Abstract
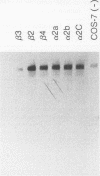
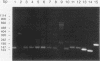
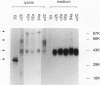
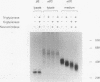
We used molecular cloning and functional analyses to extend the family of Neu differentiation factors (NDFs) and to explore the biochemical activity of different NDF isoforms. Exhaustive cloning revealed the existence of six distinct fibroblastic pro-NDFs, whose basic transmembrane structure includes an immunoglobulin-like motif and an epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like domain. Structural variation is confined to three domains: the C-terminal portion of the EGF-like domain (isoforms alpha and beta), the adjacent juxtamembrane stretch (isoforms 1 to 4), and the variable-length cytoplasmic domain (isoforms a, b, and c). Only certain combinations of the variable domains exist, and they display partial tissue specificity in their expression: pro-NDF-alpha 2 is the predominant form in mesenchymal cells, whereas pro-NDF-beta 1 is the major neuronal isoform. Only the transmembrane isoforms were glycosylated and secreted as biologically active 44-kDa glycoproteins, implying that the transmembrane domain functions as an internal signal peptide. Extensive glycosylation precedes proteolytic cleavage of pro-NDF but has no effect on receptor binding. By contrast, the EGF-like domain fully retains receptor binding activity when expressed separately, but its beta-type C terminus displays higher affinity than alpha-type NDFs. Likewise, structural heterogeneity of the cytoplasmic tails may determine isoform-specific rate of pro-NDF processing. Taken together, these results suggest that different NDF isoforms are generated by alternative splicing and perform distinct tissue-specific functions.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell G. I., Fong N. M., Stempien M. M., Wormsted M. A., Caput D., Ku L. L., Urdea M. S., Rall L. B., Sanchez-Pescador R. Human epidermal growth factor precursor: cDNA sequence, expression in vitro and gene organization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8427–8446. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosenberg M. W., Pandiella A., Massagué J. The cytoplasmic carboxy-terminal amino acid specifies cleavage of membrane TGF alpha into soluble growth factor. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1157–1165. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80064-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campion S. R., Geck M. K., Niyogi S. K. Cumulative effect of double-site mutations of human epidermal growth factor on receptor binding. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):1742–1748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. A., Weiner D. B., More K. F., Kokai Y., Williams W. V., Maguire H. C., Jr, LiVolsi V. A., Greene M. I. Expression pattern of the neu (NGL) gene-encoded growth factor receptor protein (p185neu) in normal and transformed epithelial tissues of the digestive tract. Oncogene. 1989 Jan;4(1):81–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. A., Yachnis A. T., Arai M., Davis J. G., Scherer S. S. Expression of the neu proto-oncogene by Schwann cells during peripheral nerve development and Wallerian degeneration. J Neurosci Res. 1992 Apr;31(4):622–634. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490310406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Emilia J., Bulovas K., D'Ercole K., Wolf B., Steele G., Jr, Summerhayes I. C. Expression of the c-erbB-2 gene product (p185) at different stages of neoplastic progression in the colon. Oncogene. 1989 Oct;4(10):1233–1239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobashi K., Davis J. G., Mikami Y., Freeman J. K., Hamuro J., Greene M. I. Characterization of a neu/c-erbB-2 protein-specific activating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8582–8586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudgeon T. J., Cooke R. M., Baron M., Campbell I. D., Edwards R. M., Fallon A. Structure-function analysis of epidermal growth factor: site directed mutagenesis and nuclear magnetic resonance. FEBS Lett. 1990 Feb 26;261(2):392–396. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80600-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engler D. A., Campion S. R., Hauser M. R., Cook J. S., Niyogi S. K. Critical functional requirement for the guanidinium group of the arginine 41 side chain of human epidermal growth factor as revealed by mutagenic inactivation and chemical reactivation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2274–2281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falls D. L., Rosen K. M., Corfas G., Lane W. S., Fischbach G. D. ARIA, a protein that stimulates acetylcholine receptor synthesis, is a member of the neu ligand family. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):801–815. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90407-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullick W. J., Berger M. S., Bennett P. L., Rothbard J. B., Waterfield M. D. Expression of the c-erbB-2 protein in normal and transformed cells. Int J Cancer. 1987 Aug 15;40(2):246–254. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910400221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera G. A. C-erb B-2 amplification in cystic renal disease. Kidney Int. 1991 Sep;40(3):509–513. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes W. E., Sliwkowski M. X., Akita R. W., Henzel W. J., Lee J., Park J. W., Yansura D., Abadi N., Raab H., Lewis G. D. Identification of heregulin, a specific activator of p185erbB2. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1205–1210. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S. S., Huang J. S. Purification and characterization of the neu/erb B2 ligand-growth factor from bovine kidney. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):11508–11512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowski J., Coghill G., Hopwood D., Wormsley K. G. Oncogenes and onco-suppressor gene in adenocarcinoma of the oesophagus. Gut. 1992 Aug;33(8):1033–1038. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.8.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokai Y., Cohen J. A., Drebin J. A., Greene M. I. Stage- and tissue-specific expression of the neu oncogene in rat development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8498–8501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Tumorigenic conversion of primary embryo fibroblasts requires at least two cooperating oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):596–602. doi: 10.1038/304596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupu R., Colomer R., Zugmaier G., Sarup J., Shepard M., Slamon D., Lippman M. E. Direct interaction of a ligand for the erbB2 oncogene product with the EGF receptor and p185erbB2. Science. 1990 Sep 28;249(4976):1552–1555. doi: 10.1126/science.2218496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire H. C., Jr, Jaworsky C., Cohen J. A., Hellman M., Weiner D. B., Greene M. I. Distribution of neu (c-erbB-2) protein in human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 Jun;92(6):786–790. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12696796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchionni M. A., Goodearl A. D., Chen M. S., Bermingham-McDonogh O., Kirk C., Hendricks M., Danehy F., Misumi D., Sudhalter J., Kobayashi K. Glial growth factors are alternatively spliced erbB2 ligands expressed in the nervous system. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):312–318. doi: 10.1038/362312a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J. Transforming growth factor-alpha. A model for membrane-anchored growth factors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21393–21396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsunami R. K., Yette M. L., Stevens A., Niyogi S. K. Mutational analysis of leucine 47 in human epidermal growth factor. J Cell Biochem. 1991 Jul;46(3):242–249. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240460307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani H., Black R., Kupper T. S. Human keratinocytes produce but do not process pro-interleukin-1 (IL-1) beta. Different strategies of IL-1 production and processing in monocytes and keratinocytes. J Clin Invest. 1991 Mar;87(3):1066–1071. doi: 10.1172/JCI115067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori S., Akiyama T., Yamada Y., Morishita Y., Sugawara I., Toyoshima K., Yamamoto T. C-erbB-2 gene product, a membrane protein commonly expressed on human fetal epithelial cells. Lab Invest. 1989 Jul;61(1):93–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natali P. G., Nicotra M. R., Bigotti A., Venturo I., Slamon D. J., Fendly B. M., Ullrich A. Expression of the p185 encoded by HER2 oncogene in normal and transformed human tissues. Int J Cancer. 1990 Mar 15;45(3):457–461. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910450314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peles E., Bacus S. S., Koski R. A., Lu H. S., Wen D., Ogden S. G., Levy R. B., Yarden Y. Isolation of the neu/HER-2 stimulatory ligand: a 44 kd glycoprotein that induces differentiation of mammary tumor cells. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):205–216. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90131-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peles E., Ben-Levy R., Tzahar E., Liu N., Wen D., Yarden Y. Cell-type specific interaction of Neu differentiation factor (NDF/heregulin) with Neu/HER-2 suggests complex ligand-receptor relationships. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):961–971. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05737.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plowman G. D., Culouscou J. M., Whitney G. S., Green J. M., Carlton G. W., Foy L., Neubauer M. G., Shoyab M. Ligand-specific activation of HER4/p180erbB4, a fourth member of the epidermal growth factor receptor family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1746–1750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plowman G. D., Whitney G. S., Neubauer M. G., Green J. M., McDonald V. L., Todaro G. J., Shoyab M. Molecular cloning and expression of an additional epidermal growth factor receptor-related gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):4905–4909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.4905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Press M. F., Cordon-Cardo C., Slamon D. J. Expression of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in normal human adult and fetal tissues. Oncogene. 1990 Jul;5(7):953–962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirke P., Pickles A., Tuzi N. L., Mohamdee O., Gullick W. J. Pattern of expression of c-erbB-2 oncoprotein in human fetuses. Br J Cancer. 1989 Jul;60(1):64–69. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1989.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen D., Peles E., Cupples R., Suggs S. V., Bacus S. S., Luo Y., Trail G., Hu S., Silbiger S. M., Levy R. B. Neu differentiation factor: a transmembrane glycoprotein containing an EGF domain and an immunoglobulin homology unit. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90456-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]