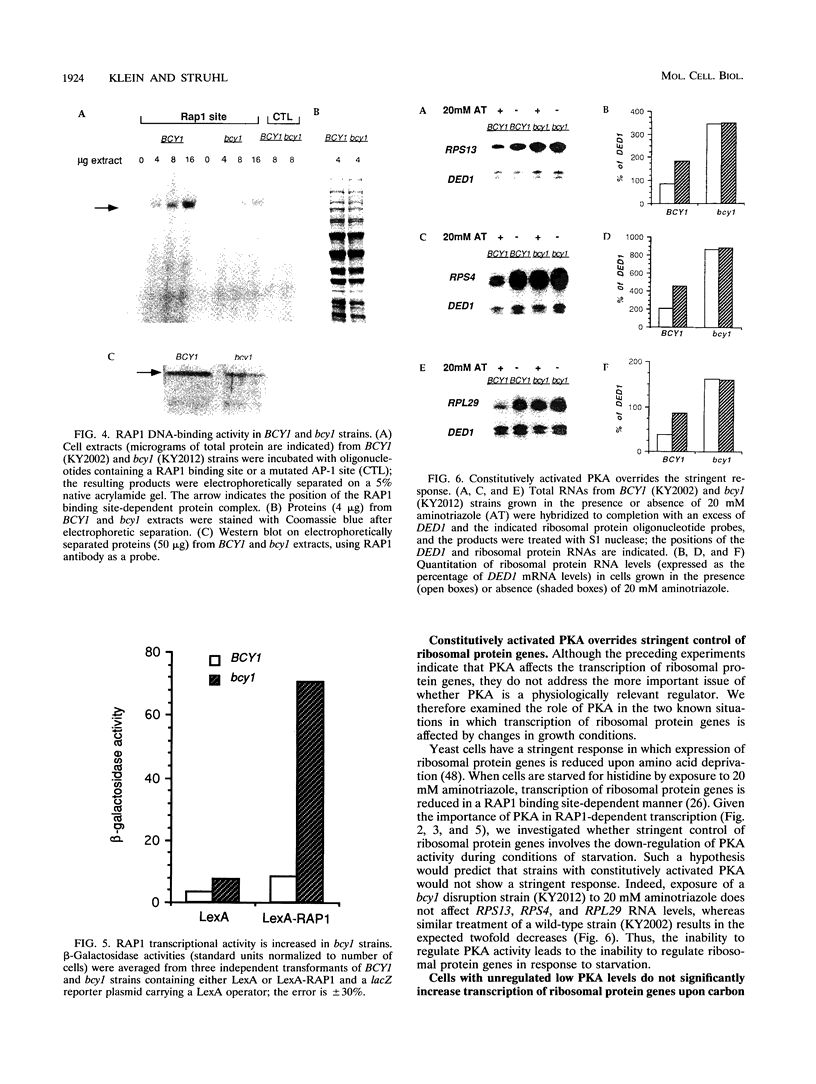
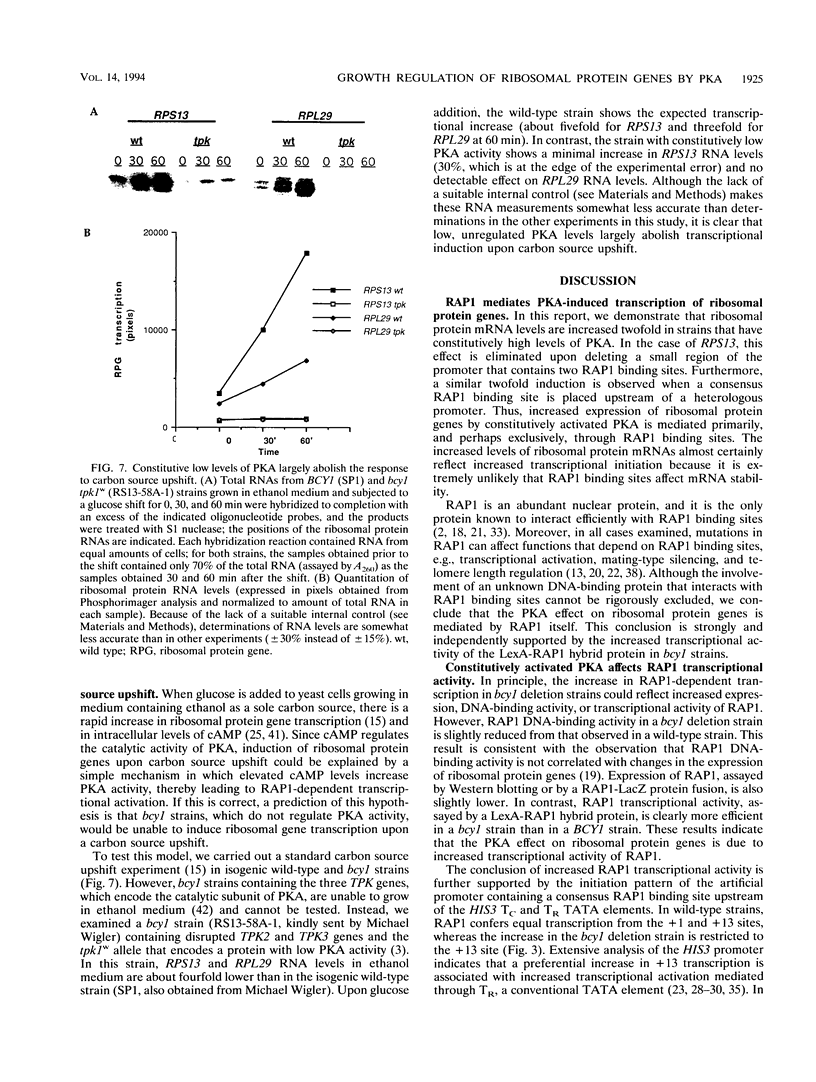
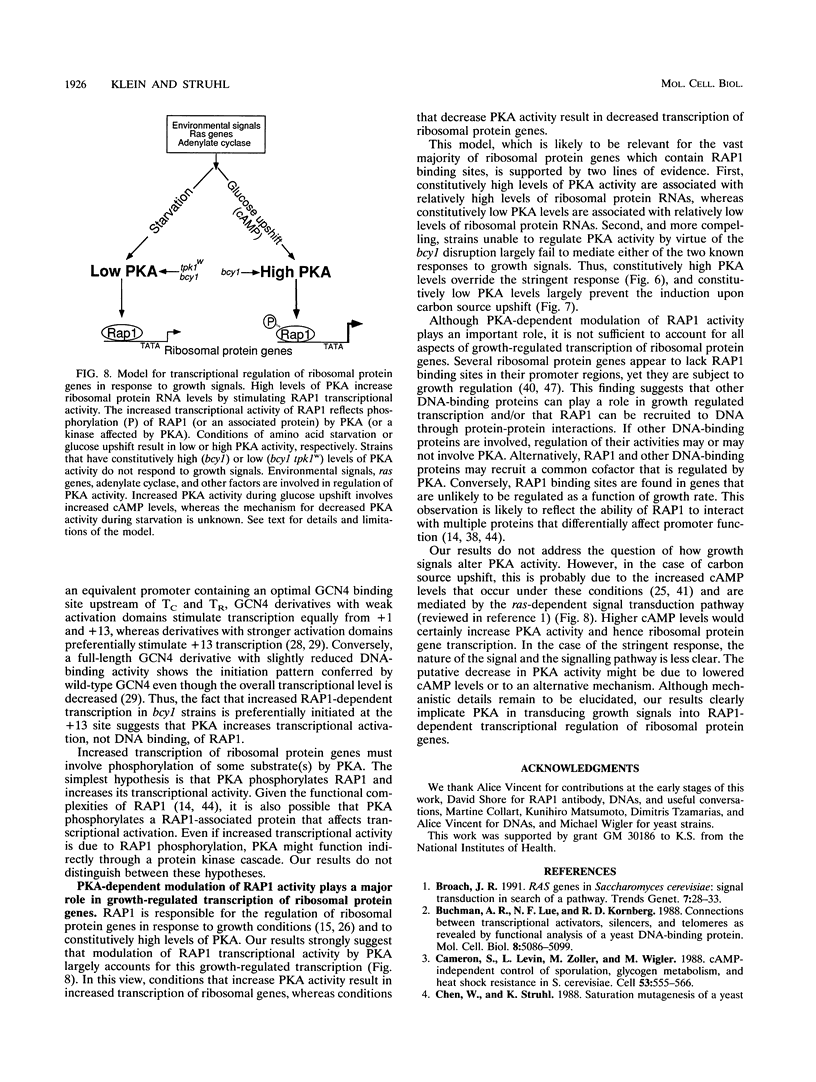
Abstract
Yeast ribosomal protein genes are coordinately regulated as a function of cell growth; RNA levels decrease during amino acid starvation but increase following a carbon source upshift. Binding sites for RAP1, a multifunctional transcription factor, are present in nearly all ribosomal protein genes and are associated with growth rate regulation. We show that ribosomal protein mRNA levels are increased twofold in strains that have constitutively high levels of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase (protein kinase A [PKA]) activity. The PKA-dependent induction requires RAP1 binding sites, and it reflects increased transcriptional activation by RAP1. Growth-regulated transcription of ribosomal protein genes strongly depends on the ability to regulate PKA activity. Cells with constitutively high PKA levels do not show the transcriptional decrease in response to amino acid starvation. Conversely, in cells with constitutively low PKA activity, ribosomal protein mRNAs levels are lower and largely uninducible upon carbon source upshift. We suggest that modulation of RAP1 transcriptional activity by PKA accounts for growth-regulated expression of ribosomal protein genes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Broach J. R. RAS genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: signal transduction in search of a pathway. Trends Genet. 1991 Jan;7(1):28–33. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90018-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Lue N. F., Kornberg R. D. Connections between transcriptional activators, silencers, and telomeres as revealed by functional analysis of a yeast DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5086–5099. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron S., Levin L., Zoller M., Wigler M. cAMP-independent control of sporulation, glycogen metabolism, and heat shock resistance in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):555–566. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90572-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W., Tabor S., Struhl K. Distinguishing between mechanisms of eukaryotic transcriptional activation with bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1047–1055. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90171-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry J. R., Johnson T. R., Dollard C., Shuster J. R., Denis C. L. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates and inactivates the yeast transcriptional activator ADR1. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):409–419. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90244-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis C. L., Fontaine S. C., Chase D., Kemp B. E., Bemis L. T. ADR1c mutations enhance the ability of ADR1 to activate transcription by a mechanism that is independent of effects on cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylation of Ser-230. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1507–1514. