Abstract
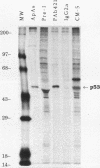
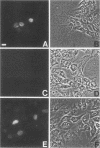
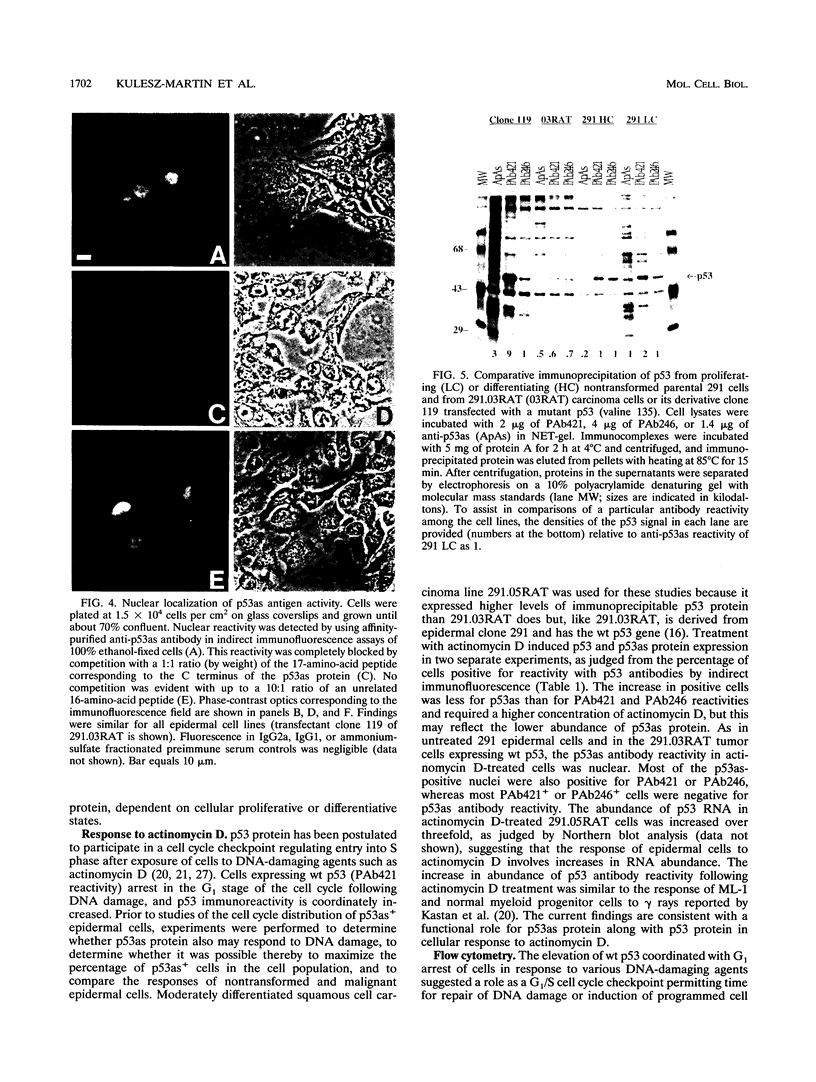
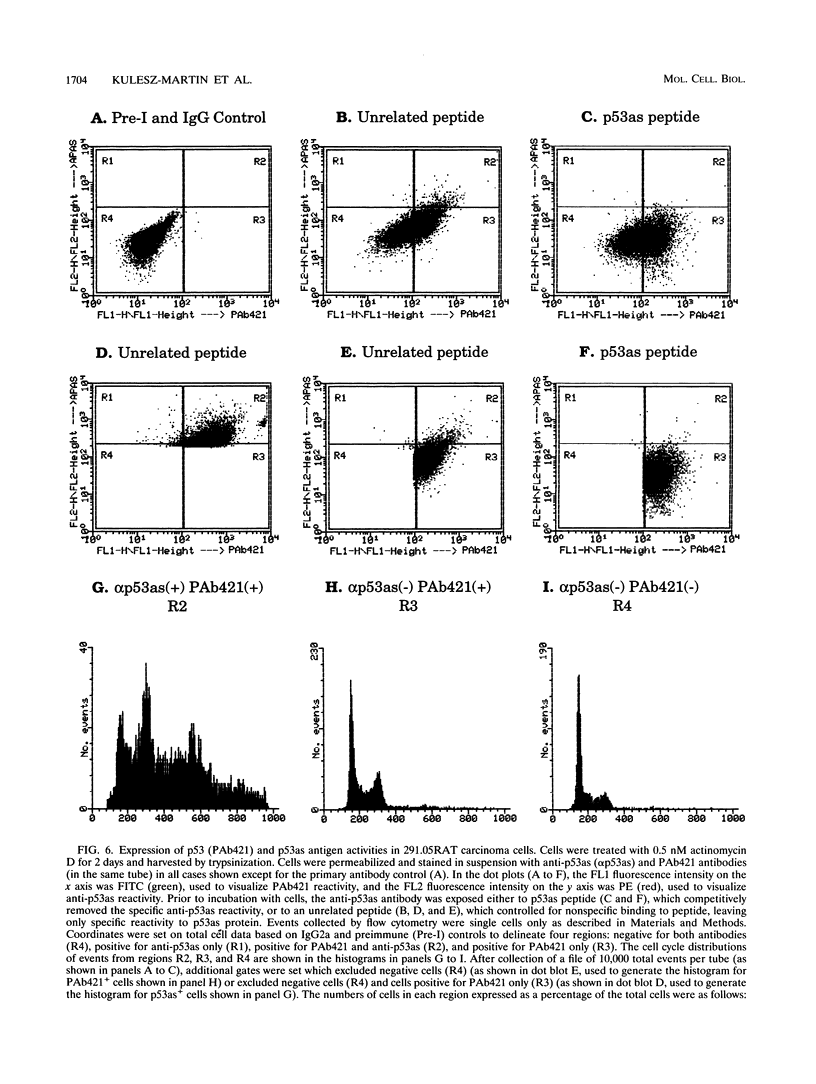
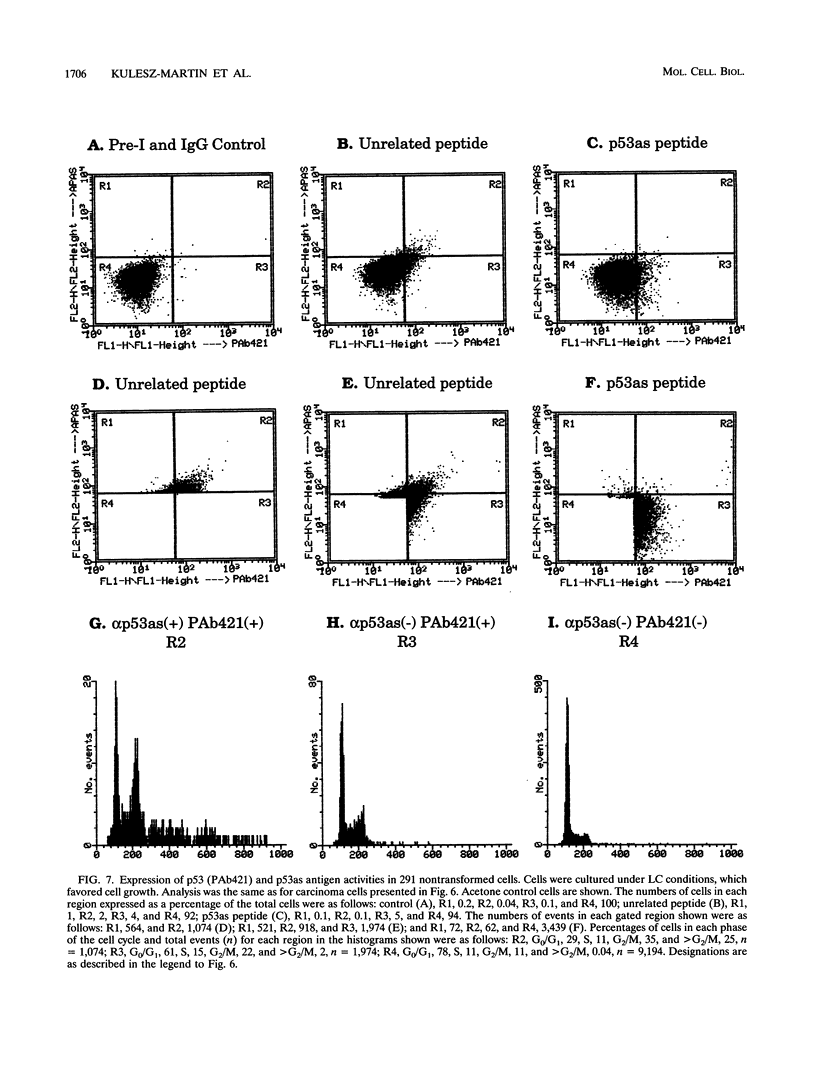
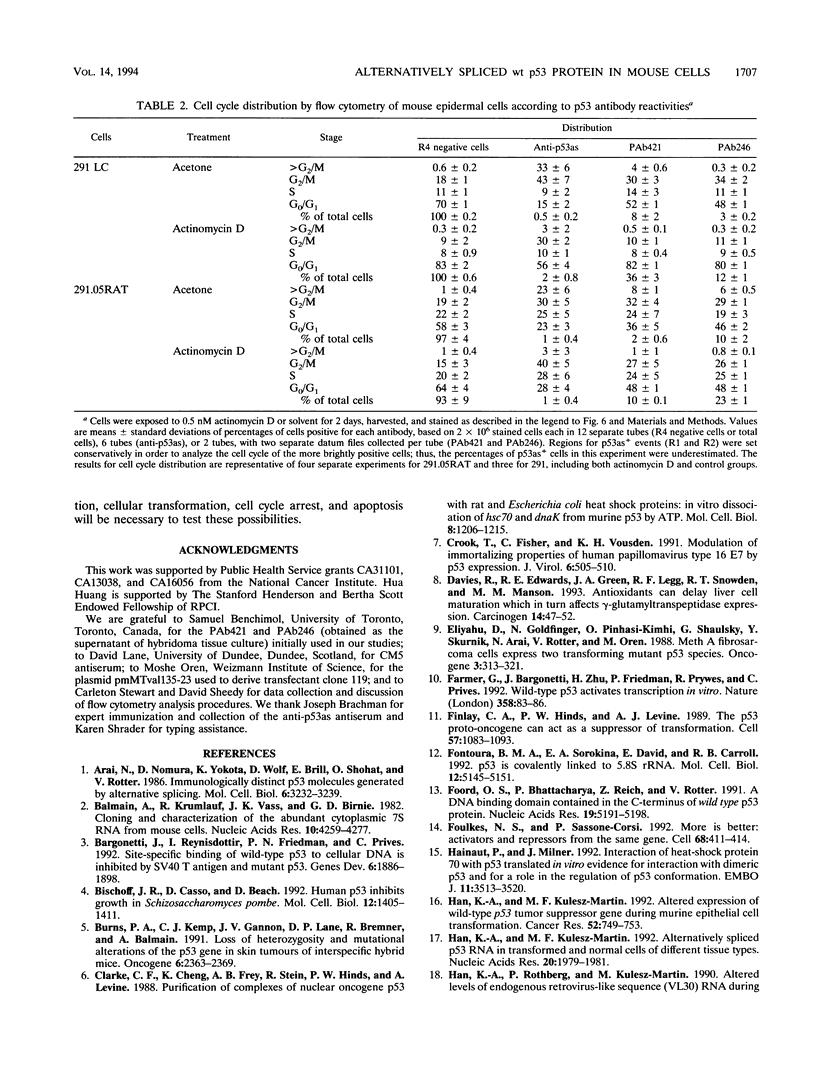
We previously demonstrated that a wild-type alternatively spliced p53 (p53as) RNA exists in mouse cultured cells and normal mouse tissues at approximately 25 to 33% of the level of the major p53 RNA form. The alternative RNA transcript is 96 nucleotides longer than the major transcript as a result of alternative splicing of intron 10 sequences. The protein expected to be generated from the p53as transcript is 9 amino acids shorter than the major p53 protein and has 17 different amino acids at the carboxyl terminus. We report here that p53as protein exists in nontransformed and malignant epidermal cells and is localized to the nucleus. In addition, p53as protein is preferentially expressed during the G2 phase of the cell cycle and in cells with greater than G2 DNA content compared with the major p53 protein, which is preferentially expressed in G1. The p53as immunoreactivity is elevated and shifted to the G1 phase of the cell cycle following actinomycin D treatment of nontransformed cells but not malignant cells. In view of the dimerization and tetramerization of p53 protein which may be necessary for its DNA binding and transcriptional activation activities, the presence of p53as protein in cells has important implications for understanding the physiological function(s) of the p53 gene.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai N., Nomura D., Yokota K., Wolf D., Brill E., Shohat O., Rotter V. Immunologically distinct p53 molecules generated by alternative splicing. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3232–3239. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balmain A., Krumlauf R., Vass J. K., Birnie G. D. Cloning and characterisation of the abundant cytoplasmic 7S RNA from mouse cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 24;10(14):4259–4277. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.14.4259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargonetti J., Reynisdóttir I., Friedman P. N., Prives C. Site-specific binding of wild-type p53 to cellular DNA is inhibited by SV40 T antigen and mutant p53. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1886–1898. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff J. R., Casso D., Beach D. Human p53 inhibits growth in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1405–1411. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns P. A., Kemp C. J., Gannon J. V., Lane D. P., Bremner R., Balmain A. Loss of heterozygosity and mutational alterations of the p53 gene in skin tumours of interspecific hybrid mice. Oncogene. 1991 Dec;6(12):2363–2369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke C. F., Cheng K., Frey A. B., Stein R., Hinds P. W., Levine A. J. Purification of complexes of nuclear oncogene p53 with rat and Escherichia coli heat shock proteins: in vitro dissociation of hsc70 and dnaK from murine p53 by ATP. