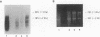Abstract
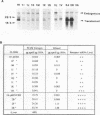
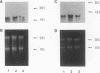
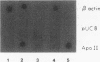
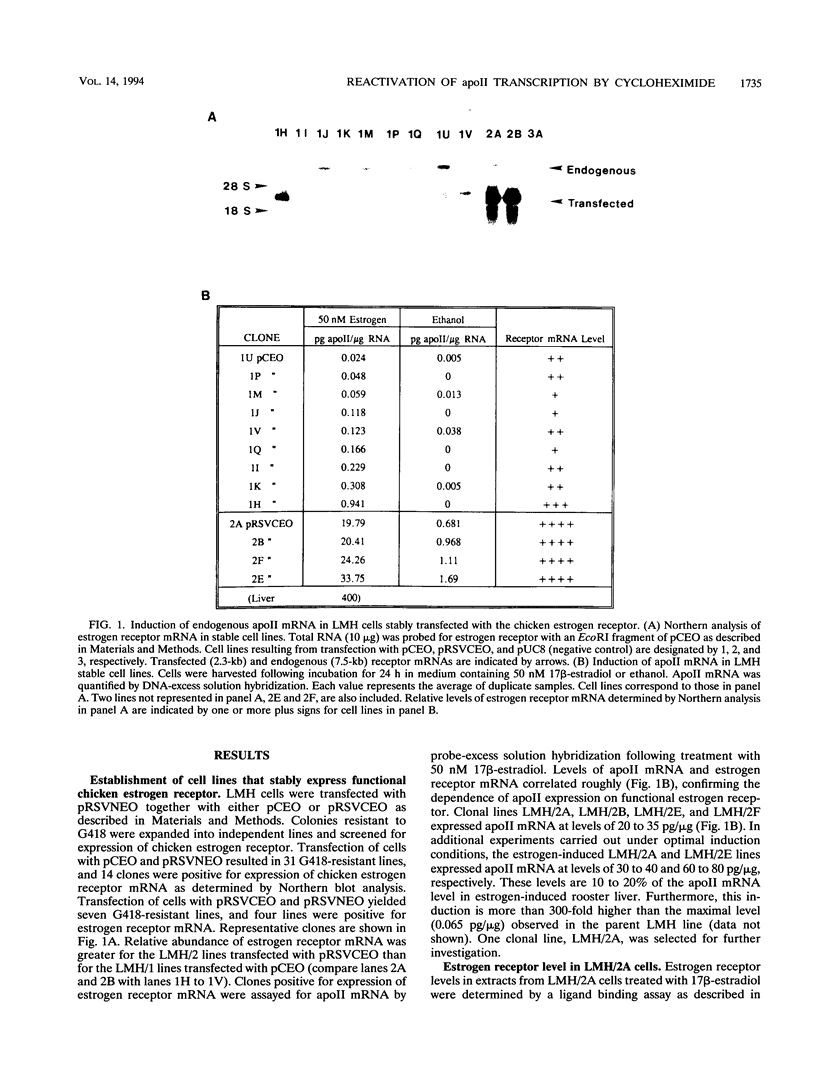
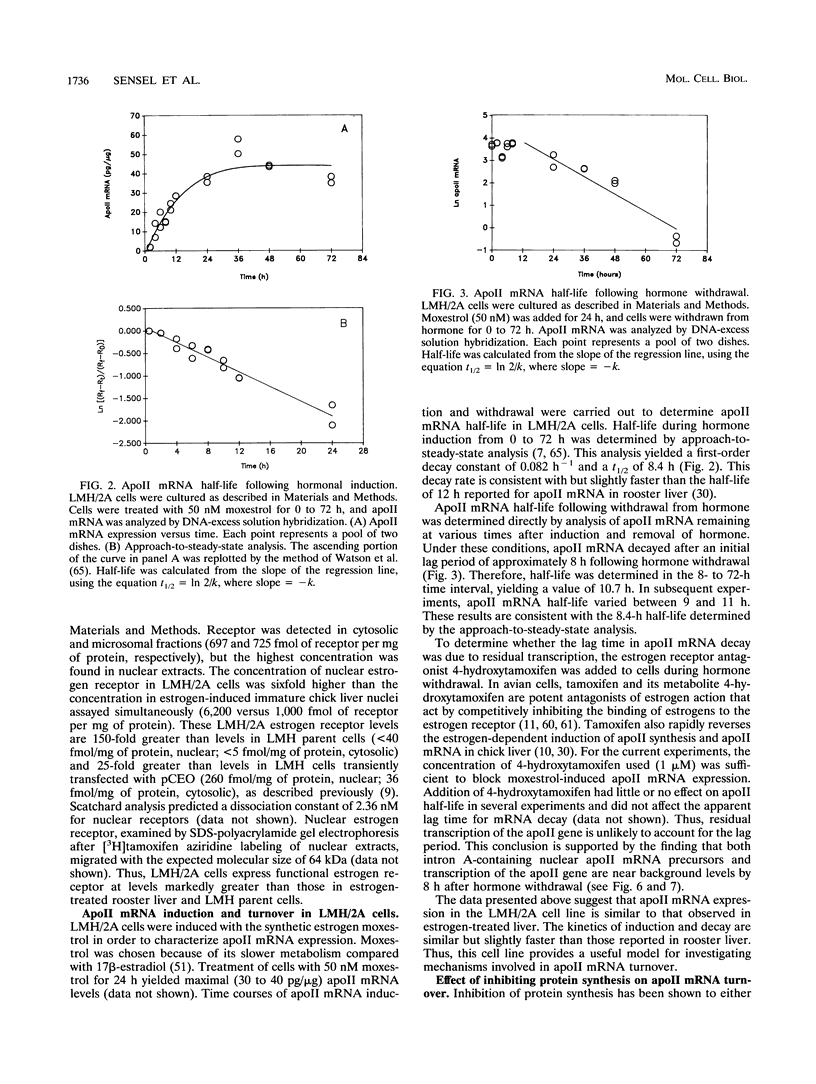
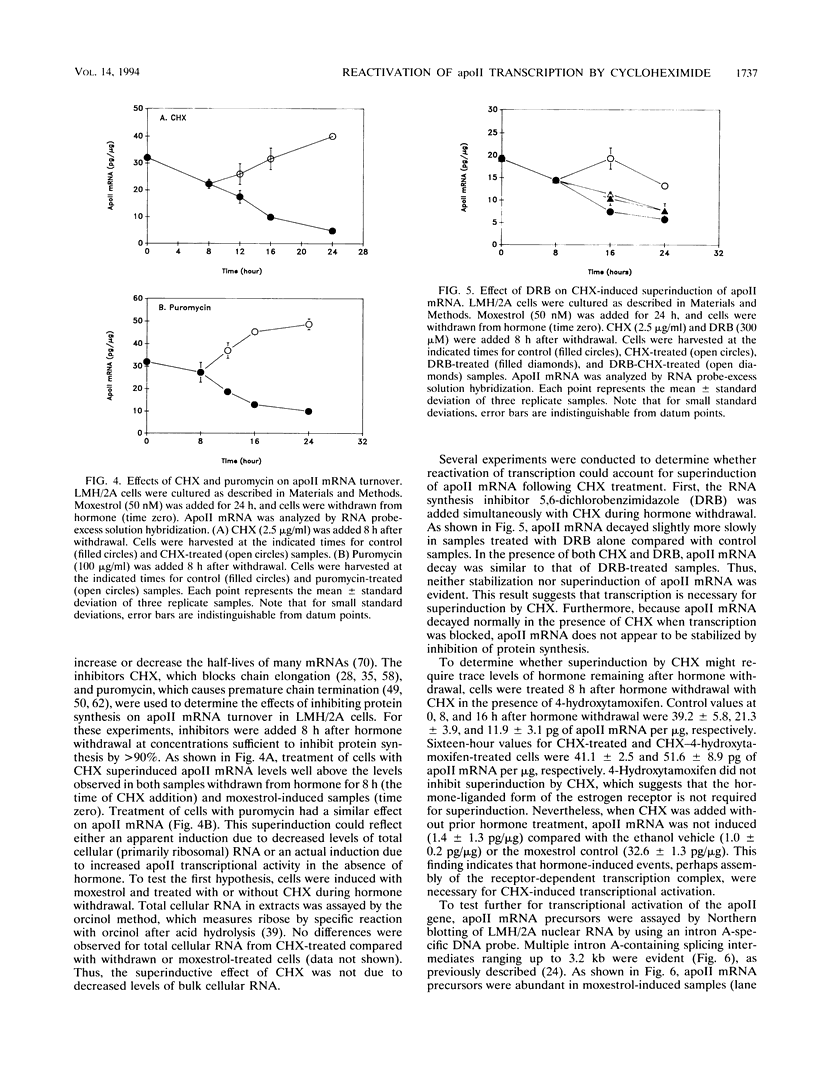
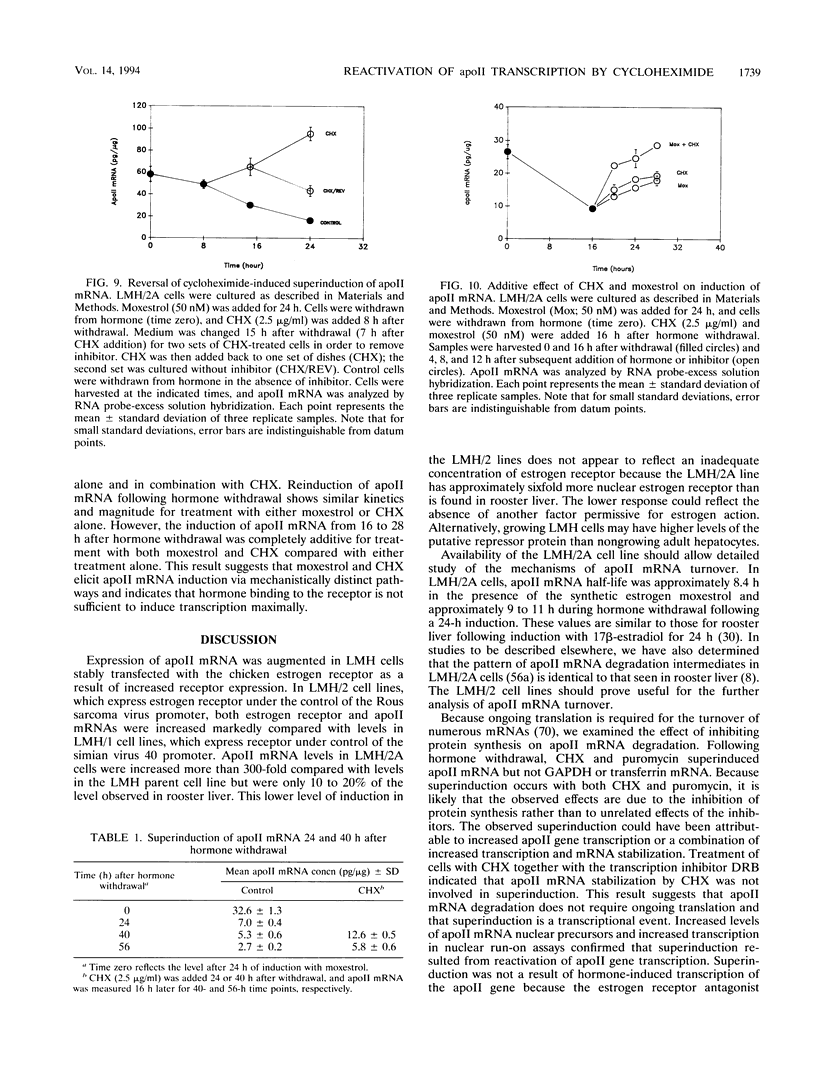
In this report, we describe apolipoprotein II (apoII) gene expression in cell lines derived by stable expression of the chicken estrogen receptor in LMH chicken hepatoma cells. In cell lines expressing high levels of receptor (LMH/2A), apoII gene expression is increased by estrogen 300-fold compared with levels in the receptor-deficient parent LMH line. LMH/2A cells show apoII mRNA induction and turnover kinetics similar to those in chicken liver. Inhibition of protein synthesis with cycloheximide (CHX) or puromycin following estrogen withdrawal superinduces apoII mRNA without affecting apoII mRNA stability. Superinduction is due to an estrogen-independent reactivation of apoII gene transcription. The apoII gene can be reactivated by CHX for up to 24 h following hormone withdrawal, suggesting that the gene is in a repressed yet transcriptionally competent state. These results reveal two distinct events necessary for termination of estrogen receptor-mediated transcription. The first event, removal of hormone, is sufficient to stop transcription when translation is ongoing. The second event is revealed by the CHX-induced superinduction of apoII mRNA following hormone withdrawal. This superinduction suggests that deactivation of estrogen receptor-mediated transcription requires a labile protein. Furthermore, reactivation of apoII gene expression by CHX and estrogen is additive, suggesting that estrogen is unable to overcome repression completely. Thus, a labile protein may act to repress estrogen receptor-mediated transcription of the apoII gene.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer T. K., Cordingley M. G., Wolford R. G., Hager G. L. Transcription factor access is mediated by accurately positioned nucleosomes on the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):688–698. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker O., Das A. T., Ab G. Protein-DNA interactions in vitro with 5'-flanking DNA fragments from the chicken vitellogenin gene. J Steroid Biochem. 1988;30(1-6):209–212. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(88)90094-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker O., Philipsen J. N., Hennis B. C., Ab G. Estrogen-inducible binding of a nuclear factor to the vitellogenin upstream region. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4557–4560. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beekman J. M., Wijnholds J., Schippers I. J., Pot W., Gruber M., Ab G. Regulatory elements and DNA-binding proteins mediating transcription from the chicken very-low-density apolipoprotein II gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5371–5377. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz E. A., Evans M. I. Functional analysis of regulatory regions upstream and in the first intron of the estrogen-responsive chicken very low density apolipoprotein II gene. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):7134–7138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin C. M., Schimke R. T. Influence of turnover rates on the responses of enzymes to cortisone. Mol Pharmacol. 1965 Sep;1(2):149–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder R., Hwang S. P., Ratnasabapathy R., Williams D. L. Degradation of apolipoprotein II mRNA occurs via endonucleolytic cleavage at 5'-AAU-3'/5'-UAA-3' elements in single-stranded loop domains of the 3'-noncoding region. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16910–16918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder R., MacDonald C. C., Burch J. B., Lazier C. B., Williams D. L. Expression of endogenous and transfected apolipoprotein II and vitellogenin II genes in an estrogen responsive chicken liver cell line. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Feb;4(2):201–208. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-2-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgna J. L., Rochefort H. Hydroxylated metabolites of tamoxifen are formed in vivo and bound to estrogen receptor in target tissues. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):859–868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Jeltsch J. M., Roberts M., Chambon P. Activation of pS2 gene transcription is a primary response to estrogen in the human breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6344–6348. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch J. B., Evans M. I., Friedman T. M., O'Malley P. J. Two functional estrogen response elements are located upstream of the major chicken vitellogenin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1123–1131. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch J. B., Fischer A. H. Chromatin studies reveal that an ERE is located far upstream of a vitellogenin gene and that a distal tissue-specific hypersensitive site is conserved for two coordinately regulated vitellogenin genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 25;18(14):4157–4165. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.14.4157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch J. B., Weintraub H. Temporal order of chromatin structural changes associated with activation of the major chicken vitellogenin gene. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):65–76. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90335-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush L., McGahan T. J., White H. B., 3rd Purification and characterization of biotin-binding protein II from chicken oocytes. Biochem J. 1988 Dec 15;256(3):797–805. doi: 10.1042/bj2560797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capony F., Williams D. L. Apolipoprotein B of avian very low density lipoprotein: characteristics of its regulation in nonstimulated and estrogen-stimulated rooster. Biochemistry. 1980 May 13;19(10):2219–2226. doi: 10.1021/bi00551a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan L., Jackson R. L., O'Malley B. W., Means A. R. Synthesis of very low density lipoproteins in the cockerel. Effects of estrogen. J Clin Invest. 1976 Aug;58(2):368–379. doi: 10.1172/JCI108481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., MacDonald R. J., Cowan N. J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W. Number and evolutionary conservation of alpha- and beta-tubulin and cytoplasmic beta- and gamma-actin genes using specific cloned cDNA probes. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet M., Perrin F., Gannon F., Krust A., Chambon P., McKnight G. S., Lee D. C., Mayo K. E., Palmiter R. Cloning of an almost full-length chicken conalbumin double-stranded cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jun 11;6(7):2435–2452. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.7.2435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colgan V., Elbrecht A., Goldman P., Lazier C. B., Deeley R. The avian apoprotein II very low density lipoprotein gene. Methylation patterns of 5' and 3' flanking regions during development and following induction by estrogen. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14453–14460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Cycloheximide stimulates early adenovirus transcription if early gene expression is allowed before treatment. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):683–692. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.683-692.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doucas V., Spyrou G., Yaniv M. Unregulated expression of c-Jun or c-Fos proteins but not Jun D inhibits oestrogen receptor activity in human breast cancer derived cells. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2237–2245. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07760.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugaiczyk A., Haron J. A., Stone E. M., Dennison O. E., Rothblum K. N., Schwartz R. J. Cloning and sequencing of a deoxyribonucleic acid copy of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase messenger ribonucleic acid isolated from chicken muscle. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 29;22(7):1605–1613. doi: 10.1021/bi00276a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan H., Penman S. Regulation of protein synthesis in mammalian cells. II. Inhibition of protein synthesis at the level of initiation during mitosis. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 28;50(3):655–670. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90091-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D. A., Shelness G. S., Nicosia M., Williams D. L. Estrogen-induced destabilization of yolk precursor protein mRNAs in avian liver. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2625–2631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C., Padmanabhan R., Howard B. H. High efficiency DNA-mediated transformation of primate cells. Science. 1983 Aug 5;221(4610):551–553. doi: 10.1126/science.6306768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Walter P., Kumar V., Krust A., Bornert J. M., Argos P., Chambon P. Human oestrogen receptor cDNA: sequence, expression and homology to v-erb-A. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):134–139. doi: 10.1038/320134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward M. A., Brock M. L., Shapiro D. J. Activation of vitellogenin gene transcription is a direct response to estrogen in Xenopus laevis liver. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):8273–8284. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.8273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan B. L. he effect of inhibitors of protein synthesis on the level of ribosomal subunits in ascites cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 May 20;182(1):264–266. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90546-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel D. I., Estolano M. G., Galeazzi D. R., Whitlock J. P., Jr Superinduction of cytochrome P1-450 gene transcription by inhibition of protein synthesis in wild type and variant mouse hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5648–5653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonat C., Rahmsdorf H. J., Park K. K., Cato A. C., Gebel S., Ponta H., Herrlich P. Antitumor promotion and antiinflammation: down-modulation of AP-1 (Fos/Jun) activity by glucocorticoid hormone. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1189–1204. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90395-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost J. P., Saluz H. P., Pawlak A. Estradiol down regulates the binding activity of an avian vitellogenin gene repressor (MDBP-2) and triggers a gradual demethylation of the mCpG pair of its DNA binding site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5771–5775. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzenellenbogen J. A., Carlson K. E., Heiman D. F., Robertson D. W., Wei L. L., Katzenellenbogen B. S. Efficient and highly selective covalent labeling of the estrogen receptor with [3H]tamoxifen aziridine. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3487–3495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi T., Nomura K., Hirayama Y., Kitagawa T. Establishment and characterization of a chicken hepatocellular carcinoma cell line, LMH. Cancer Res. 1987 Aug 15;47(16):4460–4464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kok K., Snippe L., Ab G., Gruber M. Nuclease-hypersensitive sites in chromatin of the estrogen-inducible apoVLDL II gene of chicken. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 25;13(14):5189–5202. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.14.5189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krust A., Green S., Argos P., Kumar V., Walter P., Bornert J. M., Chambon P. The chicken oestrogen receptor sequence: homology with v-erbA and the human oestrogen and glucocorticoid receptors. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):891–897. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04300.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laguë P. C., van Tienhoven A., Cunningham F. J. Concentrations of estrogens, progesterone and LH during the ovulatory cycle of the laying chicken [Gallus domesticus]. Biol Reprod. 1975 Jun;12(5):590–598. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod12.5.590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazier C. B. Ontogeny of the vitellogenic response to oestradiol and of the soluble nuclear oestrogen receptor in embryonic-chick liver. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 15;174(1):143–152. doi: 10.1042/bj1740143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusska A., Wu L., Whitlock J. P., Jr Superinduction of CYP1A1 transcription by cycloheximide. Role of the DNA binding site for the liganded Ah receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):15146–15151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORRIS A. J., SCHWEET R. S. Release of soluble protein from reticulocyte ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Feb 18;47:415–416. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90310-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo K. E., Palmiter R. D. Glucocorticoid regulation of metallothionein-I mRNA synthesis in cultured mouse cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2621–2624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell D. P., Vegeto E., O'Malley B. W. Identification of a negative regulatory function for steroid receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10563–10567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. The use of inhibitors in studies on protein synthesis. Methods Enzymol. 1974;30:261–282. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)30030-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raynaud J. P., Bouton M. M., Gallet-Bourquin D., Philibert D., Tournemine C., Azadian-Baulanger G. Comparative study of estrogen action. Mol Pharmacol. 1973 Jul;9(4):520–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richard-Foy H., Hager G. L. Sequence-specific positioning of nucleosomes over the steroid-inducible MMTV promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2321–2328. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02507.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringold G. M., Dieckmann B., Vannice J. L., Trahey M., McCormick F. Inhibition of protein synthesis stimulates the transcription of human beta-interferon genes in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3964–3968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Rangarajan P., Kliewer S., Ransone L. J., Bolado J., Yang N., Verma I. M., Evans R. M. Functional antagonism between oncoprotein c-Jun and the glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1217–1226. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90397-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Umesono K., Mangelsdorf D. J., Bolado J., Pike J. W., Evans R. M. Jun-Fos and receptors for vitamins A and D recognize a common response element in the human osteocalcin gene. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90531-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seal S. N., Davis D. L., Burch J. B. Mutational studies reveal a complex set of positive and negative control elements within the chicken vitellogenin II promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2704–2717. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelness G. S., Williams D. L. Apolipoprotein II messenger RNA. Transcriptional and splicing heterogeneity yields six 5'-untranslated leader sequences. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9929–9935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanners C. P. The effect of cycloheximide on polyribosomes from hamster cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Sep 8;24(5):758–764. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90390-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugano S., Stoeckle M. Y., Hanafusa H. Transformation by Rous sarcoma virus induces a novel gene with homology to a mitogenic platelet protein. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):321–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90284-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland R. L. Estrogen antagonists in chick oviduct: antagonist activity of eight synthetic triphenylethylene derivatives and their interactions with cytoplasmic and nuclear estrogen receptors. Endocrinology. 1981 Dec;109(6):2061–2068. doi: 10.1210/endo-109-6-2061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland R., Mester J., Baulieu E. E. Tamoxifen is a potent "pure" anti-oestrogen in chick oviduct. Nature. 1977 Jun 2;267(5610):434–435. doi: 10.1038/267434a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRAUT R. R., MONRO R. E. THE PUROMYCIN REACTION AND ITS RELATION TO PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Oct;10:63–72. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80028-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. Y., Williams D. L. Identificiation, purification, and characterization of two distinct avian vitellogenins. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 15;19(8):1557–1563. doi: 10.1021/bi00549a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson G., Davey R. A., Labarca C., Paigen K. Genetic determination of kinetic parameters in beta-glucuronidase induction by androgen. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):3005–3011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White H. B., 3rd, Merrill A. H., Jr Riboflavin-binding proteins. Annu Rev Nutr. 1988;8:279–299. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.08.070188.001431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijnholds J., Philipsen J. N., Ab G. Tissue-specific and steroid-dependent interaction of transcription factors with the oestrogen-inducible apoVLDL II promoter in vivo. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2757–2763. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03130.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilks A., Seldran M., Jost J. P. An estrogen-dependent demethylation at the 5' end of the chicken vitellogenin gene is independent of DNA synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):1163–1177. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. L., Newman T. C., Shelness G. S., Gordon D. A. Measurement of apolipoprotein mRNA by DNA-excess solution hybridization with single-stranded probes. Methods Enzymol. 1986;128:671–689. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)28099-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiskocil R., Bensky P., Dower W., Goldberger R. F., Gordon J. I., Deeley R. G. Coordinate regulation of two estrogen-dependent genes in avian liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4474–4478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Chambard J. C., Sun Y. L., Smeal T., Schmidt T. J., Drouin J., Karin M. Transcriptional interference between c-Jun and the glucocorticoid receptor: mutual inhibition of DNA binding due to direct protein-protein interaction. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1205–1215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90396-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]