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field J., Nikawa J., Broek D., MacDonald B., Rodgers L., Wilson I. A., Lerner R. A., Wigler M. Purification of a RAS-responsive adenylyl cyclase complex from Saccharomyces cerevisiae by use of an epitope addition method. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2159–2165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes N. S., Borrelli E., Sassone-Corsi P. CREM gene: use of alternative DNA-binding domains generates multiple antagonists of cAMP-induced transcription. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):739–749. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90503-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietz R. D., Sugino A. New yeast-Escherichia coli shuttle vectors constructed with in vitro mutagenized yeast genes lacking six-base pair restriction sites. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):527–534. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90185-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Montminy M. R. Cyclic AMP stimulates somatostatin gene transcription by phosphorylation of CREB at serine 133. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):675–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Yamamoto K. K., Fischer W. H., Karr D., Menzel P., Biggs W., 3rd, Vale W. W., Montminy M. R. A cluster of phosphorylation sites on the cyclic AMP-regulated nuclear factor CREB predicted by its sequence. Nature. 1989 Feb 23;337(6209):749–752. doi: 10.1038/337749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy C. F., Balderes D., Shore D. Dissection of a carboxy-terminal region of the yeast regulatory protein RAP1 with effects on both transcriptional activation and silencing. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1209–1217. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy C. F., Sussel L., Shore D. A RAP1-interacting protein involved in transcriptional silencing and telomere length regulation. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):801–814. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herruer M. H., Mager W. H., Woudt L. P., Nieuwint R. T., Wassenaar G. M., Groeneveld P., Planta R. J. Transcriptional control of yeast ribosomal protein synthesis during carbon-source upshift. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10133–10144. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeffler J. P., Meyer T. E., Yun Y., Jameson J. L., Habener J. F. Cyclic AMP-responsive DNA-binding protein: structure based on a cloned placental cDNA. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1430–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.2974179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. Functional dissection of a eukaryotic transcriptional activator protein, GCN4 of yeast. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):885–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90070-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Sentenac A. TUF, the yeast DNA-binding factor specific for UASrpg upstream activating sequences: identification of the protein and its DNA-binding domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3648–3652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraakman L. S., Griffioen G., Zerp S., Groeneveld P., Thevelein J. M., Mager W. H., Planta R. J. Growth-related expression of ribosomal protein genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 May;239(1-2):196–204. doi: 10.1007/BF00281618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz S., Shore D. RAP1 protein activates and silences transcription of mating-type genes in yeast. