Abstract
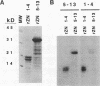
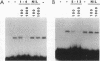
The myeloid zinc finger gene 1, MZF1, encodes a transcription factor which is expressed in hematopoietic progenitor cells that are committed to myeloid lineage differentiation. MZF1 contains 13 C2H2 zinc fingers arranged in two domains which are separated by a short glycine- and proline-rich sequence. The first domain consists of zinc fingers 1 to 4, and the second domain is formed by zinc fingers 5 to 13. We have determined that both sets of zinc finger domains bind DNA. Purified, recombinant MZF1 proteins containing either the first set of zinc fingers or the second set were prepared and used to affinity select DNA sequences from a library of degenerate oligonucleotides by using successive rounds of gel shift followed by PCR amplification. Surprisingly, both DNA-binding domains of MZF1 selected similar DNA-binding consensus sequences containing a core of four or five guanine residues, reminiscent of an NF-kappa B half-site: 1-4, 5'-AGTGGGGA-3'; 5-13, 5'-CGGGnGAGGGGGAA-3'. The full-length MZF1 protein containing both sets of zinc finger DNA-binding domains recognizes synthetic oligonucleotides containing either the 1-4 or 5-13 consensus binding sites in gel shift assays. Thus, we have identified the core DNA consensus binding sites for each of the two DNA-binding domains of a myeloid-specific zinc finger transcription factor. Identification of these DNA-binding sites will allow us to identify target genes regulated by MZF1 and to assess the role of MZF1 as a transcriptional regulator of hematopoiesis.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abate C., Luk D., Gentz R., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Curran T. Expression and purification of the leucine zipper and DNA-binding domains of Fos and Jun: both Fos and Jun contact DNA directly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1032–1036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A. The inducible transcription activator NF-kappa B: regulation by distinct protein subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 16;1072(1):63–80. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, LeClair K. P., Singh H., Sharp P. A. A large protein containing zinc finger domains binds to related sequence elements in the enhancers of the class I major histocompatibility complex and kappa immunoglobulin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1406–1414. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bavisotto L., Kaushansky K., Lin N., Hromas R. Antisense oligonucleotides from the stage-specific myeloid zinc finger gene MZF-1 inhibit granulopoiesis in vitro. J Exp Med. 1991 Nov 1;174(5):1097–1101. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.5.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Zinc finger domains: hypotheses and current knowledge. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1990;19:405–421. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.19.060190.002201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Weintraub H. Differences and similarities in DNA-binding preferences of MyoD and E2A protein complexes revealed by binding site selection. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1104–1110. doi: 10.1126/science.2174572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao X. M., Koski R. A., Gashler A., McKiernan M., Morris C. F., Gaffney R., Hay R. V., Sukhatme V. P. Identification and characterization of the Egr-1 gene product, a DNA-binding zinc finger protein induced by differentiation and growth signals. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):1931–1939. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.1931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey J. Gel retardation at low pH resolves trp repressor-DNA complexes for quantitative study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):975–979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z., Brand N. J., Chen A., Chen S. J., Tong J. H., Wang Z. Y., Waxman S., Zelent A. Fusion between a novel Krüppel-like zinc finger gene and the retinoic acid receptor-alpha locus due to a variant t(11;17) translocation associated with acute promyelocytic leukaemia. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1161–1167. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05757.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury K., Deutsch U., Gruss P. A multigene family encoding several "finger" structures is present and differentially active in mammalian genomes. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):771–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy B., Nathans D. DNA binding site of the growth factor-inducible protein Zif268. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8737–8741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desjarlais J. R., Berg J. M. Toward rules relating zinc finger protein sequences and DNA binding site preferences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7345–7349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan C. M., Maniatis T. A DNA-binding protein containing two widely separated zinc finger motifs that recognize the same DNA sequence. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):29–42. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng D. F., Doolittle R. F. Progressive sequence alignment as a prerequisite to correct phylogenetic trees. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(4):351–360. doi: 10.1007/BF02603120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hromas R., Collins S. J., Hickstein D., Raskind W., Deaven L. L., O'Hara P., Hagen F. S., Kaushansky K. A retinoic acid-responsive human zinc finger gene, MZF-1, preferentially expressed in myeloid cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14183–14187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller A. D., Maniatis T. Identification and characterization of a novel repressor of beta-interferon gene expression. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):868–879. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. The GLI gene encodes a nuclear protein which binds specific sequences in the human genome. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):634–642. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klevit R. E. Recognition of DNA by Cys2,His2 zinc fingers. Science. 1991 Sep 20;253(5026):1367–1393. doi: 10.1126/science.1896847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. At least six nucleotides preceding the AUG initiator codon enhance translation in mammalian cells. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):947–950. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letovsky J., Dynan W. S. Measurement of the binding of transcription factor Sp1 to a single GC box recognition sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 11;17(7):2639–2653. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.7.2639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishita K., Parker D. S., Mucenski M. L., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Ihle J. N. Retroviral activation of a novel gene encoding a zinc finger protein in IL-3-dependent myeloid leukemia cell lines. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):831–840. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91175-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of a five-finger GLI-DNA complex: new perspectives on zinc fingers. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1701–1707. doi: 10.1126/science.8378770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Pabo C. O. Zinc finger-DNA recognition: crystal structure of a Zif268-DNA complex at 2.1 A. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):809–817. doi: 10.1126/science.2028256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins A. S., Fishel R., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. Evi-1, a murine zinc finger proto-oncogene, encodes a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2665–2674. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Morris J. F., Tournay O. E., Cook D. M., Curran T. Binding of the Wilms' tumor locus zinc finger protein to the EGR-1 consensus sequence. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1259–1262. doi: 10.1126/science.2244209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rustgi A. K., Van 't Veer L. J., Bernards R. Two genes encode factors with NF-kappa B- and H2TF1-like DNA-binding properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8707–8710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuh R., Aicher W., Gaul U., Côté S., Preiss A., Maier D., Seifert E., Nauber U., Schröder C., Kemler R. A conserved family of nuclear proteins containing structural elements of the finger protein encoded by Krüppel, a Drosophila segmentation gene. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1025–1032. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90817-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiesen H. J., Bach C. Target Detection Assay (TDA): a versatile procedure to determine DNA binding sites as demonstrated on SP1 protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3203–3209. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. M., Moolten D., Burlein J., Romano J., Bhaerman R., Godillot A., Mellon M., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Kant J. A. Identification of a zinc finger protein that inhibits IL-2 gene expression. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1791–1794. doi: 10.1126/science.1840704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witzgall R., O'Leary E., Gessner R., Ouellette A. J., Bonventre J. V. Kid-1, a putative renal transcription factor: regulation during ontogeny and in response to ischemia and toxic injury. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1933–1942. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]