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1206–1215. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crook T., Fisher C., Vousden K. H. Modulation of immortalizing properties of human papillomavirus type 16 E7 by p53 expression. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):505–510. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.505-510.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R., Edwards R. E., Green J. A., Legg R. F., Snowden R. T., Manson M. M. Antioxidants can delay liver cell maturation which in turn affects gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase expression. Carcinogenesis. 1993 Jan;14(1):47–52. doi: 10.1093/carcin/14.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Goldfinger N., Pinhasi-Kimhi O., Shaulsky G., Skurnik Y., Arai N., Rotter V., Oren M. Meth A fibrosarcoma cells express two transforming mutant p53 species. Oncogene. 1988 Sep;3(3):313–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer G., Bargonetti J., Zhu H., Friedman P., Prywes R., Prives C. Wild-type p53 activates transcription in vitro. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):83–86. doi: 10.1038/358083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Levine A. J. The p53 proto-oncogene can act as a suppressor of transformation. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1083–1093. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontoura B. M., Sorokina E. A., David E., Carroll R. B. p53 is covalently linked to 5.8S rRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):5145–5151. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.5145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foord O. S., Bhattacharya P., Reich Z., Rotter V. A DNA binding domain is contained in the C-terminus of wild type p53 protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5191–5198. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes N. S., Sassone-Corsi P. More is better: activators and repressors from the same gene. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):411–414. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90178-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hainaut P., Milner J. Interaction of heat-shock protein 70 with p53 translated in vitro: evidence for interaction with dimeric p53 and for a role in the regulation of p53 conformation. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3513–3520. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05434.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han K. A., Kulesz-Martin M. F. Altered expression of wild-type p53 tumor suppressor gene during murine epithelial cell transformation. Cancer Res. 1992 Feb 1;52(3):749–753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han K. A., Kulesz-Martin M. F. Alternatively spliced p53 RNA in transformed and normal cells of different tissue types. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 25;20(8):1979–1981. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.8.