Abstract
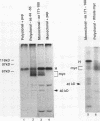
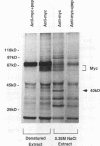
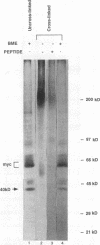
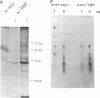
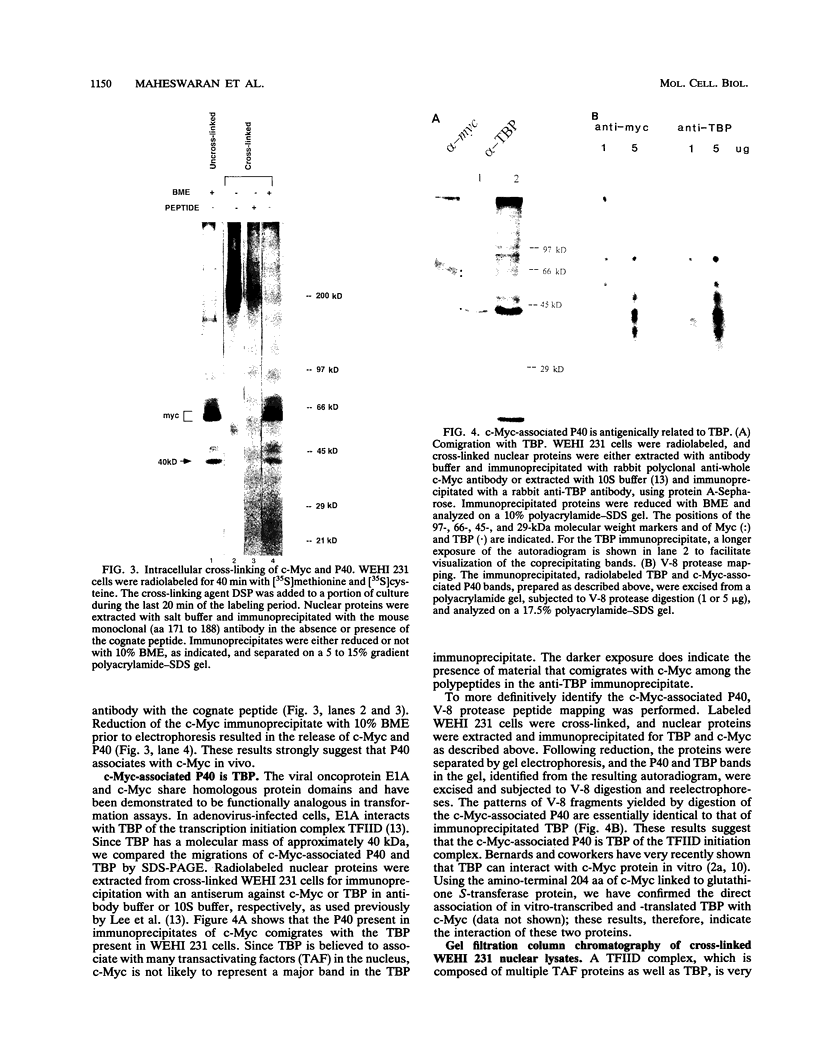
The c-myc proto-oncogene encodes nuclear phosphoproteins that bind DNA in a sequence-specific fashion and appear to function as transcriptional activators. Here we demonstrate that a 40-kDa nuclear protein coimmunoprecipitated with c-Myc specifically when nuclear proteins, extracted from nuclei of exponentially growing murine B-lymphoma WEHI 231 cells by using procedures for preparation of trans-acting factors, were reacted with anti-c-Myc antibodies made against different regions of the c-Myc protein. In contrast, preparation of nuclear lysates under denaturing conditions significantly reduced this coprecipitation. Upon incubation of WEHI 231 cells with the reversible chemical cross-linking agent dithiobis(succinimidyl propionate), the 40-kDa protein could be cross-linked to c-Myc protein intracellularly. Identification of the 40-kDa protein as the TATA-binding protein (TBP) of the TFIID transcription initiation complex was made by comigration and V-8 protease mapping, which yielded identical peptide fragments upon digestion of the 40-kDa protein and material immunoprecipitated with an anti-TBP specific antibody. Furthermore, in vitro-translated TBP bound to the amino-terminal portion of c-Myc. Column chromatography of cross-linked nuclear proteins showed TBP to be in a large-molecular-weight complex with c-Myc, consistent with a transcription initiation complex. These results indicate that intracellularly, c-Myc interacts with TBP, suggesting a mechanism of interaction of this oncoprotein with the basal transcription machinery.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amati B., Dalton S., Brooks M. W., Littlewood T. D., Evan G. I., Land H. Transcriptional activation by the human c-Myc oncoprotein in yeast requires interaction with Max. Nature. 1992 Oct 1;359(6394):423–426. doi: 10.1038/359423a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bello-Fernandez C., Packham G., Cleveland J. L. The ornithine decarboxylase gene is a transcriptional target of c-Myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7804–7808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Kretzner L., Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N., Weintraub H. Sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc protein. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1149–1151. doi: 10.1126/science.2251503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Max: a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that forms a sequence-specific DNA-binding complex with Myc. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1211–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.2006410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman R. N., Tachibana C. Y., Abrams H. D., Hann S. R. V-myc- and c-myc-encoded proteins are associated with the nuclear matrix. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):114–126. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., Abrams H. D., Rohrschneider L. R., Eisenman R. N. Proteins encoded by v-myc and c-myc oncogenes: identification and localization in acute leukemia virus transformants and bursal lymphoma cell lines. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):789–798. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90535-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., King M. W., Bentley D. L., Anderson C. W., Eisenman R. N. A non-AUG translational initiation in c-myc exon 1 generates an N-terminally distinct protein whose synthesis is disrupted in Burkitt's lymphomas. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90507-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hateboer G., Timmers H. T., Rustgi A. K., Billaud M., van 't Veer L. J., Bernards R. TATA-binding protein and the retinoblastoma gene product bind to overlapping epitopes on c-Myc and adenovirus E1A protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8489–8493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato G. J., Barrett J., Villa-Garcia M., Dang C. V. An amino-terminal c-myc domain required for neoplastic transformation activates transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5914–5920. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretzner L., Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Myc and Max proteins possess distinct transcriptional activities. Nature. 1992 Oct 1;359(6394):426–429. doi: 10.1038/359426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. S., Kao C. C., Bryant G. O., Liu X., Berk A. J. Adenovirus E1A activation domain binds the basic repeat in the TATA box transcription factor. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):365–376. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90188-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman P. M., Berk A. J. In vitro transcriptional activation, dimerization, and DNA-binding specificity of the Epstein-Barr virus Zta protein. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2560–2568. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2560-2568.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Eisenman R. N. New light on Myc and Myb. Part I. Myc. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2025–2035. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maheswaran S., McCormack J. E., Sonenshein G. E. Changes in phosphorylation of myc oncogene and RB antioncogene protein products during growth arrest of the murine lymphoma WEHI 231 cell line. Oncogene. 1991 Nov;6(11):1965–1971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maheswaran S., Park S., Bernard A., Morris J. F., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Hill D. E., Haber D. A. Physical and functional interaction between WT1 and p53 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5100–5104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä T. P., Koskinen P. J., Västrik I., Alitalo K. Alternative forms of Max as enhancers or suppressors of Myc-ras cotransformation. Science. 1992 Apr 17;256(5055):373–377. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5055.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai A., Satoh M., Hirayoshi K., Nagata K. Involvement of the stress protein HSP47 in procollagen processing in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1992 May;117(4):903–914. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.4.903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Lawe D., Ziff E. B. Association of Myn, the murine homolog of max, with c-Myc stimulates methylation-sensitive DNA binding and ras cotransformation. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):395–407. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90457-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Ziff E. B. Methylation-sensitive sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc basic region. Science. 1991 Jan 11;251(4990):186–189. doi: 10.1126/science.1987636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Usheva A., Zambetti G. P., Momand J., Horikoshi N., Weinmann R., Levine A. J., Shenk T. Wild-type p53 binds to the TATA-binding protein and represses transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):12028–12032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.12028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J., de Lange T., Ramsay G., Jakobovits E., Bishop J. M., Varmus H., Lee W. Definition of regions in human c-myc that are involved in transformation and nuclear localization. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1697–1709. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer K. F., Ingles C. J., Greenblatt J. Direct and selective binding of an acidic transcriptional activation domain to the TATA-box factor TFIID. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):783–786. doi: 10.1038/345783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama A., Kume A., Nemoto K., Lee S. Y., Asami Y., Nemoto F., Nishimura S., Kuchino Y. Isolation and characterization of s-myc, a member of the rat myc gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9144–9148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmers H. T., Sharp P. A. The mammalian TFIID protein is present in two functionally distinct complexes. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):1946–1956. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.1946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Gunzburg J., Riehl R., Weinberg R. A. Identification of a protein associated with p21ras by chemical crosslinking. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4007–4011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]