Abstract
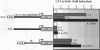
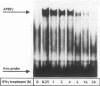
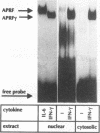
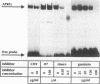
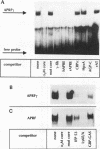
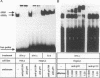
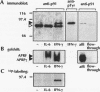
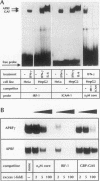
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) induce a partially overlapping set of genes, including the genes for interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF-1), intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1), and the acute-phase protein alpha 2-macroglobulin. We report here that the rat alpha 2-macroglobulin promoter is activated by IFN-gamma in human hepatoma (HepG2) cells and that the IFN-gamma response element maps to the same site previously defined as the acute-phase response element (APRE), which binds the IL-6-activated transcription factor APRF (acute-phase response factor). As was reported for fibroblasts, the IFN-gamma-regulated transcription factor GAF is phosphorylated at tyrosine after IFN-gamma treatment of HepG2 cells. IFN-gamma posttranslationally activates a protein which specifically binds to the alpha 2-macroglobulin APRE. This protein is shown to be identical or closely related to GAF. Although APRF and GAF are shown to represent different proteins, their binding sequence specificities are very similar. APRF and GAF bind equally well to the APRE sequences of various acute-phase protein genes as well as to the IFN-gamma response elements of the IRF-1, ICAM-1, and other IFN-gamma-inducible genes. Transient transfection analysis revealed that the IFN-gamma response elements of the IRF-1 and ICAM-1 promoters are able to confer responsiveness to both IFN-gamma and IL-6 onto a heterologous promoter. Therefore, APRF and GAF are likely to be involved in the transcriptional induction of these immediate-early genes by IL-6 and IFN-gamma, respectively. Taken together, these results demonstrate that two functionally distinct hormones, IL-6 and IFN-gamma, act through common regulatory elements to which different transcription factors sharing almost the same sequence specificity bind.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdollahi A., Lord K. A., Hoffman-Liebermann B., Liebermann D. A. Interferon regulatory factor 1 is a myeloid differentiation primary response gene induced by interleukin 6 and leukemia inhibitory factor: role in growth inhibition. Cell Growth Differ. 1991 Aug;2(8):401–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams D. O. Molecular interactions in macrophage activation. Immunol Today. 1989 Feb;10(2):33–35. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90298-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akira S., Isshiki H., Sugita T., Tanabe O., Kinoshita S., Nishio Y., Nakajima T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. A nuclear factor for IL-6 expression (NF-IL6) is a member of a C/EBP family. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1897–1906. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama T., Ishida J., Nakagawa S., Ogawara H., Watanabe S., Itoh N., Shibuya M., Fukami Y. Genistein, a specific inhibitor of tyrosine-specific protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5592–5595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argetsinger L. S., Campbell G. S., Yang X., Witthuhn B. A., Silvennoinen O., Ihle J. N., Carter-Su C. Identification of JAK2 as a growth hormone receptor-associated tyrosine kinase. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90415-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker T., Lew D. J., Darnell J. E., Jr Two distinct alpha-interferon-dependent signal transduction pathways may contribute to activation of transcription of the guanylate-binding protein gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5147–5153. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker T., Lew D. J., Mirkovitch J., Darnell J. E., Jr Cytoplasmic activation of GAF, an IFN-gamma-regulated DNA-binding factor. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):927–932. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08026.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delegeane A. M., Ferland L. H., Mellon P. L. Tissue-specific enhancer of the human glycoprotein hormone alpha-subunit gene: dependence on cyclic AMP-inducible elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):3994–4002. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.3994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustin M. L., Rothlein R., Bhan A. K., Dinarello C. A., Springer T. A. Induction by IL 1 and interferon-gamma: tissue distribution, biochemistry, and function of a natural adherence molecule (ICAM-1). J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):245–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilers A., Baccarini M., Horn F., Hipskind R. A., Schindler C., Decker T. A factor induced by differentiation signals in cells of the macrophage lineage binds to the gamma interferon activation site. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):1364–1373. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.1364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar M. A., Schreiber R. D. The molecular cell biology of interferon-gamma and its receptor. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:571–611. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.003035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y. A transcription factor with SH2 and SH3 domains is directly activated by an interferon alpha-induced cytoplasmic protein tyrosine kinase(s). Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):323–335. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90106-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y., Kessler D. S., Veals S. A., Levy D. E., Darnell J. E., Jr ISGF3, the transcriptional activator induced by interferon alpha, consists of multiple interacting polypeptide chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8555–8559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y., Schindler C., Improta T., Aebersold R., Darnell J. E., Jr The proteins of ISGF-3, the interferon alpha-induced transcriptional activator, define a gene family involved in signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7840–7843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganter U., Arcone R., Toniatti C., Morrone G., Ciliberto G. Dual control of C-reactive protein gene expression by interleukin-1 and interleukin-6. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3773–3779. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08554.