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hupp T. R., Meek D. W., Midgley C. A., Lane D. P. Regulation of the specific DNA binding function of p53. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):875–886. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90562-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Onyekwere O., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Craig R. W. Participation of p53 protein in the cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 1;51(23 Pt 1):6304–6311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Zhan Q., el-Deiry W. S., Carrier F., Jacks T., Walsh W. V., Plunkett B. S., Vogelstein B., Fornace A. J., Jr A mammalian cell cycle checkpoint pathway utilizing p53 and GADD45 is defective in ataxia-telangiectasia. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):587–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90593-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulesz-Martin M. F., Blumenson L. E., Manly K. F., Siracký J., East C. J. Tumor progression of murine epidermal cells after treatment in vitro with 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate or retinoic acid. Cancer Res. 1991 Sep 1;51(17):4701–4706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulesz-Martin M., Blumenson L., Lisafeld B. Retinoic acid enhancement of an early step in the transformation of mouse epidermal cells in vitro. Carcinogenesis. 1986 Sep;7(9):1425–1429. doi: 10.1093/carcin/7.9.1425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulesz-Martin M., Kilkenny A. E., Holbrook K. A., Digernes V., Yuspa S. H. Properties of carcinogen altered mouse epidermal cells resistant to calcium-induced terminal differentiation. Carcinogenesis. 1983 Nov;4(11):1367–1377. doi: 10.1093/carcin/4.11.1367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulesz-Martin M., Kozlowski P., Glurich I., Lisafeld B., Hemedinger E., Kumar V. Pemphigoid, pemphigus and desmoplakin as antigenic markers of differentiation in normal and tumorigenic mouse keratinocyte lines. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1989 Jul;22(4):279–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1989.tb00213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulesz-Martin M., Yoshida M. A., Prestine L., Yuspa S. H., Bertram J. S. Mouse cell clones for improved quantitation of carcinogen-induced altered differentiation. Carcinogenesis. 1985 Sep;6(9):1245–1254. doi: 10.1093/carcin/6.9.1245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P. Cancer. p53, guardian of the genome. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):15–16. doi: 10.1038/358015a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milne D. M., Palmer R. H., Meek D. W. Mutation of the casein kinase II phosphorylation site abolishes the anti-proliferative activity of p53. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 11;20(21):5565–5570. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.21.5565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner J. Different forms of p53 detected by monoclonal antibodies in non-dividing and dividing lymphocytes. Nature. 