Abstract
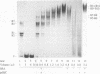
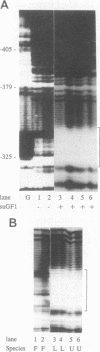
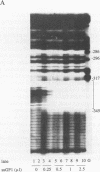
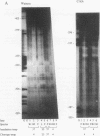
We have elsewhere reported the purification of a poly(dG).poly(dC)-binding nuclear protein (suGF1) from sea urchin embryos (J. Hapgood and D. Patterton, Mol. Cell. Biol. 14:this issue, 1994). We proposed that suGF1 may be a member of a family of G-string factors involved in developmental gene regulation, possibly via alterations in chromatin structure. In this article, we characterize the binding of purified suGF1 to 11 contiguous Gs in the H1-H4 intergenic region of a sea urchin early histone gene battery in vitro. It is shown that suGF1-DNA binding is dependent on ionic strength and requires divalent cations. Purified suGF1 forms discrete protein-DNA multimers, consistent with suGF1-suGF1 interactions. In a model for the suGF1-DNA complex derived from our footprinting and methylation interference data, suGF1 contacts the Gs in the major groove as well as one of the bordering phosphate backbones. The data are consistent with the direction of curvature of the DNA in the suGF1-DNA complex being the same as that preferred by the free DNA and exhibited by the DNA when bent around a positioned nucleosome core in vitro. However, on the basis of steric considerations, the binding of suGF1 and that of the histone octamer are predicted to be mutually exclusive. We show that suGF1 is indeed unable to bind to the G string when occupied by a histone octamer located in the major in vitro positioning frame in the H1-H4 intergenic region.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barton M. C., Madani N., Emerson B. M. The erythroid protein cGATA-1 functions with a stage-specific factor to activate transcription of chromatin-assembled beta-globin genes. Genes Dev. 1993 Sep;7(9):1796–1809. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.9.1796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhoff A. M., Tullius T. D. The unusual conformation adopted by the adenine tracts in kinetoplast DNA. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):935–943. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90702-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. P., Lewis C. D., Felsenfeld G. Properties of BGP1, a poly(dG)-binding protein from chicken erythrocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5119–5126. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey L., Roberts S. B., Heintz N. Purification of the human histone H4 gene-specific transcription factors H4TF-1 and H4TF-2. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1700–1712. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis T. L., Firulli A. B., Kinniburgh A. J. Ribonucleoprotein and protein factors bind to an H-DNA-forming c-myc DNA element: possible regulators of the c-myc gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9682–9686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R. Structural specificities of five commonly used DNA nucleases. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 15;176(4):535–557. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Travers A. A. DNA structural variations in the E. coli tyrT promoter. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):491–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Lewis C. D., Felsenfeld G. Interaction of specific nuclear factors with the nuclease-hypersensitive region of the chicken adult beta-globin gene: nature of the binding domain. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairall L., Rhodes D. A new approach to the analysis of DNase I footprinting data and its application to the TFIIIA/5S DNA complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Sep 25;20(18):4727–4731. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.18.4727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman P. J. Sequence dependence of the curvature of DNA: a test of the phasing hypothesis. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 3;24(25):7033–7037. doi: 10.1021/bi00346a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanas J. S., Hazuda D. J., Bogenhagen D. F., Wu F. Y., Wu C. W. Xenopus transcription factor A requires zinc for binding to the 5 S RNA gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14120–14125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hapgood J., Patterton D. Purification of an oligo(dG).oligo(dC)-binding sea urchin nuclear protein, suGF1: a family of G-string factors involved in gene regulation during development. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):1402–1409. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.1402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C. Homocopolymer sequences in the spacer of a sea urchin histone gene repeat are sensitive to S1 nuclease. Nature. 1982 Feb 25;295(5851):714–716. doi: 10.1038/295714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson P. D., Felsenfeld G. A method for mapping intranuclear protein-DNA interactions and its application to a nuclease hypersensitive site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2296–2300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Carner K. R., Masiarz F. R., Tjian R. Isolation of cDNA encoding transcription factor Sp1 and functional analysis of the DNA binding domain. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1079–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90594-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohwi Y., Kohwi-Shigematsu T. Altered gene expression correlates with DNA structure. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2547–2554. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohwi Y., Malkhosyan S. R., Kohwi-Shigematsu T. Intramolecular dG.dG.dC triplex detected in Escherichia coli cells. J Mol Biol. 1992 Feb 20;223(4):817–822. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90242-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolluri R., Kinniburgh A. J. Full length cDNA sequence encoding a nuclease-sensitive element DNA binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 11;19(17):4771–4771. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.17.4771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis C. D., Clark S. P., Felsenfeld G., Gould H. An erythrocyte-specific protein that binds to the poly(dG) region of the chicken beta-globin gene promoter. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):863–873. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutter L. C. Kinetic analysis of deoxyribonuclease I cleavages in the nucleosome core: evidence for a DNA superhelix. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 15;124(2):391–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90306-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyamichev V. I., Mirkin S. M., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. A pH-dependent structural transition in the homopurine-homopyrimidine tract in superhelical DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1985 Oct;3(2):327–338. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1985.10508420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastrangelo I. A., Courey A. J., Wall J. S., Jackson S. P., Hough P. V. DNA looping and Sp1 multimer links: a mechanism for transcriptional synergism and enhancement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5670–5674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pascal E., Tjian R. Different activation domains of Sp1 govern formation of multimers and mediate transcriptional synergism. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1646–1656. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterton H. G., von Holt C. Negative supercoiling and nucleosome cores. I. The effect of negative supercoiling on the efficiency of nucleosome core formation in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1993 Feb 5;229(3):623–636. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterton H. G., von Holt C. Negative supercoiling and nucleosome cores. II. The effect of negative supercoiling on the positioning of nucleosome cores in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1993 Feb 5;229(3):637–655. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumb M. A., Nicolas R. H., Wright C. A., Goodwin G. H. Multiple sequence-specific DNA binding activities are eluted from chicken nuclei at low ionic strengths. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 11;13(11):4047–4065. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.11.4047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D., Klug A. An underlying repeat in some transcriptional control sequences corresponding to half a double helical turn of DNA. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):123–132. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90866-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D. Structural analysis of a triple complex between the histone octamer, a Xenopus gene for 5S RNA and transcription factor IIIA. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3473–3482. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04106.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Carrillo A., Renaud J. Endonuclease G: a (dG)n X (dC)n-specific DNase from higher eukaryotes. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):401–407. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04769.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stellwagen N. C. Anomalous electrophoresis of deoxyribonucleic acid restriction fragments on polyacrylamide gels. Biochemistry. 1983 Dec 20;22(26):6186–6193. doi: 10.1021/bi00295a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su W., Jackson S., Tjian R., Echols H. DNA looping between sites for transcriptional activation: self-association of DNA-bound Sp1. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):820–826. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullius T. D., Dombroski B. A., Churchill M. E., Kam L. Hydroxyl radical footprinting: a high-resolution method for mapping protein-DNA contacts. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:537–558. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullius T. D., Dombroski B. A. Hydroxyl radical "footprinting": high-resolution information about DNA-protein contacts and application to lambda repressor and Cro protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5469–5473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. Helical repeat of DNA in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):200–203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P. Implications of DNA replication for eukaryotic gene expression. J Cell Sci. 1991 Jun;99(Pt 2):201–206. doi: 10.1242/jcs.99.2.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiang M., Lu S. Y., Musso M., Karsenty G., Klein W. H. A G-string positive cis-regulatory element in the LpS1 promoter binds two distinct nuclear factors distributed non-uniformly in Lytechinus pictus embryos. Development. 1991 Dec;113(4):1345–1355. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.4.1345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabel U., Schreck R., Baeuerle P. A. DNA binding of purified transcription factor NF-kappa B. Affinity, specificity, Zn2+ dependence, and differential half-site recognition. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):252–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]