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing D. P., Comeau M. R., Friend D. J., Gimpel S. D., Thut C. J., McGourty J., Brasher K. K., King J. A., Gillis S., Mosley B. The IL-6 signal transducer, gp130: an oncostatin M receptor and affinity converter for the LIF receptor. Science. 1992 Mar 13;255(5050):1434–1437. doi: 10.1126/science.1542794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger T., Andus T., Klapproth J., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Heinrich P. C. Induction of rat acute-phase proteins by interleukin 6 in vivo. Eur J Immunol. 1988 May;18(5):717–721. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Abraham L. J., Northemann W., Fey G. H. Acute-phase reaction induces a specific complex between hepatic nuclear proteins and the interleukin 6 response element of the rat alpha 2-macroglobulin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2364–2368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn F., Windle J. J., Barnhart K. M., Mellon P. L. Tissue-specific gene expression in the pituitary: the glycoprotein hormone alpha-subunit gene is regulated by a gonadotrope-specific protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2143–2153. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., David M., Finbloom D. S., Larner A. C. In vitro activation of the transcription factor gamma interferon activation factor by gamma interferon: evidence for a tyrosine phosphatase/kinase signaling cascade. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1634–1640. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito T., Tanahashi H., Misumi Y., Sakaki Y. Nuclear factors interacting with an interleukin-6 responsive element of rat alpha 2-macroglobulin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9425–9435. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanno Y., Kozak C. A., Schindler C., Driggers P. H., Ennist D. L., Gleason S. L., Darnell J. E., Jr, Ozato K. The genomic structure of the murine ICSBP gene reveals the presence of the gamma interferon-responsive element, to which an ISGF3 alpha subunit (or similar) molecule binds. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):3951–3963. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.3951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan K. D., Lindwall G., Maher S. E., Bothwell A. L. Characterization of promoter elements of an interferon-inducible Ly-6E/A differentiation antigen, which is expressed on activated T cells and hematopoietic stem cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5150–5159. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. The biology of interleukin-6. Blood. 1989 Jul;74(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause E., Wegenka U., Möller C., Horn F., Heinrich P. C. Gene expression of the high molecular weight proteinase inhibitor alpha 2-macroglobulin. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1992 Jul;373(7):509–515. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1992.373.2.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunz D., Zimmermann R., Heisig M., Heinrich P. C. Identification of the promoter sequences involved in the interleukin-6 dependent expression of the rat alpha 2-macroglobulin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1121–1138. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner A. C., David M., Feldman G. M., Igarashi K., Hackett R. H., Webb D. S., Sweitzer S. M., Petricoin E. F., 3rd, Finbloom D. S. Tyrosine phosphorylation of DNA binding proteins by multiple cytokines. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1730–1733. doi: 10.1126/science.8378773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew D. J., Decker T., Strehlow I., Darnell J. E. Overlapping elements in the guanylate-binding protein gene promoter mediate transcriptional induction by alpha and gamma interferons. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):182–191. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord K. A., Abdollahi A., Thomas S. M., DeMarco M., Brugge J. S., Hoffman-Liebermann B., Liebermann D. A. Leukemia inhibitory factor and interleukin-6 trigger the same immediate early response, including tyrosine phosphorylation, upon induction of myeloid leukemia differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4371–4379. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P., Parker V., Gluzman Y., Maniatis T. Identification of DNA sequences required for transcription of the human alpha 1-globin gene in a new SV40 host-vector system. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90411-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto M., Fujita T., Kimura Y., Maruyama M., Harada H., Sudo Y., Miyata T., Taniguchi T. Regulated expression of a gene encoding a nuclear factor, IRF-1, that specifically binds to IFN-beta gene regulatory elements. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):903–913. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91307-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Hibi M., Nakagawa N., Nakagawa T., Yasukawa K., Yamanishi K., Taga T., Kishimoto T. IL-6-induced homodimerization of gp130 and associated activation of a tyrosine kinase. Science. 1993 Jun 18;260(5115):1808–1810. doi: 10.1126/science.8511589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Briscoe J., Laxton C., Guschin D., Ziemiecki A., Silvennoinen O., Harpur A. G., Barbieri G., Witthuhn B. A., Schindler C. The protein tyrosine kinase JAK1 complements defects in interferon-alpha/beta and -gamma signal transduction. Nature. 1993 Nov 11;366(6451):129–135. doi: 10.1038/366129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima K., Kusafuka T., Takeda T., Fujitani Y., Nakae K., Hirano T. Identification of a novel interleukin-6 response element containing an Ets-binding site and a CRE-like site in the junB promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):3027–3041. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.3027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima K., Wall R. Interleukin-6 signals activating junB and TIS11 gene transcription in a B-cell hybridoma. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1409–1418. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima T., Kinoshita S., Sasagawa T., Sasaki K., Naruto M., Kishimoto T., Akira S. Phosphorylation at threonine-235 by a ras-dependent mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade is essential for transcription factor NF-IL6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2207–2211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliviero S., Cortese R. The human haptoglobin gene promoter: interleukin-6-responsive elements interact with a DNA-binding protein induced by interleukin-6. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1145–1151. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03485.