1984 Jul 12;310(5973):143–145. doi: 10.1038/310143a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner J., Medcalf E. A. Cotranslation of activated mutant p53 with wild type drives the wild-type p53 protein into the mutant conformation. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):765–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90384-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner J. The role of p53 in the normal control of cell proliferation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;3(2):282–286. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90153-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momand J., Zambetti G. P., Olson D. C., George D., Levine A. J. The mdm-2 oncogene product forms a complex with the p53 protein and inhibits p53-mediated transactivation. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1237–1245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90644-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigro J. M., Sikorski R., Reed S. I., Vogelstein B. Human p53 and CDC2Hs genes combine to inhibit the proliferation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1357–1365. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren M., Levine A. J. Molecular cloning of a cDNA specific for the murine p53 cellular tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):56–59. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C., Manfredi J. J. The p53 tumor suppressor protein: meeting review. Genes Dev. 1993 Apr;7(4):529–534. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.4.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ro Y. S., Cooper P. N., Lee J. A., Quinn A. G., Harrison D., Lane D., Horne C. H., Rees J. L., Angus B. p53 protein expression in benign and malignant skin tumours. Br J Dermatol. 1993 Mar;128(3):237–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1993.tb00164.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri B., Caamano J., Goodrow T., DiRado M., Bianchi A., Trono D., Conti C. J., Klein-Szanto A. J. Alterations of the p53 tumor suppressor gene during mouse skin tumor progression. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 15;51(24):6615–6621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider B. L., Bowden G. T., Sutter C., Schweizer J., Han K. A., Kulesz-Martin M. F. 7,12-Dimethylbenz[a]anthracene-induced mouse keratinocyte malignant transformation independent of Harvey ras activation. J Invest Dermatol. 1993 Oct;101(4):595–599. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12366051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Usheva A., Zambetti G. P., Momand J., Horikoshi N., Weinmann R., Levine A. J., Shenk T. Wild-type p53 binds to the TATA-binding protein and represses transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):12028–12032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.12028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soussi T., Caron de Fromentel C., May P. Structural aspects of the p53 protein in relation to gene evolution. Oncogene. 