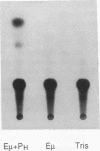
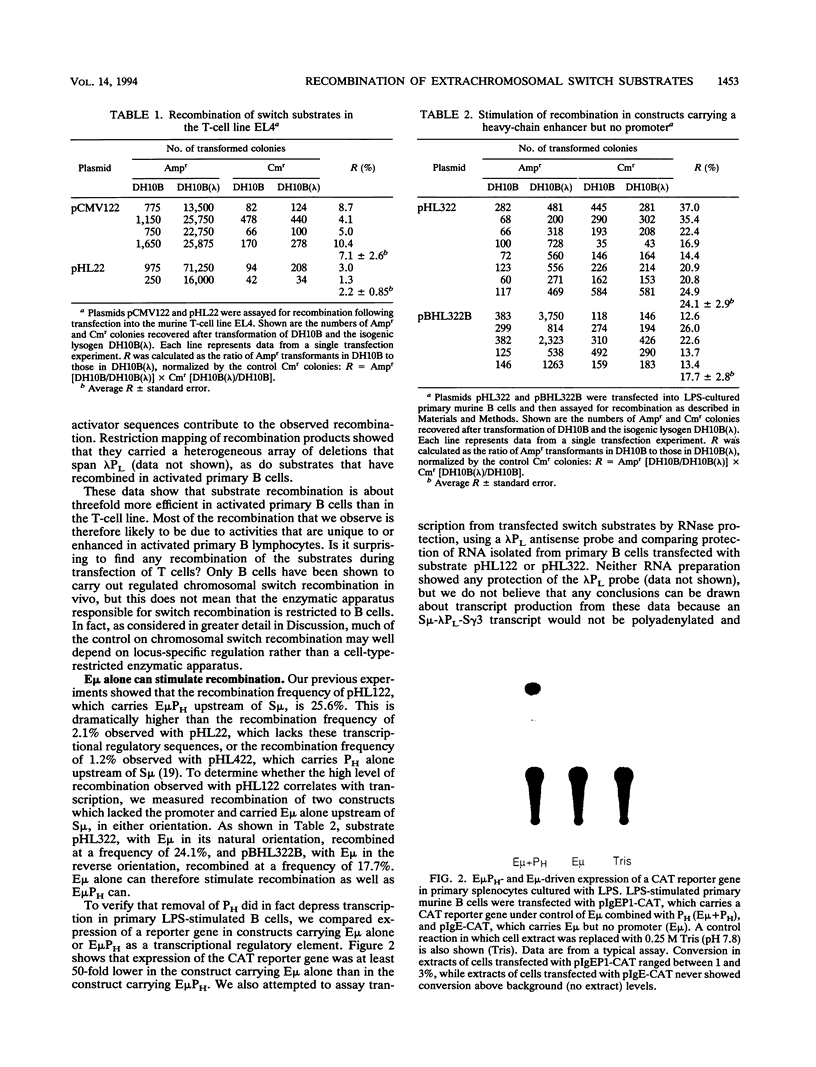
Abstract
We have used extrachromosomal substrates carrying immunoglobulin heavy-chain S mu and S gamma 3 switch region sequences to study activation and targeting of recombination by a transcriptional enhancer element. Substrates are transiently introduced into activated primary murine B cells, in which recombination involving S-region sequences deletes a conditionally lethal marker, and recombination is measured by transformation of Escherichia coli in the second step of the assay. Previously we found that as many as 25% of replicated substrates recombined during 40-h transfection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated primary cells and that efficient recombination was dependent on the presence of S-region sequences as well as a transcriptional activator region in the constructs (H. Leung and N. Maizels, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:4154-4158, 1992). Here we show that recombination of the switch substrates is threefold more efficient in LPS-cultured primary B cells than in the T-cell line EL4; the activities responsible for switch substrate recombination thus appear to be more abundant or more active in cells which can carry out chromosomal switch recombination. We test the role of the transcriptional activator region and show that the immunoglobulin heavy-chain intron enhancer (E mu) alone stimulates recombination as well as E mu combined with a heavy-chain promoter and that mutations that diminish enhancer-dependent transcription 500-fold diminish recombinational activation less than 2-fold. These observations suggest that the enhancer stimulates recombination by a mechanism that does not depend on transcript production or that is insensitive to the level of transcript production over a very broad range. Furthermore, we find that E mu stimulates recombination when located either upstream or downstream of S mu but that the position of the recombinational activator does affect the targeting of recombination junctions, suggesting that the relatively imprecise targeting of switch junctions in vivo may reflect the availability of many potential activator sites within each switch region.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams B., Dörfler P., Aguzzi A., Kozmik Z., Urbánek P., Maurer-Fogy I., Busslinger M. Pax-5 encodes the transcription factor BSAP and is expressed in B lymphocytes, the developing CNS, and adult testis. Genes Dev. 1992 Sep;6(9):1589–1607. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.9.1589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albertini A. M., Hofer M., Calos M. P., Miller J. H. On the formation of spontaneous deletions: the importance of short sequence homologies in the generation of large deletions. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):319–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90148-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alt F. W., Blackwell T. K., Yancopoulos G. D. Development of the primary antibody repertoire. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1079–1087. doi: 10.1126/science.3317825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barberis A., Widenhorn K., Vitelli L., Busslinger M. A novel B-cell lineage-specific transcription factor present at early but not late stages of differentiation. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):849–859. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Alt F. W. Mechanism and developmental program of immunoglobulin gene rearrangement in mammals. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:605–636. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.003133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L., Seymour B. W., Lebman D. A., Hiraki D. D., Christiansen J. A., Shrader B., Cherwinski H. M., Savelkoul H. F., Finkelman F. D., Bond M. W. The role of helper T cell products in mouse B cell differentiation and isotype regulation. Immunol Rev. 1988 Feb;102:5–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00739.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunnick W., Hertz G. Z., Scappino L., Gritzmacher C. DNA sequences at immunoglobulin switch region recombination sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Feb 11;21(3):365–372. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.3.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esser C., Radbruch A. Immunoglobulin class switching: molecular and cellular analysis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:717–735. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.003441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I. Integration host factor: a protein for all reasons. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):545–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90213-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese K., Cox J., Grosschedl R. The HMG domain of lymphoid enhancer factor 1 bends DNA and facilitates assembly of functional nucleoprotein structures. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90129-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. D., Nash H. A. Functional replacement of a protein-induced bend in a DNA recombination site. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):251–254. doi: 10.1038/341251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesse J. E., Lieber M. R., Mizuuchi K., Gellert M. V(D)J recombination: a functional definition of the joining signals. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):1053–1061. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.1053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh C. L., McCloskey R. P., Lieber M. R. V(D)J recombination on minichromosomes is not affected by transcription. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15613–15619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones I. M., Primrose S. B., Ehrlich S. D. Recombination between short direct repeats in a recA host. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;188(3):486–489. doi: 10.1007/BF00330053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung S., Rajewsky K., Radbruch A. Shutdown of class switch recombination by deletion of a switch region control element. Science. 1993 Feb 12;259(5097):984–987. doi: 10.1126/science.8438159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiledjian M., Su L. K., Kadesch T. Identification and characterization of two functional domains within the murine heavy-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):145–152. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung H., Maizels N. Transcriptional regulatory elements stimulate recombination in extrachromosomal substrates carrying immunoglobulin switch-region sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):4154–4158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.4154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao F., Giannini S. L., Birshtein B. K. A nuclear DNA-binding protein expressed during early stages of B cell differentiation interacts with diverse segments within and 3' of the Ig H chain gene cluster. J Immunol. 1992 May 1;148(9):2909–2917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutzker S., Alt F. W. Structure and expression of germ line immunoglobulin gamma 2b transcripts. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1849–1852. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mézard C., Pompon D., Nicolas A. Recombination between similar but not identical DNA sequences during yeast transformation occurs within short stretches of identity. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):659–670. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90434-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott D. E., Alt F. W., Marcu K. B. Immunoglobulin heavy chain switch region recombination within a retroviral vector in murine pre-B cells. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):577–584. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04793.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purkerson J. M., Isakson P. C. Interleukin 5 (IL-5) provides a signal that is required in addition to IL-4 for isotype switching to immunoglobulin (Ig) G1 and IgE. J Exp Med. 1992 Apr 1;175(4):973–982. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.4.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. B., Porter T. N., Wilson J. H. Mechanisms of nonhomologous recombination in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2599–2607. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlissel M., Voronova A., Baltimore D. Helix-loop-helix transcription factor E47 activates germ-line immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene transcription and rearrangement in a pre-T-cell line. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1367–1376. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultes N. P., Szostak J. W. A poly(dA.dT) tract is a component of the recombination initiation site at the ARG4 locus in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):322–328. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. M., Schlissel M. S., Baltimore D., DeFranco A. L. Stimulation of kappa light-chain gene rearrangement by the immunoglobulin mu heavy chain in a pre-B-cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5679–5690. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su L. K., Kadesch T. The immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer functions as the promoter for I mu sterile transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2619–2624. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szurek P., Petrini J., Dunnick W. Complete nucleotide sequence of the murine gamma 3 switch region and analysis of switch recombination sites in two gamma 3-expressing hybridomas. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):620–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voelkel-Meiman K., Keil R. L., Roeder G. S. Recombination-stimulating sequences in yeast ribosomal DNA correspond to sequences regulating transcription by RNA polymerase I. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):1071–1079. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90714-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters S. H., Saikh K. U., Stavnezer J. A B-cell-specific nuclear protein that binds to DNA sites 5' to immunoglobulin S alpha tandem repeats is regulated during differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5594–5601. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. A., Dominska M., Petes T. D. Transcription factors are required for the meiotic recombination hotspot at the HIS4 locus in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6621–6625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M., Brys A., Weiner A. M., Maizels N. A rapid method for determining the molecular weight of a protein bound to nucleic acid in a mobility shift assay. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Sep 25;20(18):4935–4936. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.18.4935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M., Hanakahi L. A., Maizels N. Purification and properties of LR1, an inducible DNA binding protein from mammalian B lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 25;268(18):13731–13737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M., Maizels N. LR1, a lipopolysaccharide-responsive factor with binding sites in the immunoglobulin switch regions and heavy-chain enhancer. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2353–2361. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuerffel R. A., Nathan A. T., Kenter A. L. Detection of an immunoglobulin switch region-specific DNA-binding protein in mitogen-stimulated mouse splenic B cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1714–1718. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuerffel R., Jamieson C. E., Morgan L., Merkulov G. V., Sen R., Kenter A. L. Switch recombination breakpoints are strictly correlated with DNA recognition motifs for immunoglobulin S gamma 3 DNA-binding proteins. J Exp Med. 1992 Aug 1;176(2):339–349. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancopoulos G. D., Alt F. W. Developmentally controlled and tissue-specific expression of unrearranged VH gene segments. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):271–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90141-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang D., Waldman A. S. An examination of the effects of double-strand breaks on extrachromosomal recombination in mammalian cells. Genetics. 1992 Dec;132(4):1081–1093. doi: 10.1093/genetics/132.4.1081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yi T. M., Stearns D., Demple B. Illegitimate recombination in an Escherichia coli plasmid: modulation by DNA damage and a new bacterial gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):2898–2903. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.2898-2903.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Bottaro A., Li S., Stewart V., Alt F. W. A selective defect in IgG2b switching as a result of targeted mutation of the I gamma 2b promoter and exon. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3529–3537. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06027.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]