Abstract
A variety of studies have now implicated the cellular transcription factor E2F as a key participant in transcription control during the cell growth cycle. Although the recent isolation of molecular clones encoding proteins that are components of the E2F activity (E2F1 and DP-1) provides an approach to defining the specific involvement of E2F in these events, definitive experiments remain difficult in the absence of appropriate genetic systems. We have now identified a Drosophila equivalent of E2F1 that we hope will allow an eventual genetic approach to the role of E2F in cellular regulatory events. A cDNA clone was isolated from a Drosophila cDNA library by using a probe containing sequence from the E2F1 DNA binding domain. The sequence of the clone, which we term drosE2F1, demonstrates considerable homology to the human E2F1 sequence, with over 65% identity in the DNA binding region and 50% identity in the region of E2F1 known to interact with the retinoblastoma gene product. A glutathione S-transferase-drosE2F1 fusion protein was capable of binding specifically to an E2F recognition site, and transfection assays demonstrated that the drosE2F1 product was capable of transcription activation, dependent on functional E2F sites as well as sequences within the C terminus of the protein. Finally, we have also identified E2F recognition sequences within the promoter of the Drosophila DNA polymerase alpha gene, and we demonstrate that the drosE2F1 product activates transcription of a test gene under the control of this promoter. We conclude that the drosE2F1 cDNA encodes an activity with extensive structural and functional similarity to the human E2F1 protein.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagchi S., Raychaudhuri P., Nevins J. R. Adenovirus E1A proteins can dissociate heteromeric complexes involving the E2F transcription factor: a novel mechanism for E1A trans-activation. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):659–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90112-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagchi S., Weinmann R., Raychaudhuri P. The retinoblastoma protein copurifies with E2F-I, an E1A-regulated inhibitor of the transcription factor E2F. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1063–1072. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90558-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandara L. R., Buck V. M., Zamanian M., Johnston L. H., La Thangue N. B. Functional synergy between DP-1 and E2F-1 in the cell cycle-regulating transcription factor DRTF1/E2F. EMBO J. 1993 Nov;12(11):4317–4324. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06116.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandara L. R., La Thangue N. B. Adenovirus E1a prevents the retinoblastoma gene product from complexing with a cellular transcription factor. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):494–497. doi: 10.1038/351494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao L., Faha B., Dembski M., Tsai L. H., Harlow E., Dyson N. Independent binding of the retinoblastoma protein and p107 to the transcription factor E2F. Nature. 1992 Jan 9;355(6356):176–179. doi: 10.1038/355176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chellappan S. P., Hiebert S., Mudryj M., Horowitz J. M., Nevins J. R. The E2F transcription factor is a cellular target for the RB protein. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1053–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90557-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chittenden T., Livingston D. M., Kaelin W. G., Jr The T/E1A-binding domain of the retinoblastoma product can interact selectively with a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1073–1082. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90559-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courey A. J., Tjian R. Analysis of Sp1 in vivo reveals multiple transcriptional domains, including a novel glutamine-rich activation motif. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cress W. D., Johnson D. G., Nevins J. R. A genetic analysis of the E2F1 gene distinguishes regulation by Rb, p107, and adenovirus E4. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6314–6325. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Figge J., Shew J. Y., Huang C. M., Lee W. H., Marsilio E., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. SV40 large tumor antigen forms a specific complex with the product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90559-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devoto S. H., Mudryj M., Pines J., Hunter T., Nevins J. R. A cyclin A-protein kinase complex possesses sequence-specific DNA binding activity: p33cdk2 is a component of the E2F-cyclin A complex. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Nocera P. P., Dawid I. B. Transient expression of genes introduced into cultured cells of Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7095–7098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson N., Howley P. M., Münger K., Harlow E. The human papilloma virus-16 E7 oncoprotein is able to bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):934–937. doi: 10.1126/science.2537532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girling R., Partridge J. F., Bandara L. R., Burden N., Totty N. F., Hsuan J. J., La Thangue N. B. A new component of the transcription factor DRTF1/E2F. Nature. 1993 Mar 4;362(6415):83–87. doi: 10.1038/362083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamel P. A., Gill R. M., Phillips R. A., Gallie B. L. Transcriptional repression of the E2-containing promoters EIIaE, c-myc, and RB1 by the product of the RB1 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3431–3438. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helin K., Lees J. A., Vidal M., Dyson N., Harlow E., Fattaey A. A cDNA encoding a pRB-binding protein with properties of the transcription factor E2F. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):337–350. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90107-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helin K., Wu C. L., Fattaey A. R., Lees J. A., Dynlacht B. D., Ngwu C., Harlow E. Heterodimerization of the transcription factors E2F-1 and DP-1 leads to cooperative trans-activation. Genes Dev. 1993 Oct;7(10):1850–1861. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.10.1850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiebert S. W., Chellappan S. P., Horowitz J. M., Nevins J. R. The interaction of RB with E2F coincides with an inhibition of the transcriptional activity of E2F. Genes Dev. 1992 Feb;6(2):177–185. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.2.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
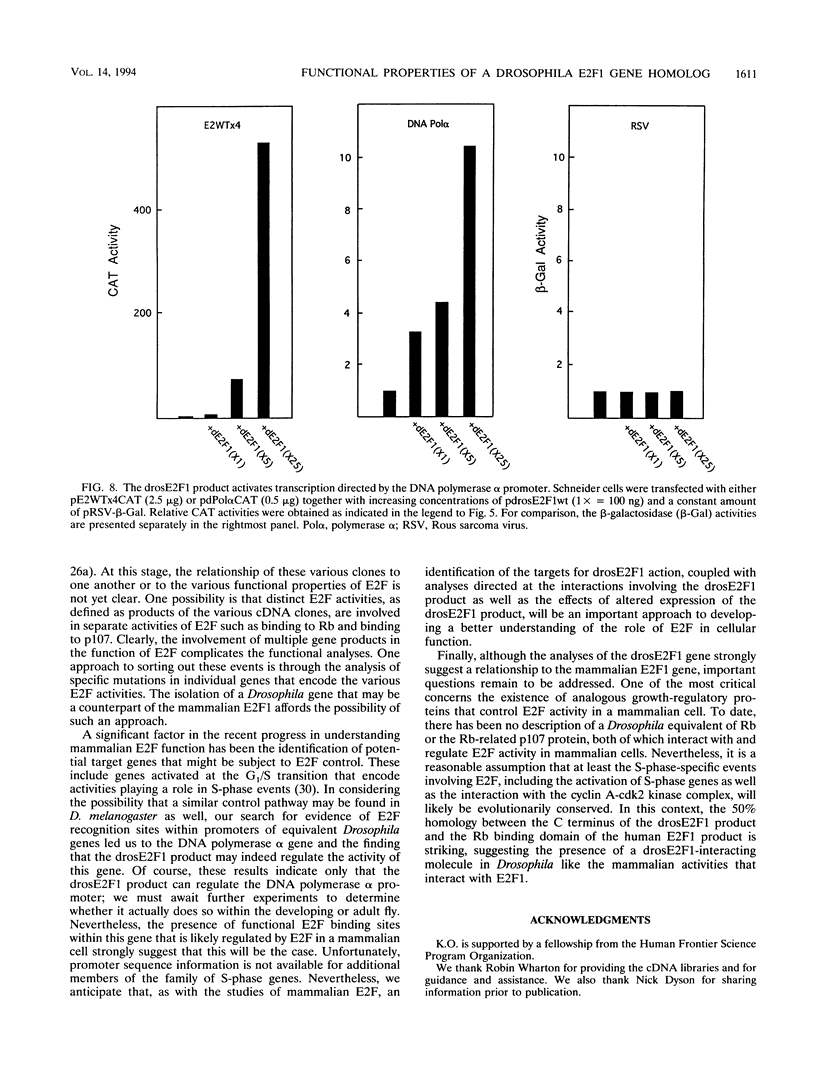
- Hirose F., Yamaguchi M., Handa H., Inomata Y., Matsukage A. Novel 8-base pair sequence (Drosophila DNA replication-related element) and specific binding factor involved in the expression of Drosophila genes for DNA polymerase alpha and proliferating cell nuclear antigen. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):2092–2099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda M. A., Nevins J. R. Identification of distinct roles for separate E1A domains in disruption of E2F complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):7029–7035. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.7029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivey-Hoyle M., Conroy R., Huber H. E., Goodhart P. J., Oliff A., Heimbrook D. C. Cloning and characterization of E2F-2, a novel protein with the biochemical properties of transcription factor E2F. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7802–7812. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. G., Schwarz J. K., Cress W. D., Nevins J. R. Expression of transcription factor E2F1 induces quiescent cells to enter S phase. Nature. 1993 Sep 23;365(6444):349–352. doi: 10.1038/365349a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaelin W. G., Jr, Krek W., Sellers W. R., DeCaprio J. A., Ajchenbaum F., Fuchs C. S., Chittenden T., Li Y., Farnham P. J., Blanar M. A. Expression cloning of a cDNA encoding a retinoblastoma-binding protein with E2F-like properties. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):351–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90108-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdi I., Reichel R., Nevins J. R. Identification of a cellular transcription factor involved in E1A trans-activation. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90386-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees E., Faha B., Dulic V., Reed S. I., Harlow E. Cyclin E/cdk2 and cyclin A/cdk2 kinases associate with p107 and E2F in a temporally distinct manner. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1874–1885. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees J. A., Saito M., Vidal M., Valentine M., Look T., Harlow E., Dyson N., Helin K. The retinoblastoma protein binds to a family of E2F transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7813–7825. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Green M. R. Transcription activation by the adenovirus E1a protein. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):39–44. doi: 10.1038/338039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeken M. R., Brady J. The adenovirus EIIA enhancer. Analysis of regulatory sequences and changes in binding activity of ATF and EIIF following adenovirus infection. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6572–6579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor G. R., Mogg A. E., Burke J. F., Caskey C. T. Histochemical staining of clonal mammalian cell lines expressing E. coli beta galactosidase indicates heterogeneous expression of the bacterial gene. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1987 May;13(3):253–265. doi: 10.1007/BF01535207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. E2F: a link between the Rb tumor suppressor protein and viral oncoproteins. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):424–429. doi: 10.1126/science.1411535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano M., Pepperkok R., Verde F., Ansorge W., Draetta G. Cyclin A is required at two points in the human cell cycle. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):961–971. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05135.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian Y., Luckey C., Horton L., Esser M., Templeton D. J. Biological function of the retinoblastoma protein requires distinct domains for hyperphosphorylation and transcription factor binding. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5363–5372. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qin X. Q., Chittenden T., Livingston D. M., Kaelin W. G., Jr Identification of a growth suppression domain within the retinoblastoma gene product. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):953–964. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shan B., Zhu X., Chen P. L., Durfee T., Yang Y., Sharp D., Lee W. H. Molecular cloning of cellular genes encoding retinoblastoma-associated proteins: identification of a gene with properties of the transcription factor E2F. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5620–5631. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirodkar S., Ewen M., DeCaprio J. A., Morgan J., Livingston D. M., Chittenden T. The transcription factor E2F interacts with the retinoblastoma product and a p107-cyclin A complex in a cell cycle-regulated manner. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90214-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slansky J. E., Li Y., Kaelin W. G., Farnham P. J. A protein synthesis-dependent increase in E2F1 mRNA correlates with growth regulation of the dihydrofolate reductase promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1610–1618. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub S. J., Prater C. A., Dean D. C. Retinoblastoma protein switches the E2F site from positive to negative element. Nature. 1992 Jul 16;358(6383):259–261. doi: 10.1038/358259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte P., Williamson N. M., Harlow E. Cellular targets for transformation by the adenovirus E1A proteins. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90984-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee A. S., Raychaudhuri P., Jakoi L., Nevins J. R. The adenovirus-inducible factor E2F stimulates transcription after specific DNA binding. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):578–585. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu L., van den Heuvel S., Helin K., Fattaey A., Ewen M., Livingston D., Dyson N., Harlow E. Inhibition of cell proliferation by p107, a relative of the retinoblastoma protein. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1111–1125. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]