1990 Jul;5(7):945–952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenger J. E., Mayr G. A., Mann K., Tegtmeyer P. Formation of stable p53 homotetramers and multiples of tetramers. Mol Carcinog. 1992;5(2):102–106. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940050204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephen C. W., Lane D. P. Mutant conformation of p53. Precise epitope mapping using a filamentous phage epitope library. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jun 5;225(3):577–583. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90386-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stürzbecher H. W., Brain R., Addison C., Rudge K., Remm M., Grimaldi M., Keenan E., Jenkins J. R. A C-terminal alpha-helix plus basic region motif is the major structural determinant of p53 tetramerization. Oncogene. 1992 Aug;7(8):1513–1523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B. Cancer. A deadly inheritance. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):681–682. doi: 10.1038/348681a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W. p53 function and dysfunction. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):523–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90421-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade-Evans A., Jenkins J. R. Precise epitope mapping of the murine transformation-associated protein, p53. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):699–706. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03686.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Hauschka S., Tapscott S. J. The MCK enhancer contains a p53 responsive element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4570–4571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf D., Harris N., Goldfinger N., Rotter V. Isolation of a full-length mouse cDNA clone coding for an immunologically distinct p53 molecule. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):127–132. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf D., Harris N., Rotter V. Reconstitution of p53 expression in a nonproducer Ab-MuLV-transformed cell line by transfection of a functional p53 gene. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90532-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yewdell J. W., Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. Monoclonal antibody analysis of p53 expression in normal and transformed cells. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):444–452. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.444-452.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonish-Rouach E., Grunwald D., Wilder S., Kimchi A., May E., Lawrence J. J., May P., Oren M. p53-mediated cell death: relationship to cell cycle control. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1415–1423. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambetti G. P., Bargonetti J., Walker K., Prives C., Levine A. J. Wild-type p53 mediates positive regulation of gene expression through a specific DNA sequence element. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1143–1152. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]