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):616–628. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longtine M. S., Wilson N. M., Petracek M. E., Berman J. A yeast telomere binding activity binds to two related telomere sequence motifs and is indistinguishable from RAP1. Curr Genet. 1989 Oct;16(4):225–239. doi: 10.1007/BF00422108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustig A. J., Kurtz S., Shore D. Involvement of the silencer and UAS binding protein RAP1 in regulation of telomere length. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):549–553. doi: 10.1126/science.2237406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan S., Struhl K. Tc, an unusual promoter element required for constitutive transcription of the yeast HIS3 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4447–4455. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchler G., Schüller C., Adam G., Ruis H. A Saccharomyces cerevisiae UAS element controlled by protein kinase A activates transcription in response to a variety of stress conditions. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):1997–2003. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05849.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mbonyi K., Beullens M., Detremerie K., Geerts L., Thevelein J. M. Requirement of one functional RAS gene and inability of an oncogenic ras variant to mediate the glucose-induced cyclic AMP signal in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3051–3057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehle C. M., Hinnebusch A. G. Association of RAP1 binding sites with stringent control of ribosomal protein gene transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2723–2735. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M., Silver P. Context affects nuclear protein localization in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):384–389. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliviero S., Struhl K. Synergistic transcriptional enhancement does not depend on the number of acidic activation domains bound to the promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):224–228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponticelli A. S., Struhl K. Analysis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae his3 transcription in vitro: biochemical support for multiple mechanisms of transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2832–2839. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roesler W. J., Vandenbark G. R., Hanson R. W. Cyclic AMP and the induction of eukaryotic gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9063–9066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotenberg M. O., Woolford J. L., Jr Tripartite upstream promoter element essential for expression of Saccharomyces cerevisiae ribosomal protein genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):674–687. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Nasmyth K. Purification and cloning of a DNA binding protein from yeast that binds to both silencer and activator elements. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Constitutive and inducible Saccharomyces cerevisiae promoters: evidence for two distinct molecular mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3847–3853. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K., Davis R. W. Production of a functional eukaryotic enzyme in Escherichia coli: cloning and expression of the yeast structural gene for imidazole-glycerolphosphate dehydratase (his3). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5255–5259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K., Hill D. E. Two related regulatory sequences are required for maximal induction of Saccharomyces cerevisiae his3 transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):104–110. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussel L., Shore D. Separation of transcriptional activation and silencing functions of the RAP1-encoded repressor/activator protein 1: isolation of viable mutants affecting both silencing and telomere length. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7749–7753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Matsumoto K., Toh-e A. Dual regulation of the expression of the polyubiquitin gene by cyclic AMP and heat shock in yeast. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):495–502. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02837.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teem J. L., Abovich N., Kaufer N. F., Schwindinger W. F., Warner J. R., Levy A., Woolford J., Leer R. J., van Raamsdonk-Duin M. M., Mager W. H. A comparison of yeast ribosomal protein gene DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8295–8312. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thevelein J. M., Beullens M. Cyclic AMP and the stimulation of trehalase activity in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae by carbon sources, nitrogen sources and inhibitors of protein synthesis. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Dec;131(12):3199–3209. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-12-3199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Cameron S., Sass P., Zoller M., Scott J. D., McMullen B., Hurwitz M., Krebs E. G., Wigler M. Cloning and characterization of BCY1, a locus encoding a regulatory subunit of the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1371–1377. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Cameron S., Sass P., Zoller M., Wigler M. Three different genes in S. cerevisiae encode the catalytic subunits of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90223-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Liebman S. W. The yeast omnipotent suppressor SUP46 encodes a ribosomal protein which is a functional and structural homolog of the Escherichia coli S4 ram protein. Genetics. 1992 Oct;132(2):375–386. doi: 10.1093/genetics/132.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R. Synthesis of ribosomes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;53(2):256–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.256-271.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]