Abstract
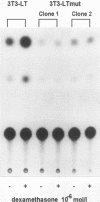
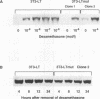
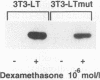
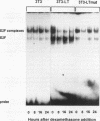
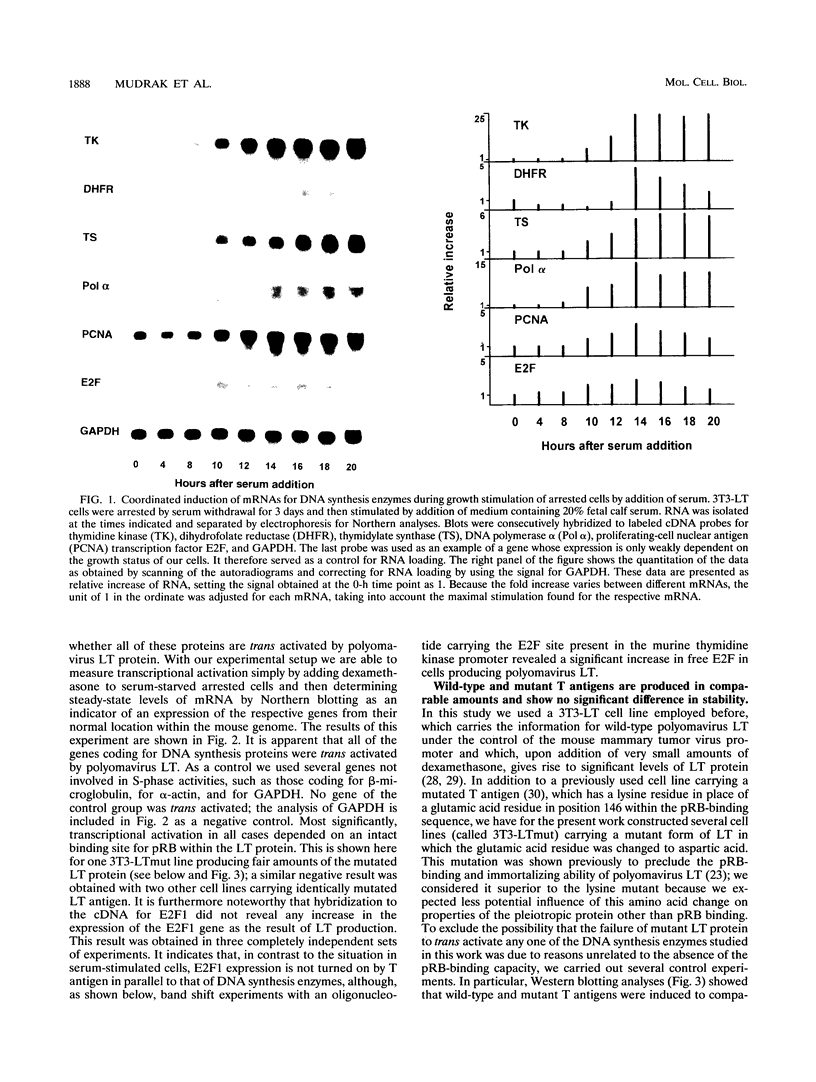
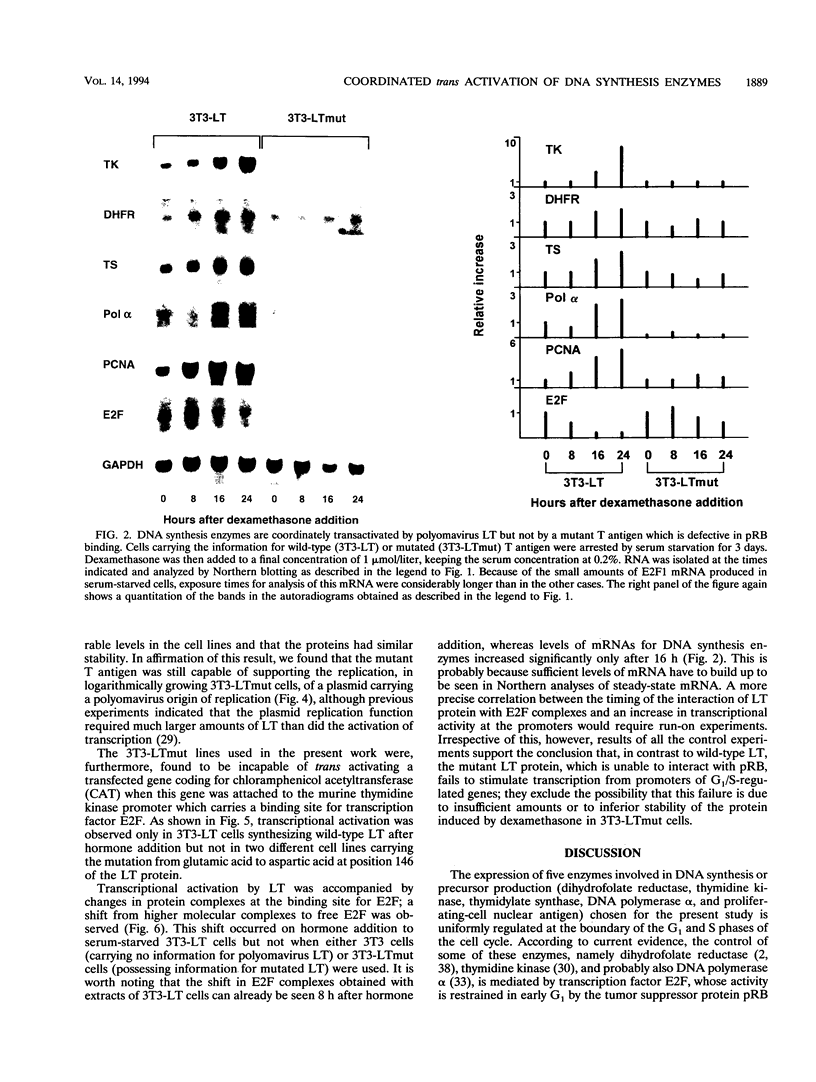
Previously constructed Swiss mouse 3T3 fibroblasts producing polyomavirus large T antigen after addition of dexamethasone were used to study the transcriptional activation by the viral protein of five genes coding for enzymes involved in DNA synthesis and precursor production, namely, dihydrofolate reductase, thymidine kinase, thymidylate synthase, DNA polymerase alpha, and proliferating-cell nuclear antigen. It was found that all these genes, whose expression is stimulated at the G1/S boundary of the cell cycle after growth stimulation by serum addition, are coordinately trans activated when T antigen is induced in cells previously growth arrested by serum withdrawal. Cell lines carrying the information for a mutant form of large T antigen, in which a glutamic acid residue in the binding site for the retinoblastoma protein was changed into aspartic acid, were constructed to test the involvement of an interaction of T antigen with the retinoblastoma protein in this reaction. It was found that the mutated T protein is incapable of stimulating transcription of any one of the genes. The promoter of three of the genes (dihydrofolate reductase, thymidine kinase, and DNA polymerase alpha) unequivocally carries binding sites for transcription factor E2F, suggesting that complexes forming with this growth- and cell cycle-regulating transcription factor are the targets for T antigen. Although there is so far no evidence that thymidylate synthase and proliferating cell nuclear antigen are regulated via E2F, our data indicate that the retinoblastoma protein still is involved in the control of these genes. mRNA for E2F itself increases in amount at the G1/S border in serum-stimulated cells but not during polyomavirus T antigen-induced transcriptional activation of DNA synthesis enzymes in arrested cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews N. C., Faller D. V. A rapid micropreparation technique for extraction of DNA-binding proteins from limiting numbers of mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2499–2499. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. C., Azizkhan J. C. Transcription factor E2F is required for efficient expression of the hamster dihydrofolate reductase gene in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4994–5002. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobrinik D., Dowdy S. F., Hinds P. W., Mittnacht S., Weinberg R. A. The retinoblastoma protein and the regulation of cell cycling. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Aug;17(8):312–315. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90443-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Furukawa Y., Ajchenbaum F., Griffin J. D., Livingston D. M. The retinoblastoma-susceptibility gene product becomes phosphorylated in multiple stages during cell cycle entry and progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1795–1798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilworth S. M., Griffin B. E. Monoclonal antibodies against polyoma virus tumor antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1059–1063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowdy S. F., Hinds P. W., Louie K., Reed S. I., Arnold A., Weinberg R. A. Physical interaction of the retinoblastoma protein with human D cyclins. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):499–511. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90137-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson N., Bernards R., Friend S. H., Gooding L. R., Hassell J. A., Major E. O., Pipas J. M., Vandyke T., Harlow E. Large T antigens of many polyomaviruses are able to form complexes with the retinoblastoma protein. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1353–1356. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1353-1356.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewen M. E., Sluss H. K., Sherr C. J., Matsushime H., Kato J., Livingston D. M. Functional interactions of the retinoblastoma protein with mammalian D-type cyclins. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):487–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90136-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girling R., Partridge J. F., Bandara L. R., Burden N., Totty N. F., Hsuan J. J., La Thangue N. B. A new component of the transcription factor DRTF1/E2F. Nature. 1993 Mar 4;362(6415):83–87. doi: 10.1038/362083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich D. W., Wang N. P., Qian Y. W., Lee E. Y., Lee W. H. The retinoblastoma gene product regulates progression through the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):293–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90181-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goutebroze L., de la Roche Saint Andre C., Scherneck S., Feunteun J. Mutations within the hamster polyomavirus large T antigen domain involved in pRb binding impair virus productive cycle and immortalization capacity. Oncogene. 1993 Mar;8(3):685–693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helin K., Ed H. The retinoblastoma protein as a transcriptional repressor. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;3(2):43–46. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90150-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helin K., Lees J. A., Vidal M., Dyson N., Harlow E., Fattaey A. A cDNA encoding a pRB-binding protein with properties of the transcription factor E2F. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):337–350. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90107-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiebert S. W., Blake M., Azizkhan J., Nevins J. R. Role of E2F transcription factor in E1A-mediated trans activation of cellular genes. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3547–3552. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3547-3552.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber H. E., Edwards G., Goodhart P. J., Patrick D. R., Huang P. S., Ivey-Hoyle M., Barnett S. F., Oliff A., Heimbrook D. C. Transcription factor E2F binds DNA as a heterodimer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3525–3529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolliff K., Li Y., Johnson L. F. Multiple protein-DNA interactions in the TATAA-less mouse thymidylate synthase promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2267–2274. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaelin W. G., Jr, Krek W., Sellers W. R., DeCaprio J. A., Ajchenbaum F., Fuchs C. S., Chittenden T., Li Y., Farnham P. J., Blanar M. A. Expression cloning of a cDNA encoding a retinoblastoma-binding protein with E2F-like properties. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):351–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90108-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. J., Onwuta U. S., Lee Y. I., Li R., Botchan M. R., Robbins P. D. The retinoblastoma gene product regulates Sp1-mediated transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2455–2463. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. J., Wagner S., Liu F., O'Reilly M. A., Robbins P. D., Green M. R. Retinoblastoma gene product activates expression of the human TGF-beta 2 gene through transcription factor ATF-2. Nature. 1992 Jul 23;358(6384):331–334. doi: 10.1038/358331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larose A., Dyson N., Sullivan M., Harlow E., Bastin M. Polyomavirus large T mutants affected in retinoblastoma protein binding are defective in immortalization. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2308–2313. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2308-2313.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees E., Faha B., Dulic V., Reed S. I., Harlow E. Cyclin E/cdk2 and cyclin A/cdk2 kinases associate with p107 and E2F in a temporally distinct manner. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1874–1885. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. F., Mathews M. B. The adenovirus E1A transforming protein activates the proliferating cell nuclear antigen promoter via an activating transcription factor site. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6397–6406. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6397-6406.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudryj M., Devoto S. H., Hiebert S. W., Hunter T., Pines J., Nevins J. R. Cell cycle regulation of the E2F transcription factor involves an interaction with cyclin A. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1243–1253. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90019-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. E2F: a link between the Rb tumor suppressor protein and viral oncoproteins. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):424–429. doi: 10.1126/science.1411535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogris E., Mudrak I., Wintersberger E. Distinct amounts of polyomavirus large T antigen are required for different functions of the protein. Oncogene. 1993 May;8(5):1277–1283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogris E., Mudrak I., Wintersberger E. Polyomavirus large and small T antigens cooperate in induction of the S phase in serum-starved 3T3 mouse fibroblasts. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):53–61. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.53-61.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogris E., Rotheneder H., Mudrak I., Pichler A., Wintersberger E. A binding site for transcription factor E2F is a target for trans activation of murine thymidine kinase by polyomavirus large T antigen and plays an important role in growth regulation of the gene. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):1765–1771. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.1765-1771.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano M., Draetta G., Jansen-Dürr P. Association of cdk2 kinase with the transcription factor E2F during S phase. Science. 1992 Feb 28;255(5048):1144–1147. doi: 10.1126/science.1312258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. G1 events and regulation of cell proliferation. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):603–608. doi: 10.1126/science.2683075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson B. E., Nasheuer H. P., Wang T. S. Human DNA polymerase alpha gene: sequences controlling expression in cycling and serum-stimulated cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2081–2095. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz J. K., Devoto S. H., Smith E. J., Chellappan S. P., Jakoi L., Nevins J. R. Interactions of the p107 and Rb proteins with E2F during the cell proliferation response. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1013–1020. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05742.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shan B., Zhu X., Chen P. L., Durfee T., Yang Y., Sharp D., Lee W. H. Molecular cloning of cellular genes encoding retinoblastoma-associated proteins: identification of a gene with properties of the transcription factor E2F. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5620–5631. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirodkar S., Ewen M., DeCaprio J. A., Morgan J., Livingston D. M., Chittenden T. The transcription factor E2F interacts with the retinoblastoma product and a p107-cyclin A complex in a cell cycle-regulated manner. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90214-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slansky J. E., Li Y., Kaelin W. G., Farnham P. J. A protein synthesis-dependent increase in E2F1 mRNA correlates with growth regulation of the dihydrofolate reductase promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1610–1618. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart N., Bacchetti S. Expression of SV40 large T antigen, but not small t antigen, is required for the induction of chromosomal aberrations in transformed human cells. Virology. 1991 Jan;180(1):49–57. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90008-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udvadia A. J., Rogers K. T., Higgins P. D., Murata Y., Martin K. H., Humphrey P. A., Horowitz J. M. Sp-1 binds promoter elements regulated by the RB protein and Sp-1-mediated transcription is stimulated by RB coexpression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3265–3269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintersberger E. Biochemical events controlling initiation and propagation of the S phase of the cell cycle. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1991;118:49–95. doi: 10.1007/BFb0031481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi M., Hayashi Y., Hirose F., Matsuoka S., Moriuchi T., Shiroishi T., Moriwaki K., Matsukage A. Molecular cloning and structural analysis of mouse gene and pseudogenes for proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2403–2410. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]