechanisms as well.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abate C., Patel L., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Curran T. Redox regulation of fos and jun DNA-binding activity in vitro. Science. 1990 Sep 7;249(4973):1157–1161. doi: 10.1126/science.2118682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Hattori K., Smeal T., Karin M. The jun proto-oncogene is positively autoregulated by its product, Jun/AP-1. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):875–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90143-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Karin M. The role of Jun, Fos and the AP-1 complex in cell-proliferation and transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 10;1072(2-3):129–157. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aufiero B., Schneider R. J. The hepatitis B virus X-gene product trans-activates both RNA polymerase II and III promoters. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):497–504. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08136.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auwerx J., Sassone-Corsi P. AP-1 (Fos-Jun) regulation by IP-1: effect of signal transduction pathways and cell growth. Oncogene. 1992 Nov;7(11):2271–2280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auwerx J., Sassone-Corsi P. IP-1: a dominant inhibitor of Fos/Jun whose activity is modulated by phosphorylation. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):983–993. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90322-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avantaggiati M. L., Natoli G., Balsano C., Chirillo P., Artini M., De Marzio E., Collepardo D., Levrero M. The hepatitis B virus (HBV) pX transactivates the c-fos promoter through multiple cis-acting elements. Oncogene. 1993 Jun;8(6):1567–1574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baichwal V. R., Tjian R. Control of c-Jun activity by interaction of a cell-specific inhibitor with regulatory domain delta: differences between v- and c-Jun. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90147-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balsano C., Avantaggiati M. L., Natoli G., De Marzio E., Will H., Perricaudet M., Levrero M. Full-length and truncated versions of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) X protein (pX) transactivate the cmyc protooncogene at the transcriptional level. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 May 15;176(3):985–992. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90379-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binétruy B., Smeal T., Karin M. Ha-Ras augments c-Jun activity and stimulates phosphorylation of its activation domain. Nature. 1991 May 9;351(6322):122–127. doi: 10.1038/351122a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., Smeal T., Defize L. H., Angel P., Woodgett J. R., Karin M., Hunter T. Activation of protein kinase C decreases phosphorylation of c-Jun at sites that negatively regulate its DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):573–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90241-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colgrove R., Simon G., Ganem D. Transcriptional activation of homologous and heterologous genes by the hepatitis B virus X gene product in cells permissive for viral replication. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):4019–4026. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.4019-4026.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faktor O., Shaul Y. The identification of hepatitis B virus X gene responsive elements reveals functional similarity of X and HTLV-I tax. Oncogene. 1990 Jun;5(6):867–872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn G. M., Eckhart W. Transcriptional regulation of early-response genes during polyomavirus infection. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2193–2201. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2193-2201.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Merrill A. H., Jr, Bell R. M. Use of sphingosine as inhibitor of protein kinase C. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:316–328. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01028-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Watanabe M., Kobayashi R. Properties and use of H-series compounds as protein kinase inhibitors. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:328–339. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai S., Bourachot B., Yaniv M. Both Jun and Fos contribute to transcription activation by the heterodimer. Oncogene. 1990 Jan;5(1):39–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai S., Yaniv M. Jun DNA-binding is modulated by mutations between the leucines or by direct interaction of fos with the TGACTCA sequence. New Biol. 1989 Nov;1(2):181–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu K. Q., Vierling J. M., Siddiqui A. Trans-activation of HLA-DR gene by hepatitis B virus X gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7140–7144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Karin M. The regulation of transcription by phosphorylation. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):375–387. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Smeal T. Control of transcription factors by signal transduction pathways: the beginning of the end. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):418–422. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kekulé A. S., Lauer U., Weiss L., Luber B., Hofschneider P. H. Hepatitis B virus transactivator HBx uses a tumour promoter signalling pathway. Nature. 1993 Feb 25;361(6414):742–745. doi: 10.1038/361742a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike K., Shirakata Y., Yaginuma K., Arii M., Takada S., Nakamura I., Hayashi Y., Kawada M., Kobayashi M. Oncogenic potential of hepatitis B virus. Mol Biol Med. 1989 Apr;6(2):151–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levrero M., Balsano C., Natoli G., Avantaggiati M. L., Elfassi E. Hepatitis B virus X protein transactivates the long terminal repeats of human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3082–3086. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3082-3086.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levrero M., Jean-Jean O., Balsano C., Will H., Perricaudet M. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) X gene expression in human cells and anti-HBx antibodies detection in chronic HBV infection. Virology. 1990 Jan;174(1):299–304. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90079-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucito R., Schneider R. J. Hepatitis B virus X protein activates transcription factor NF-kappa B without a requirement for protein kinase C. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):983–991. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.983-991.