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse R. N., Feinman R., Shuai K., Darnell J. E., Jr, Ravetch J. V. Interferon gamma-induced transcription of the high-affinity Fc receptor for IgG requires assembly of a complex that includes the 91-kDa subunit of transcription factor ISGF3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):4314–4318. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli V., Cortese R. Interleukin 6 induces a liver-specific nuclear protein that binds to the promoter of acute-phase genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8202–8206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron D., Brasier A. R., Wright K. A., Tate J. E., Habener J. F. An inducible 50-kilodalton NF kappa B-like protein and a constitutive protein both bind the acute-phase response element of the angiotensinogen gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1023–1032. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski H. B., Gilman M. Z. Cell-free activation of a DNA-binding protein by epidermal growth factor. Nature. 1993 Mar 4;362(6415):79–83. doi: 10.1038/362079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski H. B., Shuai K., Darnell J. E., Jr, Gilman M. Z. A common nuclear signal transduction pathway activated by growth factor and cytokine receptors. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1739–1744. doi: 10.1126/science.8397445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Van Dyke M. W., Gregor P. D., Roeder R. G. Multiple forms of the human gene-specific transcription factor USF. I. Complete purification and identification of USF from HeLa cell nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11985–11993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler C., Fu X. Y., Improta T., Aebersold R., Darnell J. E., Jr Proteins of transcription factor ISGF-3: one gene encodes the 91-and 84-kDa ISGF-3 proteins that are activated by interferon alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7836–7839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Sheen J. Y. A simple phase-extraction assay for chloramphenicol acyltransferase activity. Gene. 1988 Jul 30;67(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90403-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Sharp P. A., Wahli W. W., Keller M. J. A high-efficiency HeLa cell nuclear transcription extract. DNA. 1988 Jan-Feb;7(1):47–55. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuai K., Schindler C., Prezioso V. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Activation of transcription by IFN-gamma: tyrosine phosphorylation of a 91-kD DNA binding protein. Science. 1992 Dec 11;258(5089):1808–1812. doi: 10.1126/science.1281555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvennoinen O., Witthuhn B. A., Quelle F. W., Cleveland J. L., Yi T., Ihle J. N. Structure of the murine Jak2 protein-tyrosine kinase and its role in interleukin 3 signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8429–8433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims S. H., Cha Y., Romine M. F., Gao P. Q., Gottlieb K., Deisseroth A. B. A novel interferon-inducible domain: structural and functional analysis of the human interferon regulatory factor 1 gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):690–702. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh R. P., Natarajan V. A rapid affinity method for isolation and characterization of sequence specific DNA binding factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Aug 31;147(1):65–70. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80087-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strehlow I., Seegert D., Frick C., Bange F. C., Schindler C., Böttger E. C., Decker T. The gene encoding IFP 53/tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase is regulated by the gamma-interferon activation factor. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 5;268(22):16590–16595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strunk R. C., Cole F. S., Perlmutter D. H., Colten H. R. gamma-Interferon increases expression of class III complement genes C2 and factor B in human monocytes and in murine fibroblasts transfected with human C2 and factor B genes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15280–15285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taga T., Hibi M., Hirata Y., Yamasaki K., Yasukawa K., Matsuda T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Interleukin-6 triggers the association of its receptor with a possible signal transducer, gp130. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):573–581. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90438-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki T. Use and specificity of staurosporine, UCN-01, and calphostin C as protein kinase inhibitors. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:340–347. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01030-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velazquez L., Fellous M., Stark G. R., Pellegrini S. A protein tyrosine kinase in the interferon alpha/beta signaling pathway. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):313–322. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90105-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner B. J., Hayes T. E., Hoban C. J., Cochran B. H. The SIF binding element confers sis/PDGF inducibility onto the c-fos promoter. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4477–4484. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07898.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegenka U. M., Buschmann J., Lütticken C., Heinrich P. C., Horn F. Acute-phase response factor, a nuclear factor binding to acute-phase response elements, is rapidly activated by interleukin-6 at the posttranslational level. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):276–288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witthuhn B. A., Quelle F. W., Silvennoinen O., Yi T., Tang B., Miura O., Ihle J. N. JAK2 associates with the erythropoietin receptor and is tyrosine phosphorylated and activated following stimulation with erythropoietin. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):227–236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90414-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Won K. A., Baumann H. The cytokine response element of the rat alpha 1-acid glycoprotein gene is a complex of several interacting regulatory sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):3965–3978. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.3965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuraw B. L., Lotz M. Regulation of the hepatic synthesis of C1 inhibitor by the hepatocyte stimulating factors interleukin 6 and interferon gamma. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12664–12670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]