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire H. F., Hoeffler J. P., Siddiqui A. HBV X protein alters the DNA binding specificity of CREB and ATF-2 by protein-protein interactions. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):842–844. doi: 10.1126/science.1827531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offringa R., Gebel S., van Dam H., Timmers M., Smits A., Zwart R., Stein B., Bos J. L., van der Eb A., Herrlich P. A novel function of the transforming domain of E1a: repression of AP-1 activity. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):527–538. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofir R., Dwarki V. J., Rashid D., Verma I. M. Phosphorylation of the C terminus of Fos protein is required for transcriptional transrepression of the c-fos promoter. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):80–82. doi: 10.1038/348080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulverer B. J., Kyriakis J. M., Avruch J., Nikolakaki E., Woodgett J. R. Phosphorylation of c-jun mediated by MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):670–674. doi: 10.1038/353670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux P., Blanchard J. M., Fernandez A., Lamb N., Jeanteur P., Piechaczyk M. Nuclear localization of c-Fos, but not v-Fos proteins, is controlled by extracellular signals. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):341–351. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90167-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Borrelli E. Promoter trans-activation of protooncogenes c-fos and c-myc, but not c-Ha-ras, by products of adenovirus early region 1A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6430–6433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Visvader J., Ferland L., Mellon P. L., Verma I. M. Induction of proto-oncogene fos transcription through the adenylate cyclase pathway: characterization of a cAMP-responsive element. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1529–1538. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönthal A., Srinivas S., Eckhart W. Induction of c-jun protooncogene expression and transcription factor AP-1 activity by the polyoma virus middle-sized tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4972–4976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Mitchell P. J., Yen T. S. Transactivation by the hepatitis B virus X protein depends on AP-2 and other transcription factors. Nature. 1990 Mar 1;344(6261):72–74. doi: 10.1038/344072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Yen T. S., Peterlin B. M., Ou J. H. Trans-activation of the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat by the hepatitis B virus X protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8286–8290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeal T., Binetruy B., Mercola D. A., Birrer M., Karin M. Oncogenic and transcriptional cooperation with Ha-Ras requires phosphorylation of c-Jun on serines 63 and 73. Nature. 1991 Dec 12;354(6353):494–496. doi: 10.1038/354494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeal T., Binetruy B., Mercola D., Grover-Bardwick A., Heidecker G., Rapp U. R., Karin M. Oncoprotein-mediated signalling cascade stimulates c-Jun activity by phosphorylation of serines 63 and 73. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3507–3513. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki T. Use and specificity of staurosporine, UCN-01, and calphostin C as protein kinase inhibitors. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:340–347. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01030-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tratner I., Ofir R., Verma I. M. Alteration of a cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylation site in the c-Fos protein augments its transforming potential. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):998–1006. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twu J. S., Lai M. Y., Chen D. S., Robinson W. S. Activation of protooncogene c-jun by the X protein of hepatitis B virus. Virology. 1993 Jan;192(1):346–350. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twu J. S., Robinson W. S. Hepatitis B virus X gene can transactivate heterologous viral sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):2046–2050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.2046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twu J. S., Schloemer R. H. Transcriptional trans-activating function of hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3448–3453. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3448-3453.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger T., Shaul Y. The X protein of the hepatitis B virus acts as a transcription factor when targeted to its responsive element. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1889–1895. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08315.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt P. K., Bos T. J. The oncogene jun and nuclear signalling. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 May;14(5):172–175. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90268-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. Y., Zhou Z. Y., Judd A., Cartwright C. A., Robinson W. S. The hepatitis B virus-encoded transcriptional trans-activator hbx appears to be a novel protein serine/threonine kinase. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):687–695. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90135-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthoudakis S., Curran T. Identification and characterization of Ref-1, a nuclear protein that facilitates AP-1 DNA-binding activity. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):653–665. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05097.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthoudakis S., Miao G., Wang F., Pan Y. C., Curran T. Redox activation of Fos-Jun DNA binding activity is mediated by a DNA repair enzyme. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3323–3335. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05411.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahm P., Hofschneider P. H., Koshy R. The HBV X-ORF encodes a transactivator: a potential factor in viral hepatocarcinogenesis. Oncogene. 1988 Aug;3(2):169–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou D. X., Taraboulos A., Ou J. H., Yen T. S. Activation of class I major histocompatibility complex gene expression by hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):4025–4028. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.4025-4028.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot R., Foulkes N., Mulder M., Kruijer W., Sassone-Corsi P. Positive regulation of jun/AP-1 by E1A. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):192–201. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]